Photosynthesis Review and Key Concepts
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Final electron acceptor in photosynthesis
NADPH
Overall equation for photosynthesis
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + solar energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
C4 plant example
Any specific example of a C4 plant
C4 and CAM plants adaptations
Allow them to fix carbon efficiently under specific environmental conditions
Reason for cyclic photophosphorylation
Plants switch to cyclic rather than noncyclic photophosphorylation for energy production under certain conditions
Source of oxygen in glucose during Calvin cycle
The oxygen originally comes from water
Products of light-dependent reactions
ATP and NADPH
Difference in carbon fixation between C4 and CAM plants
C4 plants fix carbon in a different pathway compared to CAM plants
Location of chemiosmosis
In the thylakoid membrane
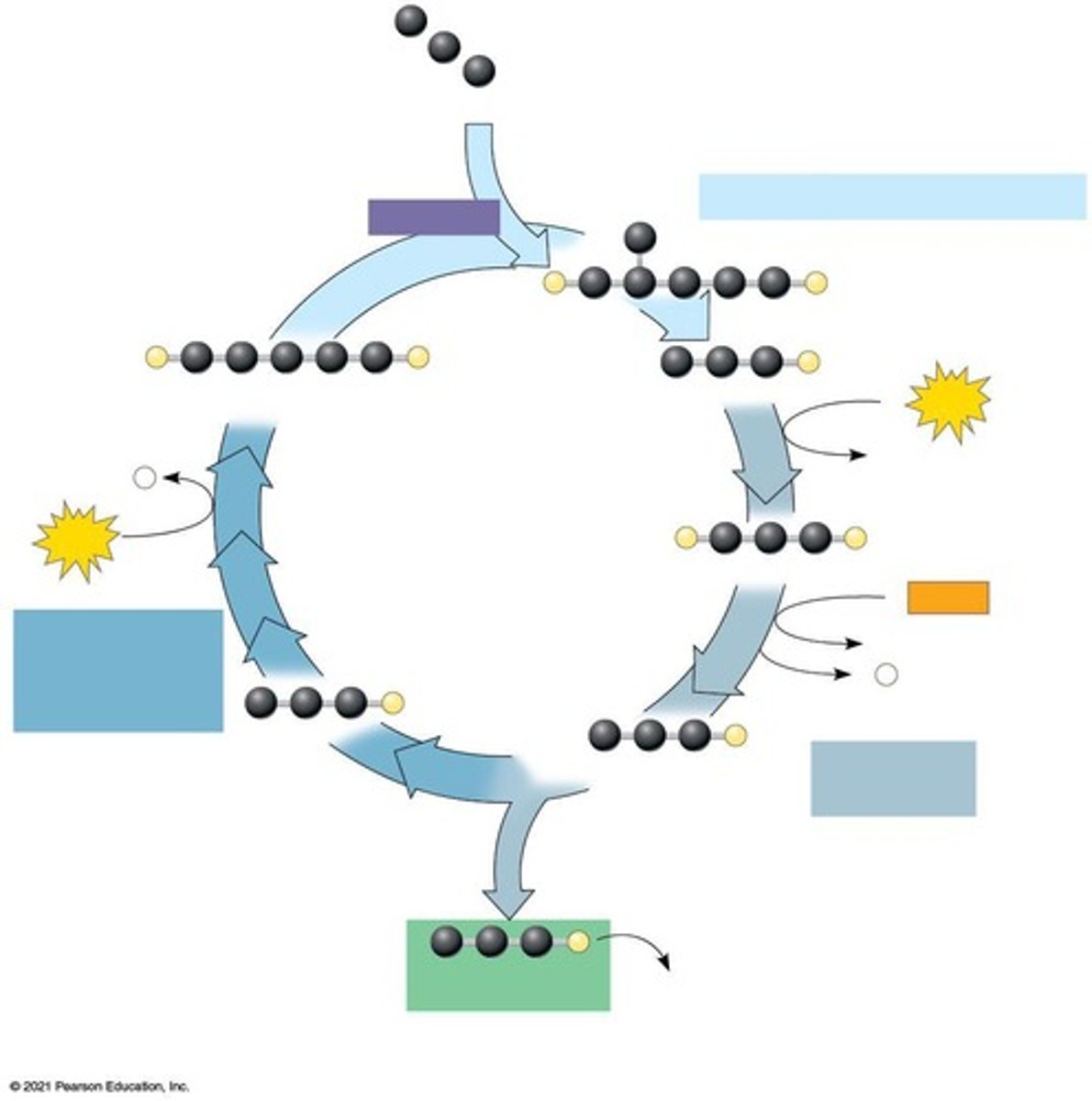
Calvin cycle turns for one glucose molecule
Six turns of the Calvin cycle are required to make one molecule of glucose
Gas released during light-dependent reactions
Oxygen
Molecule source of released gas
Water
Effect of photosynthesis stopping on Earth
Most living organisms would face extinction due to lack of oxygen and food sources
Summary of light-dependent reactions
Light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH
Summary of light-independent reactions
Carbon dioxide is fixed into glucose using ATP and NADPH produced in light-dependent reactions
NADPH
A coenzyme that carries electrons and hydrogen ions during photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis Equation
6 CO2 + 6 H2O + solar energy → C6H12O6 + 6 O2
Light Absorption
Red and blue-violet wavelengths are primarily absorbed during photosynthesis.
C4 Plants
Plants that utilize a four-carbon compound for carbon fixation, such as corn and sugar cane.
Adaptation of C4 Plants
Photosynthesize in hot, dry conditions; avoid photorespiration.
Calvin Cycle ATP Requirement
C4 plants need more ATP than NADPH to perform the Calvin cycle.
Oxygen Release
Oxygen is released to the atmosphere as a by-product of photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis Products
The main products of photosynthesis are O2, ATP, and NADPH.
C4 vs CAM Plants
In C4 plants, the Calvin cycle occurs in a separate cell from carbon fixation; in CAM plants, both occur in the mesophyll cell at different times.
Cellular Locations
Photosynthesis occurs in mitochondria or chloroplasts.
Calvin Cycle Turns
Two turns of the Calvin cycle produce one 3-carbon molecule.
Photosynthesis Processes
Splitting of water occurs in the thylakoid space; the Calvin cycle occurs in the stroma.
Oxygen Production
Oxygen is released as a by-product during the light reactions of photosynthesis.
Oxidation in Photosynthesis
When a molecule loses an electron, it is said to be oxidized.
Reduction in Photosynthesis
When a molecule gains an electron, it is said to be reduced and gains energy.
Carbon Cycle in Calvin Cycle
For each carbon atom released from the Calvin cycle, one CO2 molecule must enter; to produce PGAL, 3 CO2 must enter; to produce glucose, 6 CO2 must enter.
Impact of Stopping Photosynthesis
If photosynthesis stopped, most living organisms would die due to a shortage of energy or oxygen.
Light Energy Absorption
Light energy is absorbed by electrons from water splitting, supplying energy for ATP and NADP-H formation.
Calvin Cycle Function
Molecules of CO2 enter the Calvin cycle, where they are reduced using energy from ATP and NADP-H to construct high-energy molecules of PGAL (G3P).