Denture support, retention and stability
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
The dentures occupy a space in the mouth known as ?
The denture space
What are the limits of the denture space?
the space between the tongue, lips, cheeks and residual alveolar ridges
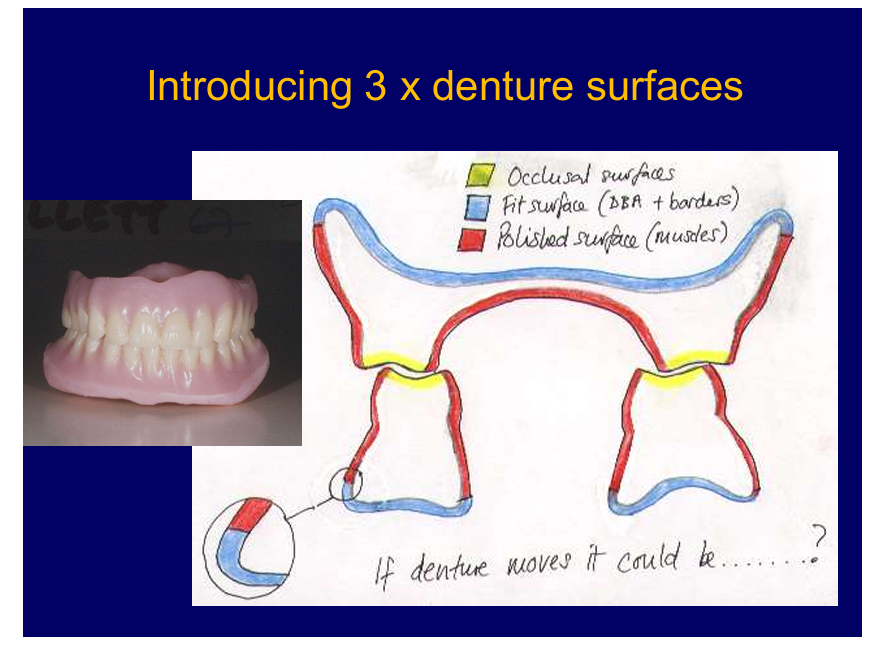
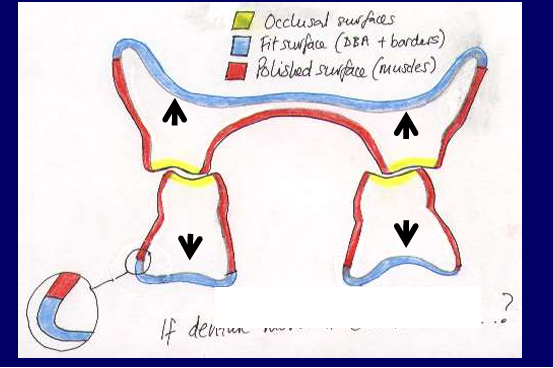
Again, what are the 3 surfaces of a denture?
polishes - oral mucosa and muscles underneath
why it moves - think of it in terms of which surface is responsible
