Cardiac SAM Exam 5
1/52
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Breed predispositions
Dobermans: DCM
Boxers: ARVC
Maine Coons: HCM
Cavaliers: Mitral valve degen
Westies: Pulmonary Fibrosis
GSD: Endocarditis
Normal Cardiac Auscultation
Point of maximal intensity
Pulmonic: Left 3 ICS
Aortic: Left 4 ICS
Mitral: Left 5 ICS
Tricuspid: Right 4 ICS
S1: Apex, Mitral, Tricuspid valves
Longer & lower pitched
S2: Base, Aortic, Pulmonic valves
Shorter & higher pitched
Abnormal Cardiac Auscultation
Diastolic dysfunction: gallop sound
S3: Ventricular gallop
S4: Atrial gallop
Systolic dysfunction: click sound
mitral/tricuspid regurge
Murmurs: valvular dysfunction
2/6 systolic murmurs common in puppies, grow out of it
Increased Sounds: High tone/heart size/output
Decreased Sounds: Low output, effusion, myocardial infarction failure, obesity, mass
Murmur Grades
Intermittent, 1 valve
Consistent, 1 valve area
Multiple valves
Multiple valves, loud
Palpable thrill
Can hear w/o stethoscope
Arterial Pulse
Weak Pulses: Poor perfusion, Shock, Heart failure, Aortic stenosis
Pulsus Paradoxus: inspiration, Pericardial dx w/ tamponade
Bounding Pulses: situational, shock, Aortic insufficiency, PDA, Hyperthyroidism
Cardiac Radiographs
DV views: best for cardiac structures
Left Enlargement:
LV: tall w/ lateral projection
LA: Loss of caudal waist, lg bronchus (cowboy)
Right Enlargement:
RV: wide silhouette, sternal contact, reversed D
Vertebral Heart Score
Equation = # Vertebral bodies starting @ 4VB + length AB
A: Carina down @ 90°
B: Widest part of heart
Normal: <10.5
Pulmonary Radiographs
VD views: best for pulmonary parenchyma
Vessels: compared to each other, proximal 1/3 of the 4th rib on lateral or 9th rib on VD
Prior diuretics may normalize pulmonary veins even w/ CHF
Echo Components
Probes Frequency
High: resolution
Low: penetration
Doppler
Colour: Blue Away, Red Toward, Green turbulence
Continuous: velocity of valve regurg
Pulse: low velocity, diastolic dx
Echo assessment of cardiac function
Systolic: Ejection fraction, Fractional shortening, Cardiac Output
Diastolic: E/A ratio (Mitral inflow), Doppler, Left Atrial Volume Index
Setting up an ECG
Position: Right Lateral
Settings: fastest paper speed, highest voltage possible
Leads:
1: R arm -> L arm
2: R arm -> L leg
3: L arm -> L leg
Reading an ECG
Use: ID ectopic beats, bradyarrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias
P-wave: Atrial depolarization, precedes QRS-complex
If not visible: increase amp, turn off filter
QRS complex: Ventricular depolarization
T wave: Ventricular repolarization
ST Segment Changes = ischemia
Heart rate: 6 sec X 10 or 1sec 25–50 mm, or marked

Sinus Rhythms
Bradycardia: outside influence
MOA: ↑ vagal tone from dx
ID: Normal PQRS, regular rhythm, slow rate
TX: atropine or glycopyrrolate
Tachycardia: outside influence
MOA: Pain, anemia, dehydration
ID: Normal PQRS, regular rhythm, fast rate


AV Blocks
1st Degree: outside influence/drugs
MOA: High vagal tone, drugs
ID: Prolonged PR, QRS for every P, regular rhythms
No treatment normally

2nd Degree
ID: Atropine response test**, not a QRS for every P, regular rhythms
TX: pacemaker(high grade), Atropine**, Glycopyrrolate, Propantheline, Isoproterenol, Theophylline, Terbutaline

