💚 MATH CONCEPTS
1/218
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
219 Terms


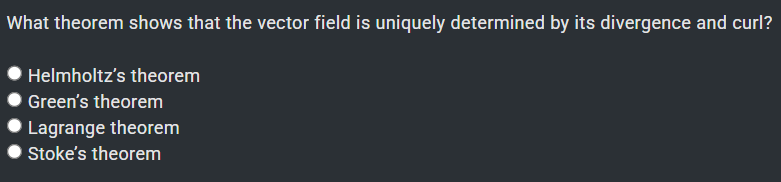
Helmholtz's theorem – States that a vector field is uniquely determined (up to boundary conditions) by its divergence and curl.
Green's theorem – Relates a line integral around a simple closed curve to a double integral over the region it encloses (2D case of Stokes).
Lagrange theorem – In math, often refers to group theory or remainder theorem, not about vector fields.
Stokes' theorem – Relates a surface integral of the curl of a vector field to a line integral around its boundary curve.
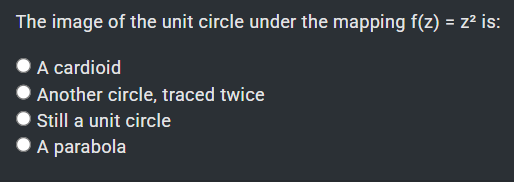
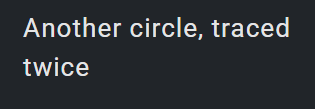

B
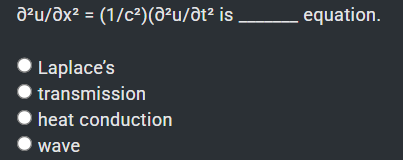
wave






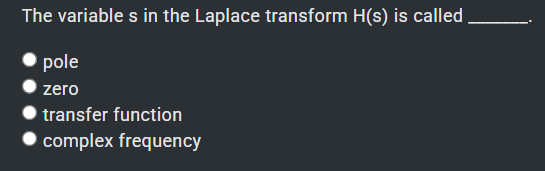
D. complex frequency
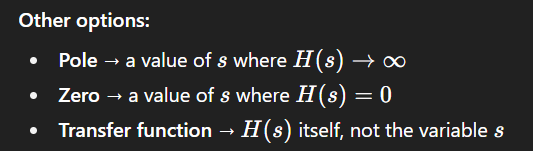


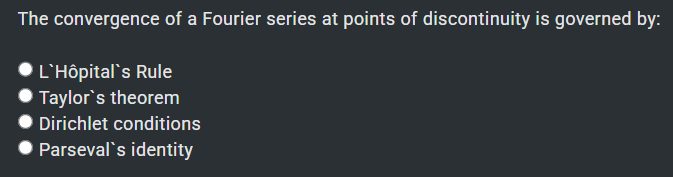
✔ Dirichlet conditions ✅
Other options:
L’Hôpital’s Rule → used to evaluate limits of indeterminate forms.
Taylor’s theorem → approximates smooth functions by polynomials.
Parseval’s identity → relates the total energy of a signal to the sum of squares of its Fourier coefficients.
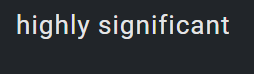
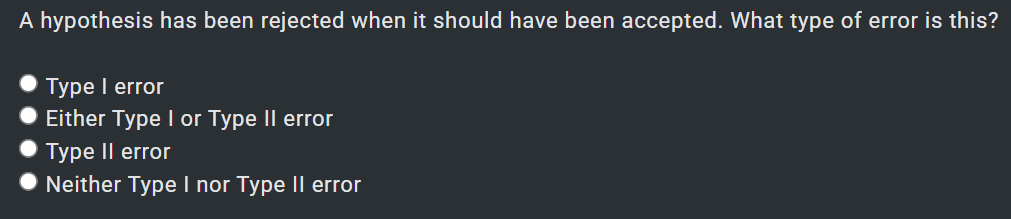
In significance test, if the level of significance is 0.01 or less,
i.e. the confidence level is 88% or more, the results are
considered to be
. none of the choices
. not significant
. highly significant
. probably significant