e.g fit surface not very well fitting - fit surface
polished surface - not right shape the muscles can exrt forces on denture causing it to move
occlusal surfaces - if they meet nicely and occlusal plane is even - denture should remain in place
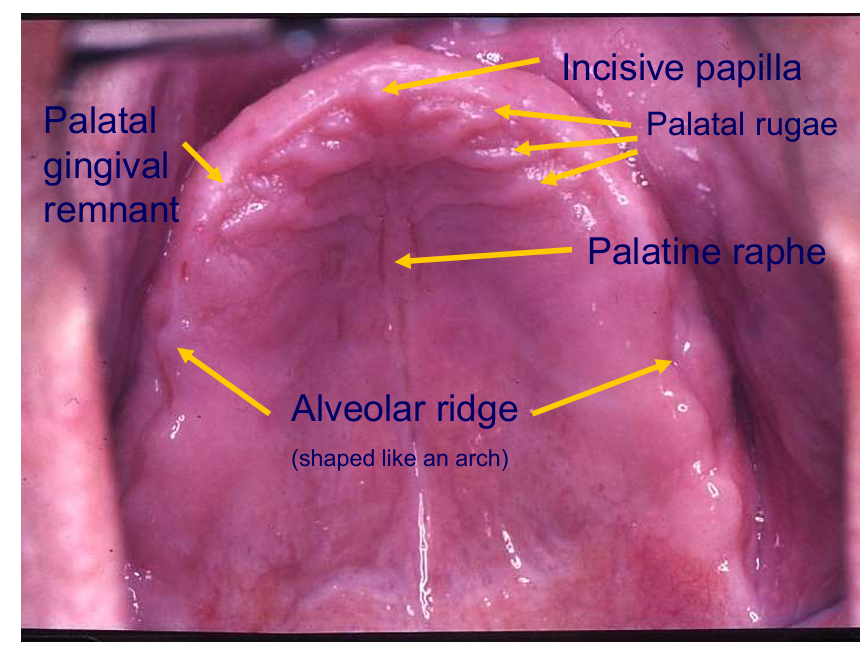
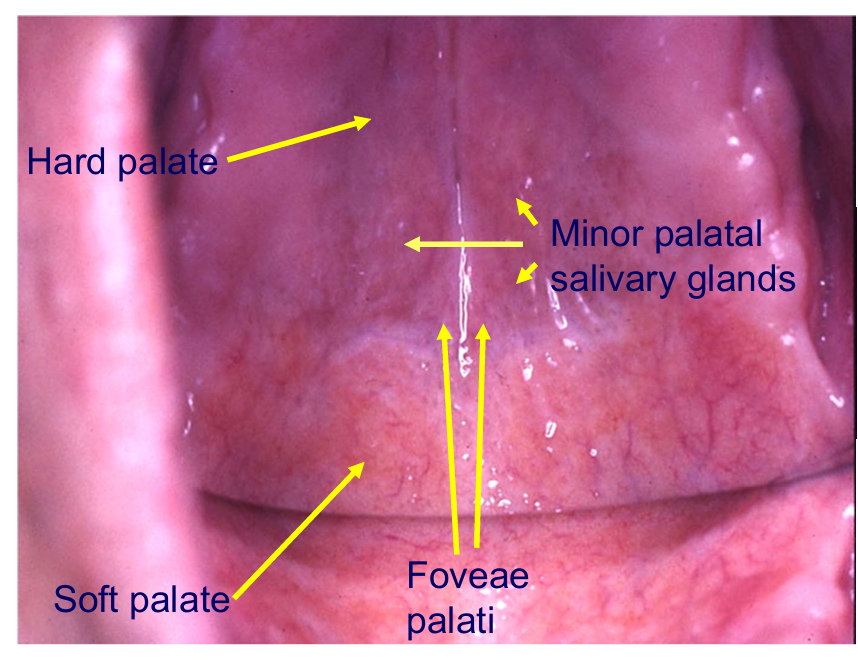
Label these areas
PGR - can guide you to the best place to position the teeth
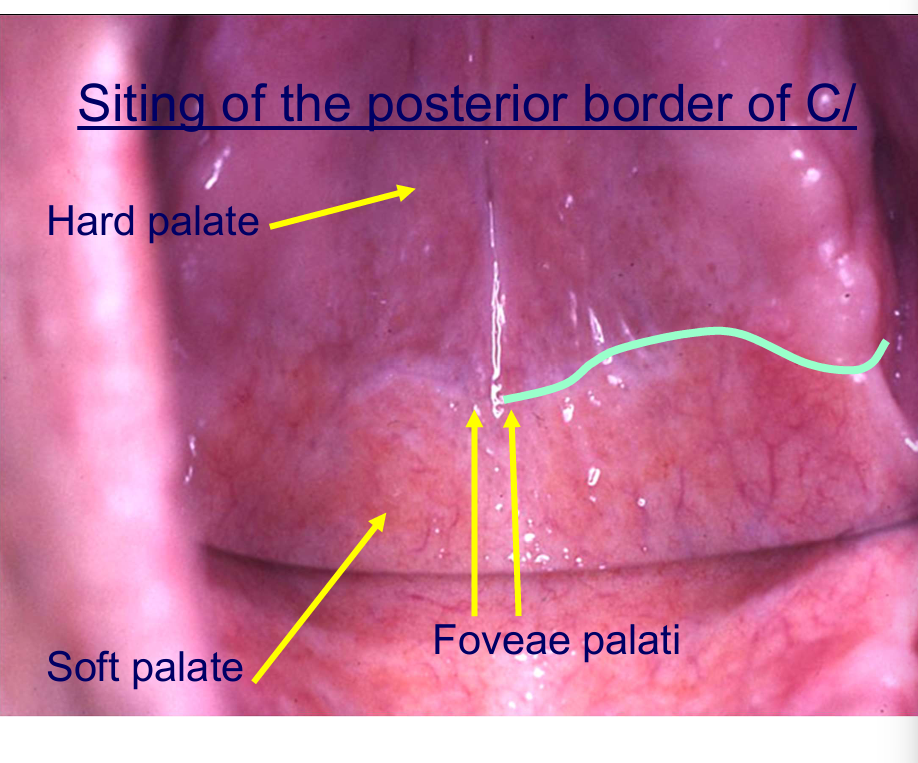
Foveae palati - two dimples where hard and soft palate meet
