Chapter 9 - Cellular Respiration and Fermentation
1/48
Earn XP
Description and Tags
I have some diagrams, if they come up as a question, just match it to its picture
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
fermentation
a process that makes a limited amount of ATP from glucose without an electron transport chain and produces an end product (lactic acid or ethyl alcohol)
catabolic
no oxygen use
aerobic respiration
oxygen is consumed as a reactant along with the fuel (glucose)
most efficient catabolic pathway
anaerobic respiration
respiration without oxygen
cellular respiration
catabolic pathways that break down organic molecules and use an electron transport chain for ATP production
C6H12O6+6O2
6CO2+6H2O+energy
Glucose (C6H12O6)
What gets oxidized in cellular respiration?
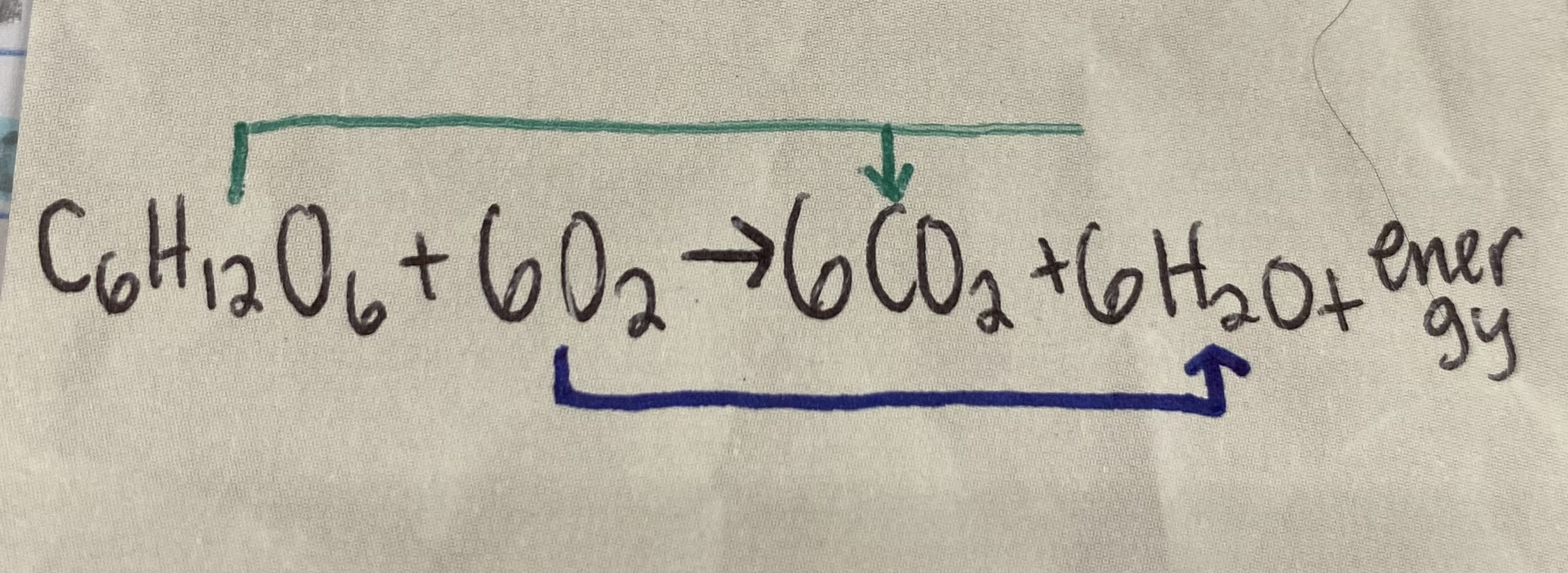
Oxygen (O2)
What gets reduced in cellular respiration?
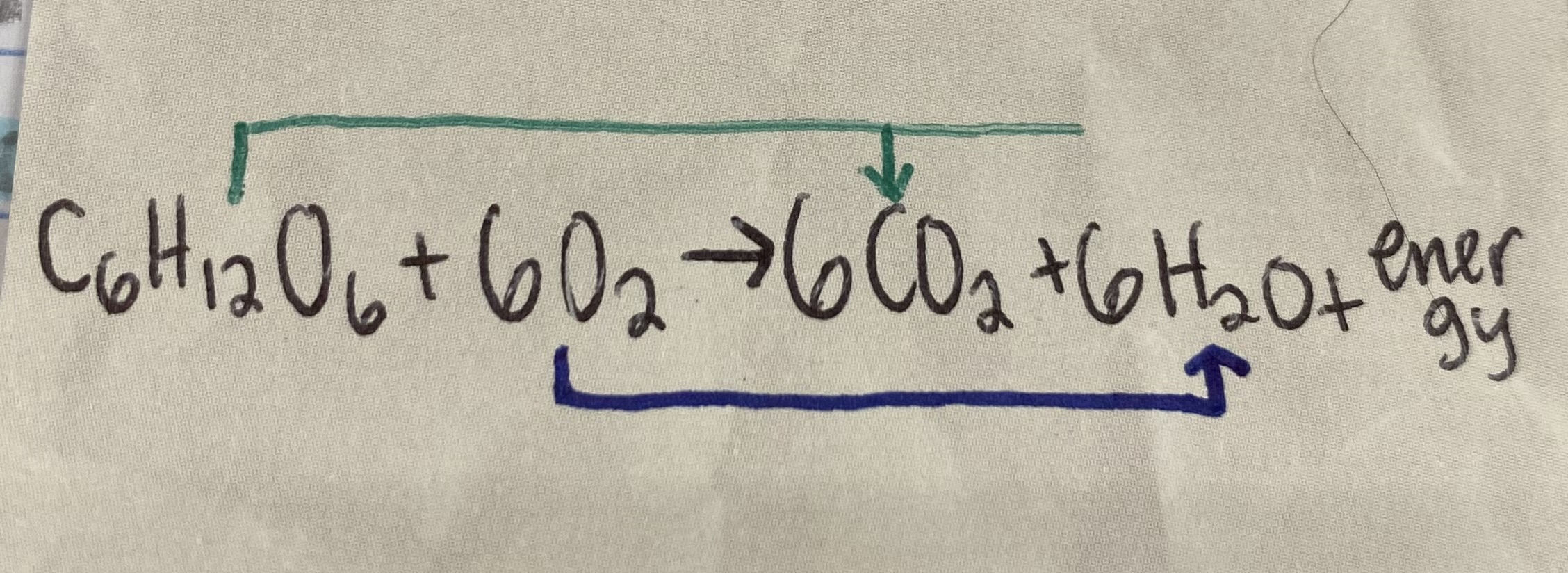
C:H
supports life (ATP)
shares electrons equally
high energy
comes from photosynthesis
oxidation
the loss of electrons from one substance
reduction
the gain of electrons to another substance
share covalent bonds
Not all redox reactions involve the complete transfer of electrons, so what do they do instead?
energy
What must be added to pull an electron away from an atom?
more energy
What is required to pull an electron from a more electronegative atom?
a shift from a lower electronegative atom to a higher electronegative atom
When does an electron lose potential energy?
