cells
1/42
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
prokaryotes
no membrane-bound organelles
unicellular
domains: bacteria and archaea
eukaryotes
membrane- bound organelles
uni- or multi- cellular
domain eukaryota
animals
plants
fungi
protista
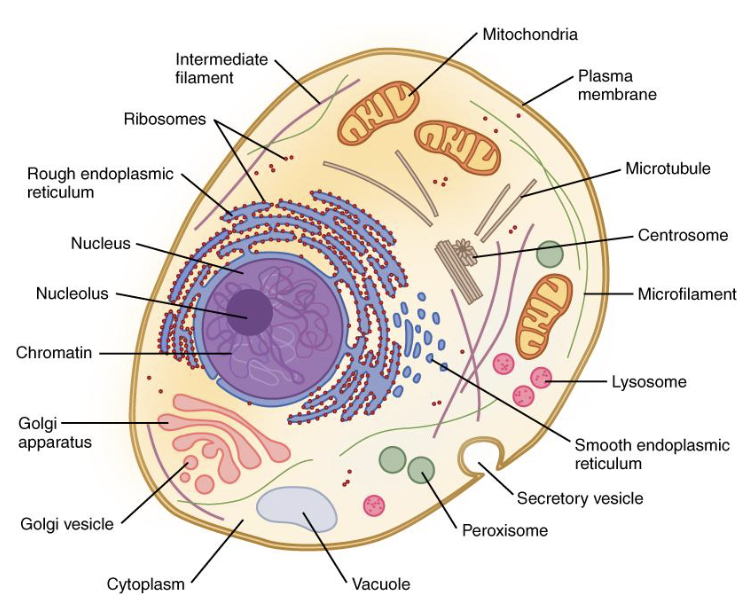
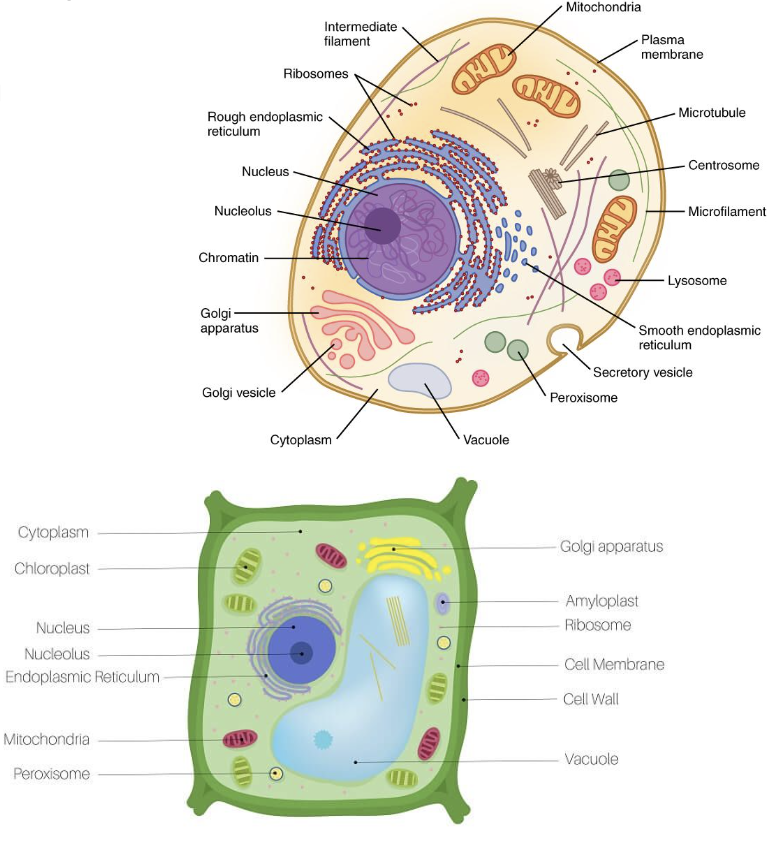
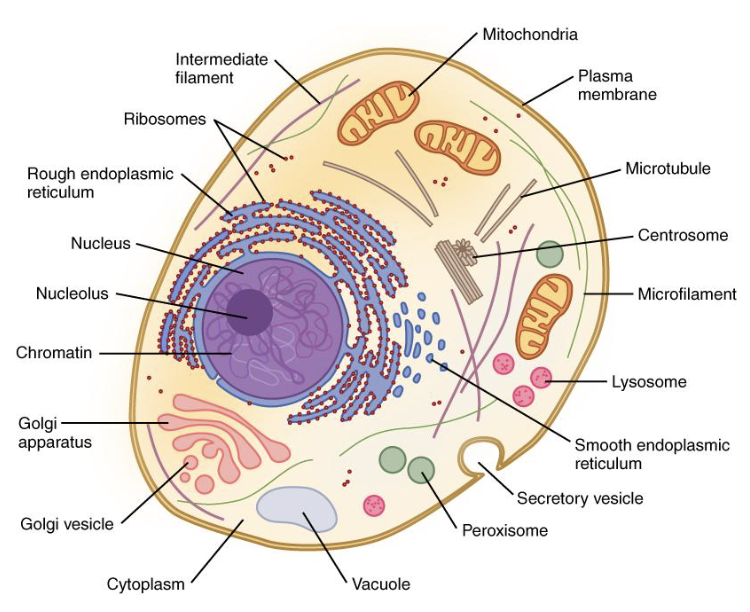
nucleus
contains genetic information in the form of chromosomes or chromatin
has nucleolus for ribosome production
surrounded by phospholipid nuclear membrane (envelope)
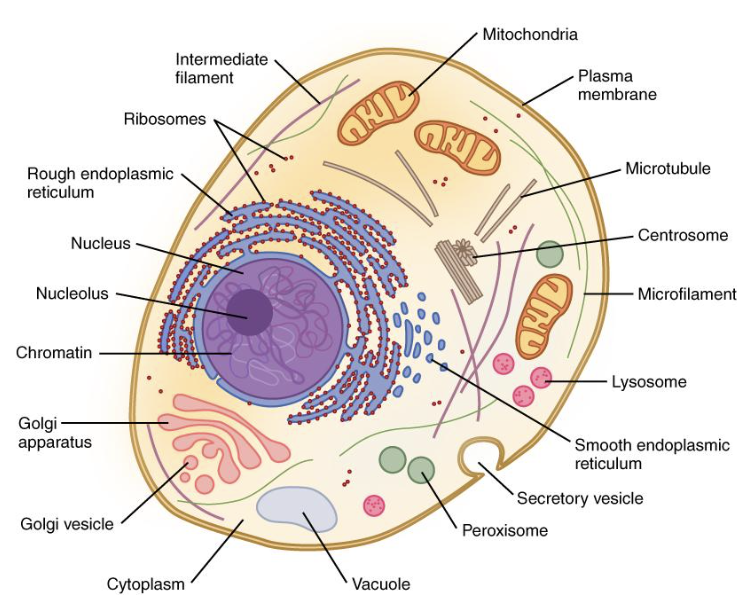
cytoplasm
”Jelly goo” that is within the cell membrane
Has organelles/ structures in it
Also found in prokaryotes
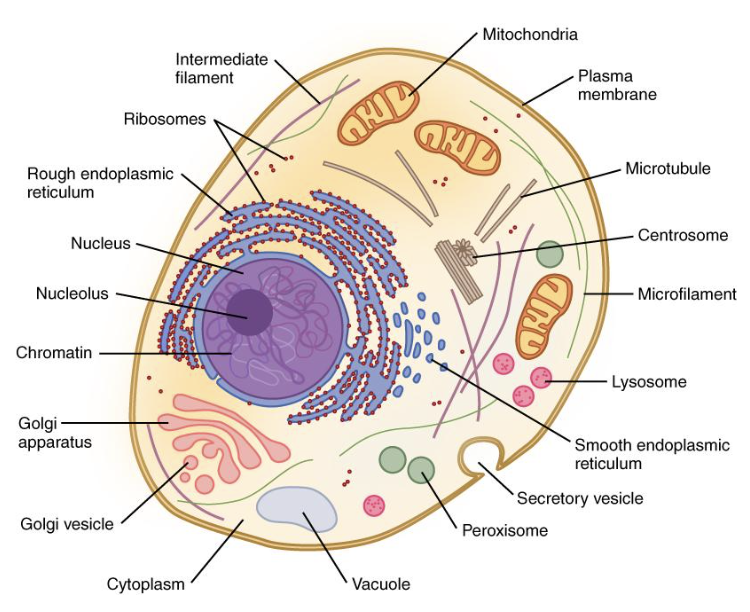
ribosomes
Structures that build proteins during protein synthesis
Free-floating or attached to the rough ER
Also found in prokaryotes