the junction between the two is the posterior border for the denture
soft palate moves and would be uncomfy for the patient
Don’t want denture to rest on frenal attachment
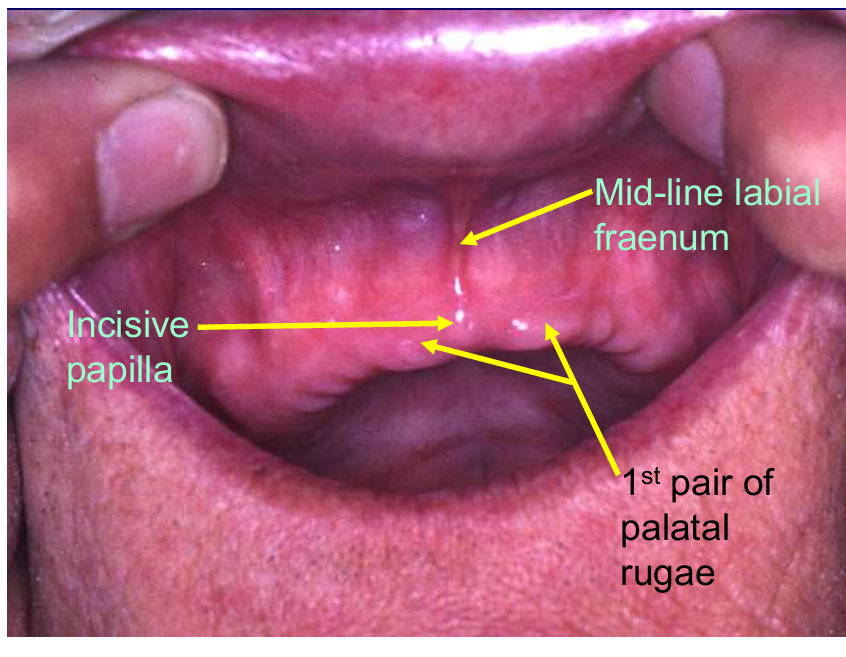
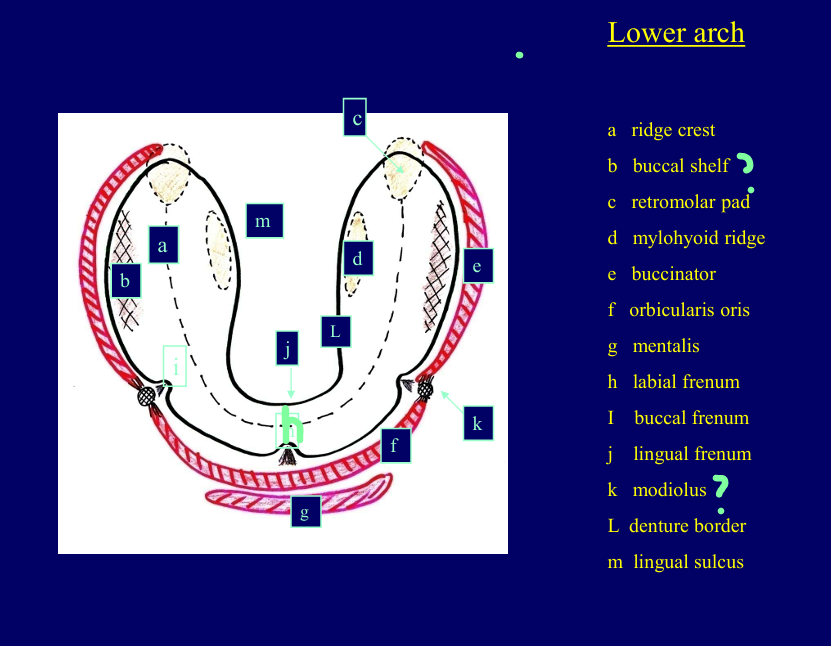
Label each letter
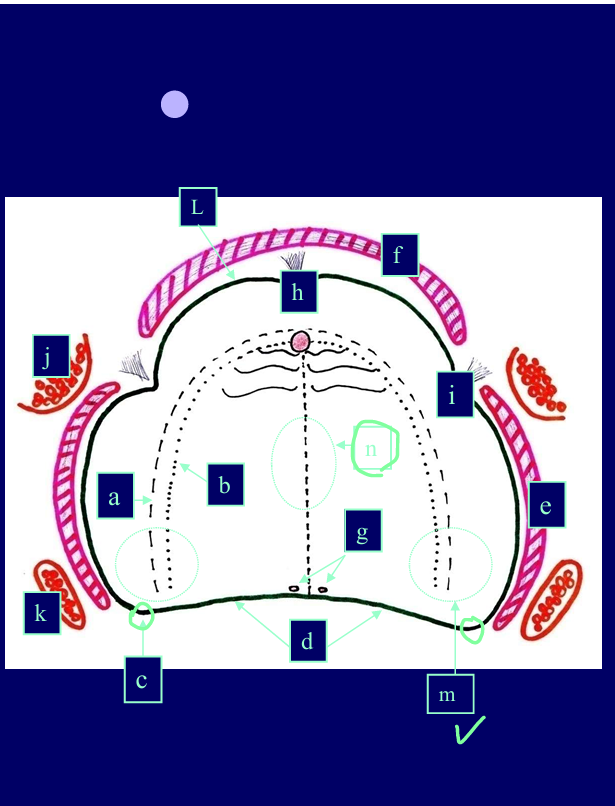
Pink - the muscles that influence the borders of the denture
Red - bone components
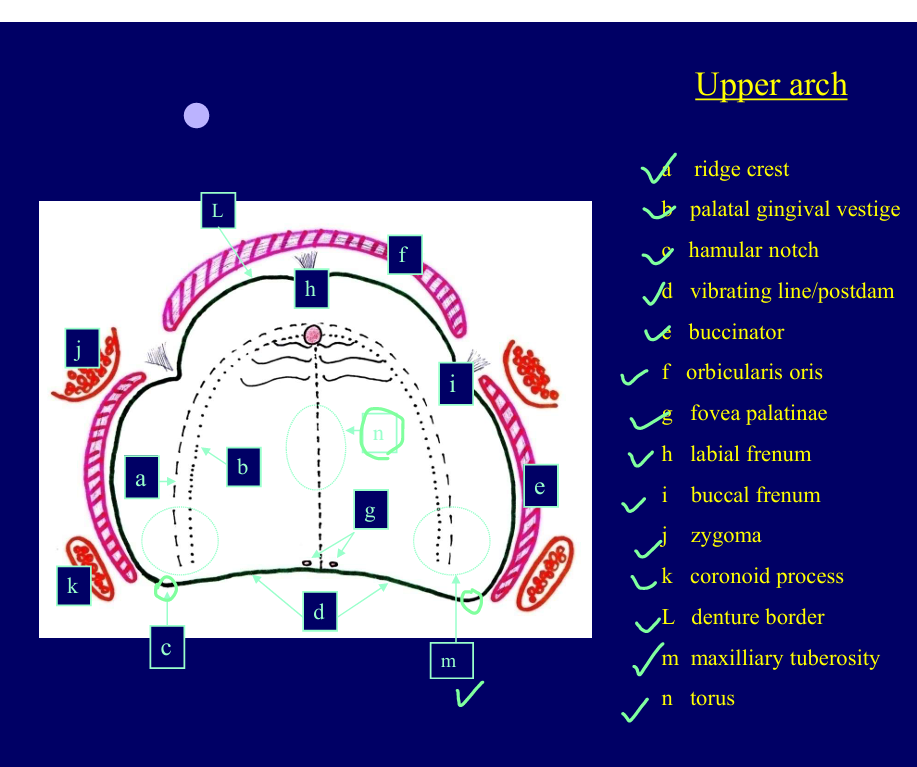
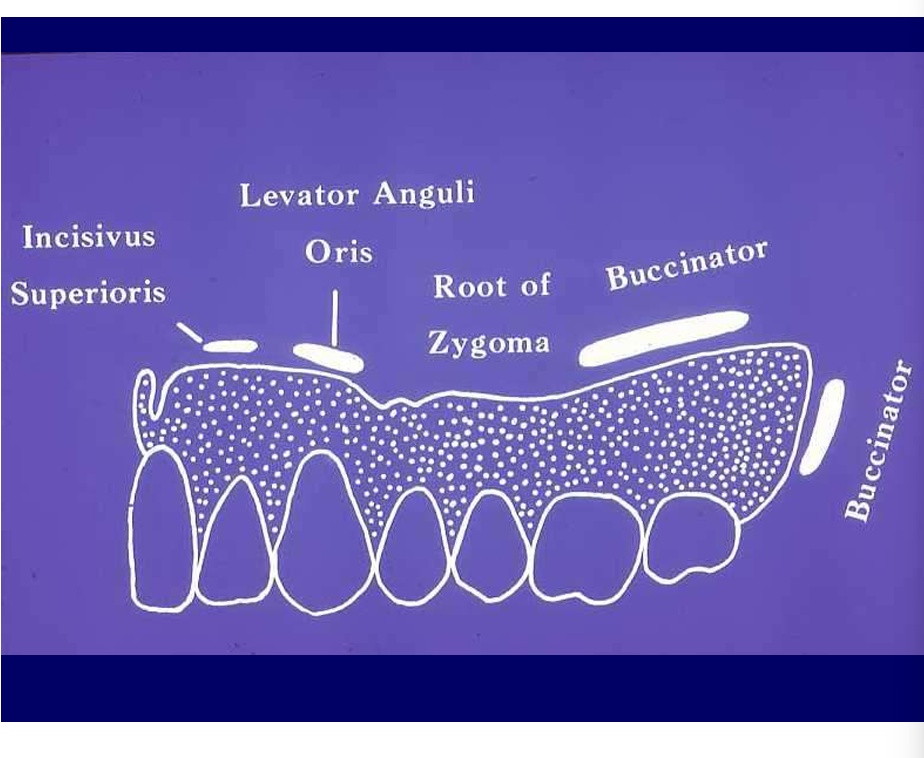
What is important about the denture vs the muscular attachment?