High grade 2nd Degree AV block: structural
Atropine test - pacemaker
3rd Degree
ID: No a QRS for every P, escape rhythms, syncope if no escape rhythm
TX: pacemaker, Atropine, Glycopyrrolate, Propantheline, Isoproterenol, Theophylline, Terbutaline



Sinus Node & Atrial Disorders
Sick Sinus Syndrome
ID: tachy-brady cardia, no escape beats, irregular rhythm, no P waves for >2 sec
TX: pacemaker, Atropine, Glycopyrrolate, Propantheline, Isoproterenol, Theophylline, Terbutaline


Atrial Standstill: CHECK Potassium
MOA: Hyperkalemia, Atrial cardiomyopathy
ID: No P waves
TX: Calcium gluconate, dextrose, Insulin, 0.9% NaCl
If k+ normal: pacemaker



Premature Complexes & Tachyarrhythmias
Atrial Premature Complexes
MOA: Valve disease, DCM, neoplasia
ID: Early P wave, QRS normal

Supraventricular / Atrial Tachycardia
ID: Narrow QRS, fast rate, abnormal P wave
TX: Digoxin, Atenolol, Diltiazem, Sotalol, Procainamide


. ^^Pathologic supraventricular tachycardia and sinus tachycardia^^

^^Sinus with supraventricular premature complex^^ L Mitral murmur
Atrial Fibrillation / Flutter
ID: No P waves, Irregular R-R intervals, sawtooth
TX: Digoxin, Diltiazem, Atenolol**, Quinidine, Amiodarone, Sotalol, Procainamide




Ventricular Premature Complexes
MOA: Boxers, Dobermans
ID: Wide bizarre QRS w/o P wave
TX: Flecainide, Sotalol, Atenolol, Amiodarone, Mexiletine, Procainamide
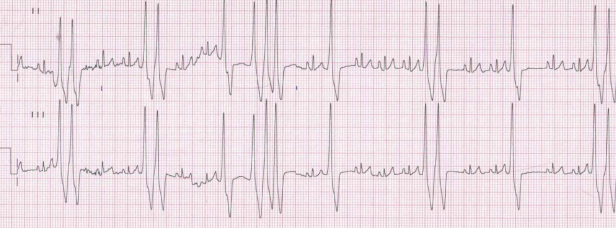

Ventricular Arrhythmias
Ventricular Tachycardia
ID: Wide, fast QRS
TX: Lidocaine, Amiodarone, Procainamide, Esmolol

Idioventricular Rhythm (slow V tach)
MOA: GDV, splenic disease, sepsis
120-160 bpm
ID: Wide, slow QRS
TX: Pain control- if needed, potassium correction
BENIGN neglect - no treatment
EX: Post operative splenectomy

Ventricular Fibrillation
ID: Chaotic, disorganized rhythm
TX: Defibrillation

Miscellaneous ECG Issues
Left Bundle Branch Block: (lead 2 + = left)
ID: Wide QRS
DDx: mimic VPC

Electrical Alternans
MOA: Pericardial effusion, supraventricular arrhythmias
ID: Alternating QRS height

Natriuretic Peptides (BNP)
MOA: Cardiac stretch or increased pressure
Use: DCM, HCM
SNAP: symptomatic cats only
Issues: Thyroid and renal dysfunction
Troponin
MOA: Myocyte Injury
Myocarditis, Ischemia, Cardiomyopathies, Neoplasia
Issues: Sepsis, Renal failure, Toxins, Systemic illness
Nutritional Cardiomyopathies
Types: Taurine, Carnitine
MOA: DCM, Cocker Spaniels
Genetic Testing for Cardiomyopathies
Use: Predictive
HCM Test: Ragdoll, Maine Coon, Sphynx
DCM/ARVC Test: Boxer, Doberman, Ridgeback, Newfie
Valvular Degeneration
MOA: Older Sm dogs, Cavaliers, Mitral > Tricuspid
Not endocarditis
Sequelae: Volume overload, resp compression, Left CHF, SupraVent arrhythmias, Chordal rupture, Left atrial tear, Jet lesions
Staging and treating Congestive Heart Failure
B: Asymptomatic w/ enlargement
TX: Pimobendan: B2 & higher, ACE inhibitors, or none, SX
B1: normal BP = no tx

