Electromagnetic radiation
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
Electromagnetic radiation
a range of electromagnetic waves consisting of oscillating electric and magnetic fields travelling at the speed of light.
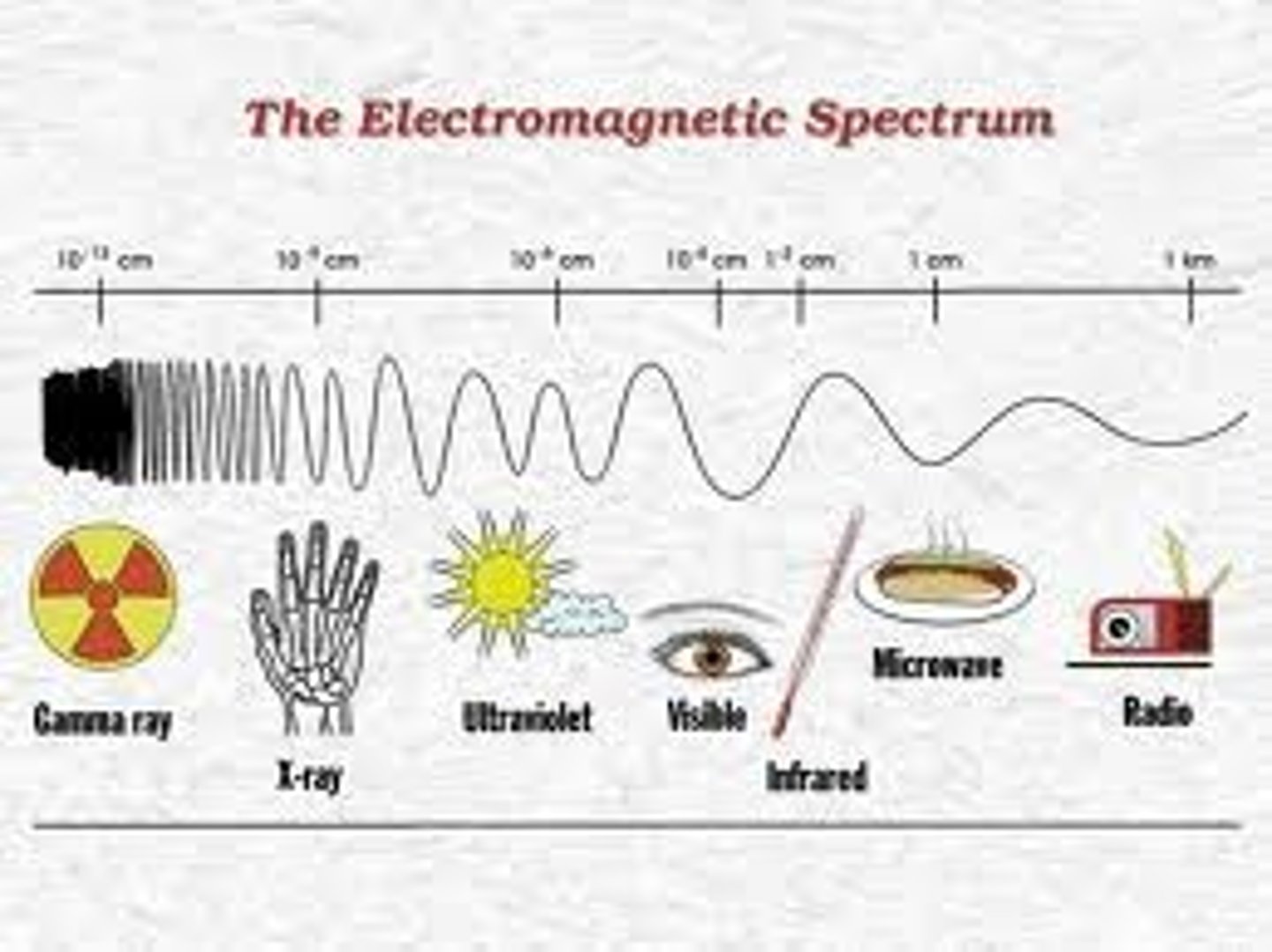
electromagnetic spectrum
the range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy gamma rays to low energy radio waves.
