module 13: aerobic gram positive rods
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
corynebacterium
found in soil & water, on skin & mucus membranes in humans & animals. pleomorphic gram positive rods. appearance: palisade (picket fence) or Chinese letter configuration. metachromatic granules visble with methylene blue. normal flora (diphtheroids) can cause opportunistic infections. diphtheriae is pathogenic
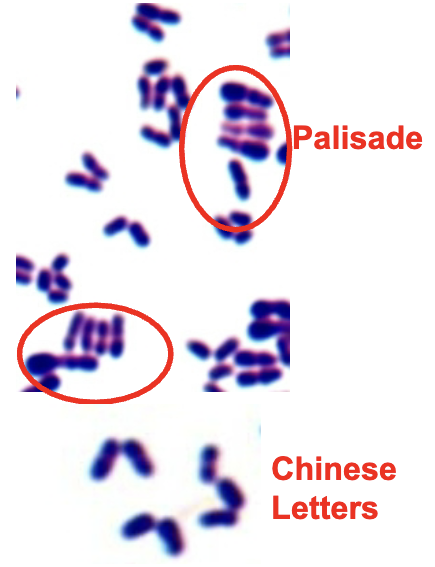
corynebacterium diphtheriae
from upper respiratory tract, humans only host. transmitted through inhalation. cytotoxic exotoxin blocks protein synthesis, enters blood & damages heart & CNS. if toxin not present, strain is not pathogenic. initial symptoms are sore throat, fever, & malaise. pseudomembrane forms in throat. myocarditis, suffocation
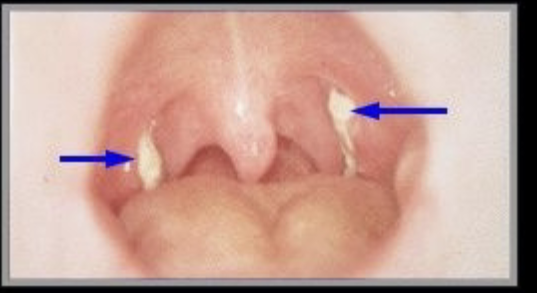
treatment & prevention of C. diphtheriae
lifelong immunity occurs after recovery. treated with antibiotics & antitoxin. DPT series of immunizations, very effective at prevention.
laboratory diagnosis of corynebacterium diphtheriae
grows on ordinary culture, specific media available, toxin production optimal at low iron concentration (too much is bad). ID toxin with ELEK test
