Ear, Nose, Paranasal Sinuses
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
The External nose has 3 main arterial supply.
identify (3)
Facial artery → Nasal Branches
Maxillary artery → Infraorbital branches
Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) → Ophthalmic branches
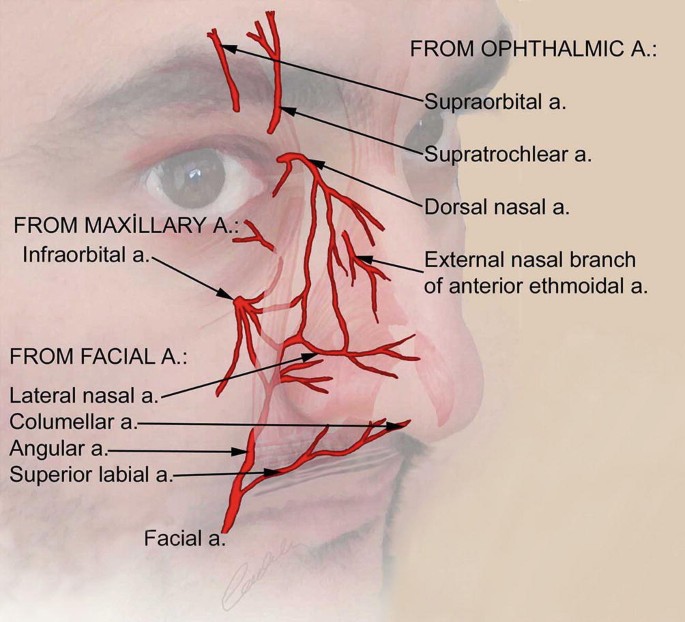
Trace out the venous drainage of the External Nose.
Angular + Lateral Nasal Vein → Facial Vein →Common Facial Vein → Internal Jugular Vein (IJV)
**All the Lymphatic Vessels from the Head and Neck ultimately drain into?
Deep Cervical Lymph Nodes
runs along the IJV
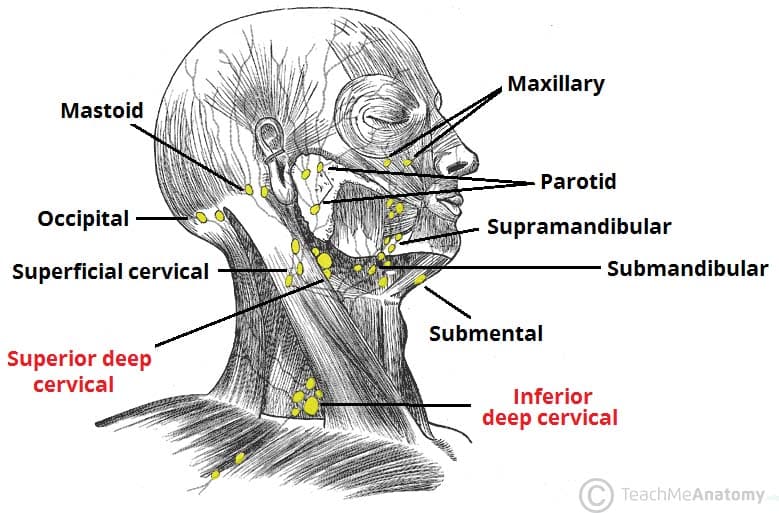
Superficial Drainage of the Face
The Anterior Neck drains into which regional lymph node group?
Anterior / superficial cervical
Occipital
Mastoid / retroauricular
Anterior / superficial cervical
Superficial Drainage of the Face
The Posterior scalp drains into which regional lymph node group?
Anterior / superficial cervical
Occipital
Mastoid / retroauricular
Occipital
Superficial Drainage of the Face
The retro-auricular area drains into which regional lymph node group?
Anterior / superficial cervical
Occipital
Mastoid / retroauricular
Mastoid
Superficial Drainage of the Face
The Upper Lip and lateral Lower lip drains into which terminal lymph node group?
Parotid
Buccal
Submandibular
Submental
Submandibular
Superficial Drainage of the Face
The Eyelids* drains into which terminal lymph node group?
Parotid
Buccal
Submandibular
Submental
parotid
** (be careful) True or False? The Right side of the External nose drains into the Thoracic Duct.
False!
Remember
Right side → Right Lymphatic Duct
Left side → Thoracic Duct
The external nose is mostly innervated by which 2 nerves?
Ophthalmic nerve → Nasocilliary branch of V1
Maxillary nerve → Infraorbital nerve from V2
***Which nerve innervates the ala of the nose?
Ophthalmic nerve
Maxillary nerve
Maxillary nerve → Infra-orbital nerve from V2
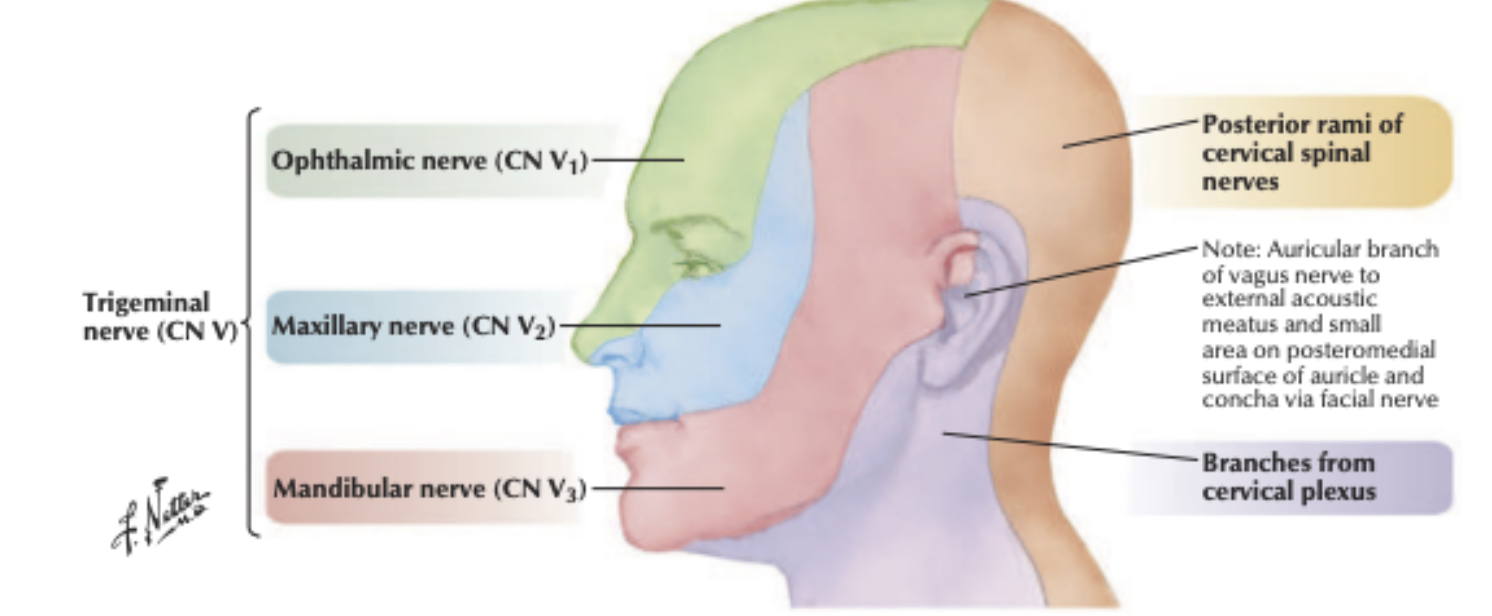
What nerve innervates the Tip of the Nose?***
Opthamic Nerve !
What is the Most Anterior part of the Nasal cavity covered by skin and has sebaceous glands, sweat glands and Vibrissae called?