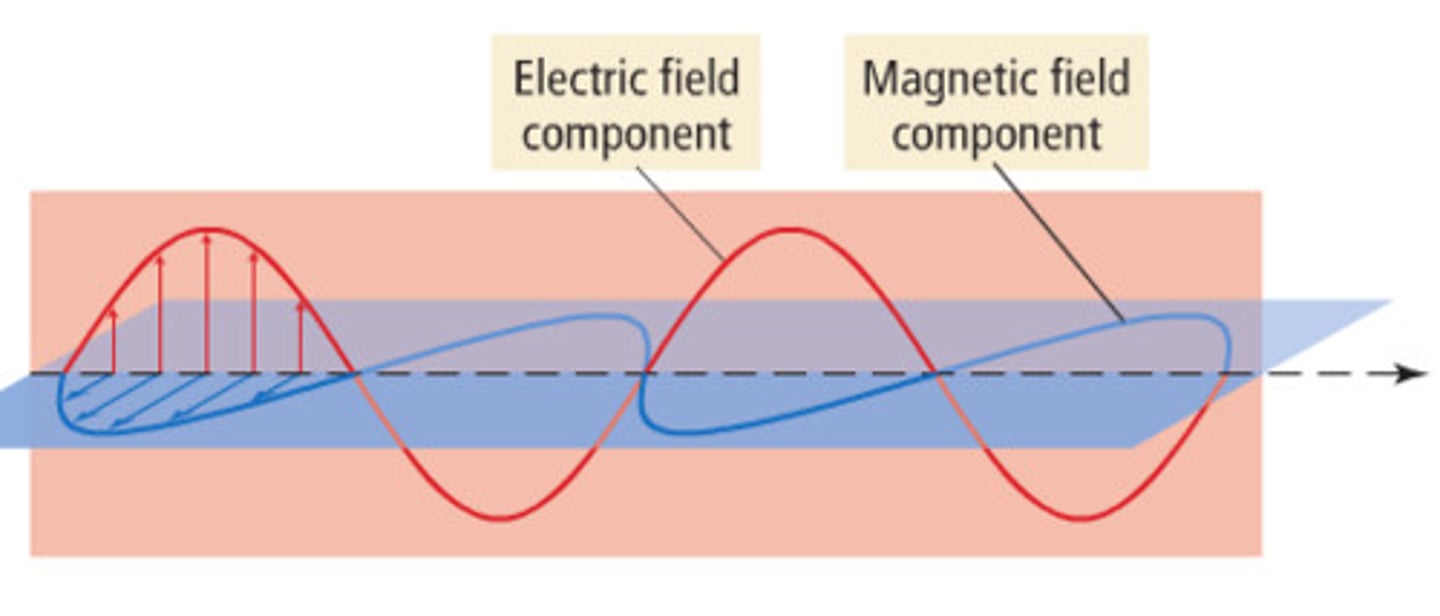
electromagnetic wave
transverse electric and magnetic fields positioned at right angles to each other and travelling through empty space at the speed of light.
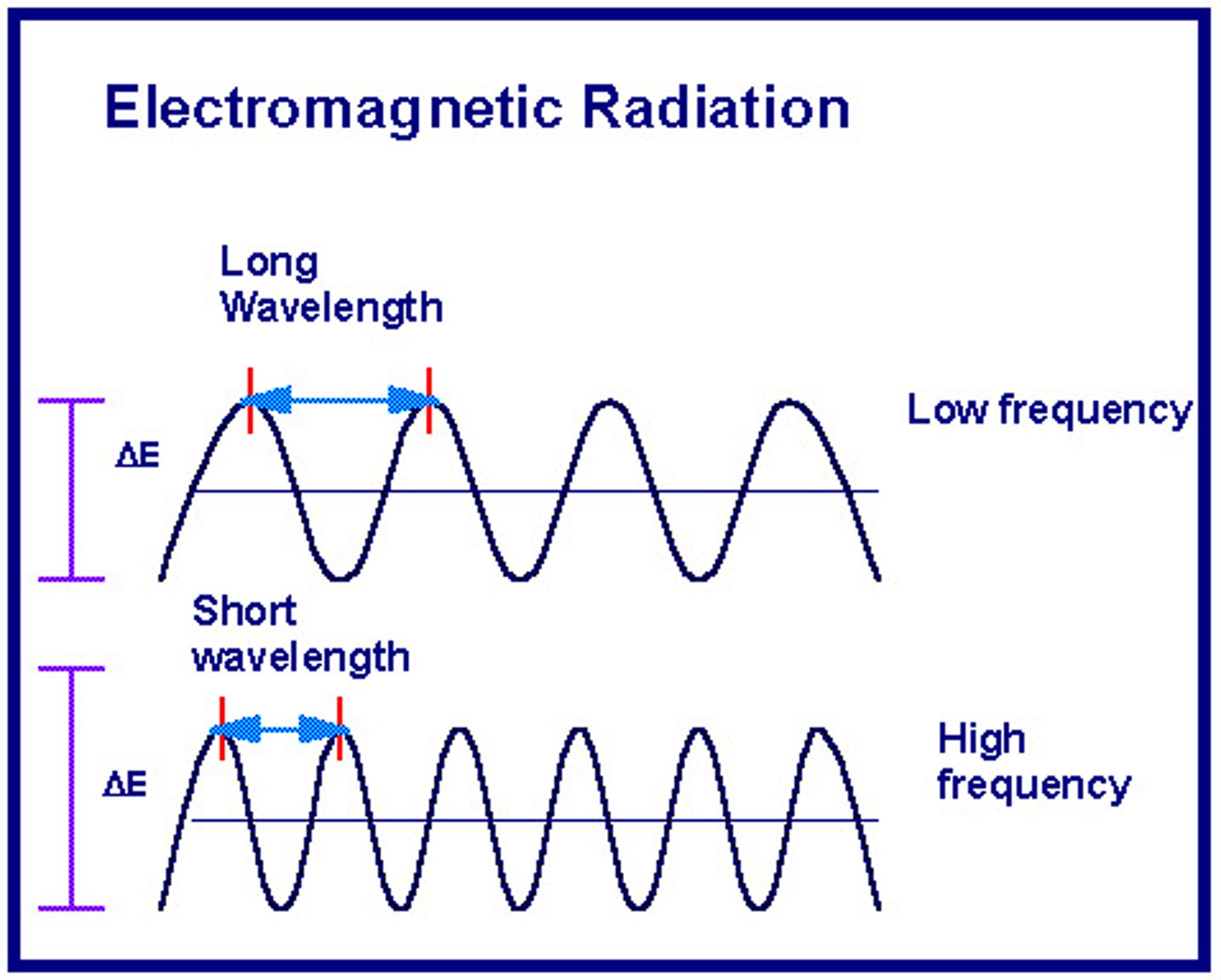
frequency
the number of waves produced per second, measured in hertz (Hz).