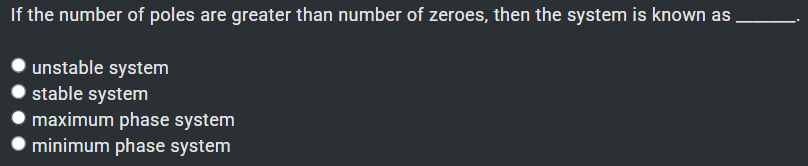
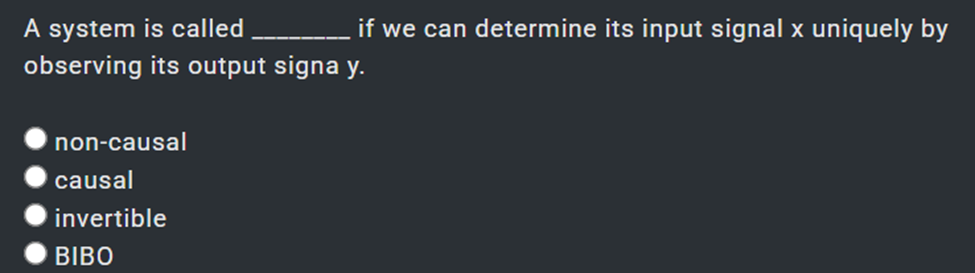
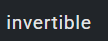
✔ minimum phase system ✅
Unstable system → occurs if any pole is in the right-half s-plane.
Stable system → all poles in left-half plane, regardless of zeros.
Maximum phase system → zeros in the right-half s-plane.



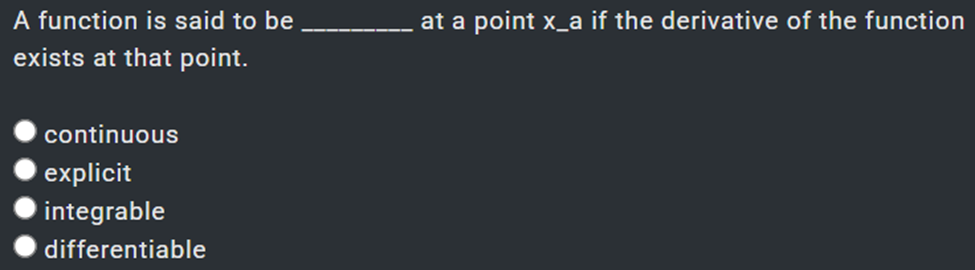
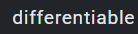
B. Complex differentiable

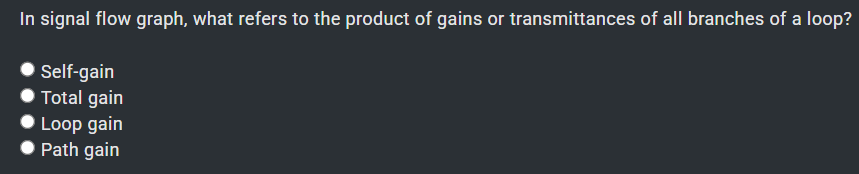
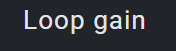




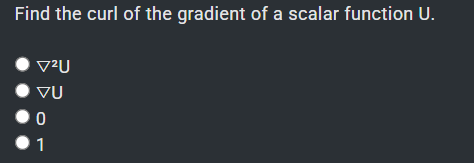
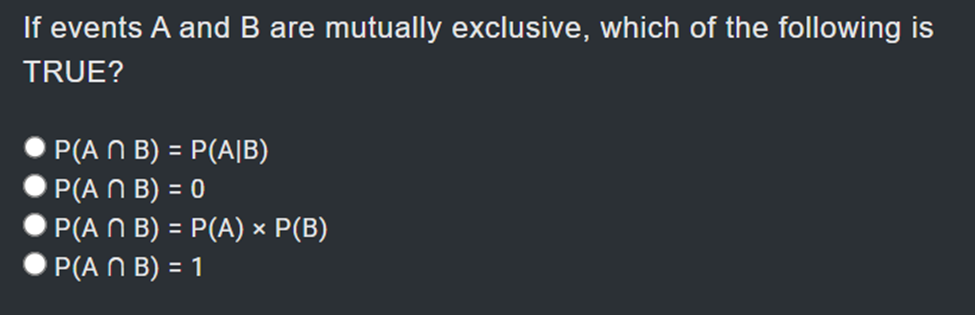
0