Nasal Vestibule
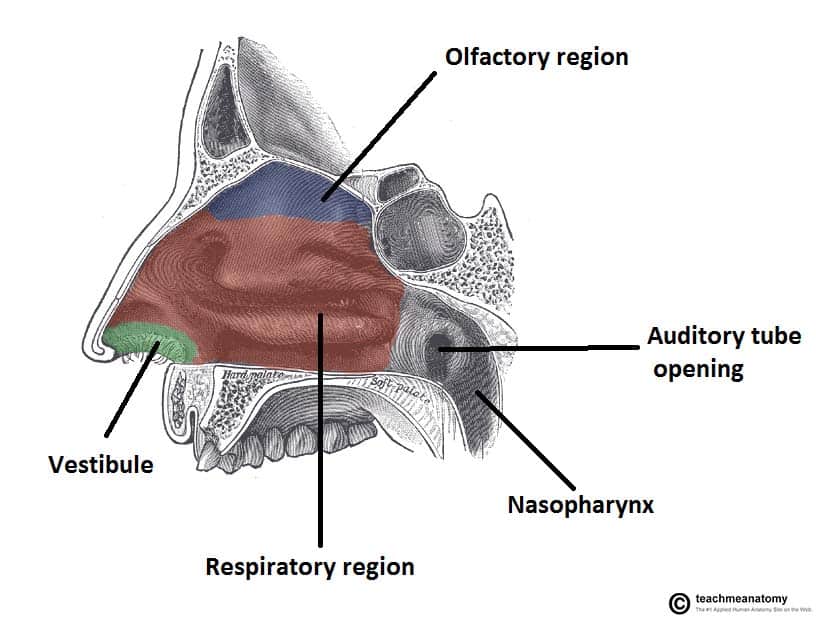
The Nasal Vestibule is lined by what?
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
Mucosa
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
The nasal cavity is lined by?
Stratified squamous keratinized epithelium
Mucosa
Mucosa
The superior 1/3 of the nasal cavity proper is known as the?
Olfactory Region
What is Olfactory epithelium known for?
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar Eipthelium without Goblet cells.
Roof
Upper part of the septum
upper surface of the superior concha
sphenoethmoidal recess
Are lined by what type of epithelium?
Olfactory Mucosa
Pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium WITHOUT goblet cells
The inferior 2/3 of the nasal cavity is also known as the Respiratory region. What type of epitheium?
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar Epithelium WITH GOBLET Cells
The Kiesselback’s Area can be found where?
Roof
medial wall of nose
Lateral wall of nose
Medial wall = Kiesselback’s area
The Nasal Turbinates (Superior, Middle, Inferior) conchae is found where?
Medial Wall
Lateral wall
Lateral wall of nose
Where can the Sphenoethmoidal recess be found?
Lateral wall
Above the superior nasal concha
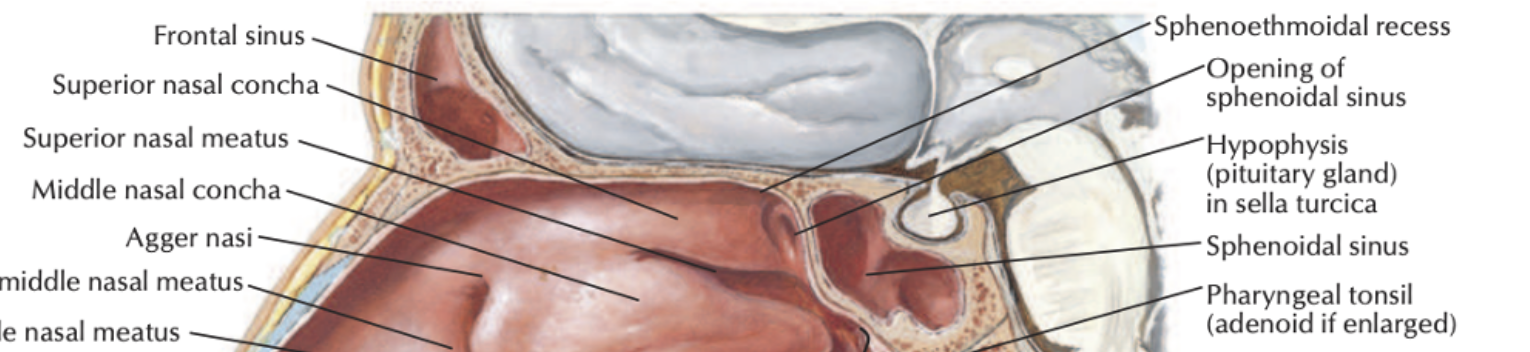
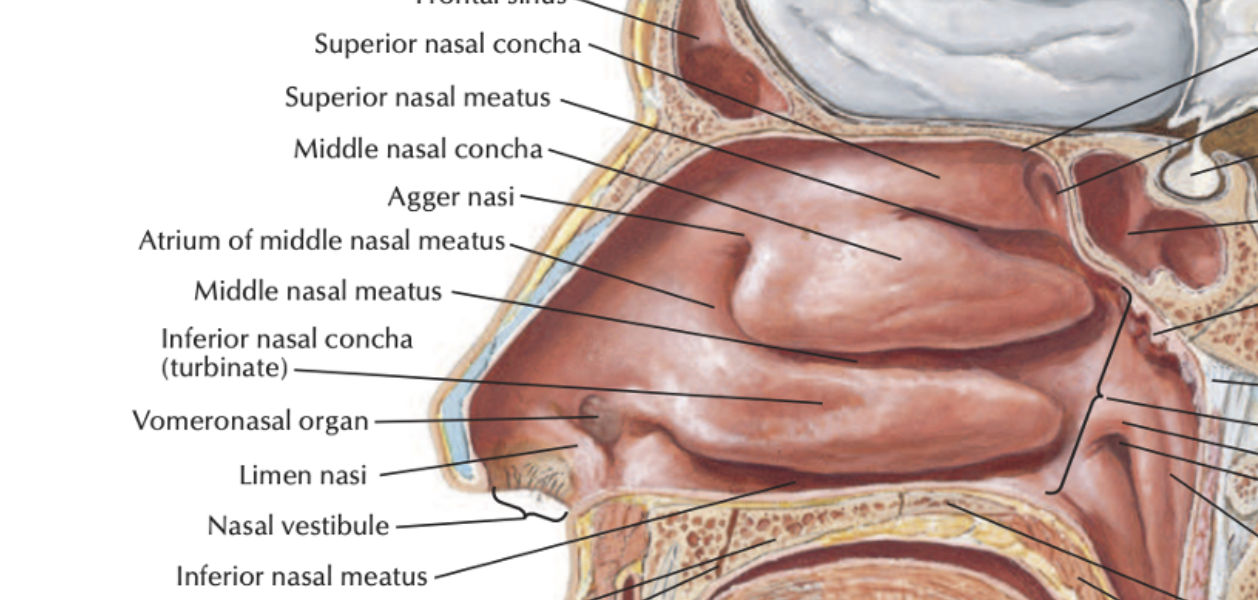
What do you call the space inbetween each Nasal Chonchae/turbinates? ***
Nasal meatus!
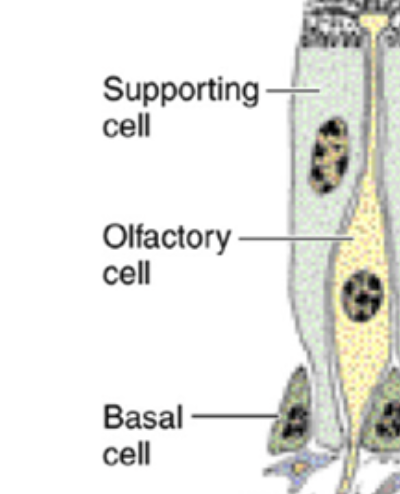
What are the main cell types found in the Olfactory Mucous Membrane?