NAD+
an electron carrier (acceptor) that keeps electrons high energy
NADH
What is the reduced form of NAD+?
electron transport chain
a sequence of membrane proteins that transport electrons down a series of redox reactions that release energy to make ATP
in the cytosol
Where does glycolysis happen?
2 pyruvates, 2 NADH, 2 ATP
What are the products of glycolysis?
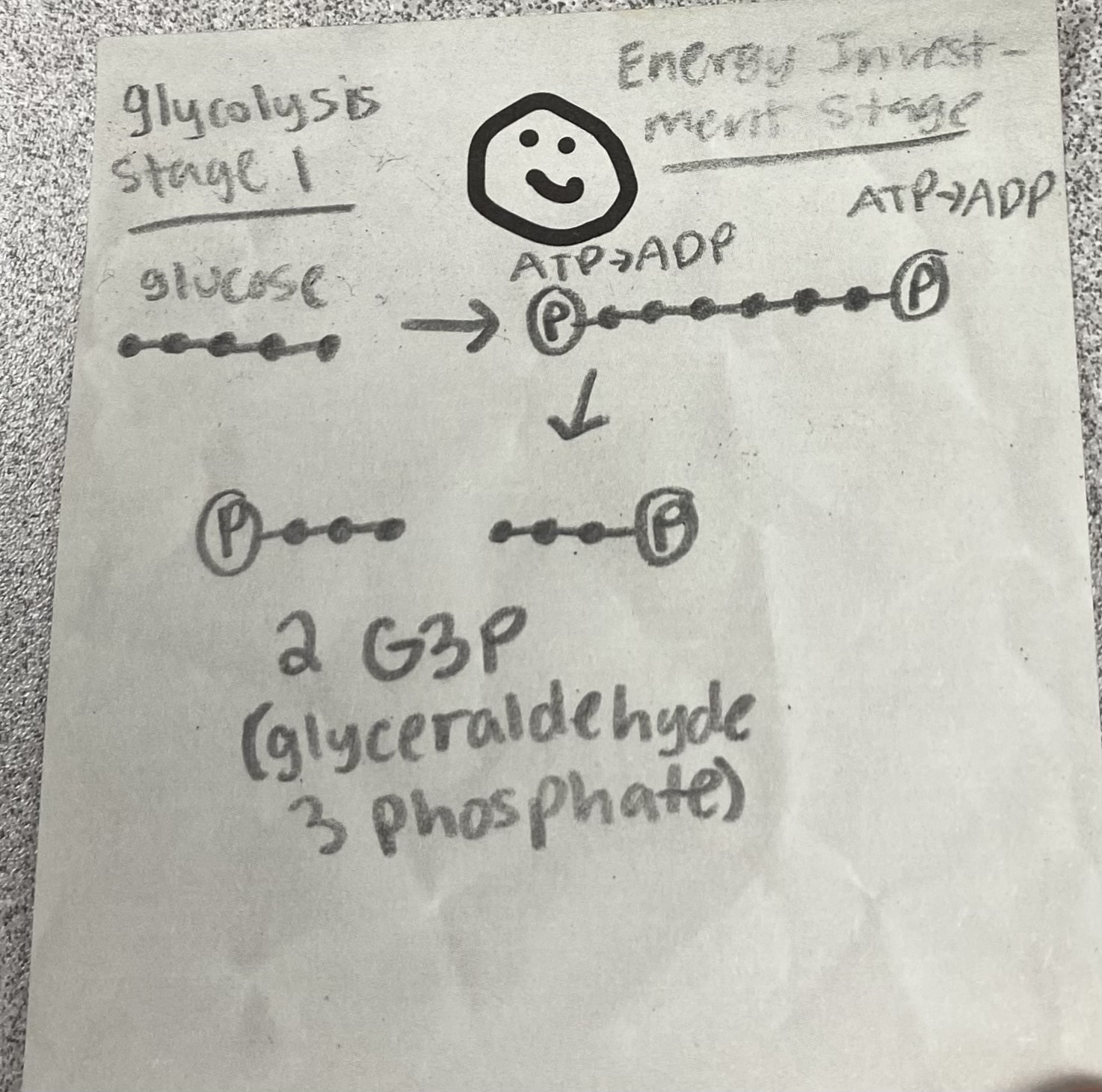
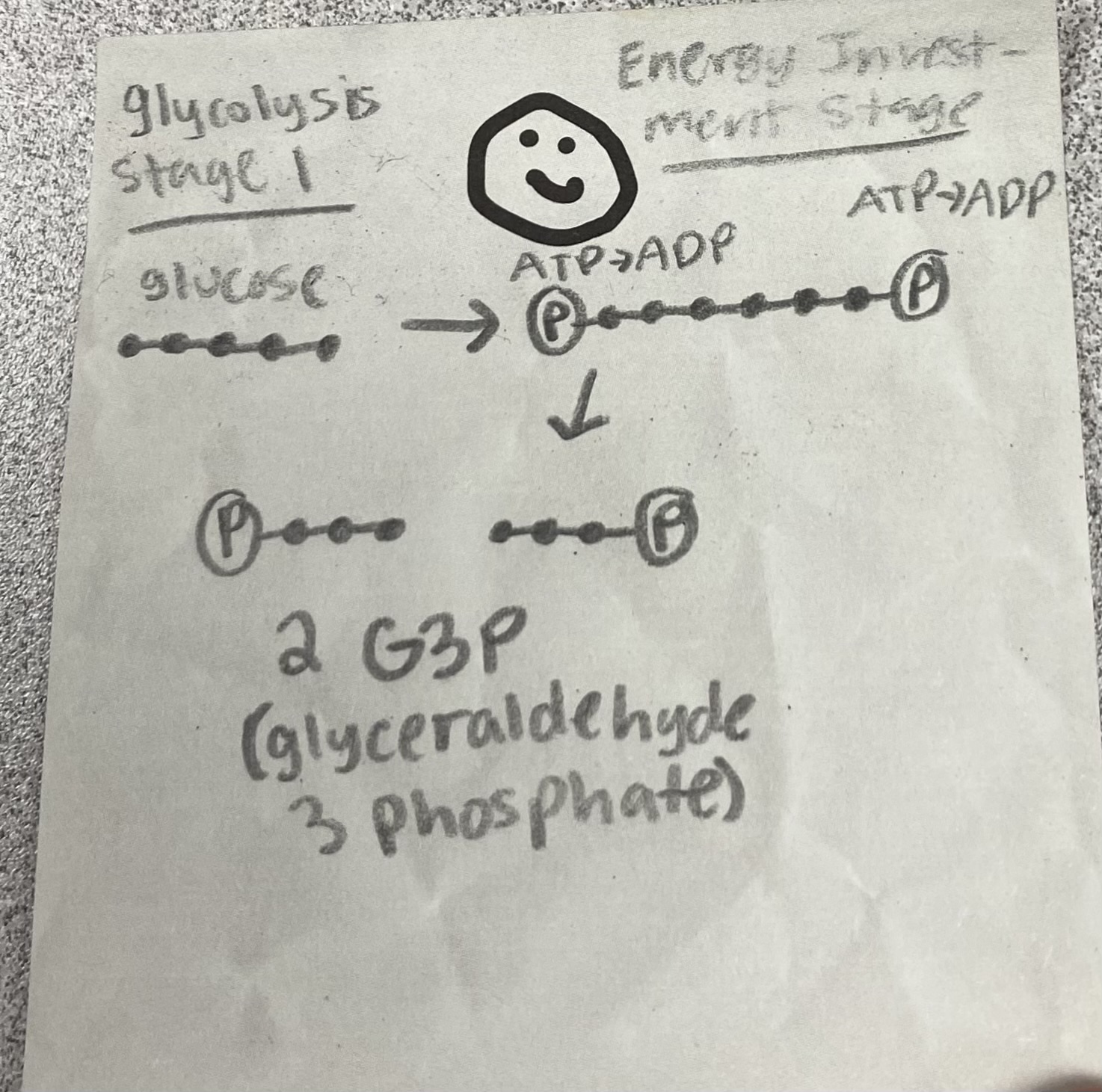


2 G3P (glyceraldehyde 3 phosphate)
What is the product of the Energy Investment Stage (Stage 1) in glycolysis?