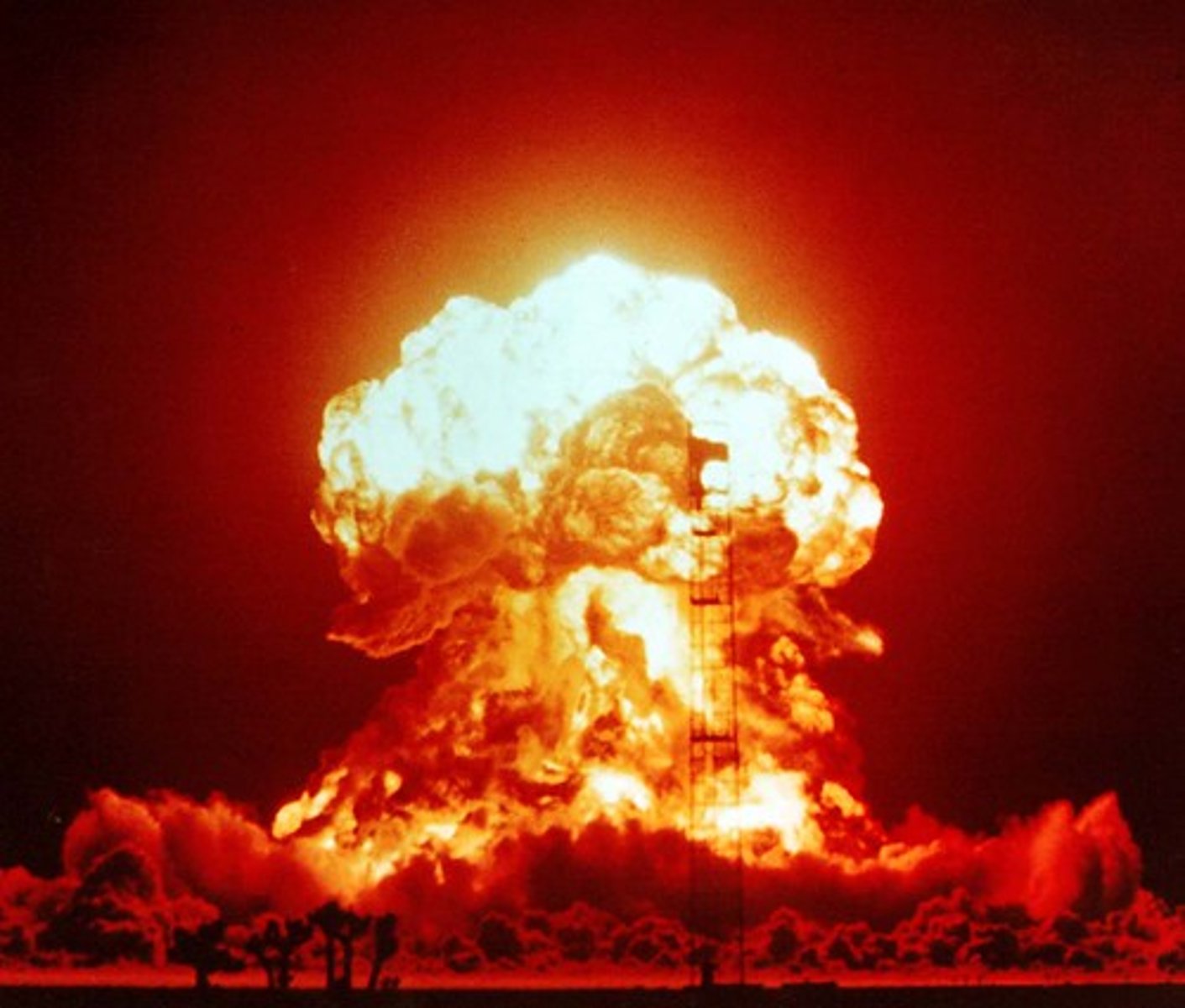
gamma rays
extremely high-energy electromagnetic radiation emitted by radioactive materials.

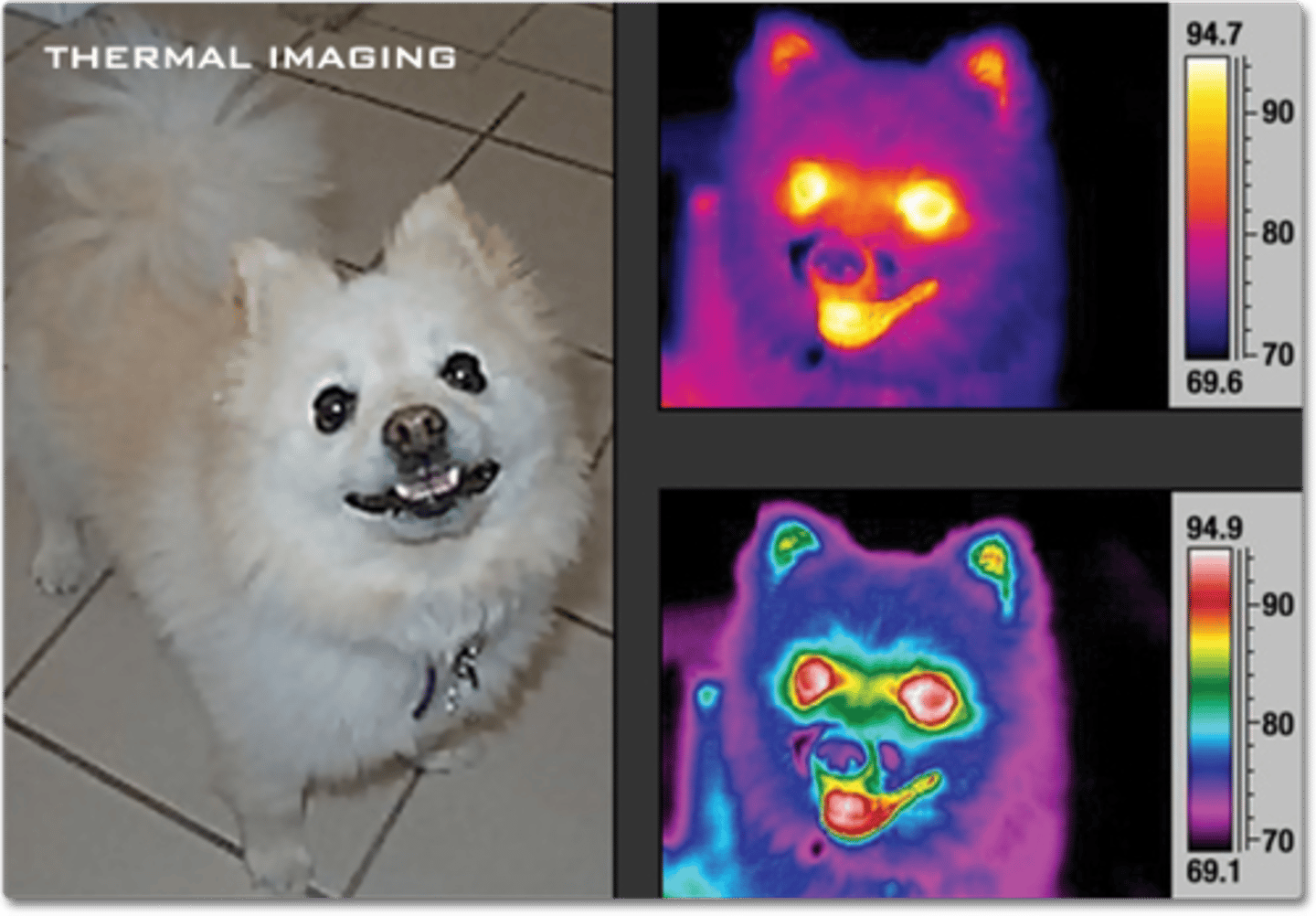
infrared radiation
a band of the electromagnetic spectrum with energies just below that of visible light, detected by our skin as heat.

