Distributed Systems 1
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
1
New cards
what is a distributed system?
a collection of loosely coupled nodes interconnected by a communication network
2
New cards
what is a site?
the location of a machine
3
New cards
what is a node?
a specific system (doesn't have to be a computer) at a site
nodes are called different names depending on context (eg. host/ machine/ site/ processor) - all mean a device connected with communication media
nodes are called different names depending on context (eg. host/ machine/ site/ processor) - all mean a device connected with communication media
4
New cards
how does a specific node in a distributed system look and view resources?
its own resources are local
the rest of the notes + their resources are remote
the rest of the notes + their resources are remote
5
New cards
can a node vary in size?
yes, may vary in size and function eg.
microprocessor vs.
large general purpose computer system
microprocessor vs.
large general purpose computer system
6
New cards
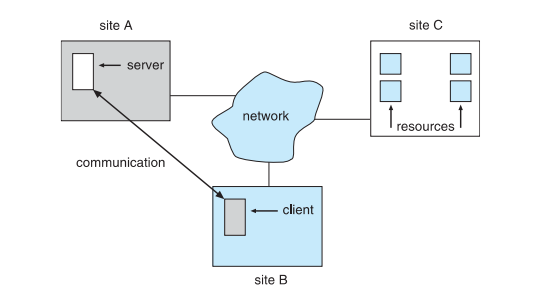
what are the main principles of a distributed system?
one node at one site (eg. a server node) has a resource that a node at a different site (eg. a client/ user node) would like to use
the network connects the sites and their resources
the network connects the sites and their resources
7
New cards
why do we need distributed systems?
resource sharing
computation speedup
reliability
communication
computation speedup
reliability
communication
8
New cards
what is resource sharing?
users at one site can use resources available at another site
eg. site A and site B
site A uses a printer at site B
site B accesses a file store at site A
\
provides mechanisms for
* sharing files at remote sites
* processing information in a distributed database
* printing files at remote sites
* using remote specialized hardware devices (such as a supercomputer)
* performing other operations
eg. site A and site B
site A uses a printer at site B
site B accesses a file store at site A
\
provides mechanisms for
* sharing files at remote sites
* processing information in a distributed database
* printing files at remote sites
* using remote specialized hardware devices (such as a supercomputer)
* performing other operations
9
New cards
what is computation speedup?
* some applications need lots of power and resources to compute
* one computation can be divided into sub-computations and distributed across various sites.
* computational speed-up is provided by running the subprocesses ==concurrently==
* allows for ==load sharing/ job migration== - moving jobs from an overloaded site to another lightly loaded site (but commercial systems don’t usually have AUOTMATED load sharing)
* one computation can be divided into sub-computations and distributed across various sites.
* computational speed-up is provided by running the subprocesses ==concurrently==
* allows for ==load sharing/ job migration== - moving jobs from an overloaded site to another lightly loaded site (but commercial systems don’t usually have AUOTMATED load sharing)
10
New cards
what is reliability?
* if one site fails then the remaining sites can continue operating making the system more reliable
* for systems with ==many large autonomous machines==, failure of one won’t affect the rest
* for systems with ==few small machines where each machine does a crucial function==, failure of one may halt the whole operation
* with enough redundancy in hardware and data, the system could continue operating even if some sites have failed
* for systems with ==many large autonomous machines==, failure of one won’t affect the rest
* for systems with ==few small machines where each machine does a crucial function==, failure of one may halt the whole operation
* with enough redundancy in hardware and data, the system could continue operating even if some sites have failed
11
New cards
how does the reliability benefit respond to site failure?
* failure of site is detected by system and action needs to be taken to recover from the failure
* system stops using the failed site resources
* function of the failed site can be moved to another site and system needs to ensure ==transfer of function== occurs correctly
* when site is repaired system must use mechanisms to ==integrate== back into the system correctly.
* system stops using the failed site resources
* function of the failed site can be moved to another site and system needs to ensure ==transfer of function== occurs correctly
* when site is repaired system must use mechanisms to ==integrate== back into the system correctly.
12
New cards
what is communication?
* users at various sites can exchange information
* low-level communication- eg. messages passed between systems
* all high-level functionality of the standalone system can be expanded to encompass the distributed system and therefore functions can be carried out over larger distances
* eg. file transfer, login, mail, remote procedure calls (RPCs)
* low-level communication- eg. messages passed between systems
* all high-level functionality of the standalone system can be expanded to encompass the distributed system and therefore functions can be carried out over larger distances
* eg. file transfer, login, mail, remote procedure calls (RPCs)
13
New cards
how have the reasons for distributed systems impacted companies?
* ==downsizing== - companies replace big mainframes with distributed networks of workstations or personal computers. this provides the company with lots of advantages
14
New cards
what are the advantages of distributed systems?
reliability
scalability
flexibility
speedup
openness
high performance
scalability
flexibility
speedup
openness
high performance
15
New cards
what is scalability?
scale up or down usage depending on if resources are needed or not needed, good because demand varies, using resources can be expensive
16
New cards
what is flexibility?
can run different operating systems
flexibility in locating resources and expanding facilities
flexibility in locating resources and expanding facilities
17
New cards
what is openess?
more users can access resources without needing different installations or licencing
18
New cards
what are the disadvantages of distributed systems?
difficult troubleshooting
less software support
high network infrastructure cost
security issues
less software support
high network infrastructure cost
security issues
19
New cards
what is difficult troubleshooting?
because different nodes communicate so more time and skill needed to pinpoint problem
20
New cards
what is less software support?
software may be in different areas so harder to support
21
New cards
what is security issues?