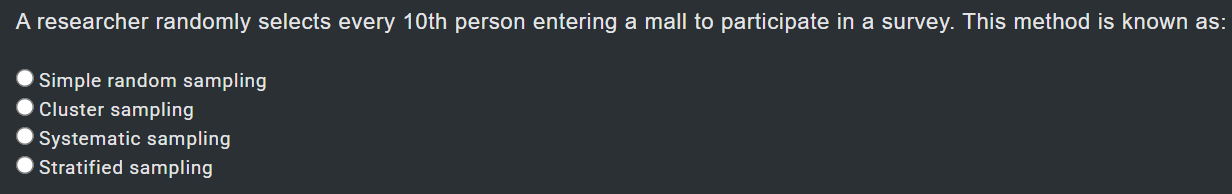
Simple random sampling → every individual has an equal chance, chosen purely at random (like drawing lots).
Stratified sampling → population is divided into subgroups (strata) and samples are taken from each.
Cluster sampling → population is divided into clusters (often geographically) and entire clusters are randomly chosen.
Systematic sampling → select every kkkth individual (e.g., every 10th person).
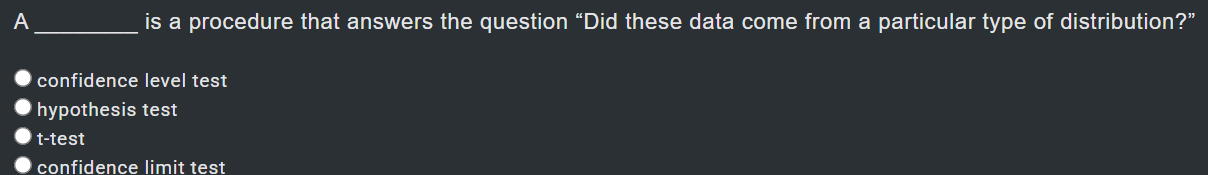
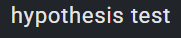
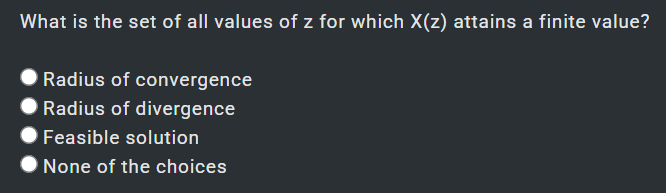



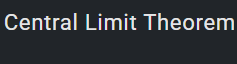
caltech
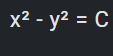

