Chemistry - 3.3.13: Amino Acids, Proteins and DNA
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
Amino acids
The building blocks of proteins
How many functional groups do amino acids have? What are they?
2 - a carboxylic acid and a primary amine
How many naturally-occurring amino acids are there?
20
Zwitterions
Ions that have a permanent positive and negative charge - overall, the molecule is neutral
Why are amino acids found as zwitterions?
The carboxylic acid group has a tendency to lose a proton to form COO-, while the amine group has a tendency to accept a proton to form NH3+
Describe the melting points of amino acids and why they are like that.
High melting points - they are ionic
Describe the solubility of amino acids and why they are like that.
Dissolve well in water but poorly in non-polar solvents - they are ionic
What happens to amino acids in strongly acidic conditions?
The amine group gains a proton (is protonated) to form a positive ion (NH3+)
What happens to amino acids in strongly alkaline solutions?
The carboxylic acid group loses a proton (is deprotonated) to form a negative ion (COO-)
Proteins
Sequences of amino acids joined by peptide bonds
Dipeptide
A peptide with two amino acids
What forms when proteins are hydrolysed?
A mixture of its constituent amino acids
What bonds may be present between the amino acids of a protein chain?
Hydrogen bonds, ionic attractions and sulfur-sulfur bonds
In amino acids, what do hydrogen bonds form between?
The C=O and N-H groups
In amino acids, what do ionic attractions form between?
Between groups on the side chains of amino acids (if a COO- or NH3+ are present)
What amino acid can form disulfide bridges?
Cystine
What are the levels of protein structure?
Primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary
Primary structure of a protein
The sequence of amino acids along a protein chain
How might the primary structure of a protein be represented?
With drawings of the amino acids or their 3 letter abbreviations
What holds together the primary structure of proteins?
Covalent bonds between the amino acids (peptide / amide links)
Secondary structure of a protein
The folding of a protein chain into an alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
What holds together the secondary structure of proteins?
Hydrogen bonds between C=O and N-H
Tertiary structure of proteins
The folding of the secondary structure into a three dimensional shape
What holds together the tertiary structure of proteins?
Hydrogen bonds, ionic interactions and sulfur-sulfur bonds
How can amino acids be separated and identified?
By thin-layer chromatography
What developing agents would you use when separating amino acids with TLC?
Developing agents like ninhydrin or UV light
Enzymes
Protein-based catalysts (biological catalysts)
How do enzymes work? (4)
They have a stereospecific active site
The reacting molecule is complementary to the active site and binds to it
The active site holds the reacting molecules in the right orientation to react
The products are released so the process may repeat.
What type of proteins are enzymes?
Globular proteins
Active site
A cleft/crevice in an enzyme where the reaction takes place and where the reacting molecule binds to the enzyme
What are some active sites described as?
Stereospecific
Why are some active sites stereospecific?
They can only catalyse reactions of one or other of a pair of enantiomers
How do drugs inhibit enzymes?
They have a similar shape to the substrate so bind to the active site instead, blocking it
How might the action of enzymes be reduced?
By denaturing them or by blocking their active sites
How might drugs used to reduce the action of enzymes be designed and why?
By using computer modelling - can predict the shapes of proteins, enabling them to predict their properties
What is DNA? What is it made up of?
It is a polymer made up of monomers called nucleotides
What are nucleotides made up of?