all of them
What cells can do glycolysis?
OAA (oxaloacetrate)
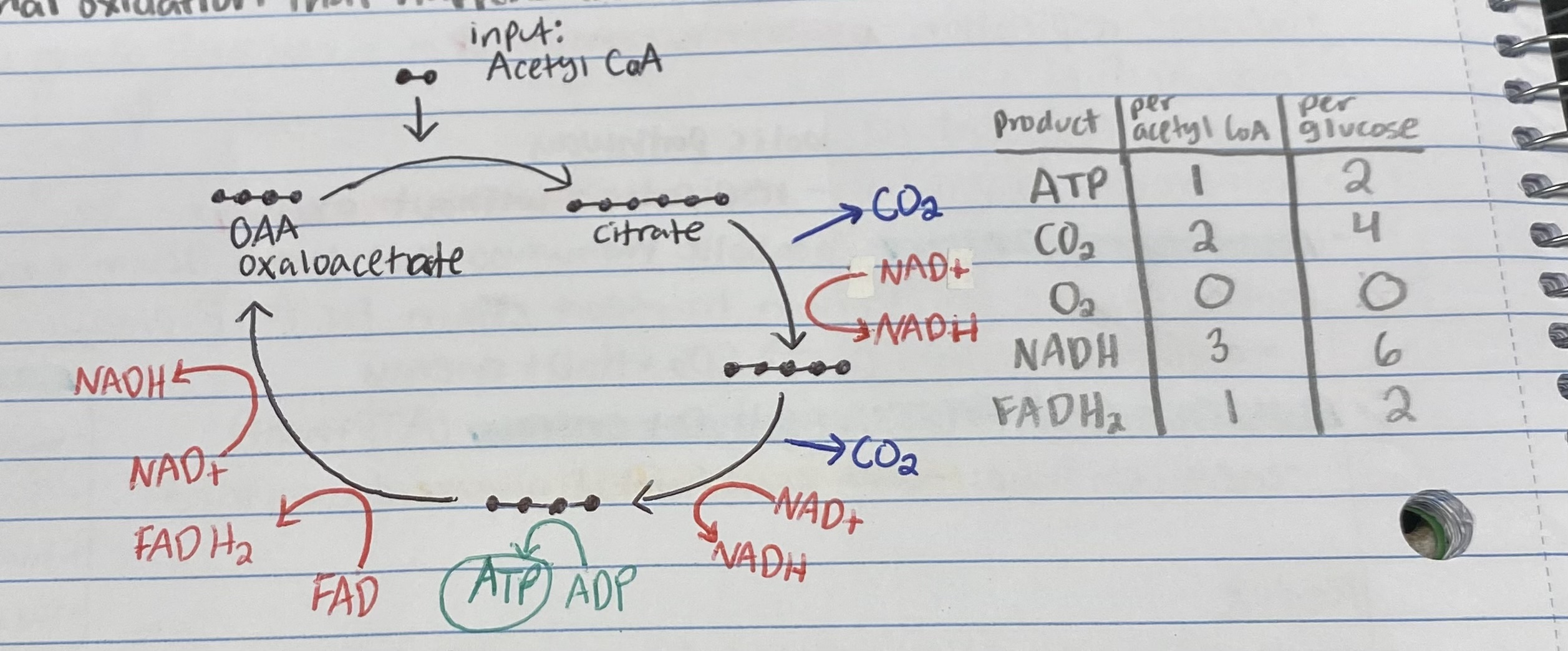
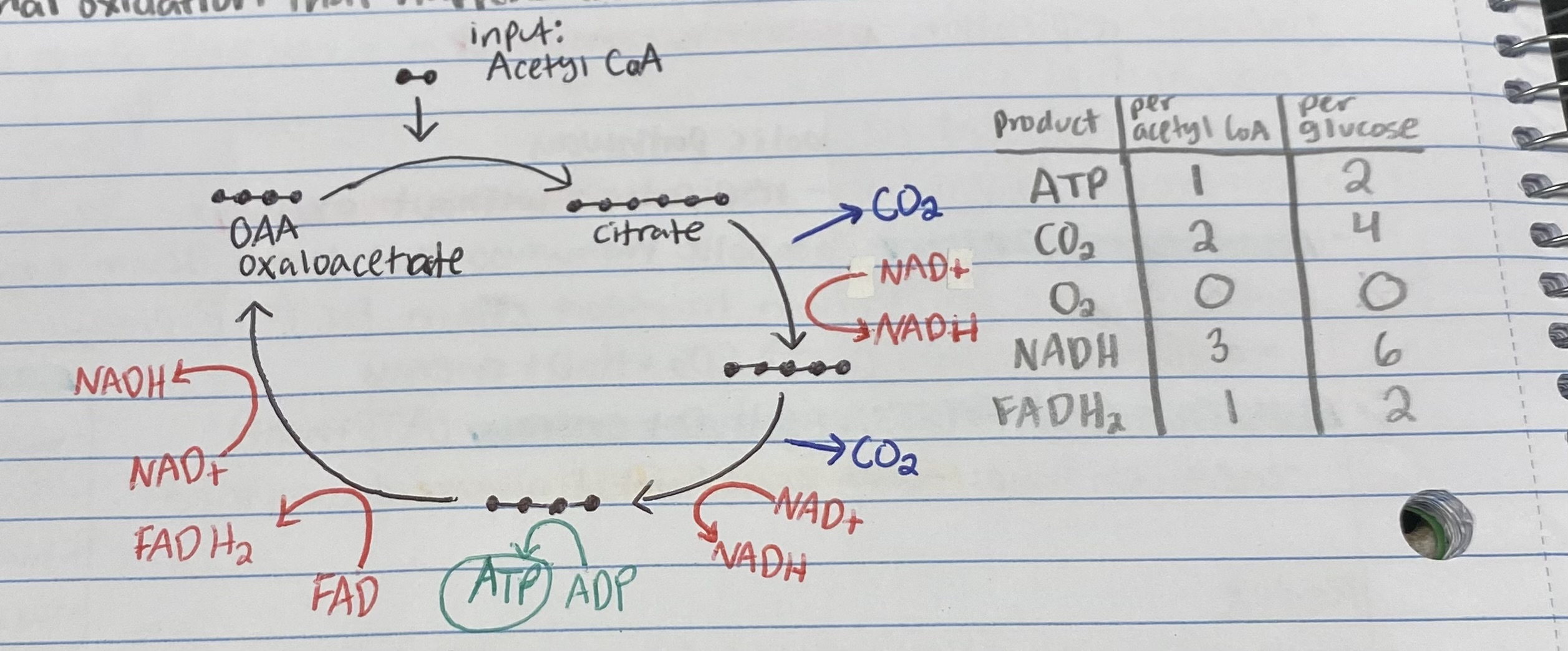
What is attached to Acetyl CoA in the Kreb’s Cycle?