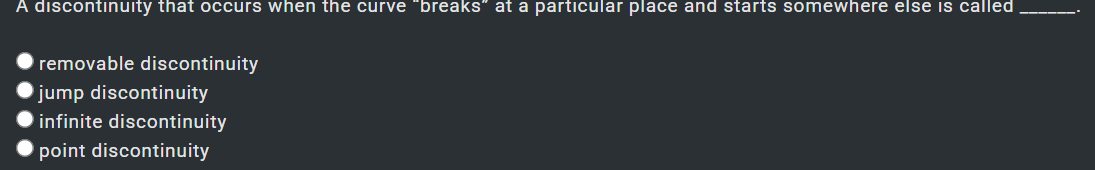



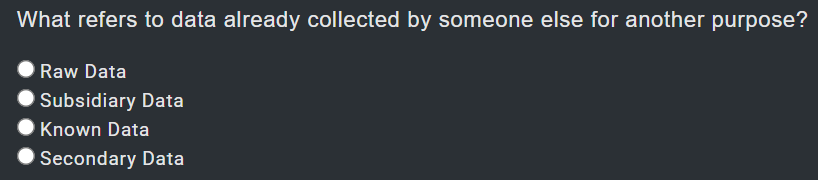
opposite pag kay normal


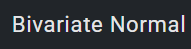

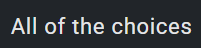



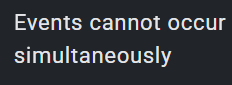
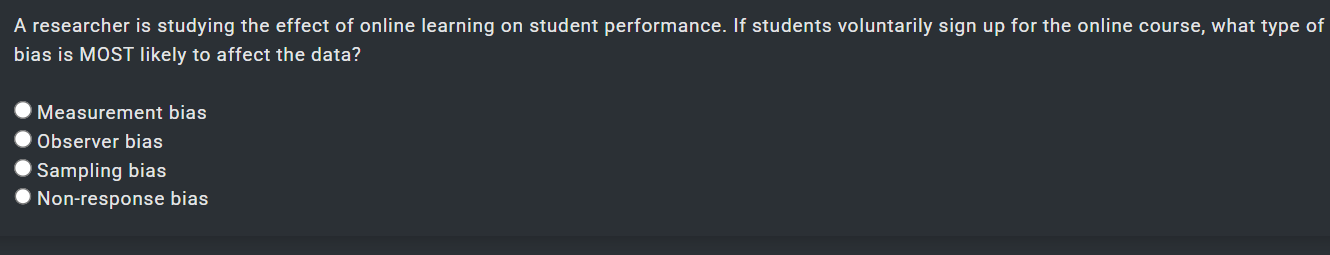
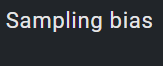

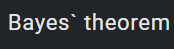

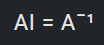
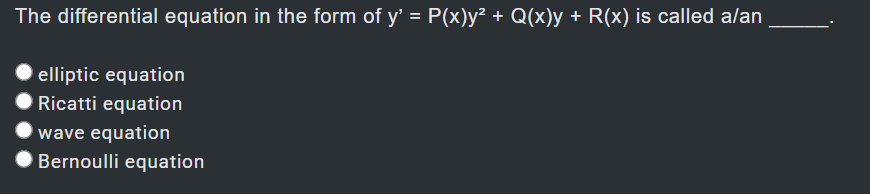
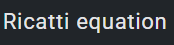

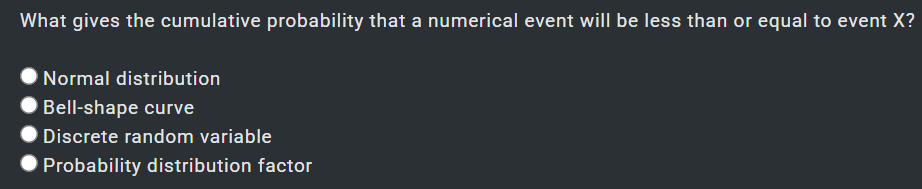

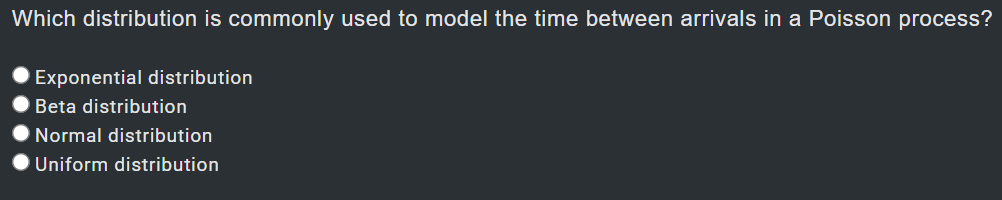
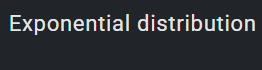

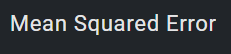

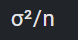
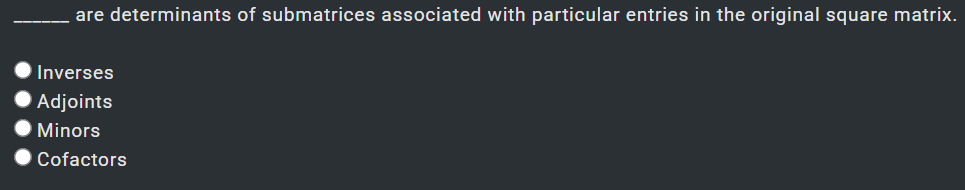