accessing remote resources can be taken advantaged of eg. DDoS attacks can be sent and spread
22
New cards
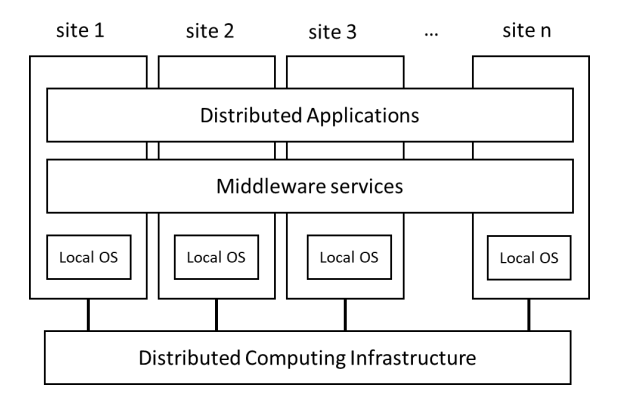
what is the organisation of distributed systems?
a layered architecture
different sites connected by a distributed computing infrastructure (eg. cloud, grid)
each site has a local OS
distributed applications and middleware services span across all sites in the system
different sites connected by a distributed computing infrastructure (eg. cloud, grid)
each site has a local OS
distributed applications and middleware services span across all sites in the system
23
New cards
what are distributed applications?
applications that can run and communicate alongside applications on other sites, the user of the local node does not realise the app is being distributed
24
New cards
what are middleware services?
software acting like a hook to enable communication between different nodes
25
New cards
what is the distributed computing infrastructure?
the physical infrastructure that connects sites in a distributed system
26
New cards
what is the importance of layered architecture?
important because responsibility is divided (different responsibility for different layers) to support transparency, troubleshooting, updating
networks complex and thus need to be organised
networks complex and thus need to be organised
27
New cards
what is a layered architecure?
layers communicate and show an interface to other layers, so the layers know what information is sent or required but not what exactly is happening
all layers + between layers have security measures
common for all distributed systems
all layers + between layers have security measures
common for all distributed systems
28
New cards
what are examples of distributed systems?
grid computing
cloud computing - remote computers, virtualisation of hardware to use as cloud resources (VM to contribute resources)
blockchain
internet of things
DDoS
all layered architectures
cloud computing - remote computers, virtualisation of hardware to use as cloud resources (VM to contribute resources)
blockchain
internet of things
DDoS
all layered architectures
29
New cards
what is grid computing?
uses special software to enable several computers to work together on a common problem as if they were a massively parallel supercomputer (even when the machine not in use)
nodes could be running software, data processing, connected to the grid
nodes could be running software, data processing, connected to the grid
30
New cards
what are distributed simulations?
communicate to form a bigger simulation
need to all be synchronised
need to all be synchronised
31
New cards
what is cloud computing?
using a network of remote servers hosted on the Internet to store, manage, and process data, (virtualisation of hardware) rather than a local server or a personal computer.
32
New cards
what services does cloud computing offer?
SaaS - software as a service
PaaS - platform as a service
IaaS - infrastructure as a service
PaaS - platform as a service
IaaS - infrastructure as a service
33
New cards
What is SaaS (Software As A Service)?
software that we don't install but lets us access other resources, eg. office 365 allows using word without downloading it
34
New cards
What is PaaS (Platform as a Service)?
platform to provide services that we need to access the resources
example: Google app engine, Azure
example: Google app engine, Azure
35
New cards
What is IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)?
the hardware used to provide the service
36
New cards
what are the different models of cloud computing
Private - eg. between company and employee cloud
Community - for a government
Public - accessible to all, eg. google
Hybrid
different model used depending on what security is required
Community - for a government
Public - accessible to all, eg. google
Hybrid
different model used depending on what security is required
37
New cards
what are the different resources for cloud computing?
Single/multi CPU, GPU, HPC, storage, etc
38
New cards
what are the different operating systems for cloud computing
eg. OpenStack, OpenNebula, Proprietary: used to create a cloud OS
Virtualises hardware of services to create cloud resources for users
Virtualises hardware of services to create cloud resources for users
39
New cards
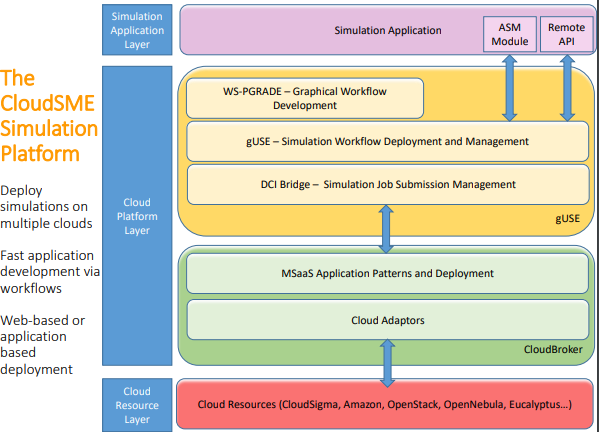
what is the cloudSME simulation platform?
API - can be an interface to let us access the services of another application
40
New cards
what is blockchain?
A decentralised architecture (peer to peer), digital ledger system for recording business transactions and events
41
New cards
what is a shared ledger?
a resource used by members in a network to record digital transactions
each member stores an identical copy of the shared ledger
changed to the ledger are reflected in all copies creating transparency and trust
each member stores an identical copy of the shared ledger
changed to the ledger are reflected in all copies creating transparency and trust
42
New cards
what is the internet of things?
the idea that everything / every device could be given an ip address and put on the internet
homogenous connected devices
homogenous connected devices
43
New cards
What is a DDoS attack?
distributed denial of service attack - sending large amounts of traffic from multiple sources to a service or website, intending to overwhelm it so that authorised user are not able to access