Supporting / sustentacular cell
Olfactory Cell
Basal Cell
Bowman’s Glands
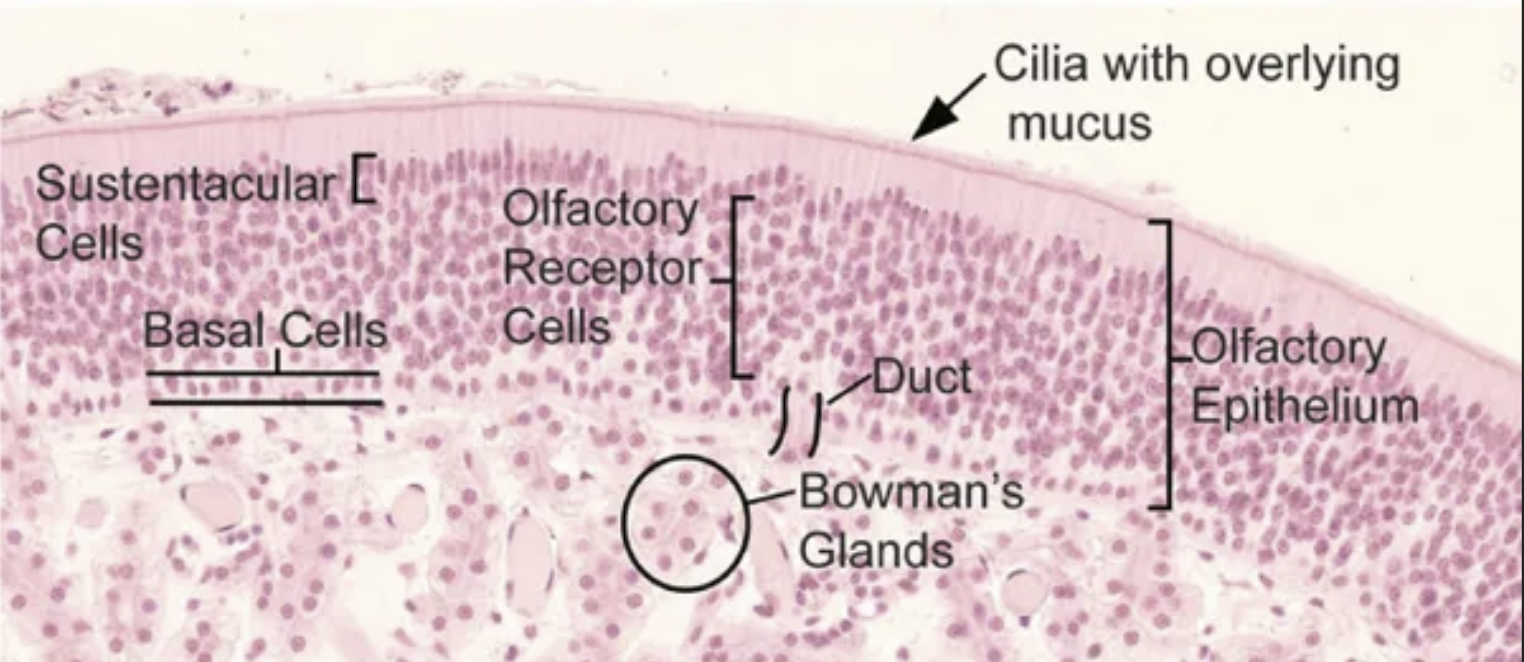
T or F. Supporting cells are “sandwhiched” in between the Basal and Olfactory Cells
True!
_ cells can differentiate into either supporting or olfactory cells and is regenerated every 2-3 months.
Basal Cells!
Classify what type of gland Bowman’s glands are.
PURELY SEROUS
Function of Olfactory Epithelium?
Reception of Olfactory stimuli
Function of Respiratory Epithelium?
Warm, Moisten and clean inspired air
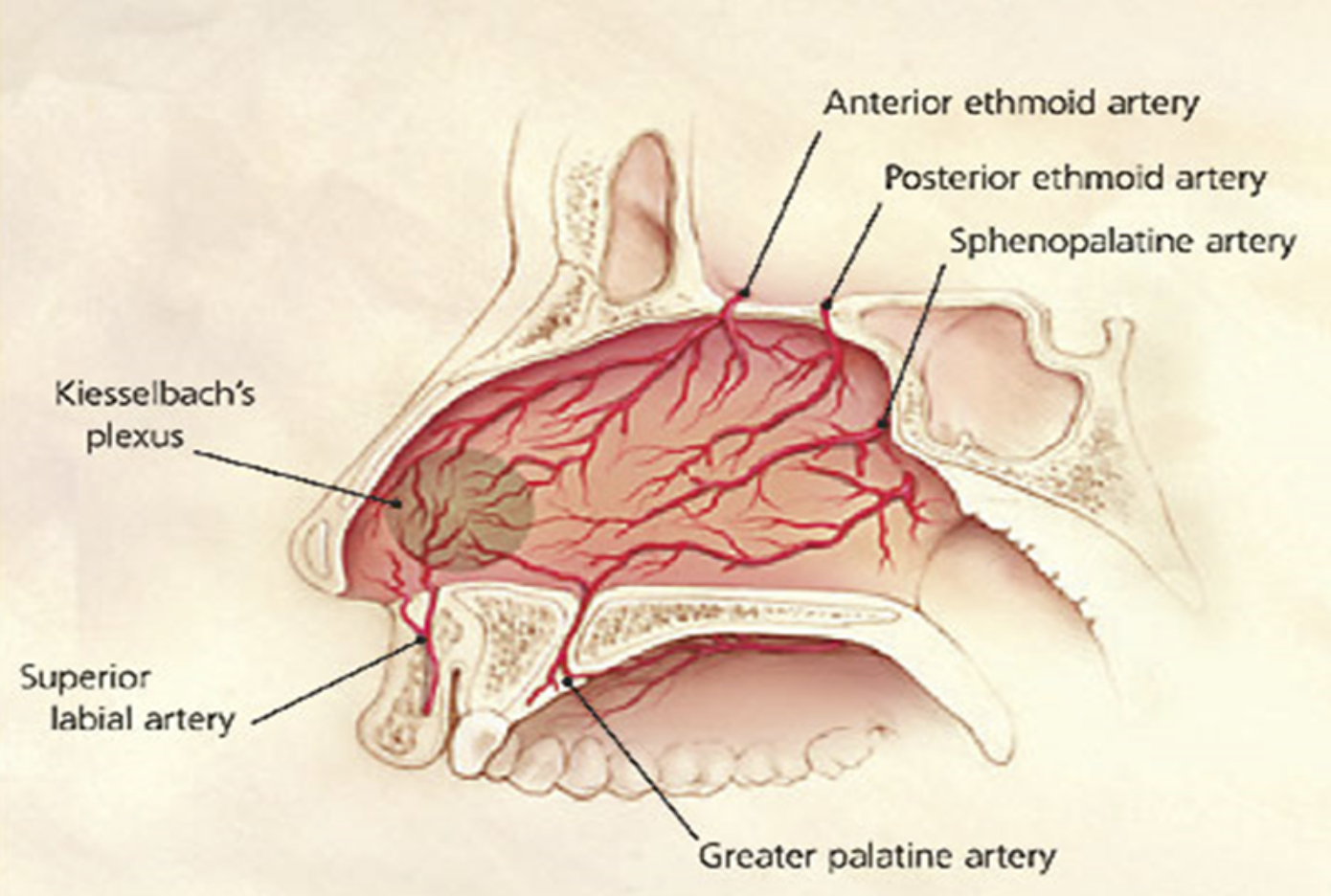
Which area in the nose is where
5 Arteries Anastomose
Prone to Epistaxis
Kiesselbach’s plexus
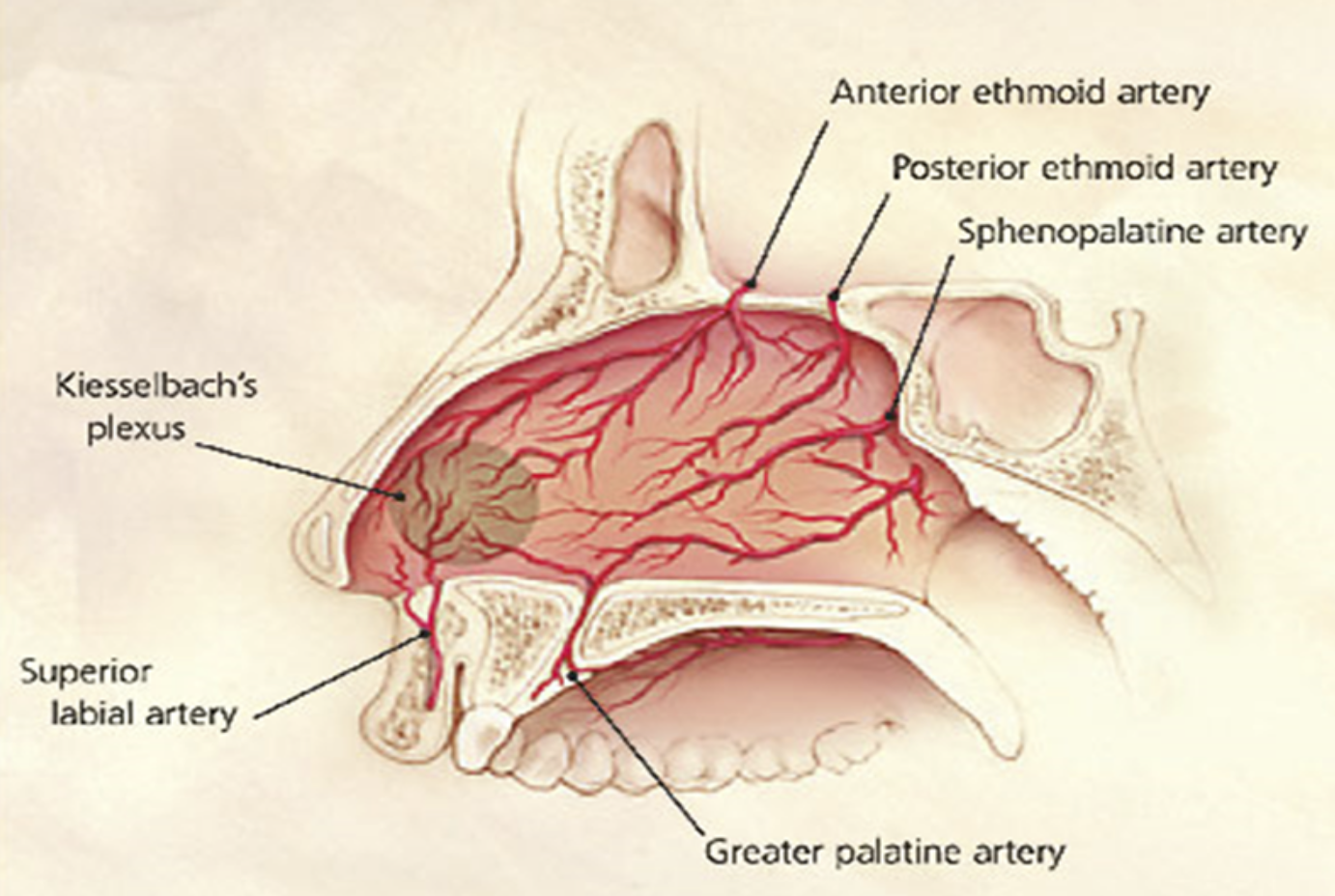
What is the anastomosis of the ethmoid and sphenopalatine artery called?