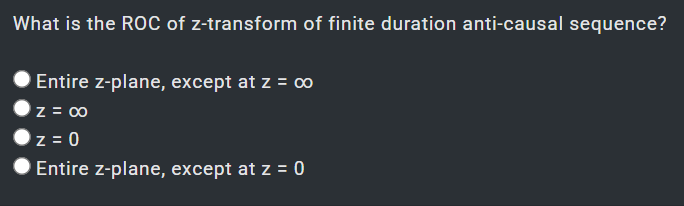
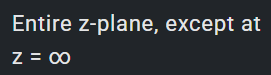
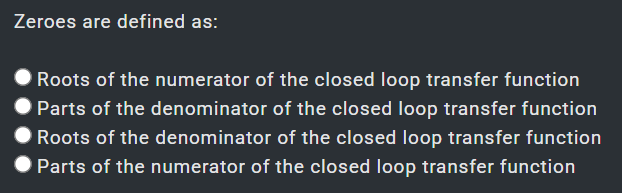

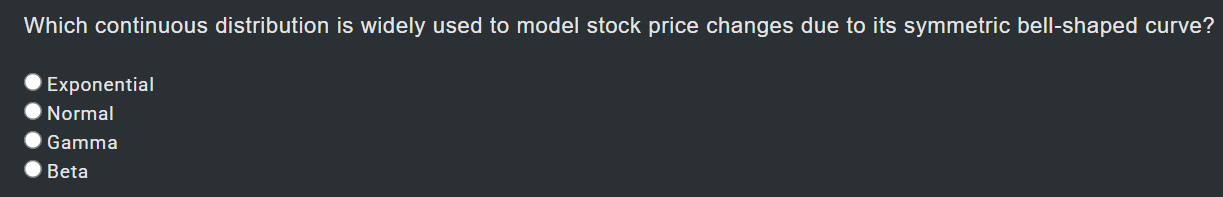

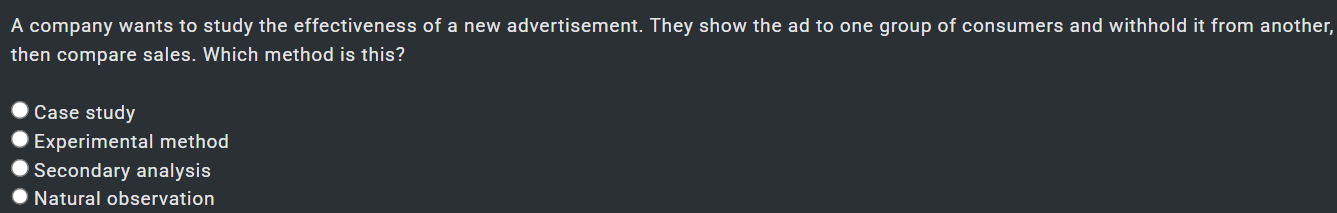

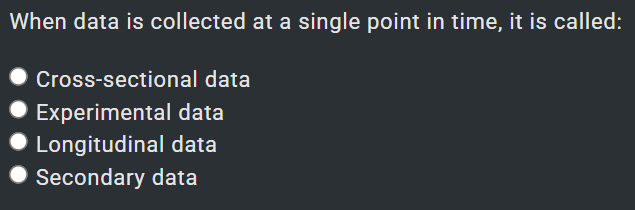
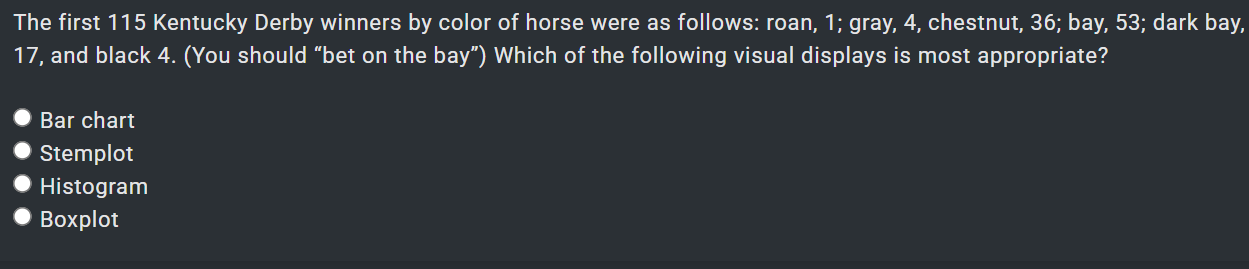