the muscles that attach into the bone around the sulcus area
if the denture is too long in those areas - the muscle attachments will press onto edges of denture
push denture out
rubbing - pain
there are structures underneath you don’t want to press on
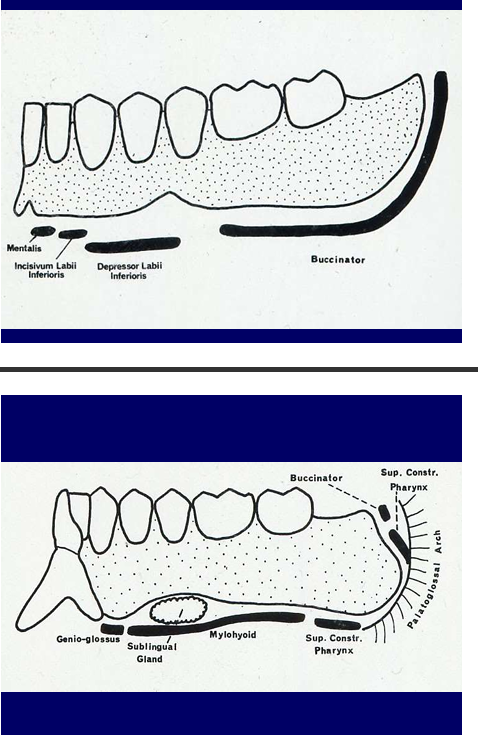
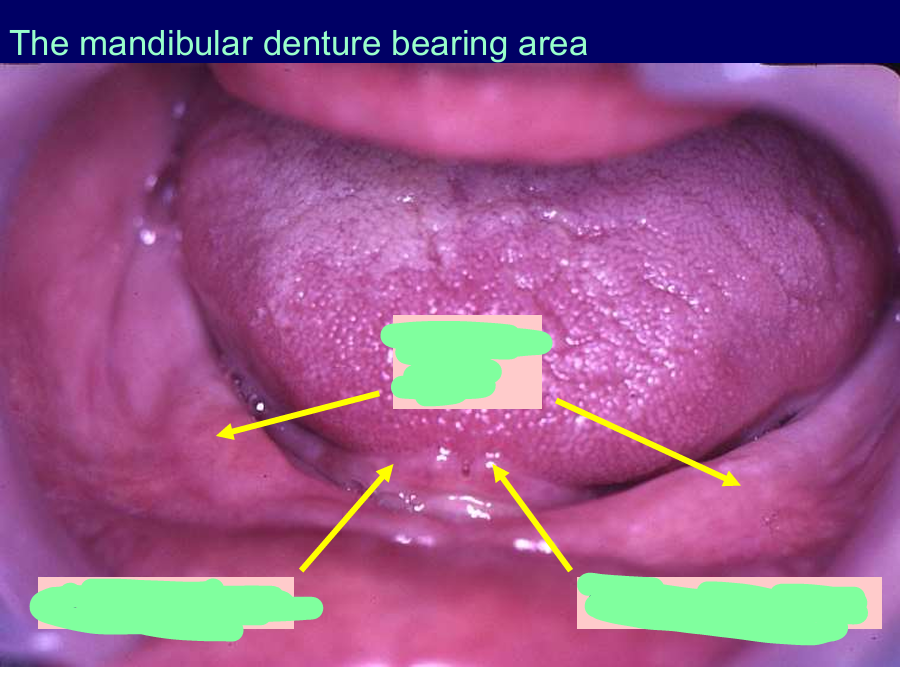
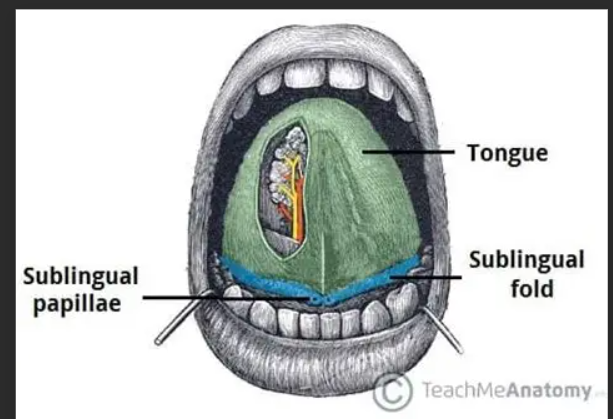
Label these
alveolar ridge
left - sublingual folds
right - sublingual papilla
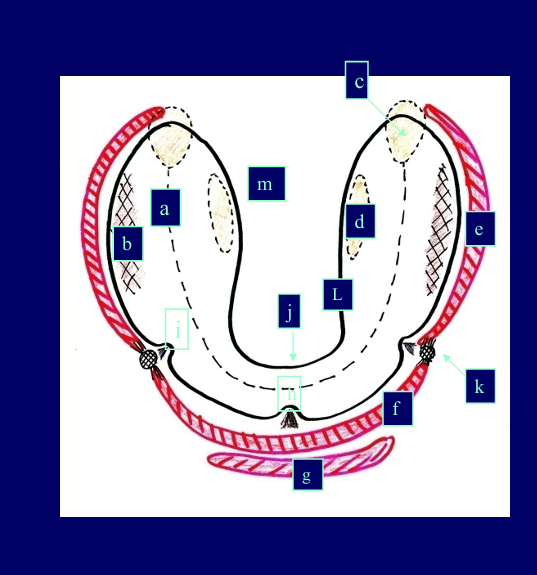
What structures do the labels represent?
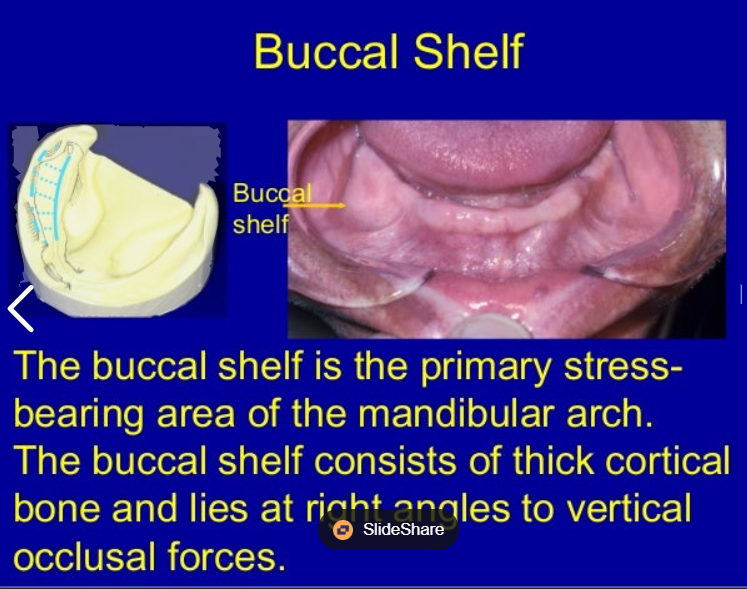
What is the buccal shelf?