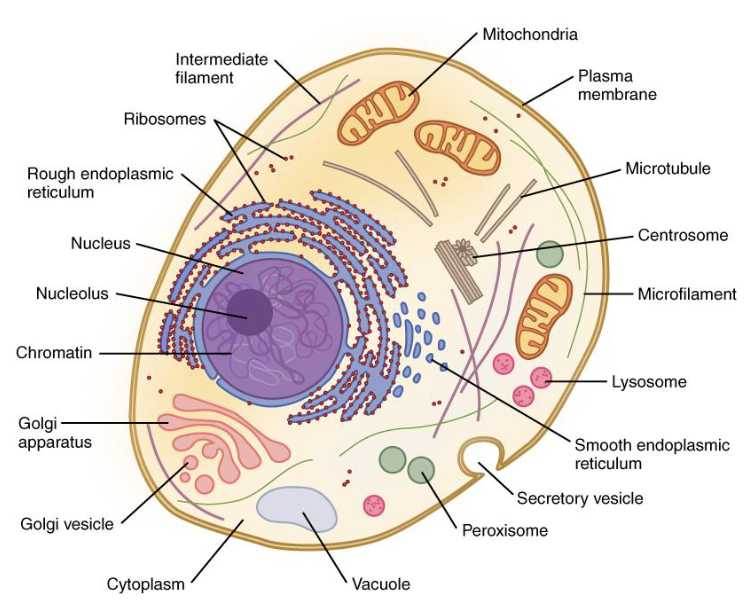
rough ER
Help with protein production and shipping
Have ribosomes attached
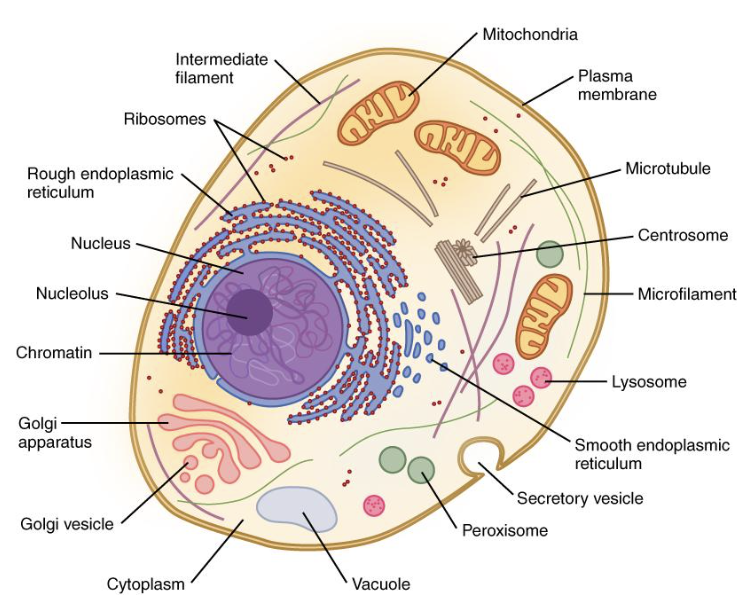
smooth ER
Synthesis of lipids
Detoxification
Storage of calcium ions
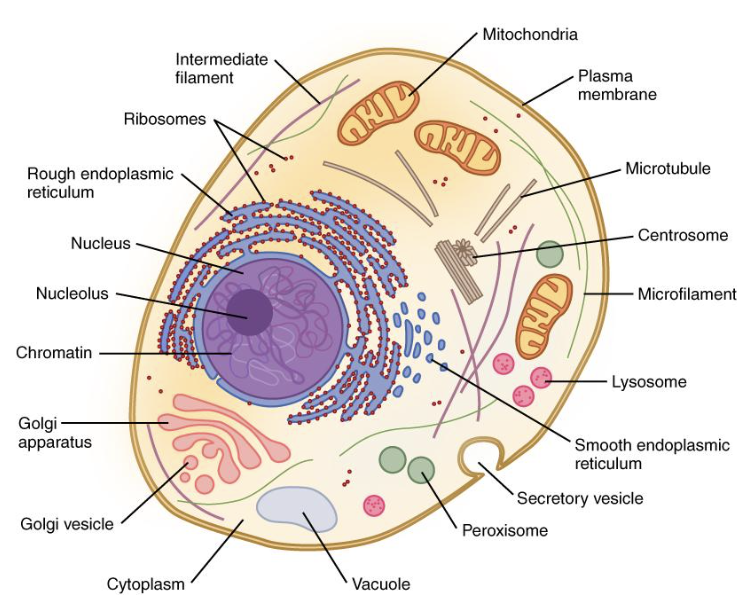
golgi apparatus
“Warehouse” for receiving, sorting, and shipping of proteins
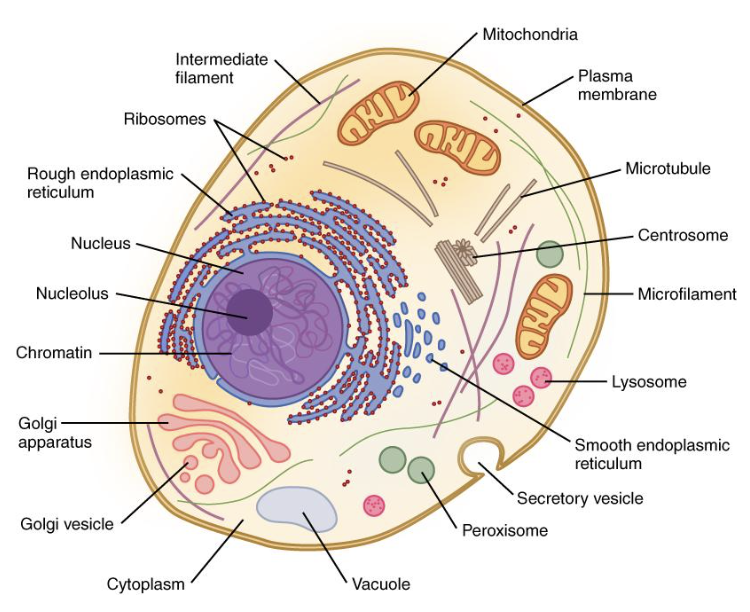
vesicles
Small “containers” made from ER or golgi membrane that move products around the cell
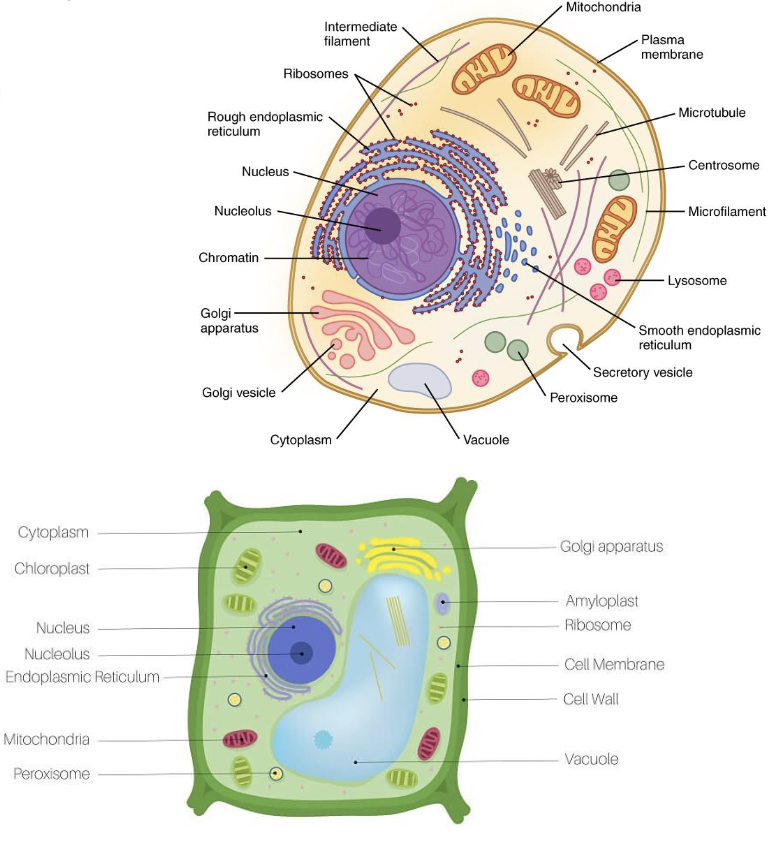
vacuoles
Large vesicles for storing products
Plant cells have a large one filled with water
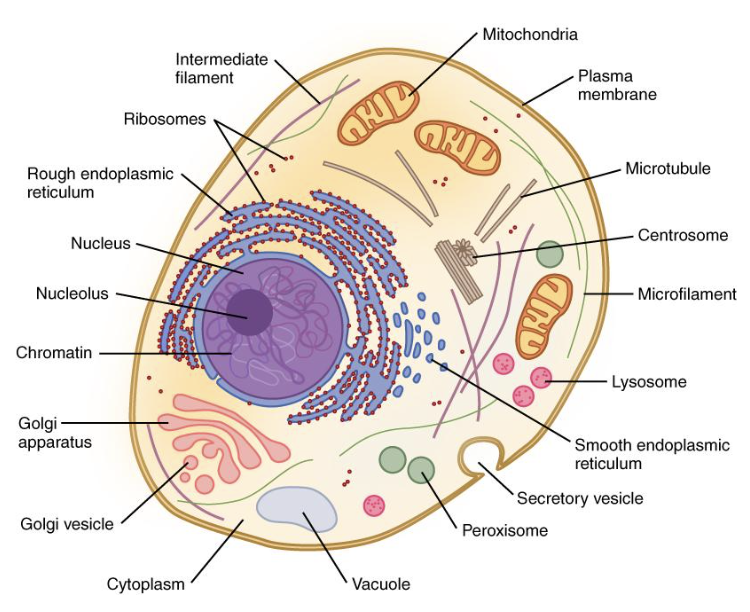
lysosomes
Digestive organelle where larger molecules are broken down
Contain hydrolytic enzymes
mitochondria/mitochondrion
Site of cell respiration
ATP is generated
Found in both plants AND animals