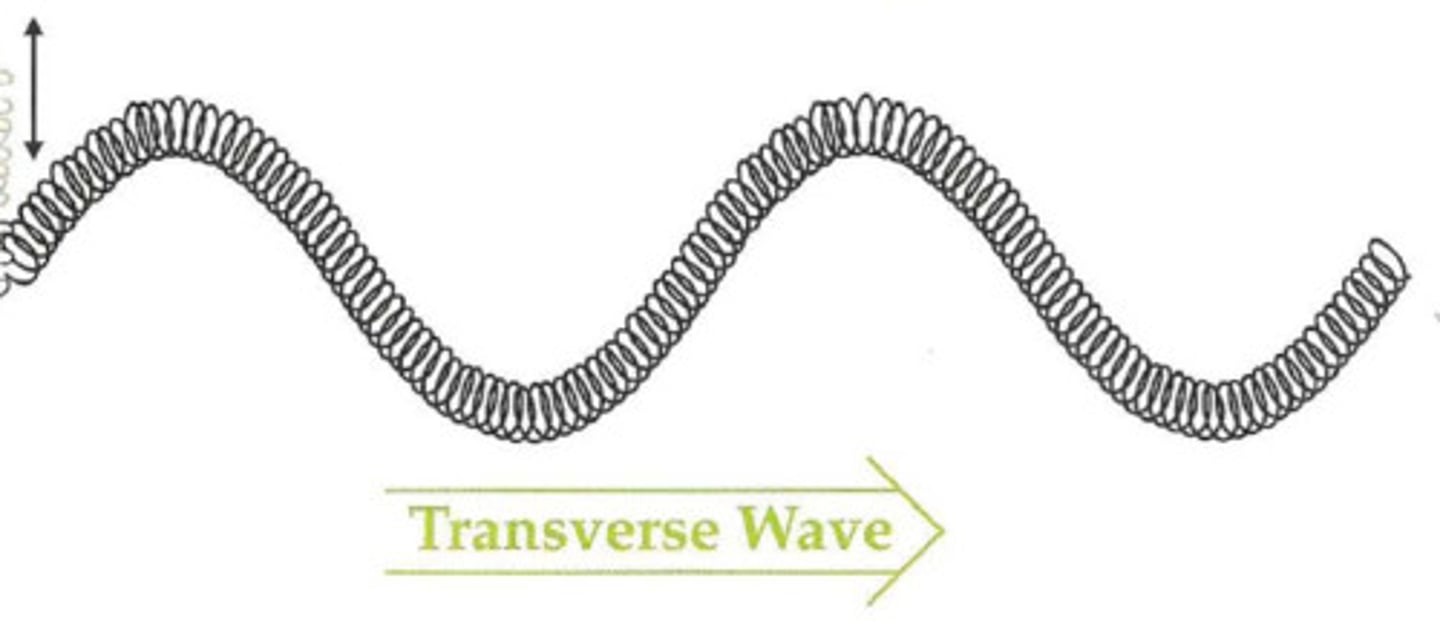
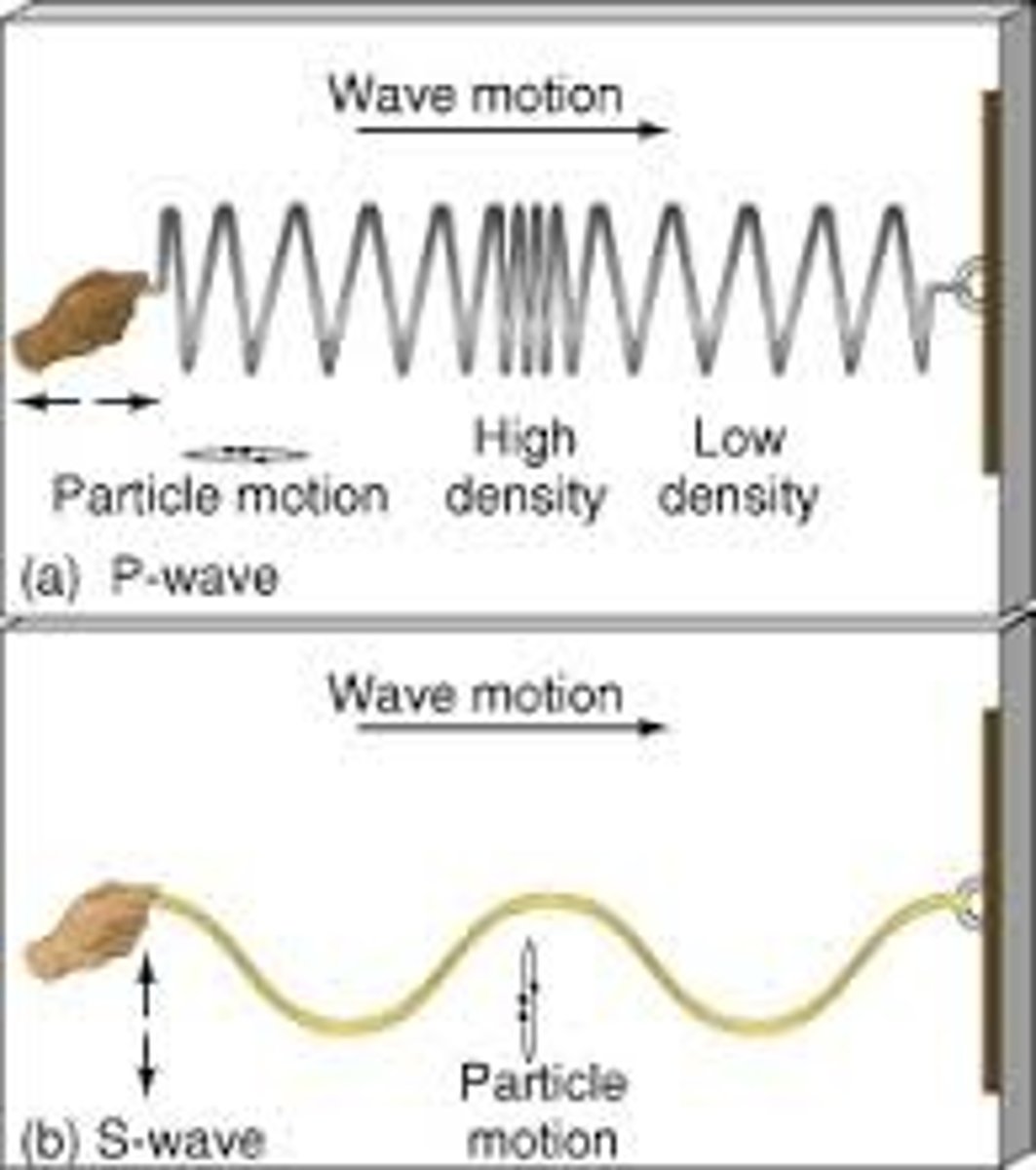
transverse waves
a wave in which its particles vibrate at right angles to the direction of motion of the wave itself.
microwaves
electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from a fraction of a millimetre to tens of centimetres, used in communication and cooking.

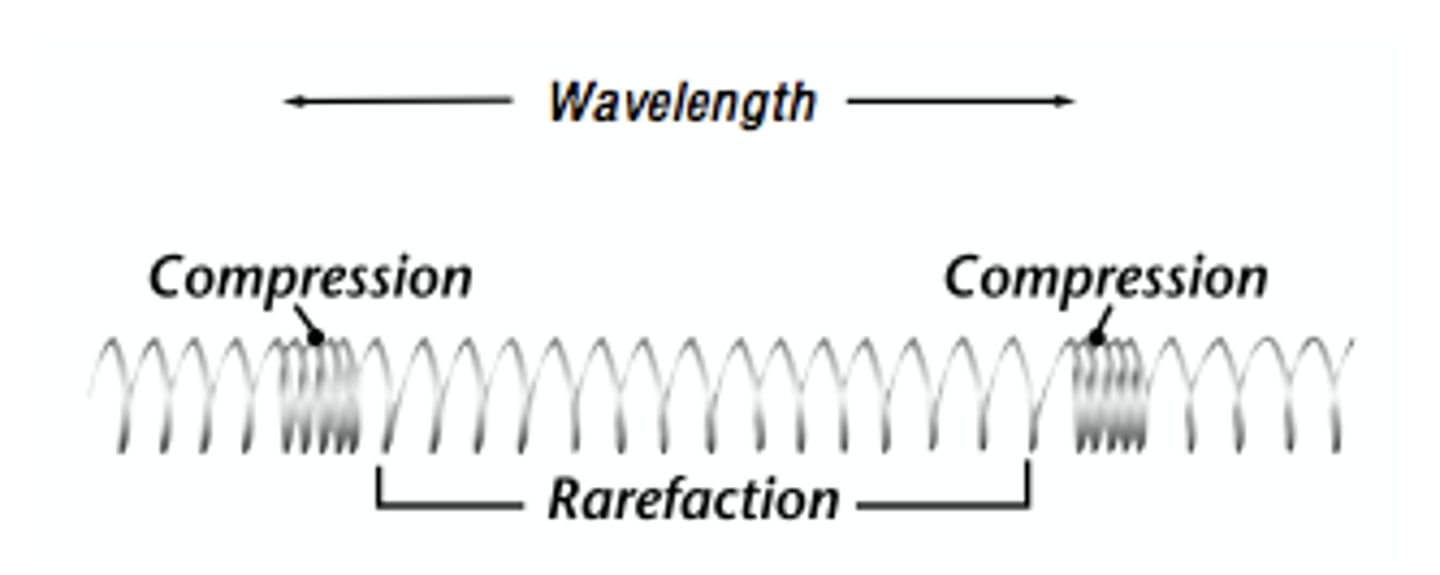
longitudinal wave
a wave in which the particles travel in the sane direction as the direction as that of the wave itself.