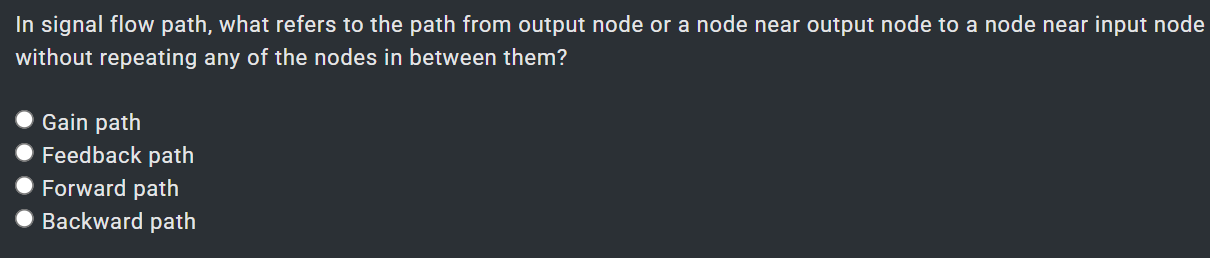




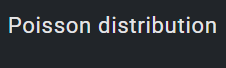
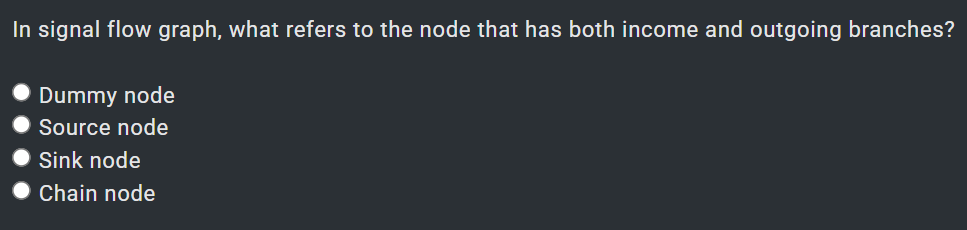
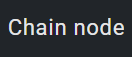
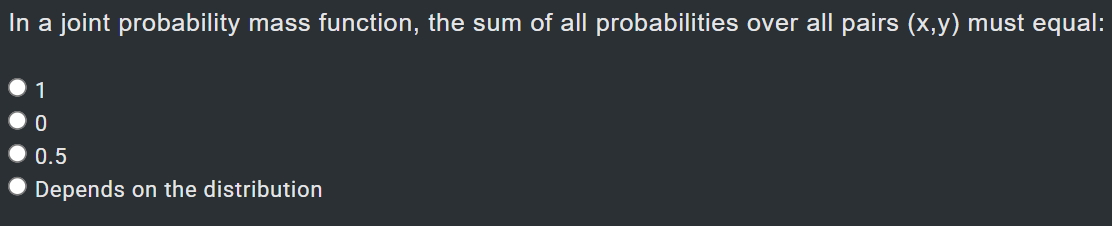
1
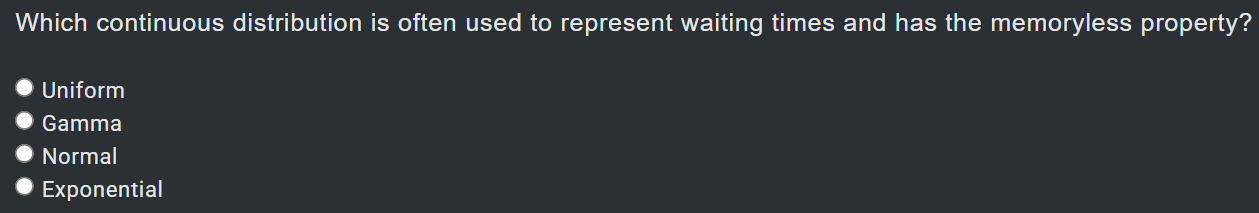