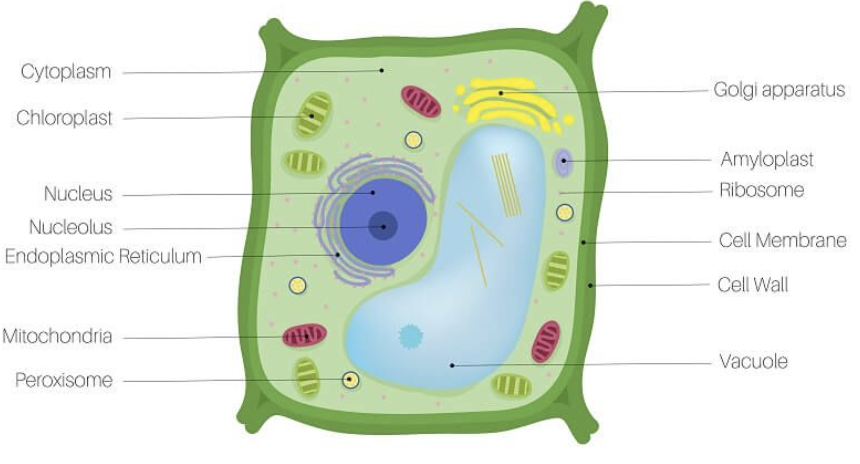
chloroplast
Site of photosynthesis
Converts energy from the sun into sugar molecules
Plants/algae only
centrosome
Helps with cell division (mitosis) in animal cells
Contain centrioles
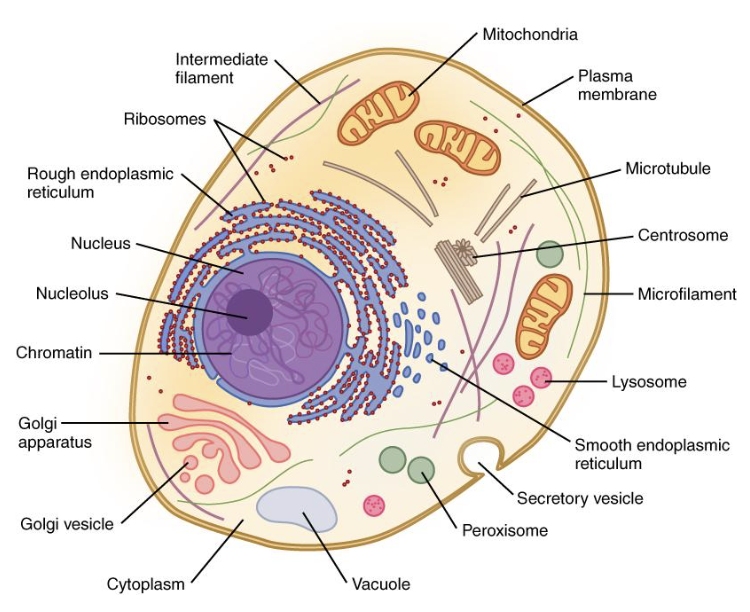
cytoskeleton
Reinforces cell’s shape
Helps with cell movement
Includes:
MicrofilamentsIntermediate
filaments
Microtubules
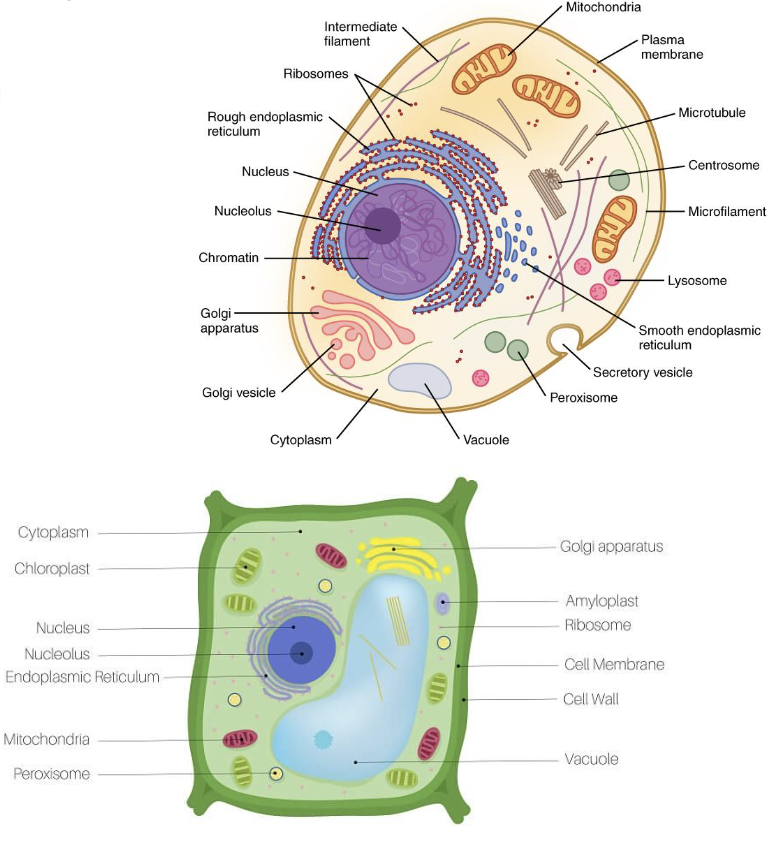
cell (plasma) membrane
Found in plants, animals, and prokaryotes
protection for cell
fixed environment for cell
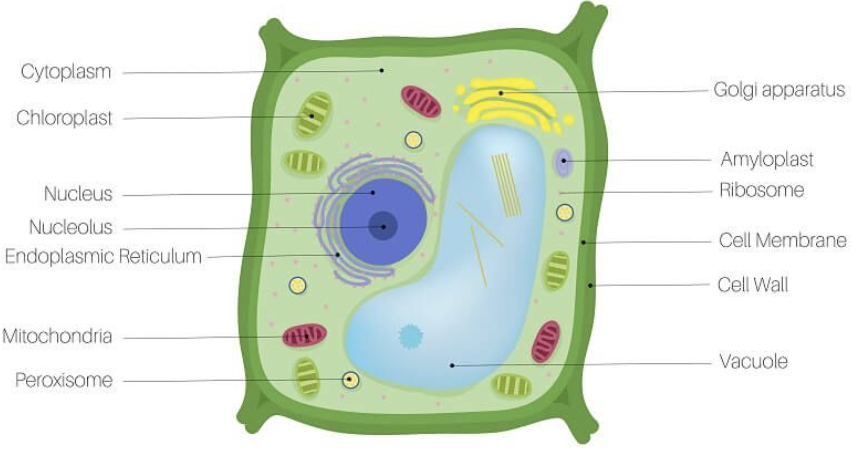
cell wall
Protects, maintains shape, helps with structure
Made of cellulose
Found in plant cells and some prokaryotes
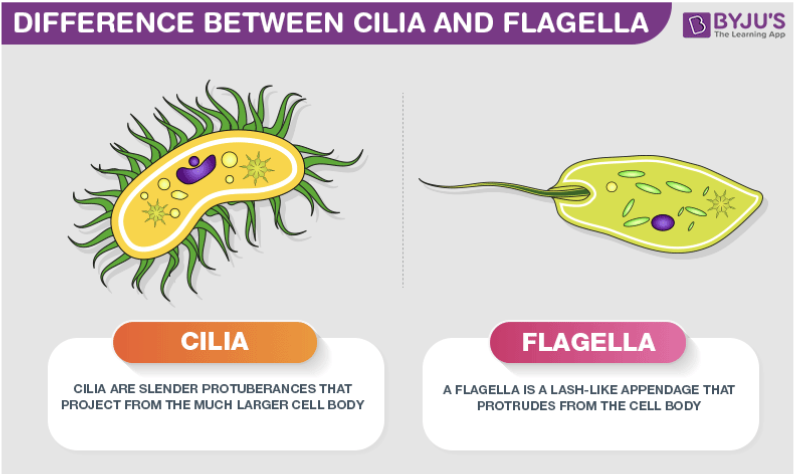
cilia (cilium)
Short appendages containing microtubules present on some eukaryotes
Used in locomotion
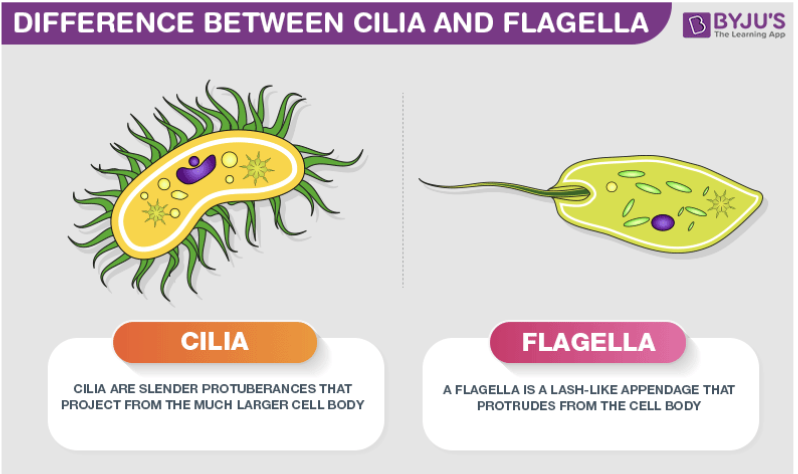