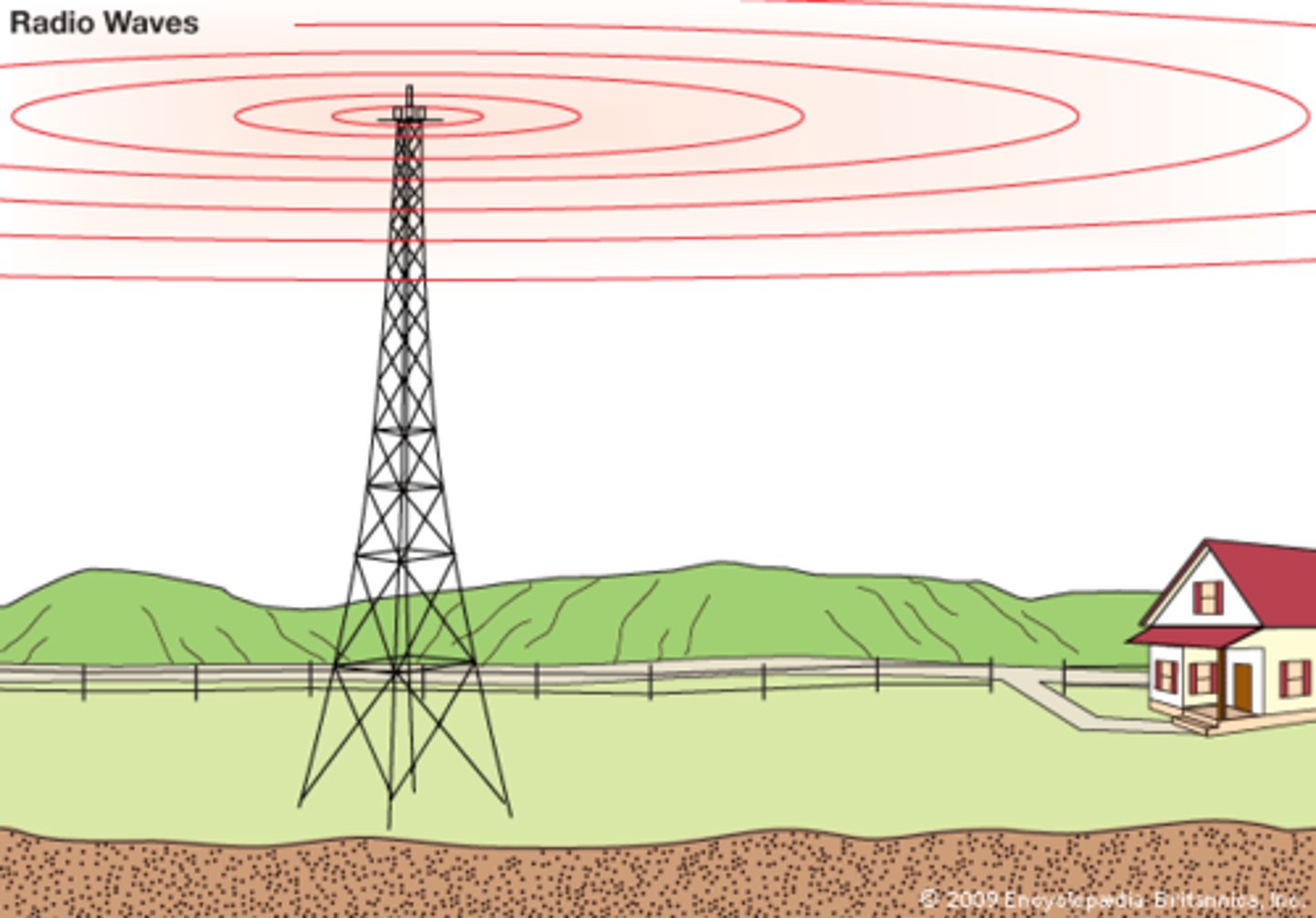
radio waves
electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from hundreds of meters to tens of centimetres, used in communication.
ultraviolet (UV) light
a band of electromagnetic radiation with energies just above those of visible light, contained in sunlight.

