LECTURE 14: Emerging and Zoonotic Diseases
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
endemic diseases
tuberculosis
respiratory infections
diarreal diseases
malaria
helminths (worms)
emerging/reemerging diseases
aids
mutidrug resistant TB
dengue
hanta (HPS)
lyme disease
ebola
leptospirosis
cholera in the americas
covid 19
key factors in endemic diseases
poverty
poor sanitation/hygiene
malnutrition
overcrowding
key factors in emerging diseases
international trade and travel
economic development and land use
deforestation
new roads, mines, plantations
contact with wild animals
ecological and climate change
behavioural and demographic cange
technology and industry
microbial adaptation (antibiotic resistance)
breakdown of public health
susceptibility: lack of immunity
the convergence model
factors influencing the outcome of microbial infections
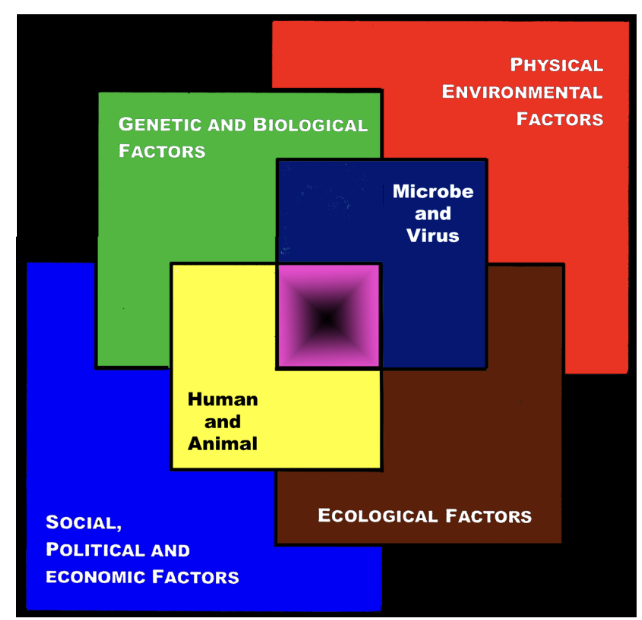
center of the box represents the convergence of factors leading to the emergence of infectious disease
black center represents unknown factors: “black box”
model indicates that all factors are interlocking
zoonotic infection
a human infectious disease originating from an animal reservoir and not requring the human as part of its life cycle
infectious agent/disease that can successfully circulate among animals without the host
diseases where human is required for life cycle are NOT zoonotic
helminths
other infections with animal intermediate
current zoonotic diseases may be due to…
more recent exposure of humans to microorganism
slower evolution of host-parasite relationship
Diseases that were zoonootic, but now exclusively human
small pox virus evolved from camelpox virus
measles virus from reinderpest virus of cattle
mycobacterium tuberculosis from M.bovis
HIV from SIV (simian immunodeficiency virus)
ebola virus
linear non-segmented ss - RNA genome
filovrius: appears as filamentous particles in the shape of a hook
first discovered near ebola river in Congo
ebola virus: natural reservoir
fruit bats in the Pteropodidae family are considered the natural host
ebola virus: transmission TO humans
transmitted to people from wild animals
close contact with blood, secretions, organs, or other bodily fluids of infected animals
in africa, infection has been documented through the handling of infected champanzees, gorillas, fruit bats, monkeys, forest antelope, and porcupines found ill/dead in rainforest
ebola virus: transmission AMONG humans
direct contact with blood or bodily fluids of an infected symptomatic person
exposure to objects (needles) that have been contaminated with infected secretions
viruses often spread through families and friends that come in close contact with infectious secretions when caring for ill persons
ebola virus: transmission in health care settings
hospital staff not wearing appropriate protective equipment: masks, gowns, gloves
lack of proper cleaning and disposal of instruments (needles, syringes)
inadequate sterilization of instruments reused
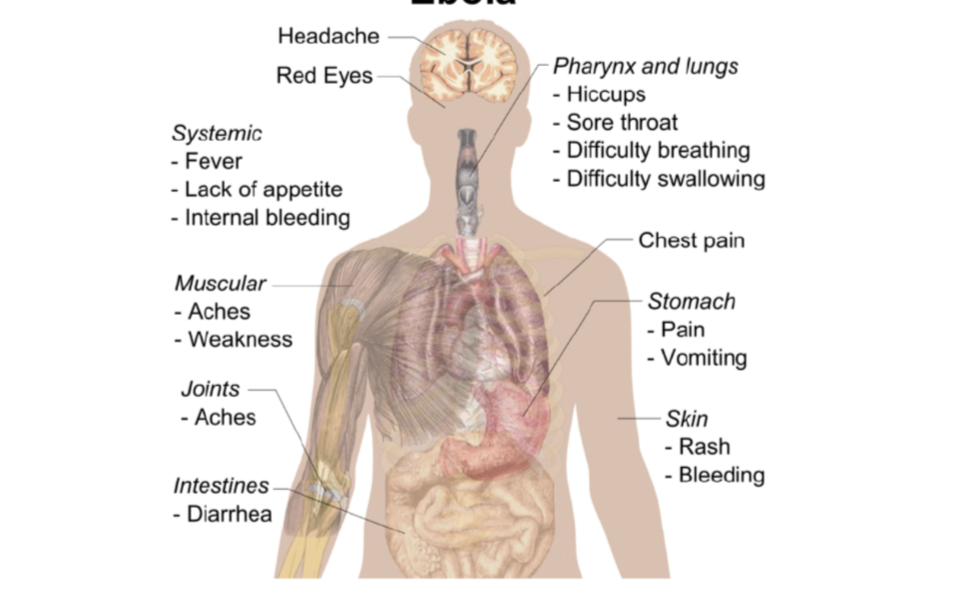
symptoms of ebola
treatment of ebola
balance pateints fluids and electrolytes
maintaining oxygen status and blood pressure
treating for any complicating infections
monoclonal antibodies
ebola prevention
express ebola glycoprotein on surface of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV), a benign virus that causes asymptomatic or mild flu-like symptoms in humans
rabies
ss - RNA, enveloped virus
rhabdovirus: rod/bullet shaped
most deadly infectious disease known
does not follow iceberg pattern
reservoirs of rabies
wild and domestic animals
rabid cat
fox
bat
mongoose
racoon
skunk
transmission of rabies
virus shed into saliva and transmitted when animal bites the human
