larger covalent substances
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
10 Terms
Q: What is a polymer and how is it formed?
A polymer is a large molecule made by joining many small molecules called monomers in a repeating chain through covalent bonds
What is the repeating section of a polymer called?
The repeating unit.
How is the repeating unit shown in a polymer diagram?
It’s drawn in brackets with bonds extending out of each side and an n after the brackets.
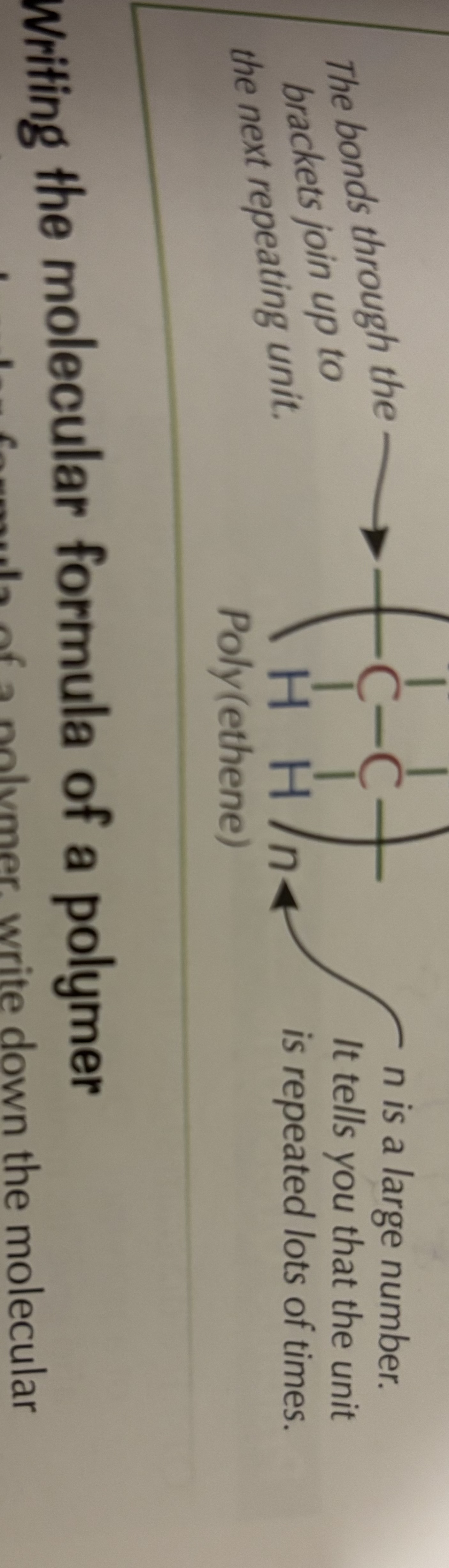
Why do polymers have high melting and boiling points compared to simple molecules?
Because the intermolecular forces between the long polymer chains are stronger, requiring more energy to overcome.
What kind of bonds are broken when a polymer melts?
Only the intermolecular forces between polymer chains — not the covalent bonds inside the molecules.
What are giant covalent structures?
Substances with a huge network of atoms bonded together by strong covalent bonds.
Examples of giant covalent structures?
Diamond, graphite, and silicon dioxide (SiO₂).
Why do giant covalent structures have high melting and boiling points?
Because many strong covalent bonds must be broken to melt or boil them.
Why is diamond hard?
Each carbon atom is bonded to four others in a strong, 3D network.
How are graphite and diamond similar?
Both are allotropes of carbon with giant covalent structures.