What is the modiolus?
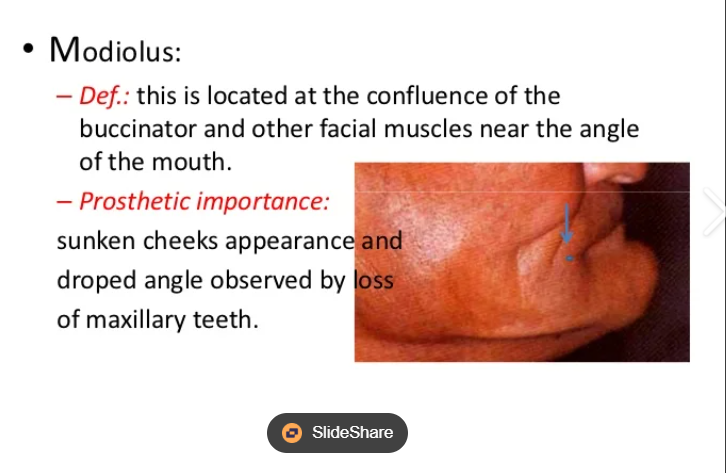
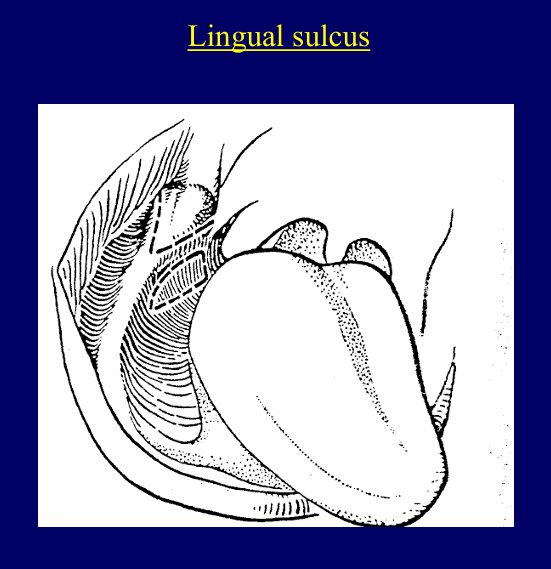
What is the importance of this image?
Floor of the mouth is always moving so if you make the border/flange o the denture too long in this area, the floor of the mouth as it moves could lift the denture
What are two distinct denture movement situations that must be understood?
Dentures move either:
1. whilst in mouth with jaws at rest
2. during function e.g speaking/chewing
Keeping dentures in place:
How are they kept in place? (6)
saliva - suction - mainly applicable to c/c dentures
muscles can press - (can also displace!!)
teeth push dentures back onto tissues where they are resting
gravity for lower
partial dentures only
teeth - metal framework - stop denture tipping or rotating

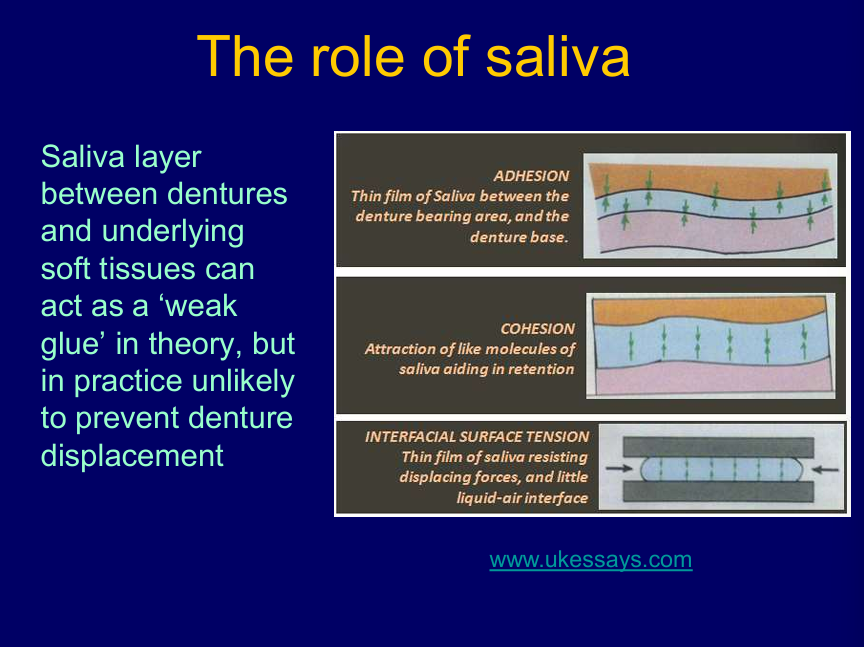
What is the role of saliva?
what are the 3 mechanisms of saliva in preventing denture displacement?
Saliva layer between dentures and underlying soft tissues can act as a ‘weak glue’ in theory but in practice unlikely to prevent denture displacement
adhesion between the denture bearing area and denture base
cohesion between molecules of saliva
interfacial surface tension resisting displacing forces
What is this seal called?