enters via animal bite/skin break, replicates locally, migrates to neurones
may also be transmitted via exposure to bat feces
pathogenesis of rabies
virus multiples initially in tissue around bite
travels up nearby peripheral nerves to brain (1-3 months), then destroys cells in the CNS
moves to salivary glands
clinical manifestations of rabies
spinal cord, brain: acute encephalitis
infection to symptoms: 20-60 days
pain at site of wound: bat bites may be painless
neck pain around 2 months later
loss of control of movement
throat muscle paralysis: difficulty swallowing
drooling
hydrophobia (fear of water)
behaviour change: extreme agitation
coma
death 3 months after exposure
diagnosis of rabies
usually after death, using autopsy material from animal or human
negri bodies in the brain
PCR of brain / other material
samples taken from wound
fluorescent antibody test
PCR
treatment of rabies
no established antiviral treatment available
immunological treatment:
passive immunization injected
active immunization with inactivated vaccine; 2 injections in the arm, each 1 week apart
secondary prevention
virtually 100% effective
rabies prevention
animal control
required vaccinations of dogs
quarantine of imported animals in countries/areas that are rabies free
wildlife surveillance and reducing stray, unvaccinated dog and cat population
vaccination of people at risk of exposure
occupational
outdoor work with wildlife exposure
laboratory personnel
travelers to high risk areas
education of the public
toxoplasmosis
Toxoplasma gondii
protozoan parasite
Apicomplexa phylum
reservoir: cats and other feline
definitive host: cat
reservoir of toxoplasmosis
cats and other felines
transmission of toxoplasmosis
cats are definitive host: sexual cycle occurs only in intestine of feline family
transmission occurs from ingestion of material contaminated with cat feces
bird, rodents, ungulates, humans are intermediate hosts
T.Gondii forms cysts in their tissues
transmission can occur from eating undercooked beef
toxoplasmosis epidemiology
ubiquitous
invades all cell types
worldwide zoonosis
seropositivity increases with age
opportunistic infection associated with AIDS
clinical manifestations of toxoplasmosis
infection in most adults asymptomatic due to control by the immune system
infection severe and possibly fatal in immunocompromised individuals due to encephalitis, neurologic diseases
small children: fever, rash, pneumonia, encephalitis
toxoplasmosis effect on fetus
T.gondii can cross placenta in 40% of fetuses of non-immune mothers
mismarriage
12% of babies die shortly after birth
<20% are normal after age 4
damage to central nervous system
hydrocephaly
blindness
mental impairment
motor disturbances
diagnosis of toxoplasmosis
direct smear of material from spinal fluid or blood
ELISA serum antibody test
PCR
treatment of toxoplasmosis
sulfonamides, pyrimethamine, sulfadiazine (inhibit folic acid synthesis)
protozoans need folic acid in greater quantity than host cells
prevention of toxoplasmosis
avoid eating raw or undercooked meat
prophylactic antimicrobials for a non-immune pregnant woman who has been exposed
don’t have a cat, or have an indoor-only cat
if there is an indoor-outdoor cat
use hygienic food preparation practices
keep cats off kitchen counters and eating table
wash hands between handling cat and preparing food
be cautious in handling kitty litter
pregnant women should not empty kitty litter
effect of toxoplasmosis on mice
mice infected with toxoplasmosis lose their instinctive fear of the smell of cats
parasites effect may be permanent
toxoplasma and behaviour manipulation in animals
animals: greater predation of intermediate host by definitive host
increased non specific movements, more active