2 Acetyl CoA, 2 NADH, 2 CO2
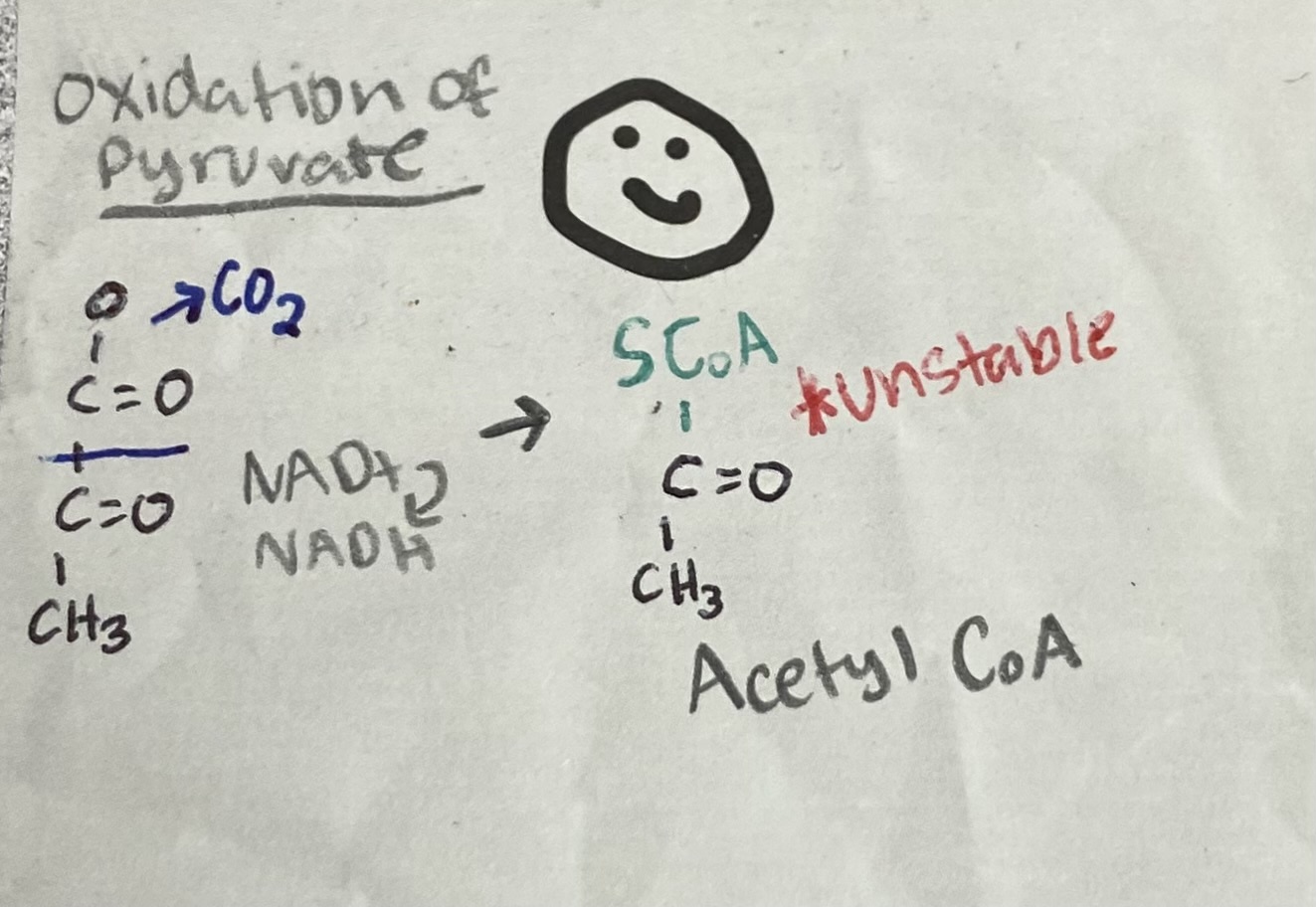
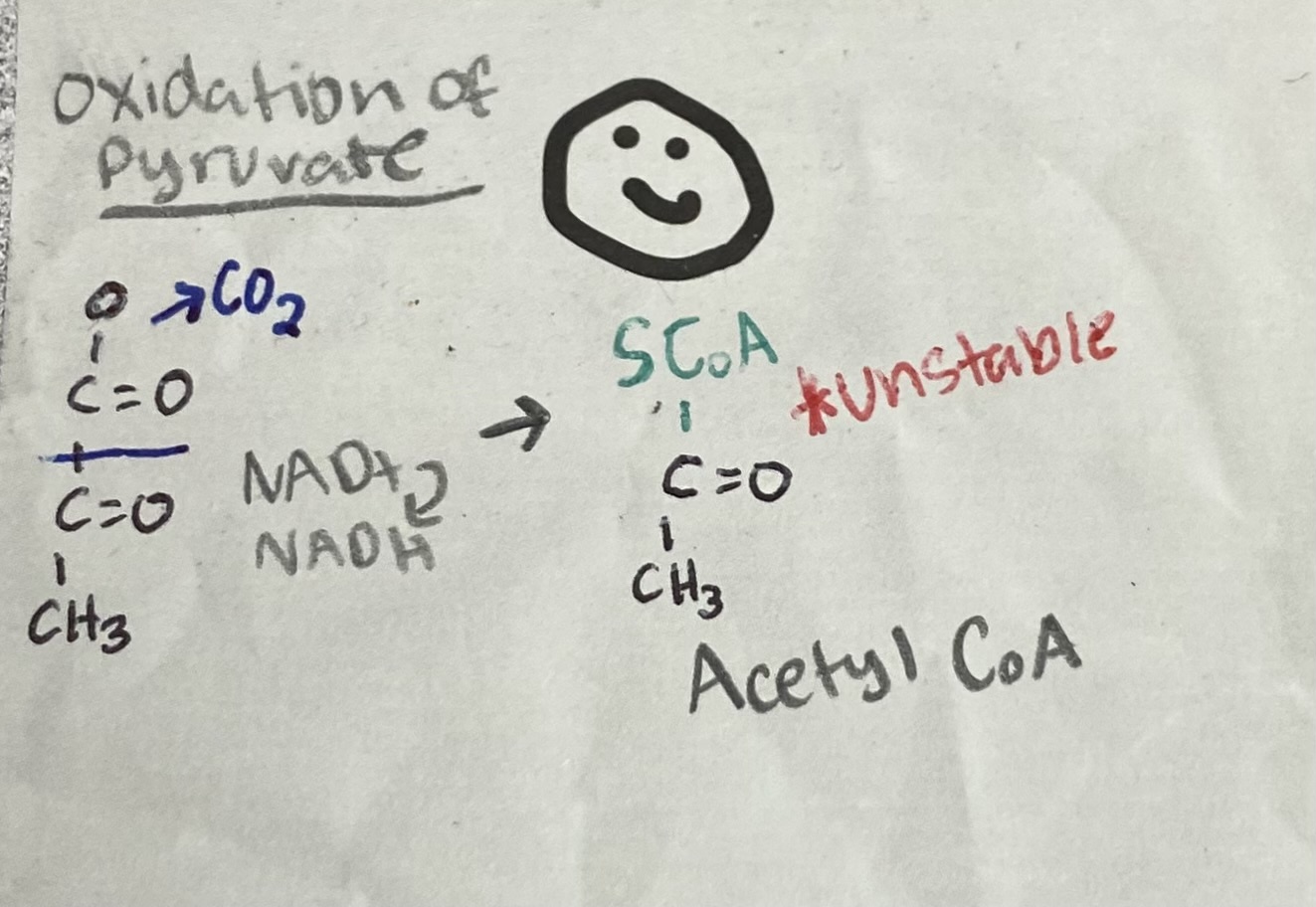
What are the products of the oxidation of pyruvate?
entrance to mitochondria
When/Where does the oxidation of pyruvate happen?
mitochondrial matrix
Where does the Kreb’s Cycle happen?
2, 4, 0, 6, 2
How many of each of the following products are produced by ONE GLUCOSE in the Kreb’s Cycle? (list in order)