flagella (flagellum)
“Tail-like” appendage found on some eukaryotes
Used in locomotion
what determines cell function?
size, shape, surface area
organelles present or absent
quantity of different organelles
endosymbiotic theory (endosymbiosis)
Mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free-living prokaryotes engulfed by an early ancestor of eukaryotic cells
The engulfed cell formed a relationship with the host cell
Over the course of evolution, merged into a single organism
osmosis
Diffusion of water
Movement down its concentration gradient: from where there is more water (less solute) to less water (more solute)
“Water wants to even things out”
hypotonic
less solute, more water
hypertonic
more solute, less water
isotonic
same amount of solute and water
water potential
Solute potential + pressure potential
Ψ = Ψp + Ψs
Water moves from regions of high water potential to regions of low water potential.
solute potential
determined by solute concentration; always negative
pressure potential
pressure from membranes/walls; can be positive or negative
The molar concentration of a sugar solution in an open beaker* is 0.3M.
Calculate the water potential at 27 degrees C. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
-1 (0.3 M) x (0.0831L bars/mole K) x (300)
-7.48 bars of solute potential
Phospholipid bilayer structure
Hydrophilic head
Hydrophobic tails
Amphipathic
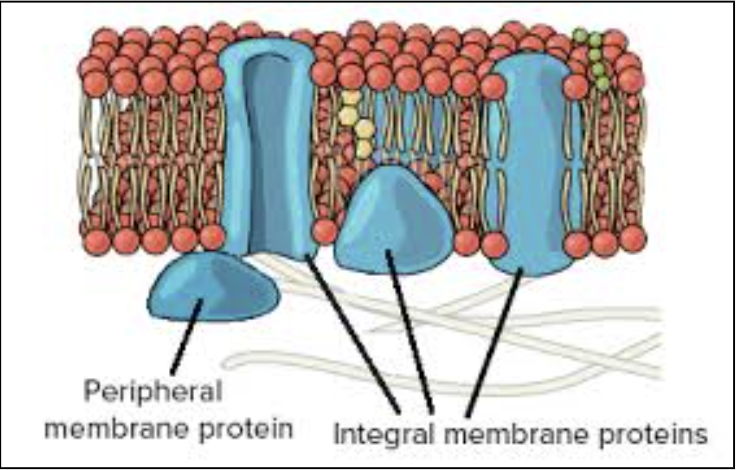
Proteins
Peripheral proteins: bound to surface of membrane
Integral proteins: penetrate hydrophobic core
Transmembrane proteins: span entire membrane
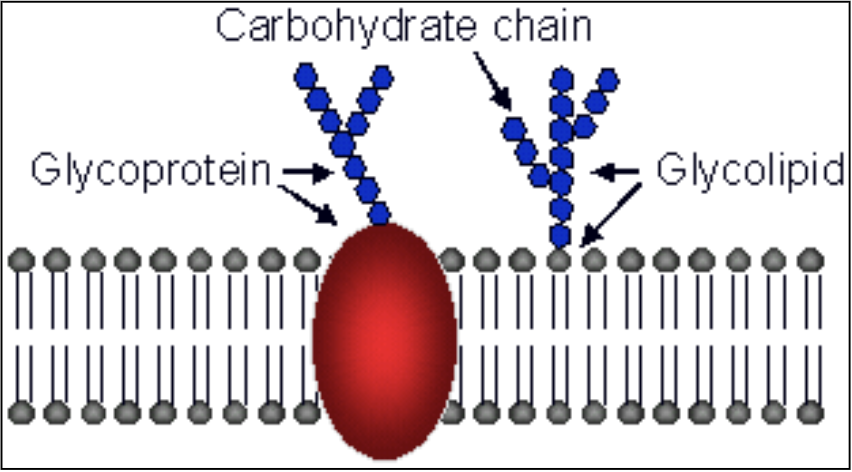
carbohydrates (in the cell)
Glycoproteins: oligosaccharides bonded to proteins
Glycolipids: oligosaccharides bonded to lipids