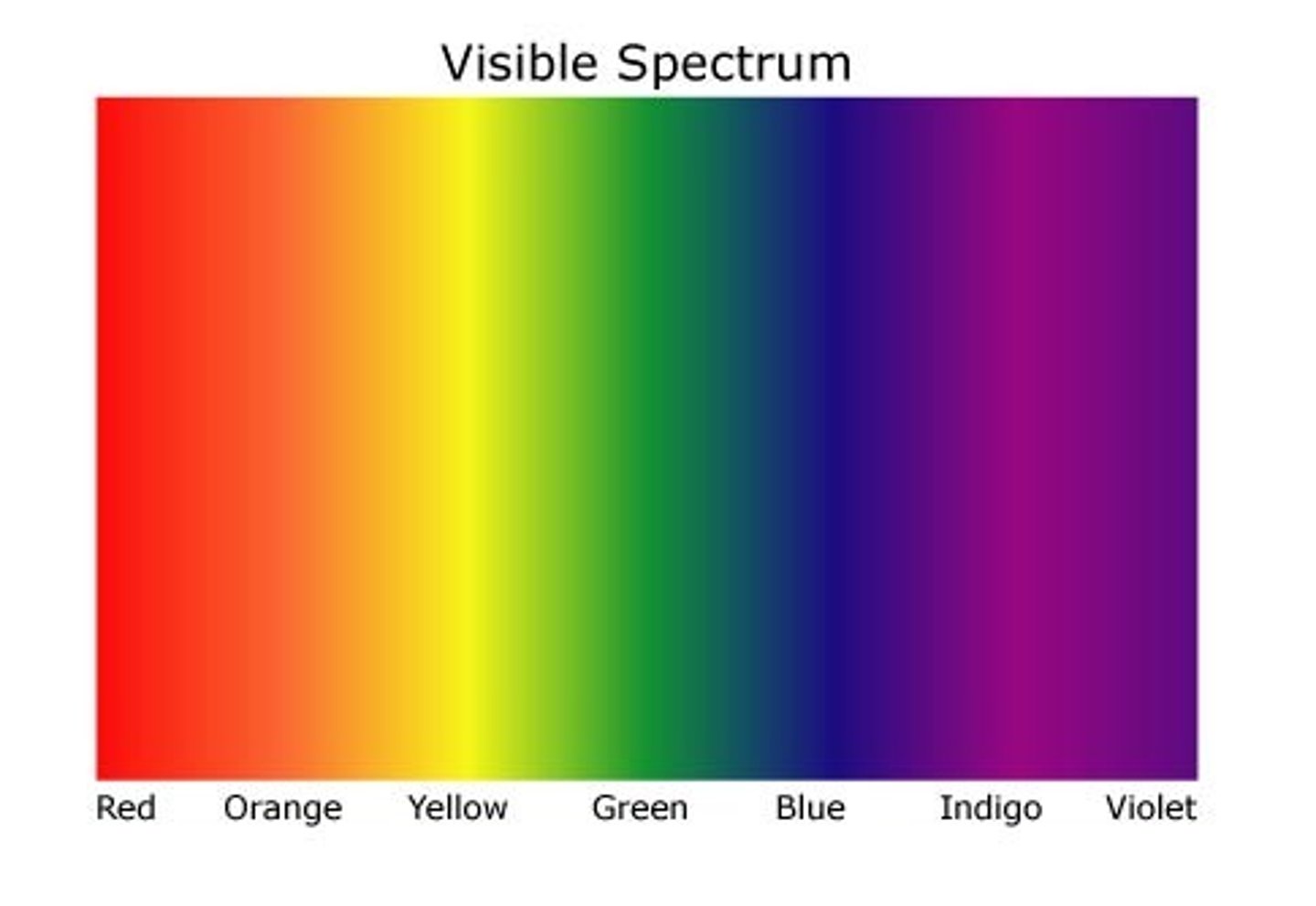
visible light
a band of electromagnetic radiation detected by our eyes.
wave motion
the transfer of energy without transferring matter.
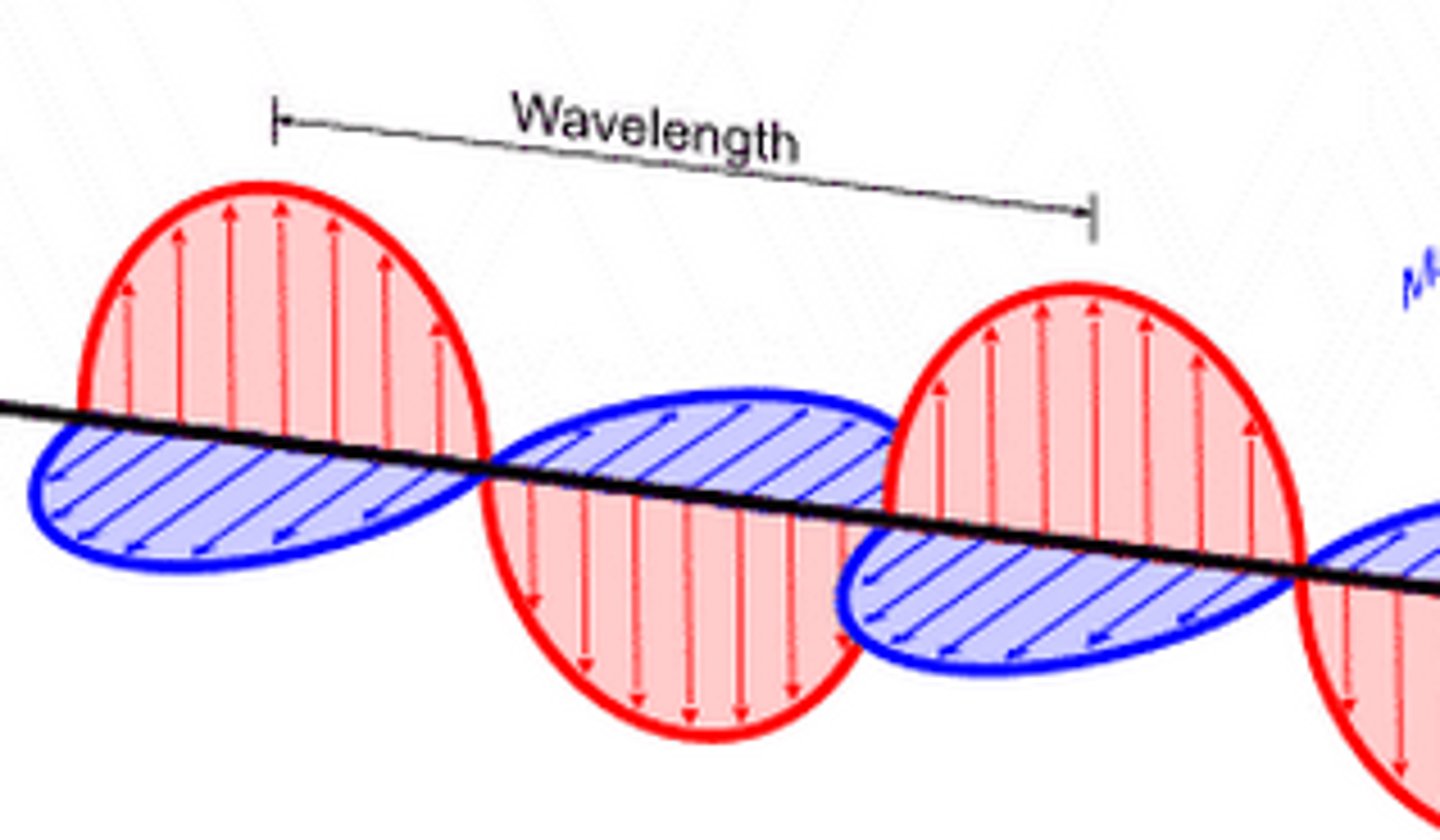