ATP, CO2, O2, NADH, FADH2
An electron carrier (acceptor) that works similarly to NADH
What is FADH2?
ATP synthase
the enzyme that makes ATP from ADP and inorganic phosphate
substrate-level phosphorylation
formation of ATP by the transfer of a phosphate group to ADP from a substrate (such as a carbon skeleton)
oxidative phosphorylation
the production of ATP from the energy from the ETC
substrate-level
Is glycolysis substrate-level or oxidative phosphorylation?
substrate-level
Is the Kreb’s cycle substrate-level or oxidative phosphorylation?
oxidative phosphorylation
Is the ETC substrate-level or oxidative phosphorylation?
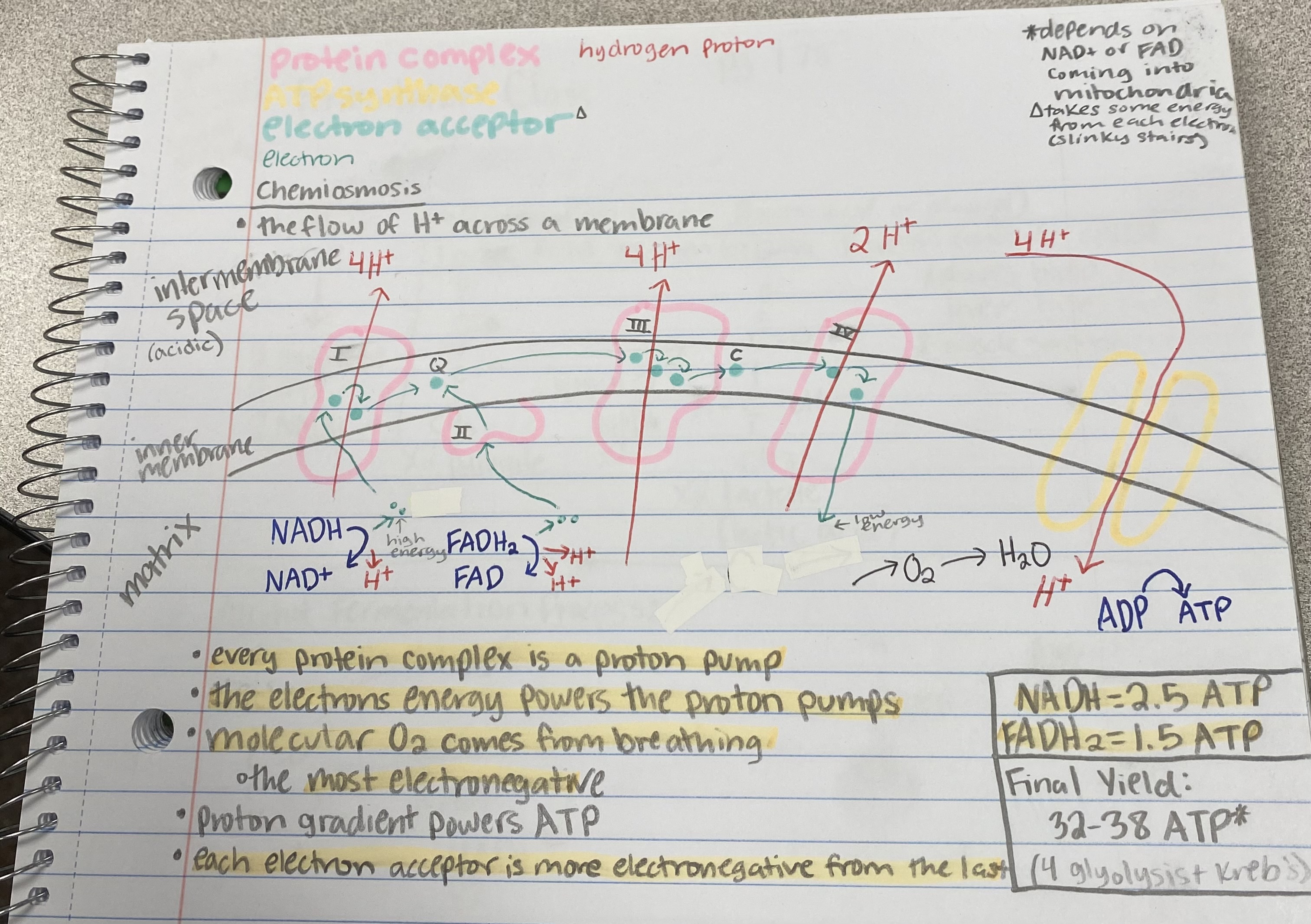
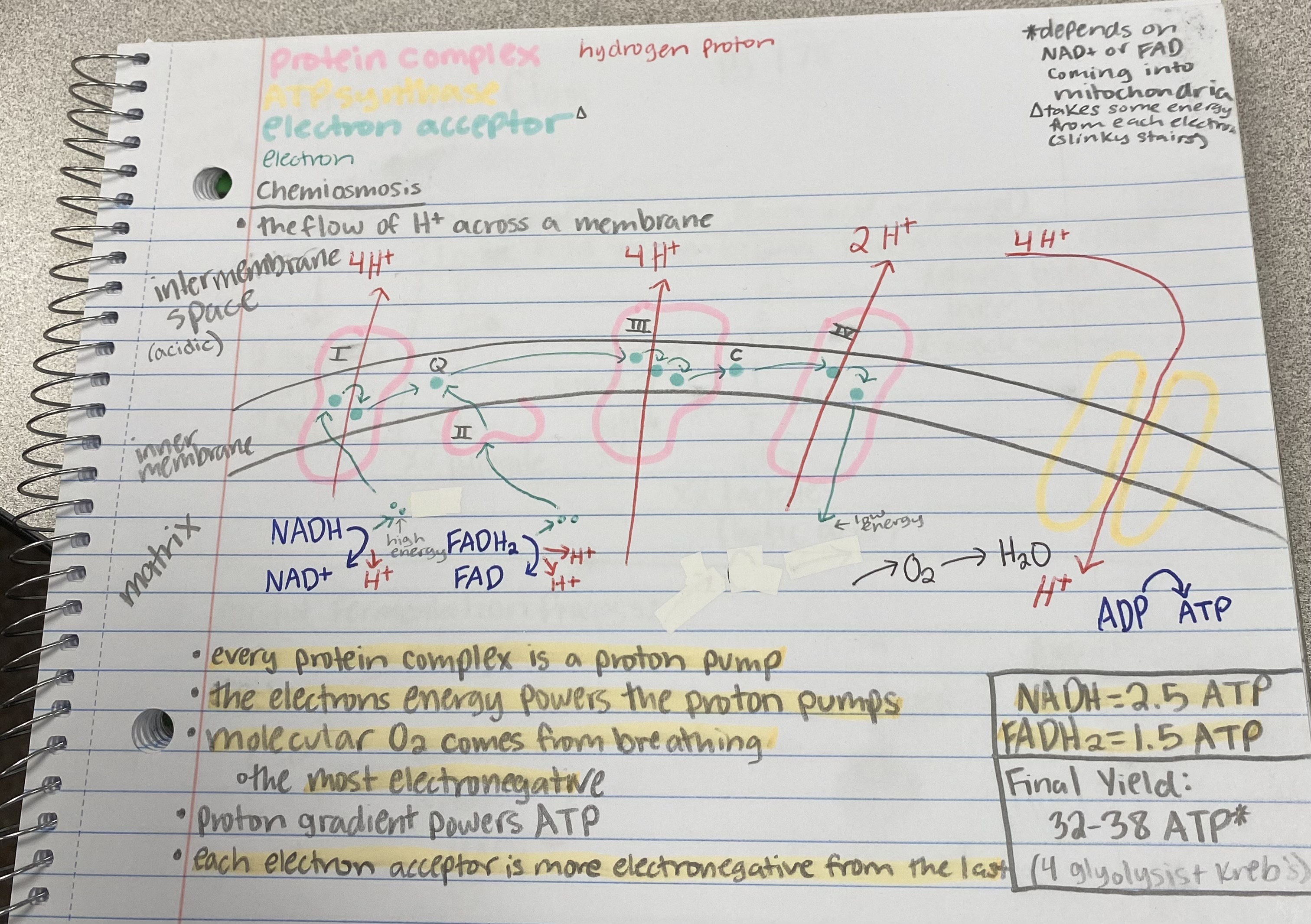
proton pump
What do protein complexes in the ETC act as?
electron energy