C: CHF signs present
TX: Pimobendan, ACE inhibitors, Furosemide: C & higher, Spironolactone, SX

D: Refractory CHF
ID: BUN 85, Creat 2.5
TX: Pimobendan, ACE inhibitors, Furosemide, Spironolactone, Injectable Lasix, Hydrochlorothiazide, Nitroglycerin, SX

Pulmonary Hypertension
MOA: Right-sided murmur, lung disease, heartworm, L→R shunts, thromboembolism
West Highland White Terriers
CS: Weakness, Shortness of breath, Fainting/syncope, Cough
ID: R side enlargement, Enlarged pulmonary arteries, HW testing, RPAD <30%
Consider heat-fix HW testing
TX: Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, Pimobendan, Sildenafil, Clopidogrel, Toceranib, SX, Immiticide, Diroban


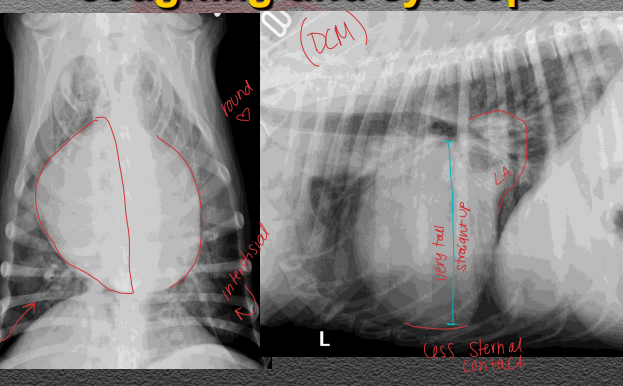
Dilated Cardiomyopathy (DCM)
MOA: Great Danes, Dobermans, Wolfhounds, Ragdoll, Maine Coon, Sphynx
CS: Resp distress, coughing, exercise intolerance, syncope/sudden death, ascites
ID: Low-grade murmur, Soft S1/S2, Crackles/wheezes, A-fib, tachycardia, LV & atrium dilation, systolic dysfunction
TX: Mexiletine, ACE Inhibitors, Furosemide, Pimobendan, Spironolactone, Digoxin
Avoid boutique, exotic, grain-free diets


Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy (ARVC)
MOA: Boxers, Irish Wolfhounds, Ragdoll, Maine Coon, Sphynx
CS: Asymptomatic, exercise intolerance, syncope/sudden death
ID: Holter test
TX: Sotalol, Mexiletine, Atenolol, Fish oils

Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
MOA: LV/LA wall thickening
Breeds: Ragdoll, Maine Coon, Sphynx
ID: Echo, genetic test, high BNP, pulmonary infiltrates
Rule out: Hyperthyroidism, Hypertension, Hypersomatotropism
TX: Furosemide, ACE Inhibitor, Clopidogrel, LMWH, Aspirin, Atenolol, Diltiazem: (if asthma/bronchitis)


Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy (HOCM)
MOA: Mitral valve pulled toward septum during systole causing LVOT obstruction
Subtype of HCM
ID: SAM of mitral valve on ECHO
TX: Atenolol, Furosemide, ACE Inhibitor (Enalapril), Clopidogrel, LMWH, Aspirin, Atenolol, Diltiazem

Restrictive Cardiomyopathy (RCM)
MOA: Endocardial fibrosis, impaired ventricular filling
Breeds: Ragdoll, Maine Coon, Sphynx
ID: Normal wall thickness and systolic function, Bi-atrial dilation, atrial arrhythmias may occur
TX: Furosemide, ACE Inhibitor, Clopidogrel, LMWH, Aspirin, Atenolol, Diltiazem