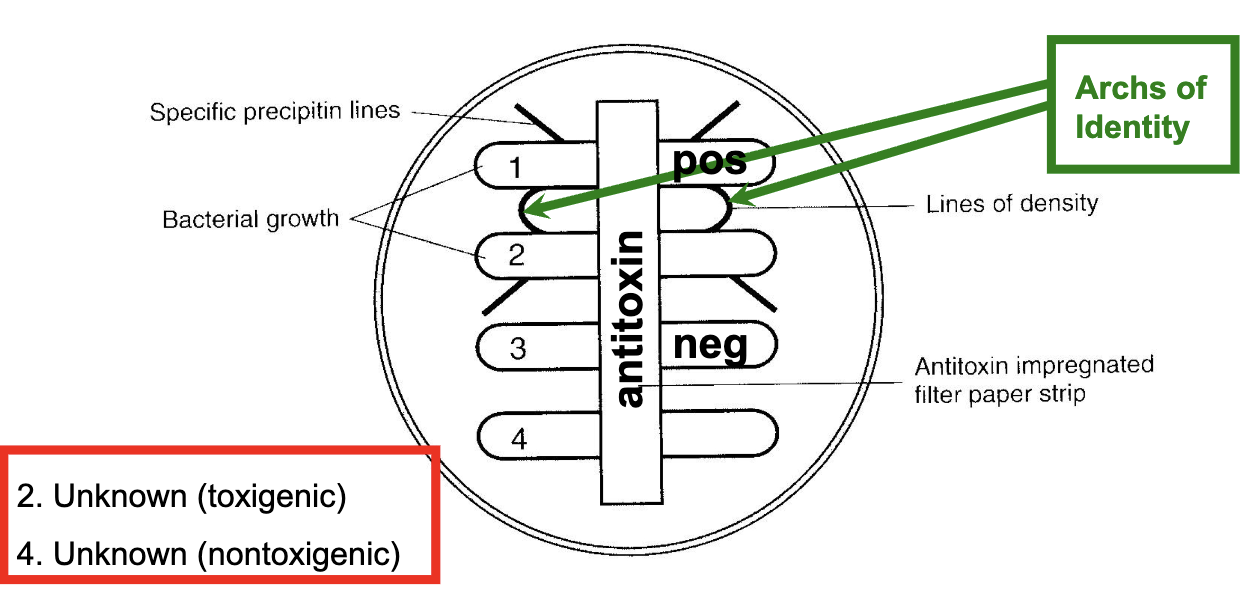
ELEK in vitro toxigenicity test
detects diptheria toxin based on principle of immunodiffusion. heavy inoculum of test organism (controls & unknowns) is streaked onto plated medium in a single line. antitoxin impregnated in strip of sterile filter paper on agar. incubate for 24 hours. if organism is toxigenic, visible line of Ag-Ab precipitate will form
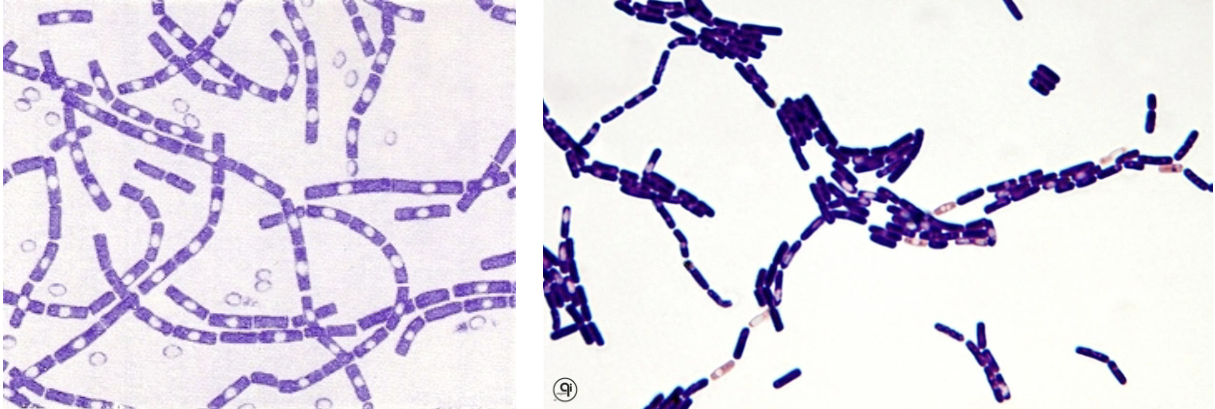
bacillus
commonly found in soil. aerobic gram positive rod. spores are formed when organism is present in environment (no spores in vivo). important species: anthracis, cereus
bacillus anthracis
transmitted by direct contact (cutaneous), inhalation (pulmonary), & ingestion (GI). edema factor (EF): edema, hemorrhage. protective antigen (PA): edema production. lethal factor (LF): respiratory center depression, decreased respiration, death. treated with penicillin, doxycycline, fluroquinolines (cipro)
laboratory diagnosis of bacillus anthracis
DNA hybridization. culture: aerobic, nonhemolytic “ground glass” that are tenacious (sticky), curling (medusa head), capsulated, nonmotile, long chains.