What powers the proton pumps in the ETC?
breathing
Where does the molecular O2 come from in chemiosmosis?
32-38 ATP
What is the final yield of ATP from cellular respiration?
there is a limited amount of NAD+
Why can’t glycolysis exist on its own?
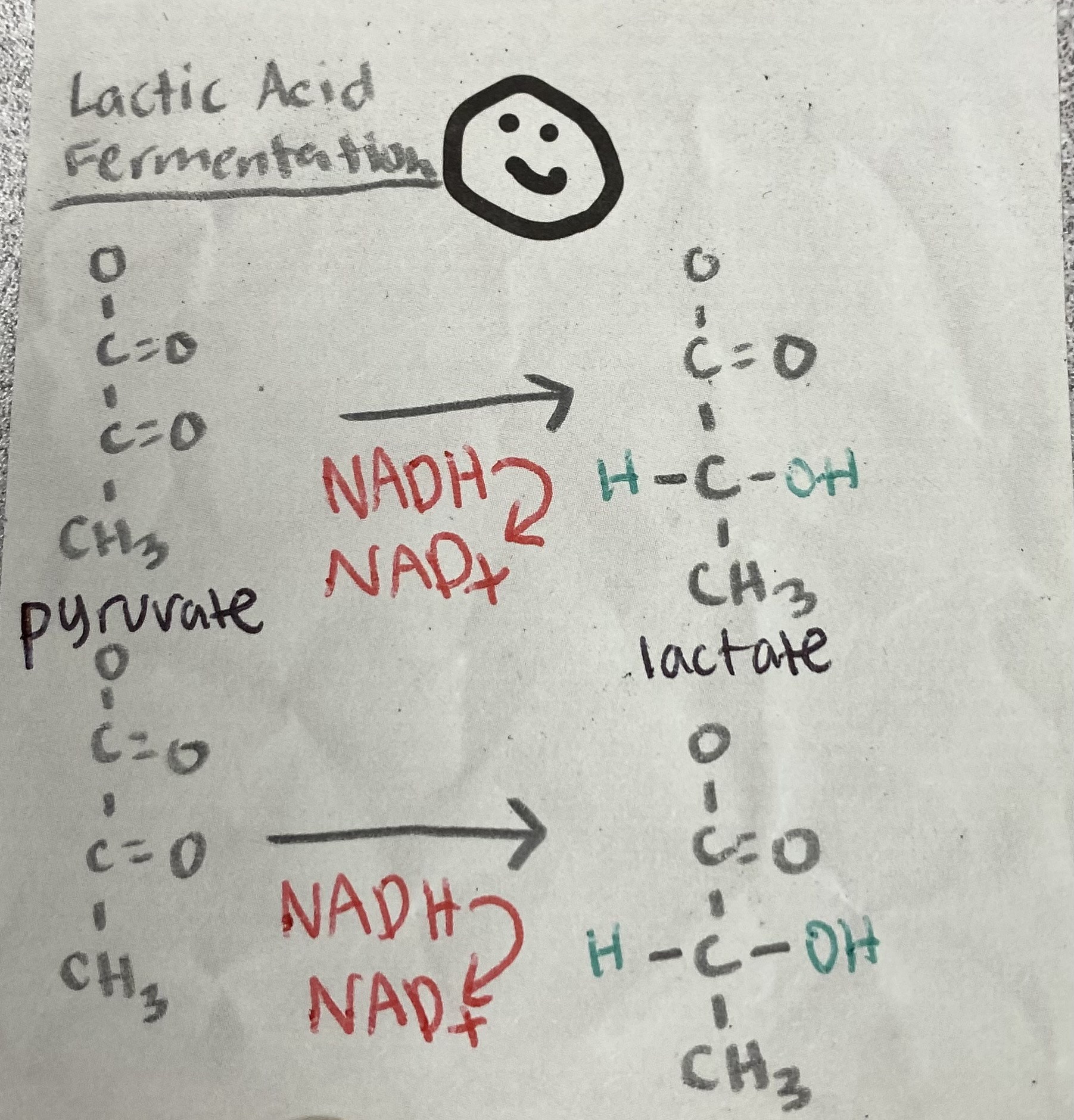
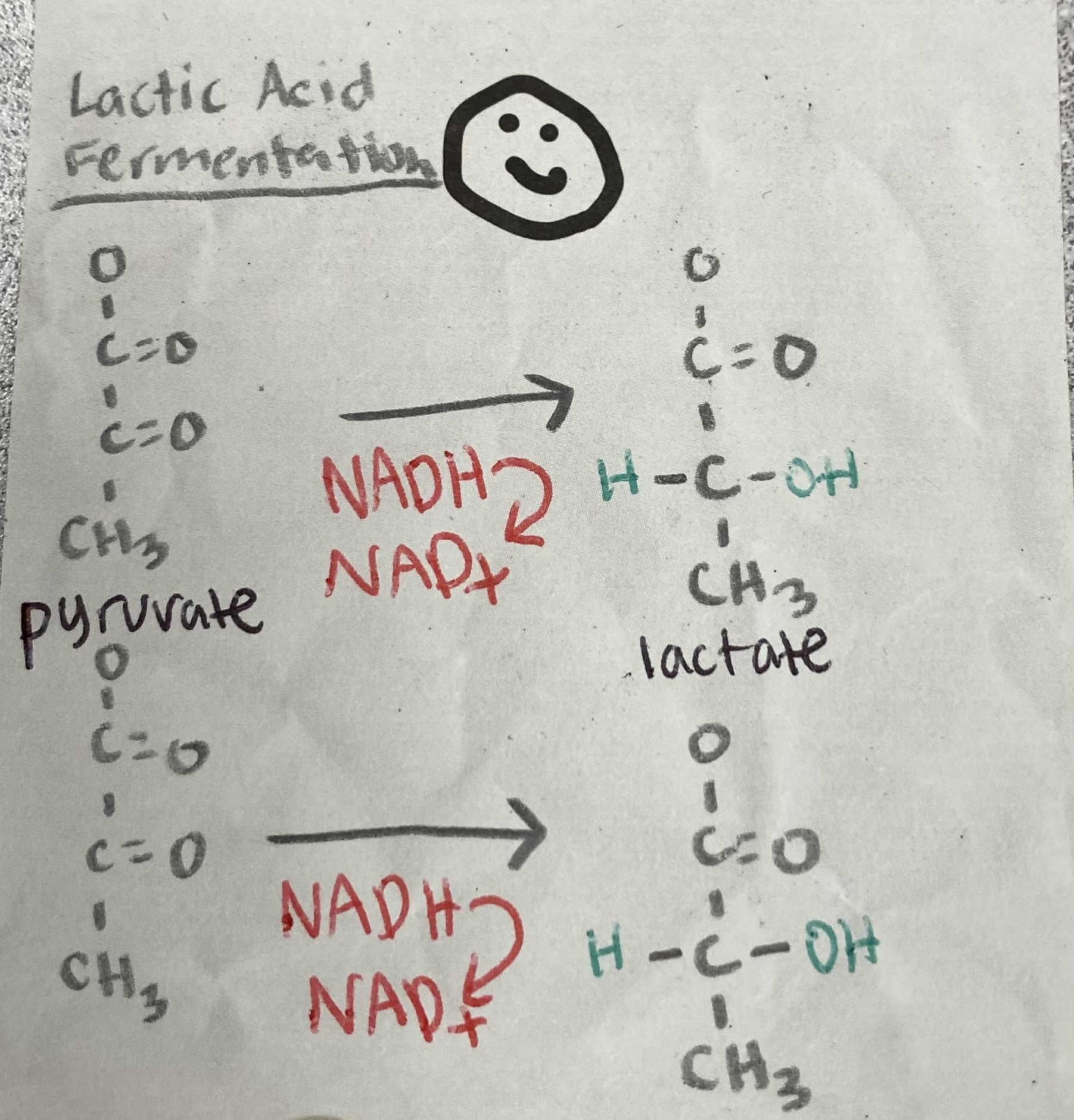
2 NAD+, 2 lactate
What are the products of Lactic Acid Fermentation?