Unclassified Cardiomyopathy (UCM)
MOA: Doesn’t fit into HCM/RCM/DCM categories
Breeds: Ragdoll, Maine Coon, Sphynx
ID: Atypical or mixed patterns
TX: Symptomatic dependent
Heart Failure
MOA:
Right Side: Pulmonary edema
Left Side: Ascites, pleural or pericardial effusion
CS: Dyspnea, crackles/wheezes, coughing (dogs), pleural effusion (cats), abdominal distension, fluid wave, hepatomegaly, muffled heart/lung sounds
Cats don't cough
ID: Echo, BNP, Troponin, T4 (cats >7y), ECG, BP, LA enlargement, pulmonary venous congestion, pulmonary infiltrates
TX: Nitroglycerin, Pimobendan, Butorphanol, Dobutamine, Nitroprusside, Furosemide, ACE inhibitor
Avoid: Fluids, beta-blockers, diltiazem
Common Cardiac Medications
Nitroglycerin: Preload, CHF
Furosemide: Preload, CHF
ACE inhibitor: Afterload, CHF, cardioprotective
-pril
Pimobendan: Inodilator, CHF
Sedation: Butorphanol
Dobutamine: Cardiogenic shock (cats)
Nitroprusside: If hemoptysis and normotensive
Sildenafil: PDE-5 inhibitor, hypertension
Tadalafil: PDE-5 inhibitor, hypertension
L-arginine: nitric oxide precursor, hypertension
Theophylline: PDE-4 inhibitor, hypertension
Beta blockers: Antiarrhythmic, not for CHF, cardioprotective
olol
Hypercoagulation Disorders
MOA: Heart dx, protein-losing dx, hyperadrenocorticism (Cushing’s), IMHA, neoplasia
CS:
Right Heart Emboli: Respiratory signs (dyspnea, tachypnea)
Left Heart Emboli: Limb paralysis, seizures, acute renal failur
ID: TEG, Sonoclot, Antithrombin III levels, Proteinuria
TX: Opioids, Heparin, Clopidogrel, Aspirin, Dabigatran, Apixaban / Rivaroxaban, SX
Aortic Thromboembolism in Cats
MOA: Often left side, HCM, saddle thrombus
CS: Absent/reduced pulses, cold limbs, pain, LMN signs, quick-to-bleed toenails
ID: Elevated CK/ALT/AST, ECHO
TX: Opioids, Heparin, Clopidogrel, Aspirin, Dabigatran, Apixaban / Rivaroxaban, SX
Prognosis: 50/50, watch for reperfusion injury

Pulmonic Stenosis
MOA: Dogs, valvular > sub/supravalvular, congenital
CS: Left systolic murmur
TX: Beta blockers, Balloon valvuloplasty (not for Boxers/Bulldogs)


Patent Ductus Arteriosus (PDA)
MOA: Persistent connection between pulmonary artery and aorta, congenital
CS: Continuous murmur, hyperdynamic (water hammer) femoral pulses
ID: Echo, rads, Doppler with continuous flow peak velocity >4 m/s
TX: Surgical ligation, ductal occlusion (ACDO)

Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD)
MOA: #1 congenital defect, communication between R and L ventricles; paramembranous > muscular or subpulmonic
Left side overload
ID: Echo and Doppler with high velocity
TX: Palliative pulmonic banding, ACE inhibitors, Pimobendan, Diuretics

Subaortic Stenosis (SAS)
MOA: Valvular or supravalvular
CS: Loud left basilar systolic murmur, weak pulses
TX: Beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, Furosemide
Not surgical candidates

Tricuspid Valve Dysplasia
MOA: Labs, thickened valve, shortened chordae, tethered leaflets, congenital
CS: Right apical systolic murmur
ID: Splintered QRS on ECG
TX: Furosemide, Enalapril, Pimobendan