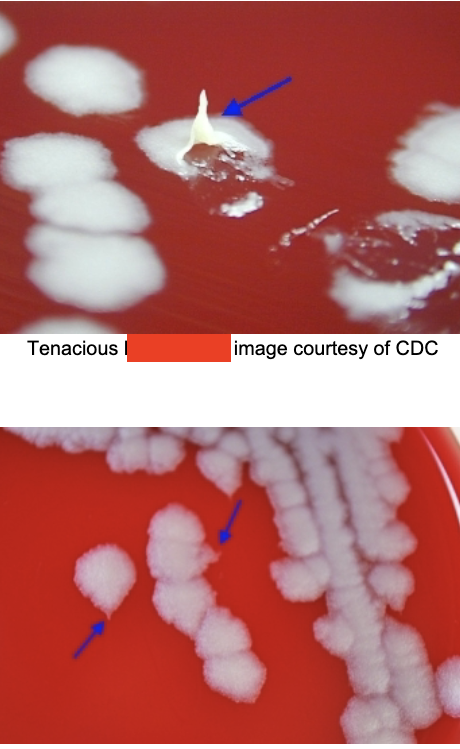
cutaneous anthrax
occurs in wounds like skin cuts, abrasions, insect bites that become infected. dark area appears in center of wound, which ulcerates & dries forming black nodular area, known as eschar (black eschar). localized, no complications
inhalational anthrax
aka woolsorter’s disease. inhalation of spores contacted by handling animal fibers & hides that contain spores. respiratory infection with fever & cough. rapid progression to respiratory distress & cyanosis. toxins enter bloodstream. toxemia, death
gastrointestinal anthrax
occurs when spores ingested. abdominal pain, nausea, anorexia, vomiting. fatality rate high because harder to diagnose. toxins may enter blood. toxemia, death
prevention & clean-up of anthrax
life-long immunity against exotoxins after recovery. isolate patients with disease, specimen handling precautions, vaccines. spores can survive a long time: use oxidizing agents & non-oxidizing agents (destroy spores)
bacillus cereus
localized infections of eyes, burn sites, traumatic wounds. bacteremia, septicemia, pneumonia, meningitis, food poisoning. treatment of infections (opportunistic): antibiotics. treatment of food poisoning typically self-limiting
emetic form of B. cereus
due to heat stable emetic toxin. from fried or boiled rice stored at room temp. re-heating does not remove or denature toxin. incubation period < 6 hours. nausea, vomiting. lasts 8-10 hours
diarrheal form of B. cereus
due to heat labile enterotoxin. from meats, soups, vegetables, sauces. incubation period > 6 hours. abdominal pain, diarrhea. lasts 20-36 hours
listeria monocytogenes
animals carry this in intestines, but don’t become ill. eating contaminated food can lead to human infection. associated with ready-to-eat food like hot dogs & lunch meats. also in raw milk & soft cheeses. bacteria is destroyed if reheated to steaming hot before ingestion.

laboratory diagnosis of listeria monocytogenes
gram positive rod that resembles lancet shape of streptococcus. beta hemolysis. capable of growth at 4C. high salt concentrations. umbrella pattern of motility at room temp, but not human body temp.
risk populations for L. monocytogenes
pregnant women (premature labor, septic abortion). newborn infants (early onset sepsis, late onset meningitis). elderly. immunocompromised
listeriosis
flu-like symptoms occur (fever, chills). CNS involvement: headache, stiff neck, confusion, loss of balance, convulsions. vertical transmission from mother to fetus by crossing placental barrier → miscarriage, stillbirth, systemic infections, granulomatosis infantisepicum
fetal listeriosis: early-onset (granulomatosis infantiseptica)
infected infant presents with serious illness at birth, potentially fatal. premature delivery common, baby born with low birth weight. tends to have sepsis, respiratory distress, fever, rash
fetal listeriosis: late-onset
neonates usually full-term & were healthy babies in utero. infant becomes infected late in utero or during delivery: symptoms appear hours to days after birth. meningitis or sepsis follows. chance of survival higher than other one
treatment & prevention of listeriosis
antibiotics: ampicillin + aminoglycosides, penicillins, macrolides. for neonates: treat mother with antibiotics during pregnancy. for food infections: wash hands & surfaces with hot soapy water, always clean refrigerator spills, don’t cross-contaminate, reheat food to steaming hot, refrigerate & freeze perishables within 2 hours