Saliva layer between dentures and underlying soft tissues help to make a seal around the dentures to give suction - peripheral seal
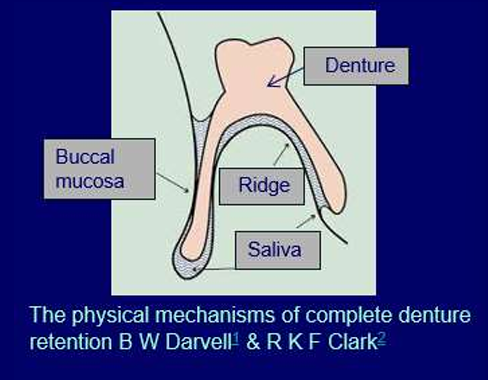
What are important factors in the role of saliva?
well fitting denture - fits the alveolar ridges quite well
you want a thin layer - not too thick
saliva not too thick in - consistency
Shorter flanges - more saliva more likely to get air underneath - longer flanges - presses on muscles
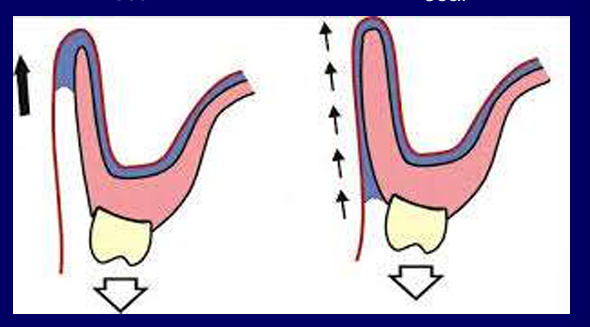
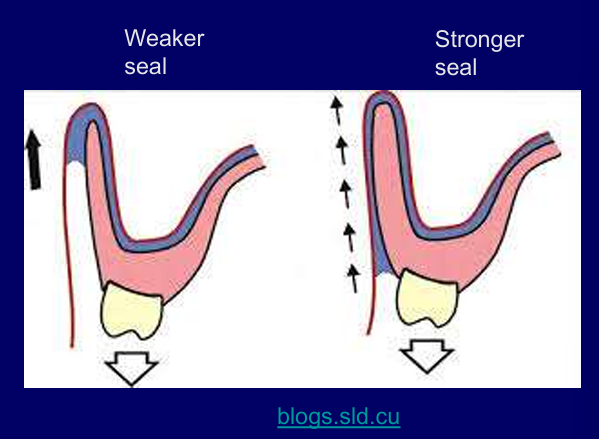
What is important about the thickness of the flanges?
A denture flange that is too thin does not work as well as one that fills the width of the sulcus
less likely to get air underneath, saliva layer receded so easier to get air there disrupting the seal
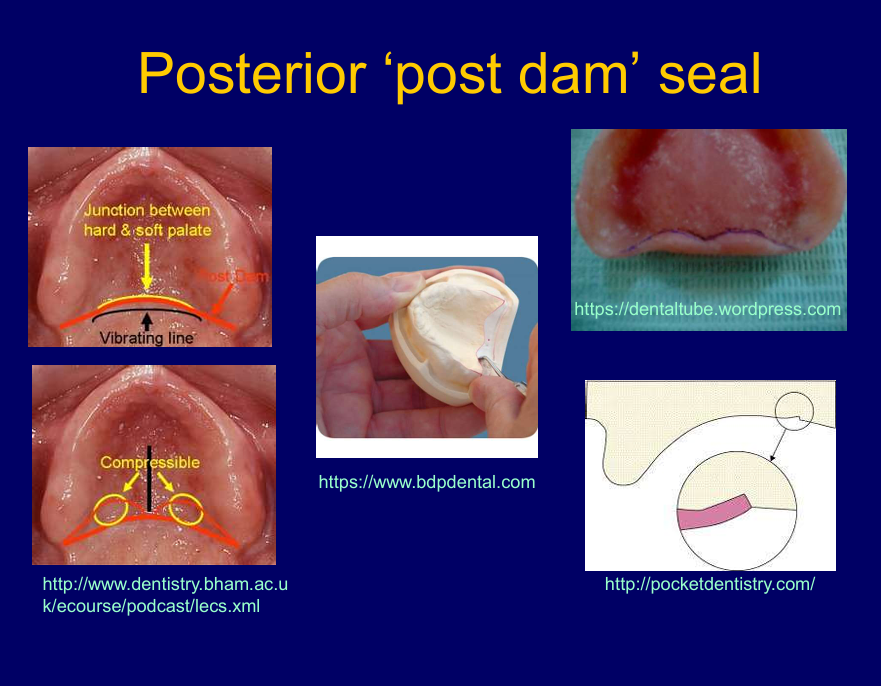
Again, where do you want the posterior ‘post dam’ seal to be?
The junction between the soft and hard palate or vibrating line
that area the tissues are quite compressible,
want seal all around the denture
back of denture provide a ridge of acrylic on the inside fitting surface that’s lightly digs in the mucosa - post dam
created by cutting a groove in the cast between the hamular notches resulting in a raised bit of acrylic to maintain the seal and stop air from getting into the back of the denture
seal only applies to complete dentures as as soon as there is a natural tooth, air can get in around that tooth, teeth compromise the seal
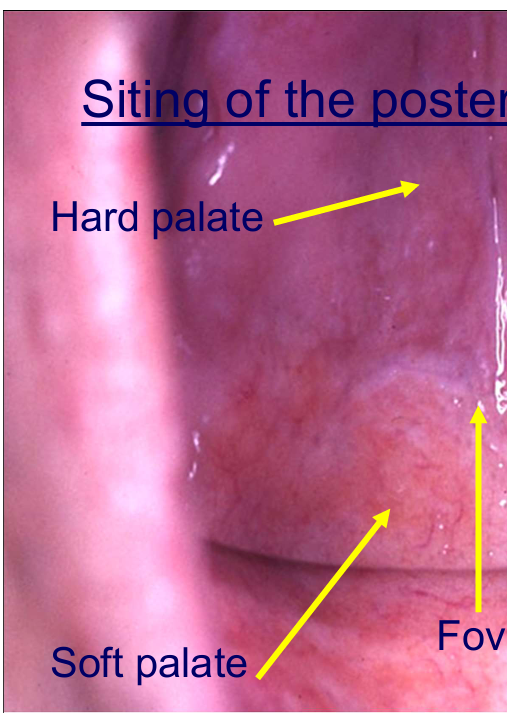
Again where do you put the post dam?