Mitral Valve Dysplasia
MOA: Thickened valve, short chordae, restricted leaflet motion, congenital
CS: Murmur at left apex, supraventricular arrhythmias
TX: ACE inhibitor, Pimobendan
Atrial Septal Defect (ASD)
MOA: Septum primum, septum secundum, sinus venosus, patent foramen ovale; congenital
CS: Right volume overload, no murmur, Split S2 heart sound
TX: Surgical closure

Reversed Shunts (PDA, ASD, VSD)
MOA: Pulmonary hypertension, R → L shunting, congenital
CS: No murmur, cyanosis, exercise intolerance, polycythemia
TX: Phlebotomy, Hydroxyurea, Sildenafil, L-arginine, Pimobendan

Persistent Right Aortic Arch (PRAA)
MOA: Congenital
CS: GI upset
ID: Rads
TX: Surgical excision of ligamentum arteriosum

Pericardiocentesis
Indications:
Diagnostic sampling
Treatment for cardiac tamponade or hemodynamically significant effusion
Technique:
Right side, 4th/5th intercostal space, just dorsal to costochondral junction



Aortic Body Tumor (ABT)
MOA: Brachycephalic breeds, pericardial disease
CS: Collapse, weakness, dyspnea, cough, vomiting, muffled heart/lung sounds, weak femoral pulses, pulsus paradoxus, ascites
ID: Electrical alternans on ECG with ventricular ectopy, globoid heart on rads, pericardiocentesis, cytology
TX: Pericardectomy


Hemangiosarcoma (HSA)
MOA: Right atrium/auricle, pericardial disease
CS: Collapse, weakness, dyspnea, cough, vomiting, muffled heart/lung sounds, weak femoral pulses, pulsus paradoxus, ascites
ID: Same as ABT
TX: Doxorubicin (chemo)

Peritoneopericardial Diaphragmatic Hernia (PPDH)
MOA: Congenital, abnormal fusion of septum transversum with pleuroperitoneal folds
Not related to trauma
CS: Collapse, weakness, dyspnea, cough, vomiting, muffled heart/lung sounds, weak femoral pulses, pulsus paradoxus, ascites
ID: Electrical alternans on ECG w/ ventricular ectopy, globoid heart on rads, pericardiocentesis, cytology, ultrasound
TX: Surgery if necessary (NOT ALWAYS NEEDED)

Interpreting Blood Pressure Readings
Systolic: Pressure during ventricular contraction
Diastolic: Pressure during relaxation
MAP: Average pressure during cardiac cycle
MAP = (2 × Diastolic + Systolic) ÷ 3
MAP = Diastolic + 1/3(Systolic – Diastolic)
Methods of Measuring Blood Pressure
Doppler: Non-invasive
Cuff = 40% of limb
Average 5 readings, 30 sec
Oscillometric: Automated, anesthesia patients, gives HR
Invasive: Arterial Line, direct, Gold standard
Systemic Hypertension
MOA: Cushing’s, Hyperthyroidism, CKD, Pheochromocytoma
Lowers testing threshold
ID: MAP >145 mmHg, Systolic >180 mmHg (dogs) or >160 mmHg (cats)
TX: Na nitroprusside, Hydralazine, Amlodipine, ACE inhibitors, Telmisartan (cats)

Endocarditis
MOA: Bacteremia (bartonella) mitral/aortic valves, L > R side, Lg dogs, GSD, males
Subaortic stenosis: Only structural dx w/ increased risk
Recent corticosteroid use
CS: Fever, Lameness, Seizures, Heart murmur, CHF signs, Hyperdynamic pulses
Dental disease: No significant correlation
ID: Culture - 3 different samples, 3 different sites
CBC/Chem/UA: infection signs
ECG: Premature atrial/ventricular beats, AV block
Echo: Vegetative valve lesions, Regurgitation
Bartonella: PCR/serology - takes too long
TX: Azithromycin, Doxycycline + enrofloxacin, Gentamicin/aminoglycosides, Furosemide, ACE inhibitor, pimobendan, spironolactone
No gold standard therapy for Bartonella