Both help with cell-to-cell recognition
steroids
Cholesterol: regulates cell membrane fluidity
diffusion
Movement of particles from area of high concentration to low concentration
Movement down its concentration gradient
Does not require energy
Diffusion through the phospholipid bilayer
passive transport
no additional energy required
Small, nonpolar (hydrophobic) molecules
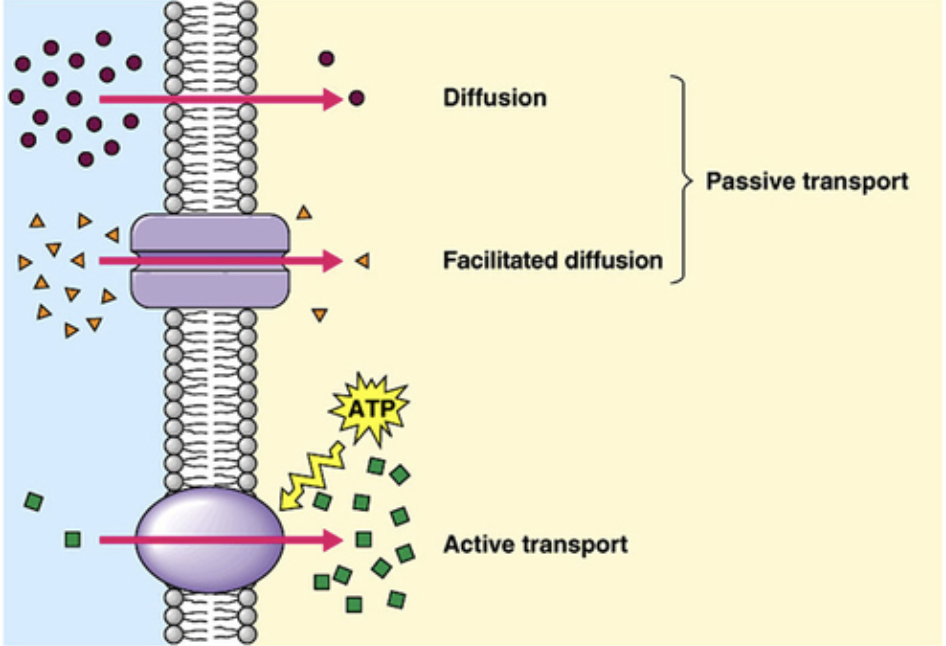
facilitated diffusion through transport proteins
passive transport
no additional energy required
Can move larger, polar molecules
2 types of transport proteins
Channel proteins
Carrier proteins
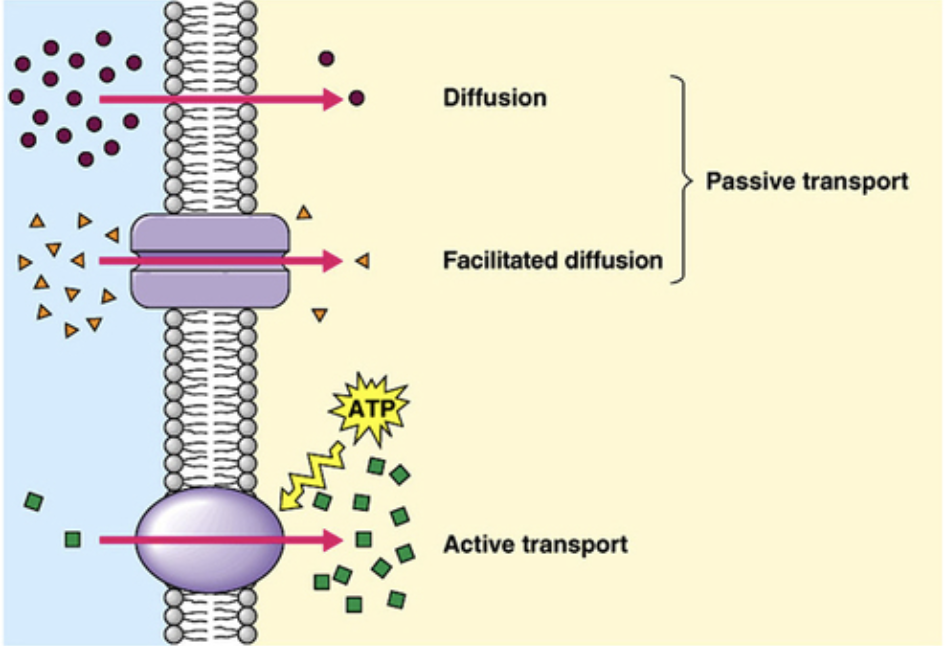
active transport
additional energy (ATP)
Moves substances against their concentration gradients through transmembrane protein
bulk transport
Moves large molecules across cell membrane
additional energy (ATP)