Kiesselbach’s plexus
Woodruff’s Plexus
Woodruff’s Plexus
Kiesselbach’s plexus is composed of which 5 arteries?
Anterior Ethmoid artery
Posterior Ethmoid artery
Sphenopalatine artery
Greater Palatine artery
Superior Labial artery
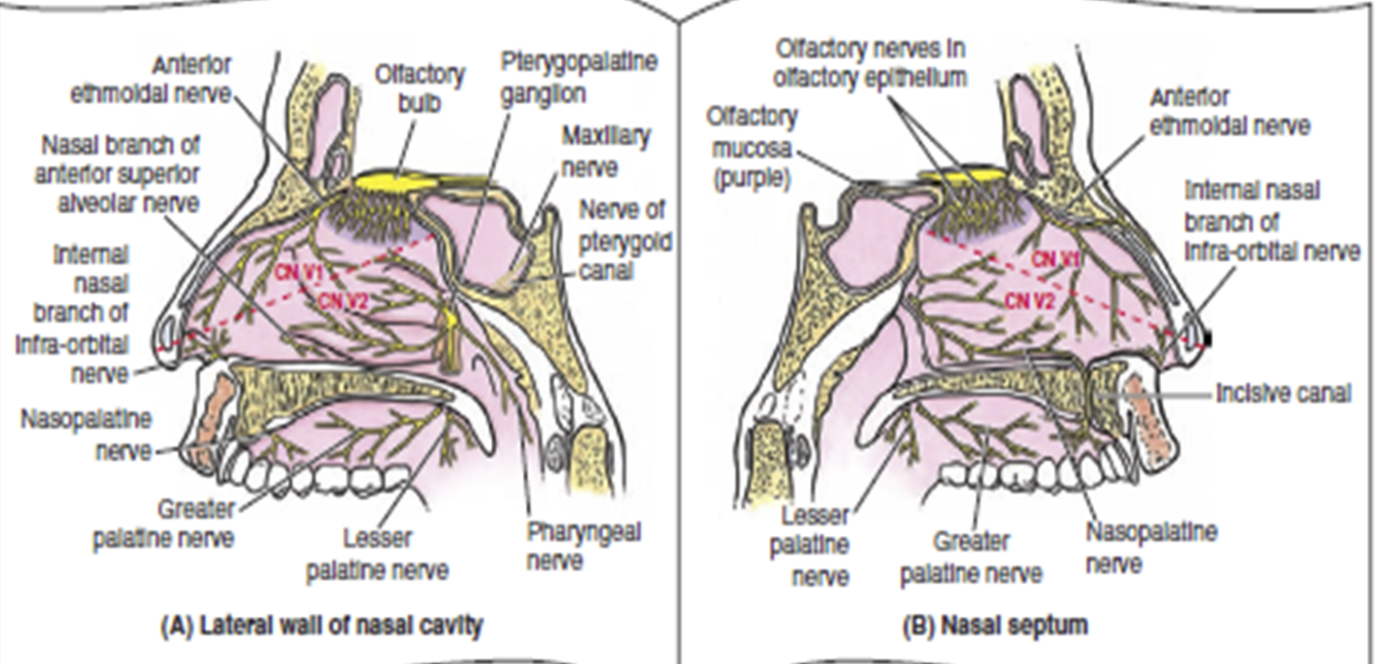
The area above the line is innervated by (?) nerve?
The area below the line is innervated by (?) nerve?
Ophthalmic Nerve V1
Maxillary nerve V2
The external nose is mainly innervated by (?) nerve except (??)
Ophthalmic Nerve
Ala of nose → Maxillary nerve
The forehead area is mainly innervated by which nerve?
Ophthalmic Nerve
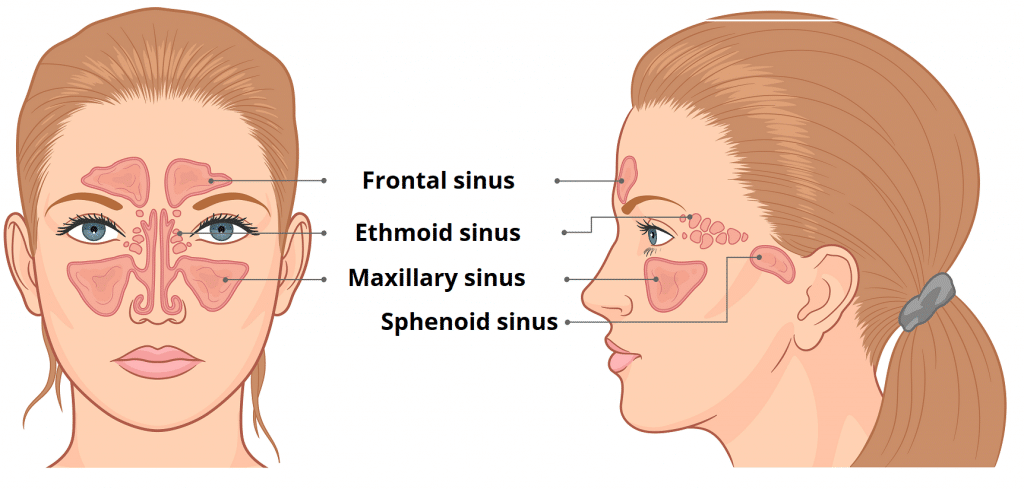
Which sinus is most frequently Infected???
Maxillary Sinus
**The paranasal sinuses are lined by what type of Epithelium?
Respiratory Epithelium
Pseudostratifed ciliated columnar epithelium with Goblet cells
Functions of Paranasal Sinuses?
Resonating chambers for Voice
Reduce weight of skull
Humidify air
Support immune defense of nasal cavity
Which PNS is
rudimentary at birth but enlarges at 8 y/o
the Largest
pyrimidal shaped
Most frequently infected sinus in human body
maxillary sinus
The maxillary sinnus drains into the middle meatus via (???)