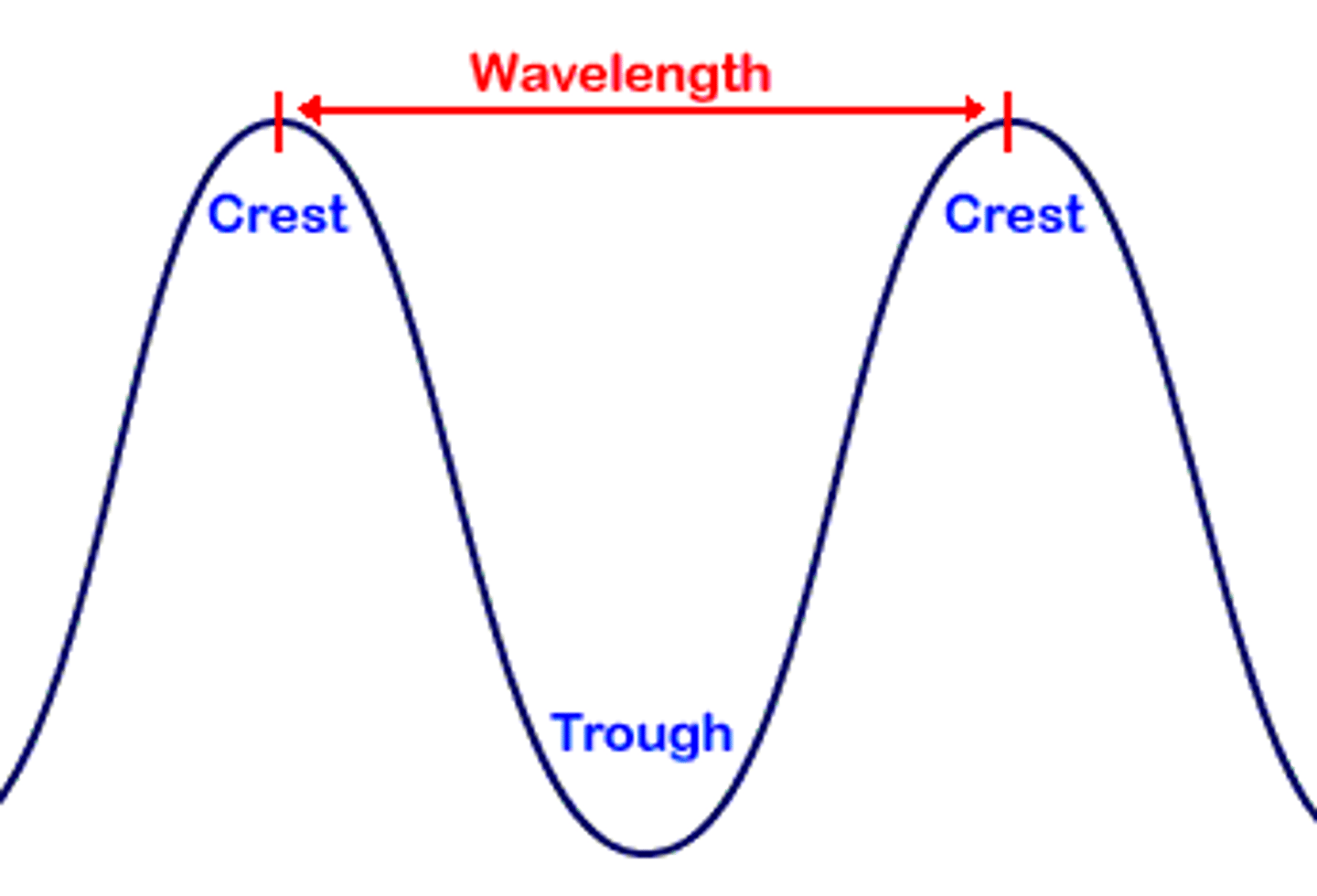
wavelength
the distances between successive wave crests, measured in metres.
x-rays
high-energy electromagnetic radiation that can penetrate materials.