Molecules packaged in transport vesicles (phospholipid “containers”)
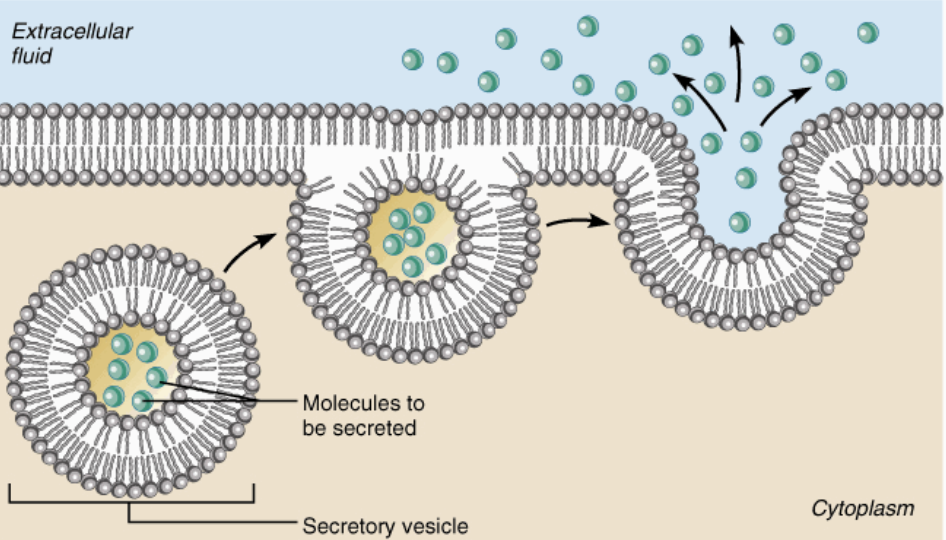
exocytosis
additional energy (ATP)
moving molecules from inside to outside cell membrane
Vesicle fuses with cell membrane, releases contents outside
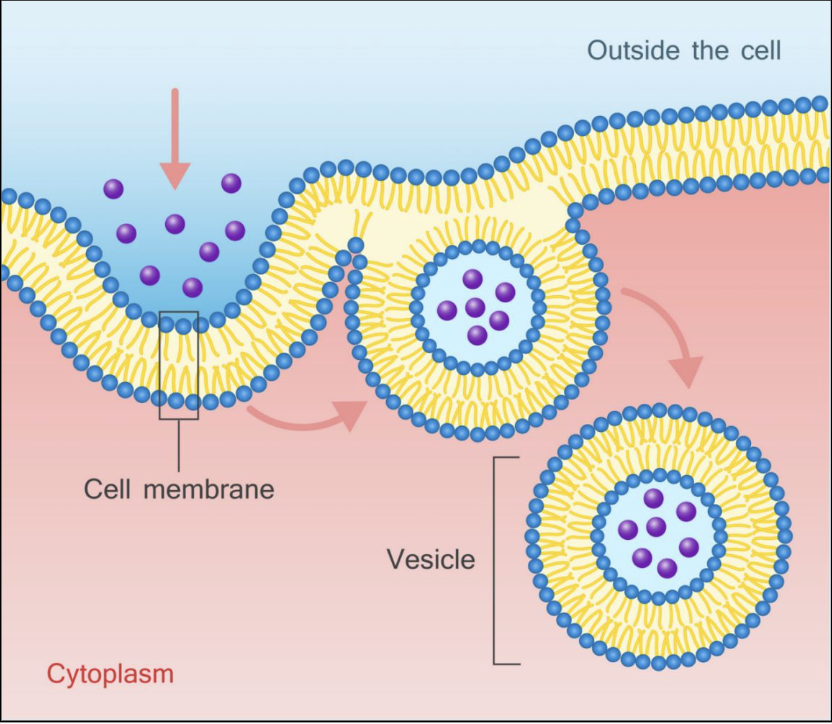
endocytosis
moving molecules from outside to inside cell membrane
New vesicle formed of cell membrane containing molecules to be moved inside
energy required (ATP)
What is the solute potential (Ψs) of a 0.5M sugar solution at 22 degrees Celsius under
standard atmospheric conditions, Ψp=0 Bars
-12.3 bars
The value for Ψ in a potato tissue was determined to be -3.3 bars. If you the potato
tissue and place it in a 0.1 M solution of sucrose at 20 degrees Celsius in an open
beaker, what is the Ψ of the solution and in which direction would the new flow of
water be? If you used a 0.1M solution of NaCl instead of sucrose, in which direction
would the new flow of water be?
-2.43 bars; water will flow into the potato tissue; with NaCl, water will flow out of the potato tissue
protein production
DNA in nucleus
Specific segment/chunk of DNA = gene
mRNA built from gene (transcription)
mRNA comes out from nucleus via nuclear pore
Bound Ribosome clamps onto mRNA, reads in 3 letter words
Assembles primary structure of protein (translation)
Protein released from ribosome into ER
Protein modified in ER
Goes to golgi apparatus via transport vesicle (little pouch of membrane)
Vesicle get "pulled" along via motor proteins on cytoskeletal fibers
Vesicle fuses with golgi membrane, releases protein
Golgi modifies & packages protein
Repackaged in another vesicle
Motor proteins take to cell membrane
Vesicle fuses to membrane and releases protein via exocytosis