SEMILUNAR HIATUS
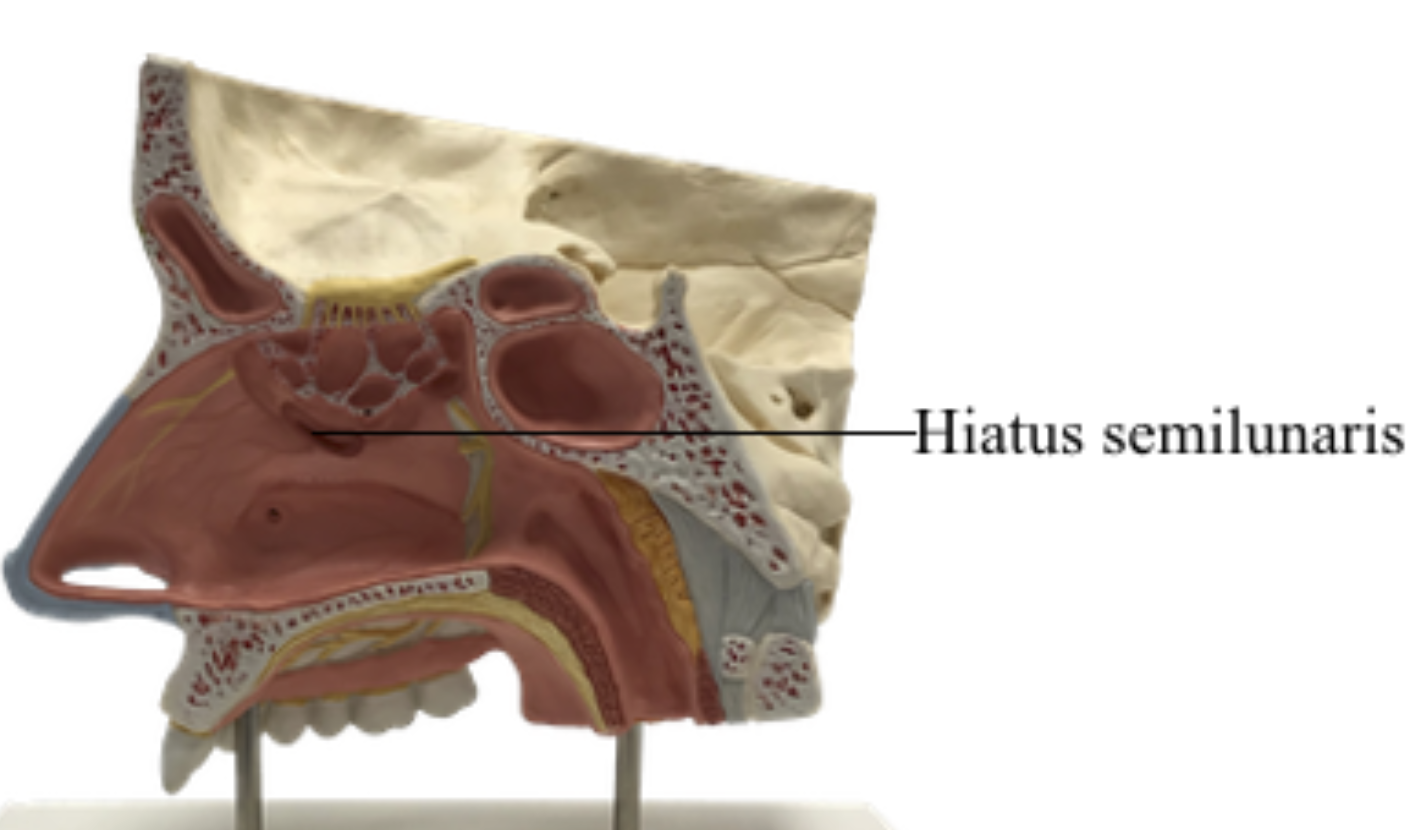
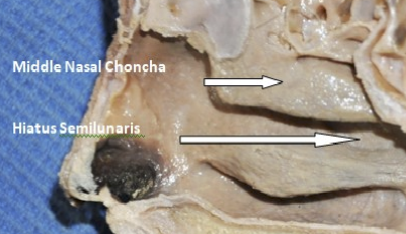
T or F? The Frontal sinus can only be detected from Age 7 onwards.
true
T or F? The Ethmoidal sinus can be recognized in CT scans before Age 2 BUT NOT IN RADIOGRAPH.
true!
when an infection blocks drainage and causes erosion of the middle wall of the orbit, the infection can spread to which specific structure to cause Optic Neuritis?
A.
The posterior ethmoidal sinus
B.
The orbital floor
C.
The dural nerve sheath that surrounds the optic nerve
D.
The Ophthalmic artery
The dural nerve sheath that surrounds the optic nerve
*Which two vital structures are mentioned as passing through the optic canal?
A.
Oculomotor nerve and Ophthalmic vein
B.
Maxillary nerve and Lacrimal artery
C.
Optic nerve and Ophthalmic artery
D.
Trochlear nerve and Superior orbital artery
Optic nerve and Ophthalmic artery
What are the 3 main parts of the Ear?
External
middle tympanic
inner labyrinth

Another name of the External Ear?
Auricle or Pinna
What is the hollow depression in the middle of the Auricle that continues to become the external auditory meatus?
Concha
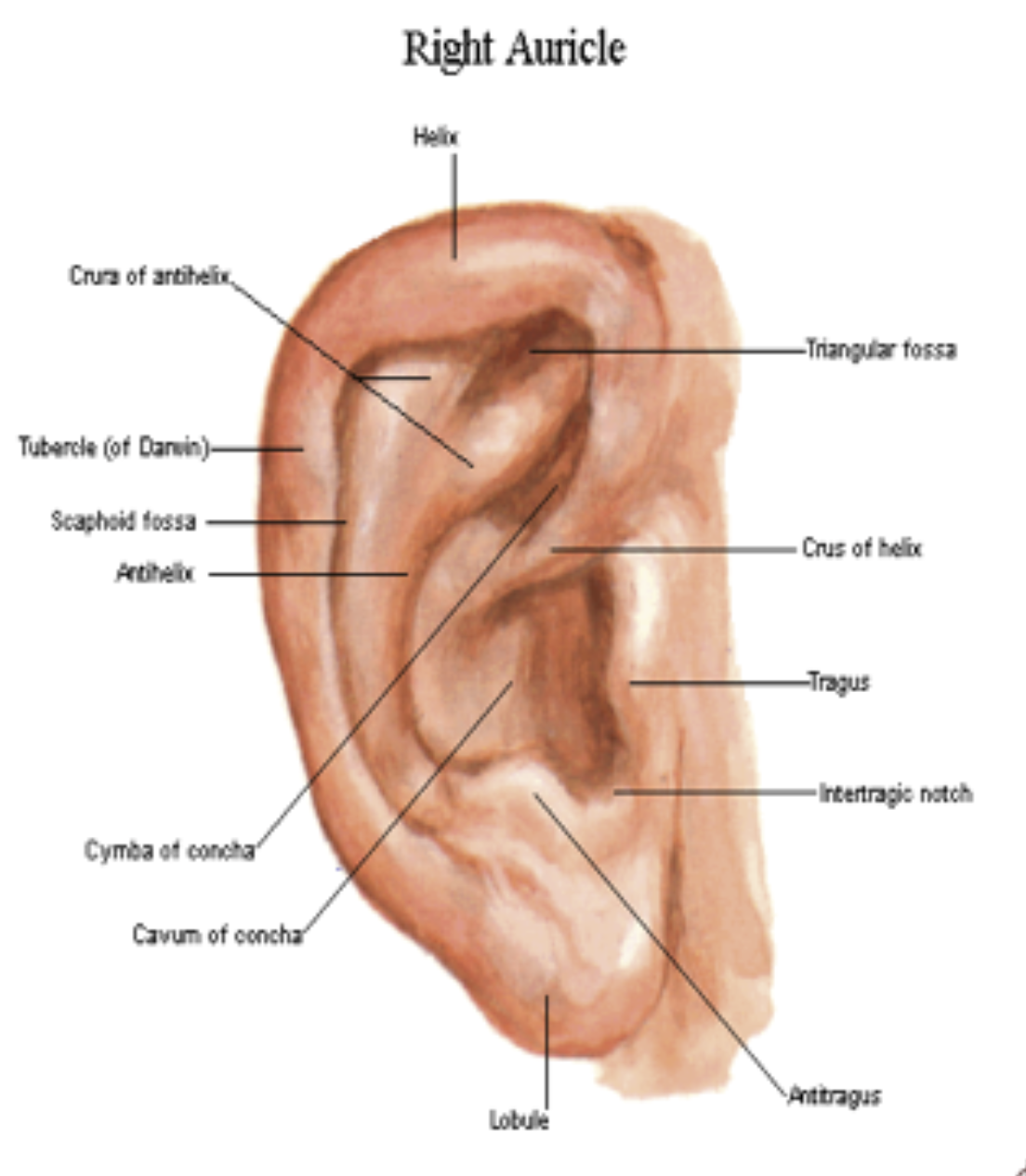
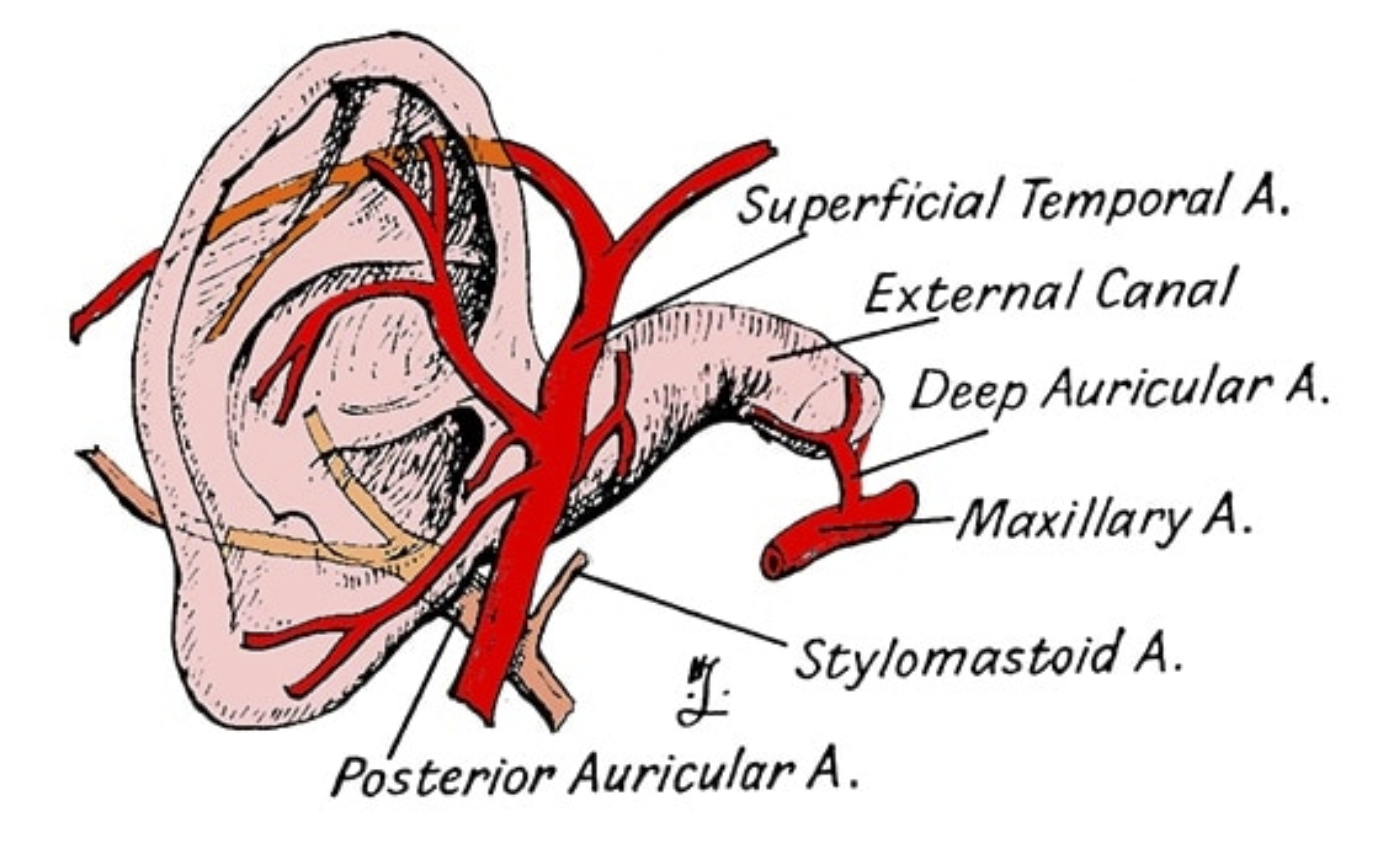
What are the 2 main Arterial supply of the Ear?
Posterior Auricular artery
Superficial temporal artery
*Both from External Carotid Artery (ECA)
What are the 2 main Venous drainage of the Ear?