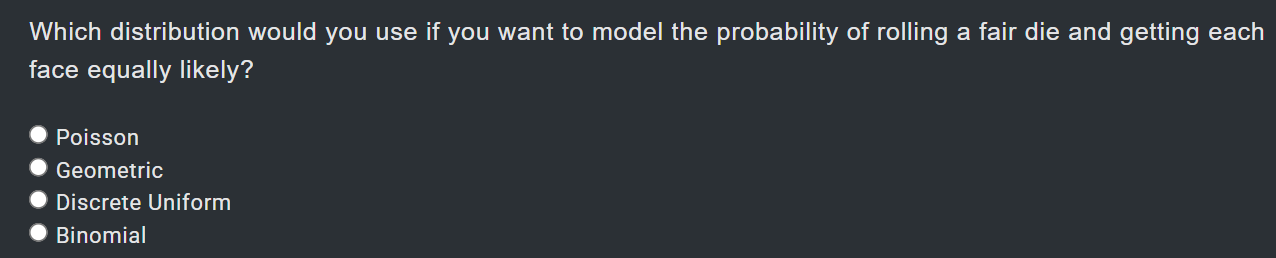
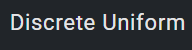

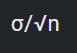






x



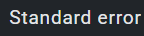
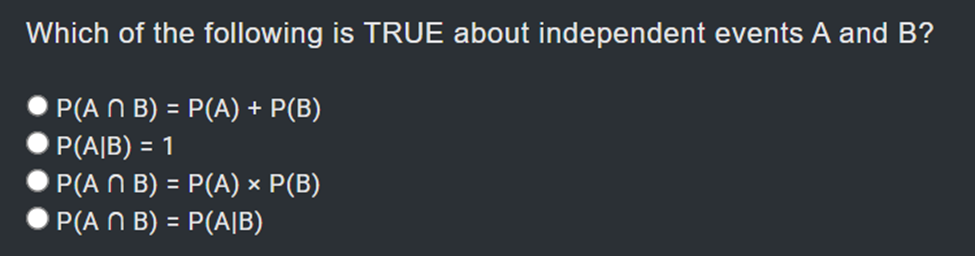
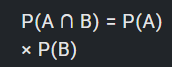
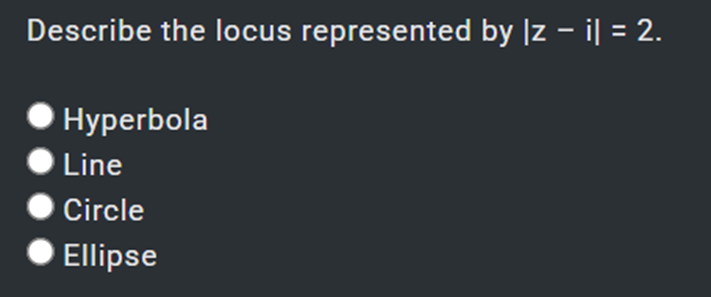
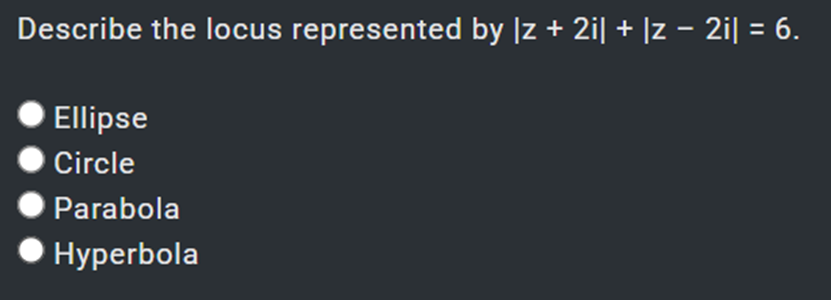
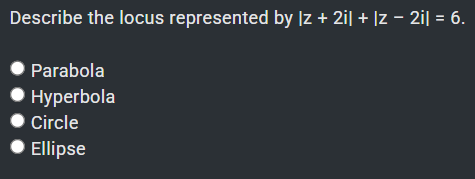
Circle