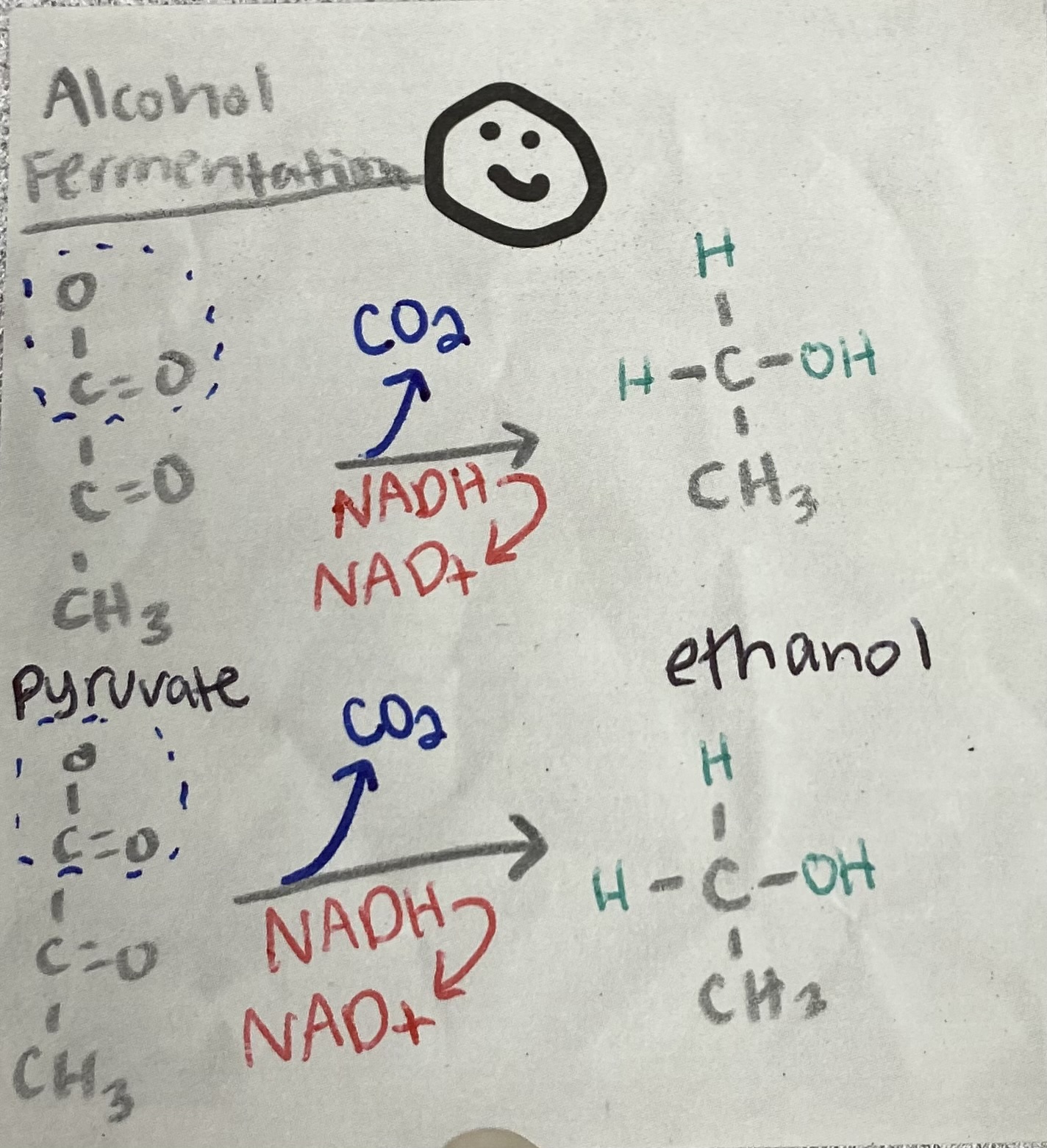
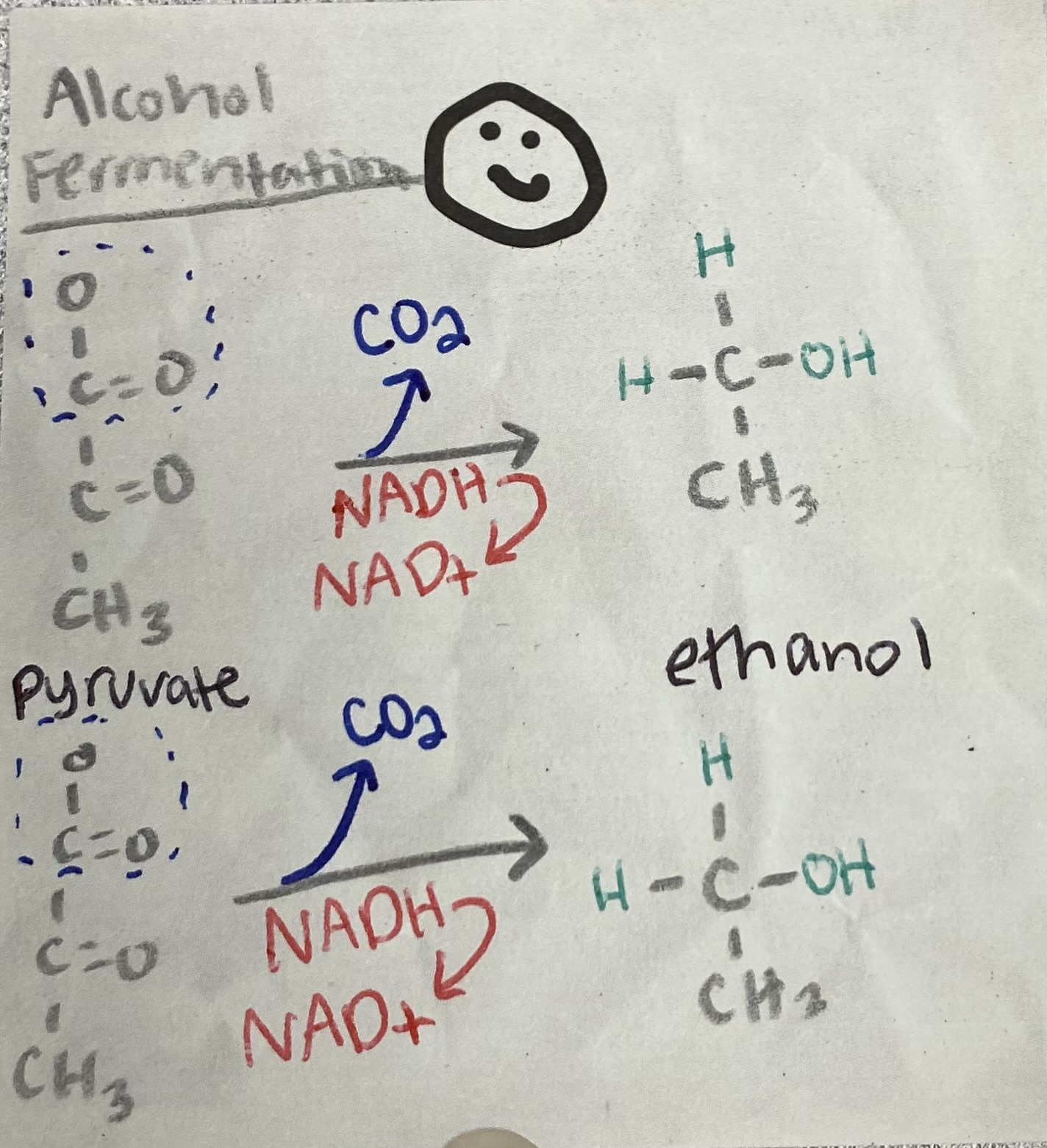
2 NAD+, 2 CO2, 2 ethanol
What are the products of Alcohol Fermentation?
2
How many ATPs are produced in fermentation?
obligate anaerobes
organisms that only carry out fermentation and anaerobic respiration
oxygen can kill them
some bacterias