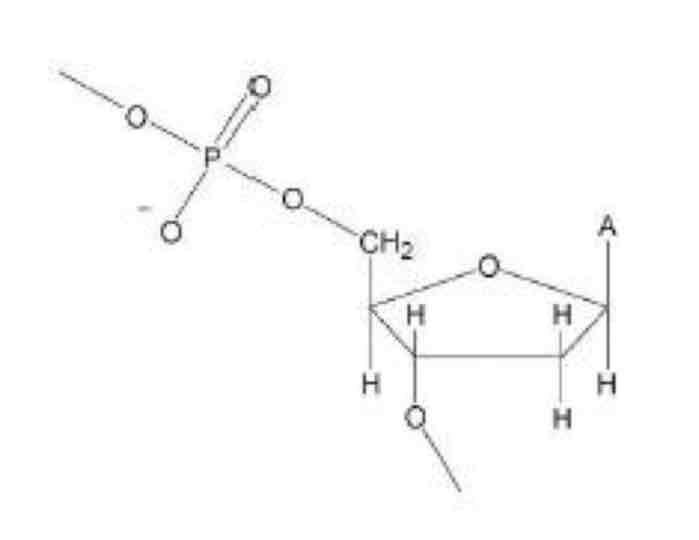
A phosphate ion, a 2-deoxyribose sugar and an organic base
What does DNA stand for?
Deoxyribonucleic acid
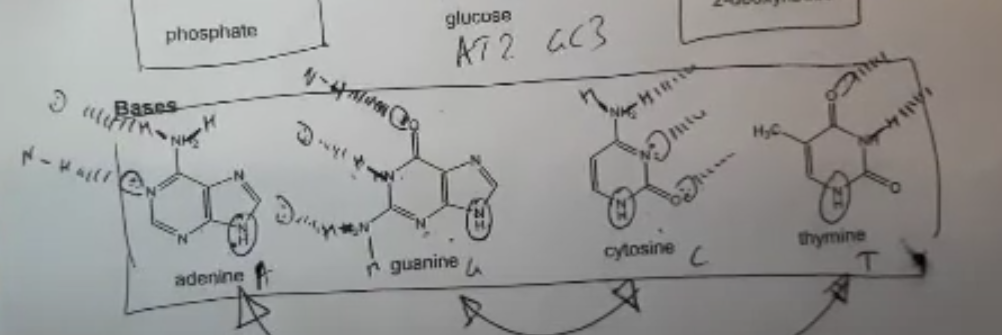
What are the four inorganic bases of DNA?
Adenine, thymine, cytosine and guanine
How does DNA exist as?
2 complementary strands arranged as a double helix
How do nucleotides join together?
In a condensation reaction between the OH groups of the phosphate ion on one nucleotide and the OH group on the deoxyribose sugar on another nucleotide - this eliminates a molecule of water
What bonds are present in DNA?
Covalent bonds between the phosphate of one nucleotide and deoxyribose sugar of another + hydrogen bonds between the complementary bases of the 2 strands
What are the complementary base pairings of DNA?
A-T, C-G
What happens to DNA during cell division?
The hydrogen bonds of the double helix break and the strands unravel so the DNA may be replicated
Cisplatin
An anti-cancer drug
What is the structure of cisplatin?
Square planar
What is the formula of cisplatin?
PtCl2(NH3)2
How does cisplatin work? (4)
It bonds to the the nitrogen atoms on 2 adjacent guanine bases on a strand of DNA
A ligand substitution reaction takes place - the chloride ions on cisplatin are displaced by water, while the water molecules are then displaced by the nitrogen on guanine
The nitrogen atoms of the guanine molecules form dative covalent bonds with platinum
This distorts the shape of DNA so cell replication cannot take place
Why does cisplatin have side effects?
It also bonds to the DNA in healthy cells, not just cancerous ones, so healthy cells that replicate quickly are significantly affected
Why does cisplatin have a greater effect on cancerous cells than healthy ones?
The cancerous cells are replicating faster
Complementary
The two strands must have base sequences that all match A to T and C to G
Draw a phosphate bonded to a 2-deoxyribose
Why do hydrogen bonds form in the secondary structure of proteins? (4)
Nitrogen and oxygen are very electronegative
So C=O and N-H are polar
This means hydrogen bonds form between O and H
As the lone pair of electrons on O is strongly attracted to the positive dipole on H
What makes amino acids more polar?
They have a more positive charge
How are the DNA bases arranged on the AQA data sheet? Label the hydrogen bonds + where the base forms a bond with the 2-deoxyribose sugar.