mark where you think the posterior border should be with a pen when you take the impassion on a disinfected dry impression
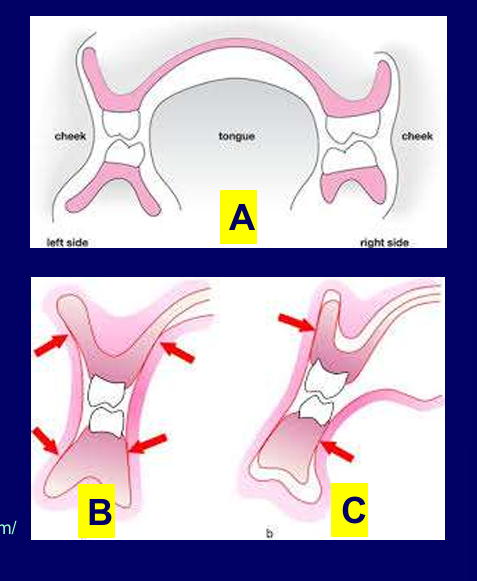
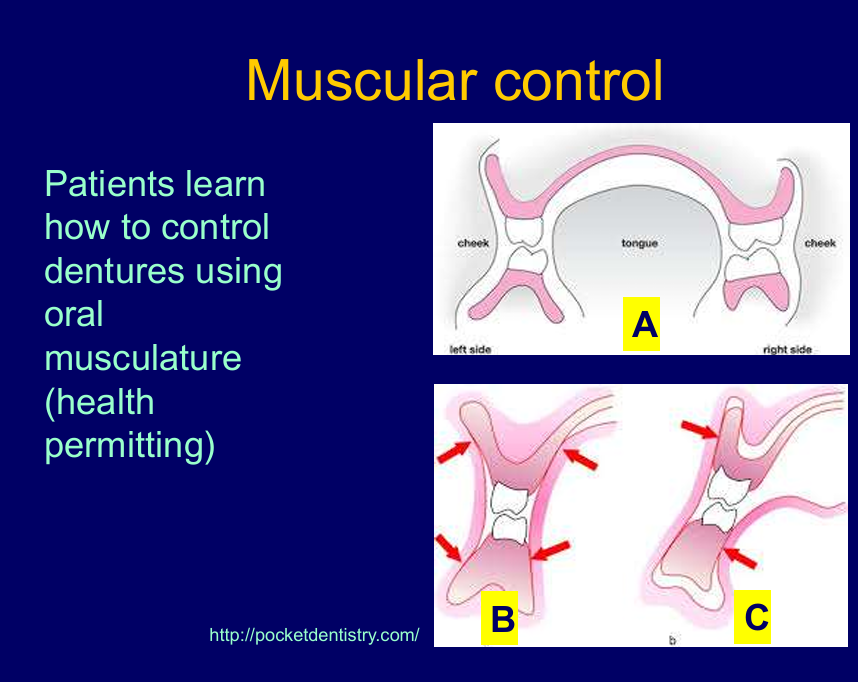
How can muscular control keep dentures from displacement?
Muscles from cheek and tongue should balance out - dentures more likely to stay in place - A and B - where the forces are acting
C- muscles can start to dislodge dentures - teeth are too far buccal so muscle push back
in the lower arch it is too lingual so muscle of tongue push back on denture causing it to lift
suction effect in lower is more difficult and if its not great suction and not provided much space for tongue denture can move
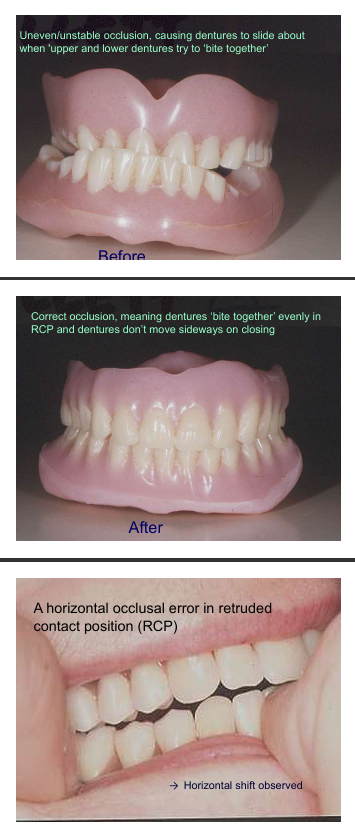
Upper and lower teeth can help keep dentures in place when patient bite together or chews food,
These teeth cannot go together/bite
teeth don’t meet together causing them slide when teeth meet evenly
Stops dentures moving about sideways
if occlusal error horizontal shift may still occur , when pt closes together the denture teeth must close in a denture ICP so ICP=RCP
what 2 things contribute to stability?
If something has good support and retention it will have good stability
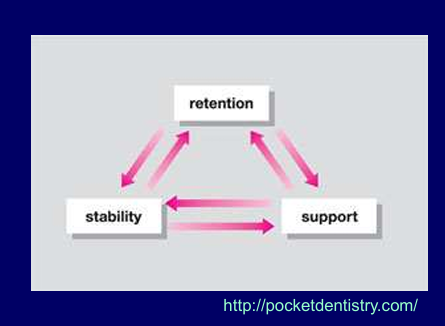
What is the definition of support?
Resistance of a denture to displacement (movement) towards the tissues (especially when subjected to occlusal loads on teeth)
Complete denture supports largely depends on 2 things?
Amount of coverage of underlying tissues or denture bearing area - the more the better
Condition (firmness) of underlying tissues or denture bearing areas - the firmer the better
Try cover the maximum ideal area - not saying extend denture beyond ideal area
Which is usually better supported an upper or lower complete denture and why?
Upper denture because there is a larger fit surface and it covers more underlying soft-tissues and bone
Which denture is less likely to cause trauma to the underlying tissues?
UPPER, because occlusal forces are distributed over a greater surface area of underlying soft-tissues and bone - supported better
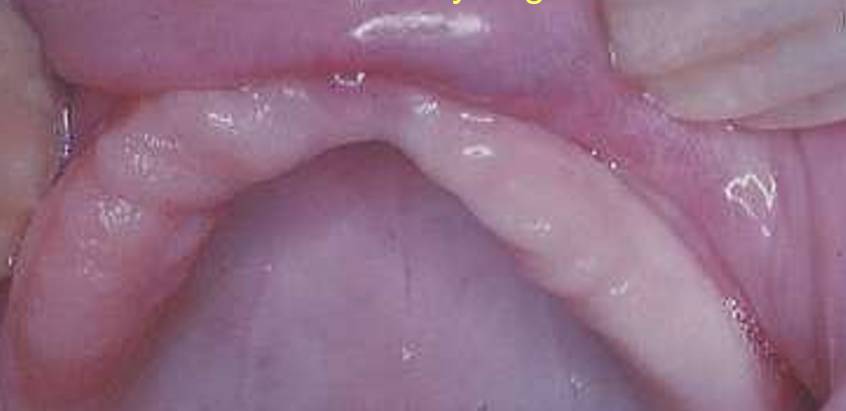
What is the problem with this?