Posterior Auricular Vein
Superficial temporal Vein
Which specific area of the auricle is drained by the Superficial parotid lymph nodes?
A.
The entire medial surface of the auricle
B.
Superior half, lateral surface
C.
Inferior half, both medial and lateral surfaces
D.
Superior half, medial surface
Superior half, lateral surface
According to the clinical correlation, an abscess in the lobule of the auricle would initially cause enlargement and pain in which group of lymph nodes?
A.
Deep cervical group of lymph nodes
B.
Submandibular lymph nodes
C.
Superficial cervical group of lymph nodes
D.
Mastoid/retroauricular lymph nodes
Superficial cervical group of lymph nodes
A patient has an infected boil on the medial surface of the auricle, near the superior half. Which lymph node group is expected to be involved?
A.
Mastoid/retroauricular and deep cervical lymph nodes
B.
Superficial cervical lymph nodes
C.
Superficial parotid lymph nodes
D.
Jugulo-omohyoid lymph nodes
Mastoid/retroauricular and deep cervical lymph nodes
Which nerve, originating from the cervical plexus, provides sensation to the large majority of the inferior and posterior surfaces of the auricle?
A.
Lesser occipital nerve
B.
Auriculotemporal nerve
C.
Great auricular nerve
D.
Auricular branch of the vagus nerve
Great auricular nerve
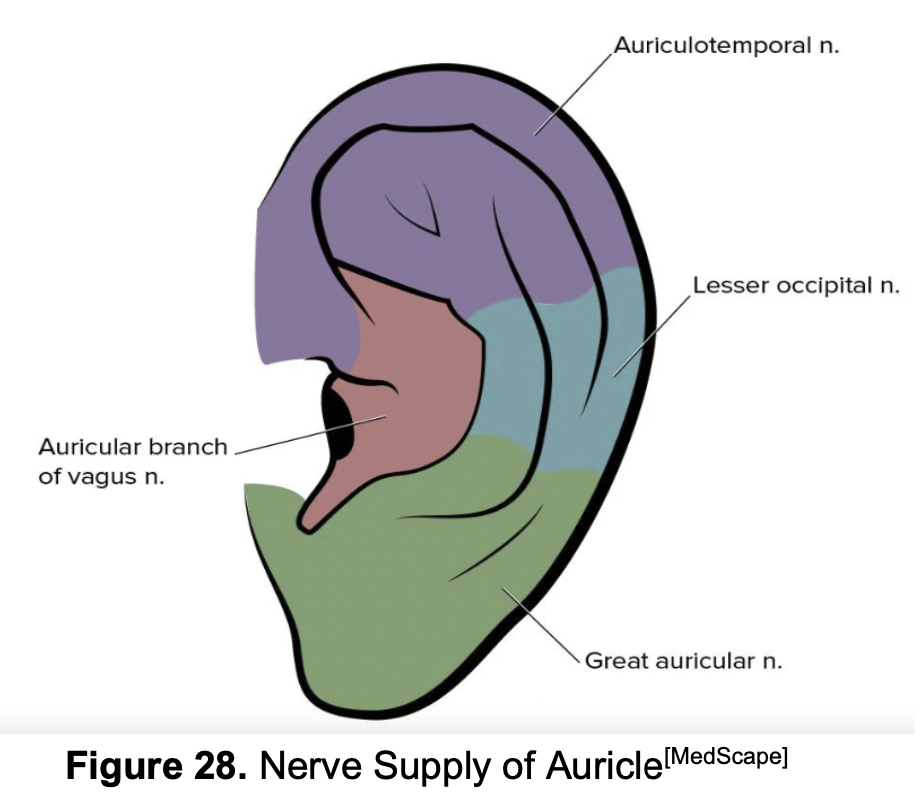
The auriculotemporal nerve is a branch of which major cranial nerve?