reduced neophobic behaviour (less fear of new scents, sounds)
reduced aversion (fatal attraction) to cat urine
reduced learning behaviours
toxoplasma and behaviour manipulation in humans
humans (chronic infection)
schizophrenia
suicide attempts associated with seropositivity to T Gondii
epilepsy
Congenital toxoplasmosis may reduce brain function
loss of psychomotor performance
men become more jealous, emotionally unstable, suspicious, short tempered, low self esteem
women and men more anxious
plague
Yersinia pestis
gram - cocobaccilius
reservoirs: praire, rat, chipmunk, squirrel
transmission of plague
requires the flea as a vector
bacteria multiply in flea gut and block it, causing flea to regurgitate infected material when flea feeds on a new host
flea is in a starving state so bites frantically
bubonic plague
Y. pestis multiplies in lymph fluid and lodges in lymph node nearest the site of flea bite
bubo = enlarged lymph node black from hemorrhage and fever occur within 2-6 days
disease not communicable among humans at this stage
pneumonic plague
occurs in 5% of plague cases
bacteria enter blood and disseminate to lungs, causing pneumonia
within 1-3 days skin becomes bluish to black from hemorrhage and lack of oxygen (black death)
disease is communicable among humans in this stage through respiratory route
mortality virtually 100% within a few days if early treatment not given
diagnosis of plague
patient sample from a bubo or gram stain (gram - coccobacillus)
direct smear made with laboratory antibody bacteria
rapid dipstick test for field testing of humans measures Y.pestis in human blood reacted with laboratory antibody to Y.pestis
treatment of plague
lancing/drainage of buboes
steptomycin, doxycycline, other antimicrobials
treatment effective if given early enough but diseased may not be recognized early enough
prevention of plague
surveillance for dead rodents in endemic areas
if surveillance shows positive animals, rodent extermination in residential areas
posting of warning signs
inspection of ships for rats to prevent transport to a new area
rat guards on mooring ropes
education of tourists not to feed squirrels and chipmunks out of their hands
use insect repellant outdoors in endemic areas
prophylatic antimicrobial after probable exposure
vaccination for people in high risk occupation
anthrax
bacillus anthracis
large, gram + bacilli, facultative anaerobe, endospore forming
endospores only form under aerobic conditions
zoonotic disease
herbivores: sheep, goats, cattle, reindeer - acquired for contaminated soil
carnivores infected from consuming meat
reservoir: animals (contaminated soil)
transmission of anthrax
human: contact with endospores during occupational exposure on farms/industries= wool, hides, meat, bones
wool sorters disease: respiratory anthrax
clinical manifestations of anthrax
cutanous anthrax: skin lesions, center black and necrotic
intestinal anthrax: symptoms mimic food poisoning
lesions/ulcerations in digestive tract
can lead to septicemia and death
outbreak from unpasteurized goats milk cheese
respiratory: most deadly; most concern with bioterrorism
symptoms similar to flu
inhaled into lungs, spores germinate in alveoli
phagocytized by macrophages, replicate
anthrax diagnosis
blood culture
gram stain
culture of external lesions
serological tests
PCR assays
treatment of anthrax
ciprofloxacin (fluoroquinolone)
penicillin
doxycycline
erythromycin
prevention of anthrax
human vaccine: 6 doses over 18 months
reduce exposure to endospocres
dispose of infected animals properly
vaccinate animals
one health triad
encompassing the collaborative goals providing optimal health for people, animals (domestic and wild) and the environment by considering interactions between all 3 systems