A flabby ridge caused by fibrous replacement of alveolar bone, which does not provide good support because it is wobbly
A denture should have a firm foundation of soft tissues underneath to stop it moving towards tissues or tipping

How do you check the support of a complete denture?
press down on occlusal surface, both sides at once and see if it moves
look to see how much area is covered
look for signs of trauma to tissues - may need to extend coverage
What is the definition of retention?
Is the ability of a denture to resist displacement away from the denture bearing area in a direction perpendicular to the surface of the tissues - while at rest
What is the definition of stability?
the ability of the denture to resist movement in relation to the underlying bone during function (eating and drinking), in any direction
if an upper denture has poor retention, what does it do?
it drops down when mouth is at rest
If a lower denture has poor retention, what does it do?
it lifts up when mouth is at rest
If an upper denture has poor stability, what does it do?
it moves about during function - eating/speech (usually happens when lingual flange is too long)
if a lower denture has poor stability what does it do?
it moves about during function
What does retention of a complete denture depend on? (6)
very weak - dry mouth no possible adhesion
denture is good fit so saliva layer is thin
want it to extend to sulcus area to get seal and suction (limited seal if natural teeth), border seal = peripheral seal
suitable polished surface shape - muscles of tongue and cheek can help keep denture in place or try dislodge the denture


take an accurate master impression (thin even layer of material important for accuracy an must include the maximum surface area possible)
Where should the posterior border of an C/ be placed?
between hard and soft palate - junction
tissue is displaceable but not too far back where it can be interfered with by the moving soft palate
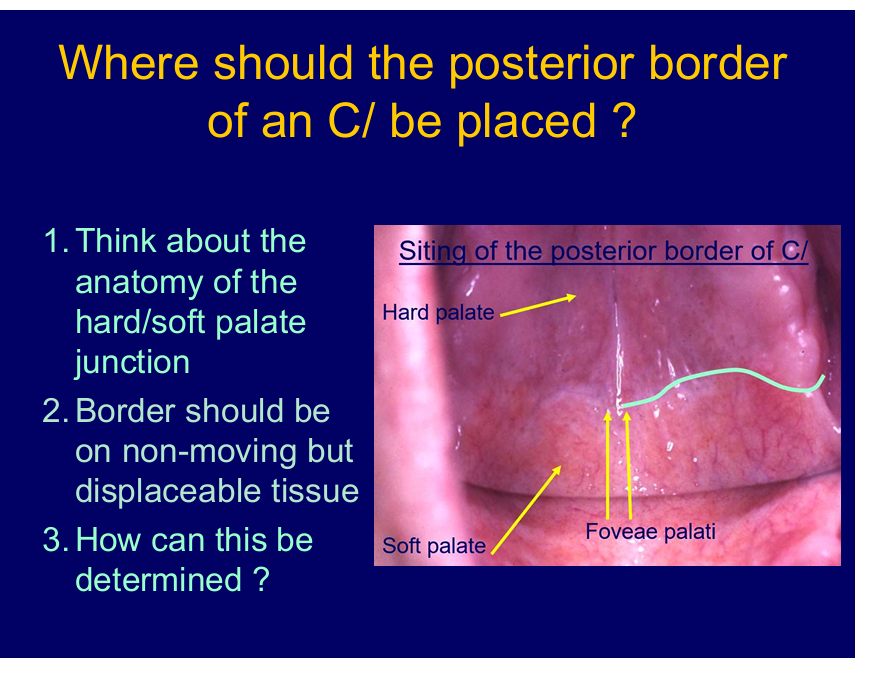
What are some clinical clues for where the border must be? (4)
colour change
foveae palati
palpate
ahhh - vibrating line

How do you check the retention of a denture?
hold onto the denture teeth and try pull denture away from tissues (downwards if upper denture and upwards if lower)
press firmly onto incisal edges of upper anterioir teeth and see if back of denture drops (checks the post dam area)
What can affect the stability of complete dentures? (9)
support
retention
area
consistency
polished surface/tooth position (e.g upper ant teeth places too far forwards will cause the upper lip sticks out and lip pushes back causing dislodge )
alveolar bone
correct vertical and horizontal
freedom to make excursive movements (slide over each other)
level of occlusal plane - if too high the tongue finds it difficult to control lower denture
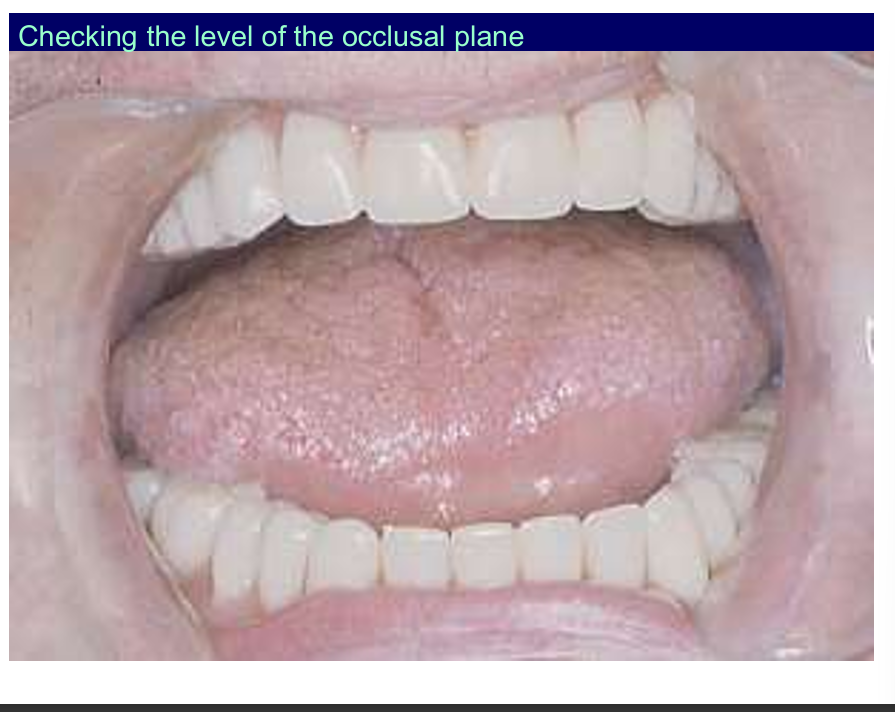
what are you looking for when checking the occlusal plane?
the tongue can sit nicely on the occlusal surface of the lower denture is what your are trying to achieve
how do oyu check the stability of a complete denture? (3)
1- moving
2- press on one area
3- movement during speech or eating