A.
Facial nerve (CN VII)
B.
Trigeminal nerve (CN V), specifically the mandibular branch
C.
Vagus nerve (CN X)
D.
Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
Trigeminal nerve (CN V), specifically the mandibular branch
If a patient reports numbness in the helix (superior rim) and crus of the helix (the ridge leading into the concha), which nerve is most likely affected?
A.
Great auricular nerve
B.
Auricular branch of the vagus nerve
C.
Lesser occipital nerve
D.
Auriculotemporal nerve
Auricular branch of the vagus nerve
(NOTE!) The cough reflex upon ear cleaning is a clinical phenomenon specifically associated with which part of the nervous system supplying the ear?
A.
Motor innervation of the facial nerve (CN VII)
B.
Sympathetic innervation via the cervical plexus
C.
Sensory innervation of the trigeminal nerve (V3)
D.
Parasympathetic innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X)
Parasympathetic innervation from the vagus nerve (CN X)
The external auditory canal is approximately (? to ?) cm in length.
2-3 cm in length
The outer 1/3 of the External auditory canal is also known as?
Cartilaginous portion
Osseous portion
outer 1/3 of the External auditory canal = Cartilaginous
The inner 2/3 of the External auditory canal is also known as?
Cartilaginous portion
Osseous portion
inner 2/3 of the External auditory canal = Osseous portion
What type of glands can be found in the Cartilaginous portion of the External Auditory Canal?
Ceruminous glands → Cerumen or Earwax
Can you find Ceruminous glands in the Inner Osseous portion of the External Auditory Canal?
No!
What are the 3 main arterial supplies of the EAC?
Superficial Temporal Artery (terminal branch of ECA)
Posterior Auricular Artery
Maxillary Artery → Deep Auricular branch
In INFANTS, the EUC can be straightened by pulling the Pinna (?) and (?) or (?)
Infants
Down and back
Postero-inferiorly
In Adults, the EUC can be straightened by pulling the Pinna (?) and (?) or (?)
Adults
Up and Back
Postero-superiorly
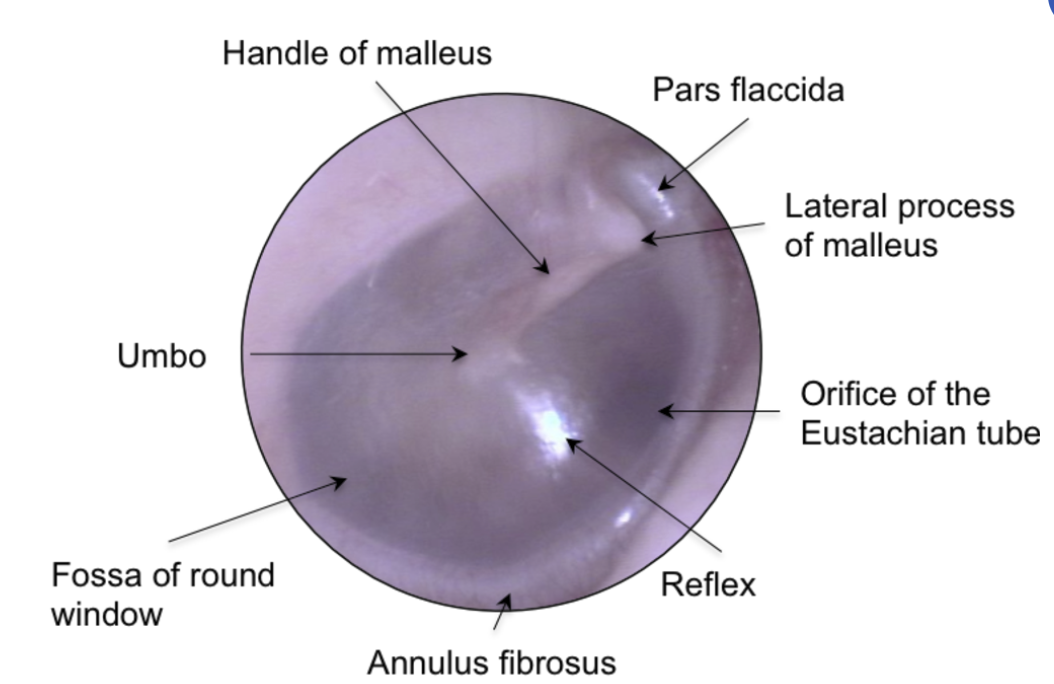
The Tympanic membrane is supported by a fibrocartilaginous ring called?
Annulus Fibrosus Tympanicus
Which part of the tympanic membrane has
all complete 3 layers
Modified thin skin
Mucous membrane
intermediate fibrous stratum (Middle fibrous layer)
is supported by the Annulus Fibrosus tympanicus
Pars Tensa
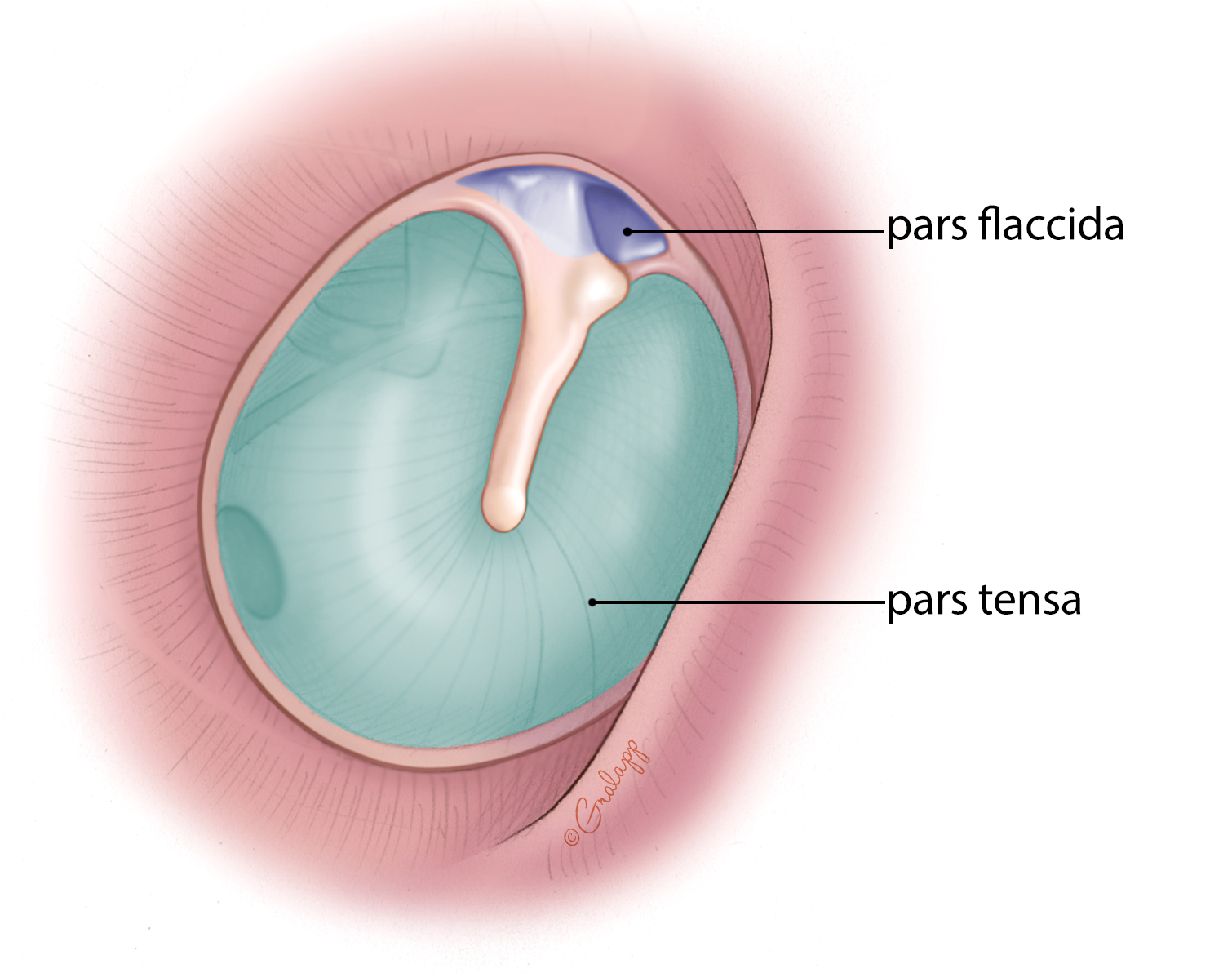
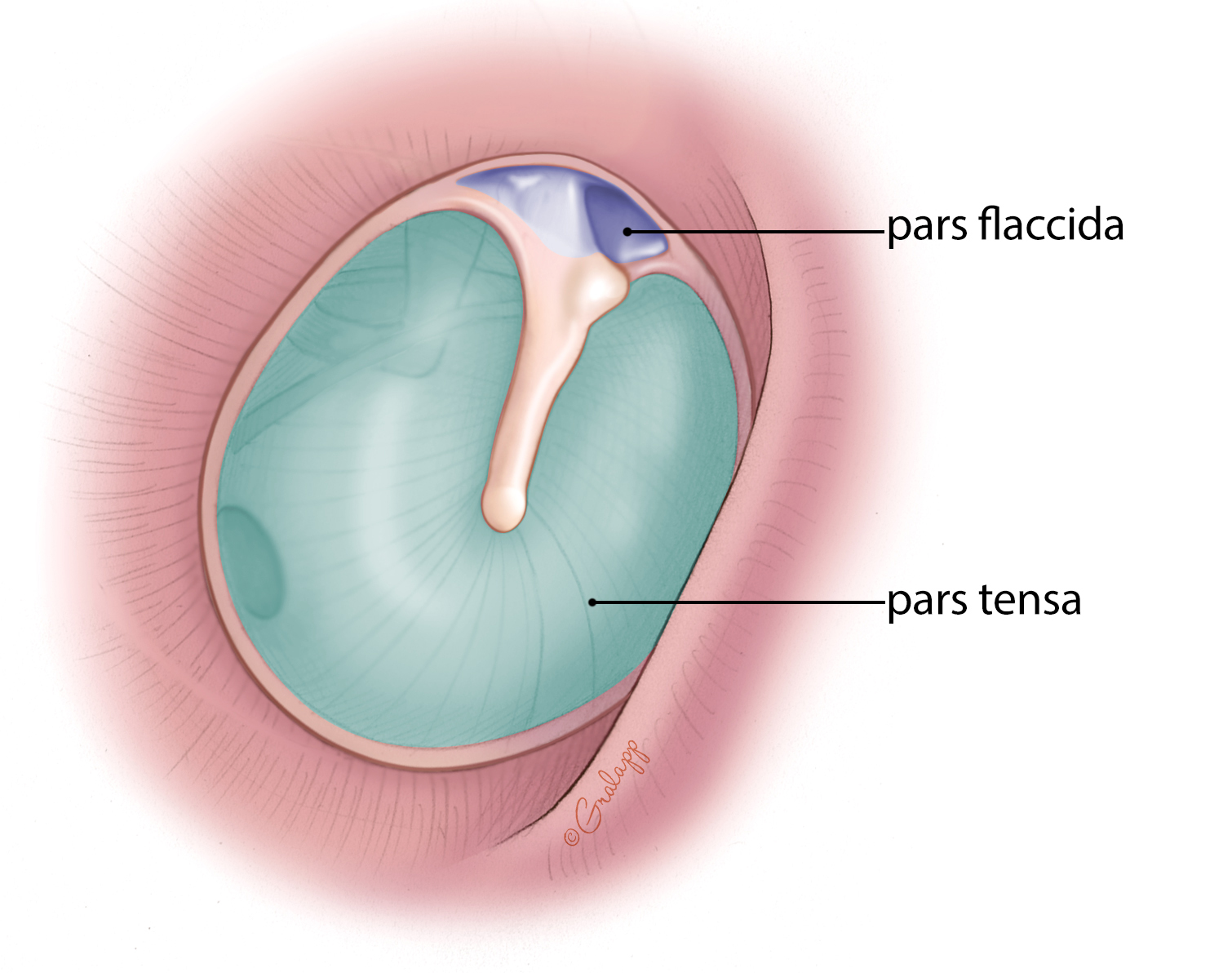
The Pars Flaccida is devoid of which layer?
Middle Fibrous Layer
is the Pars flaccida supported by the annulus fibrous tympanicus?
NO
The cone of light is located in which quadrant?
Antero-inferior quadrant
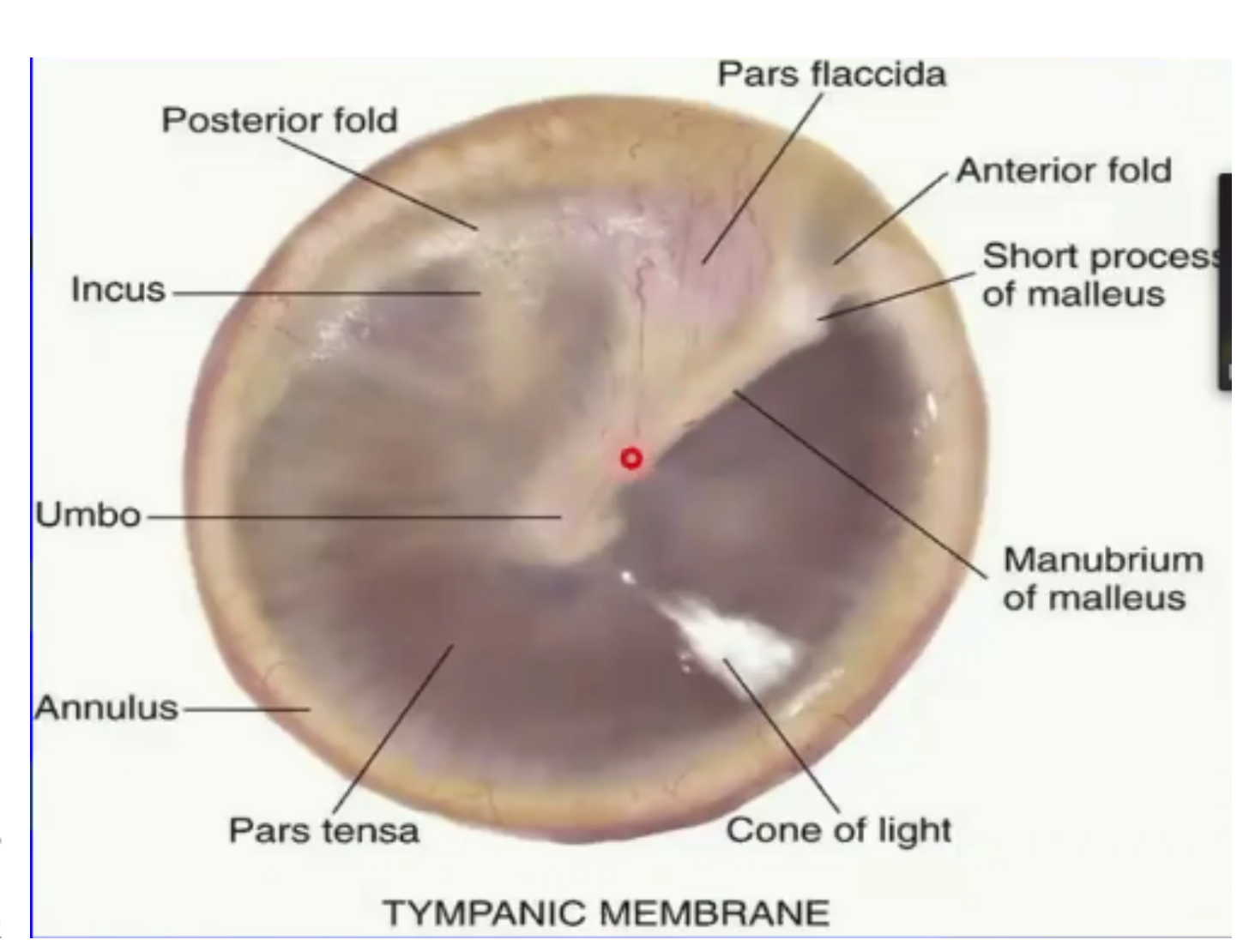
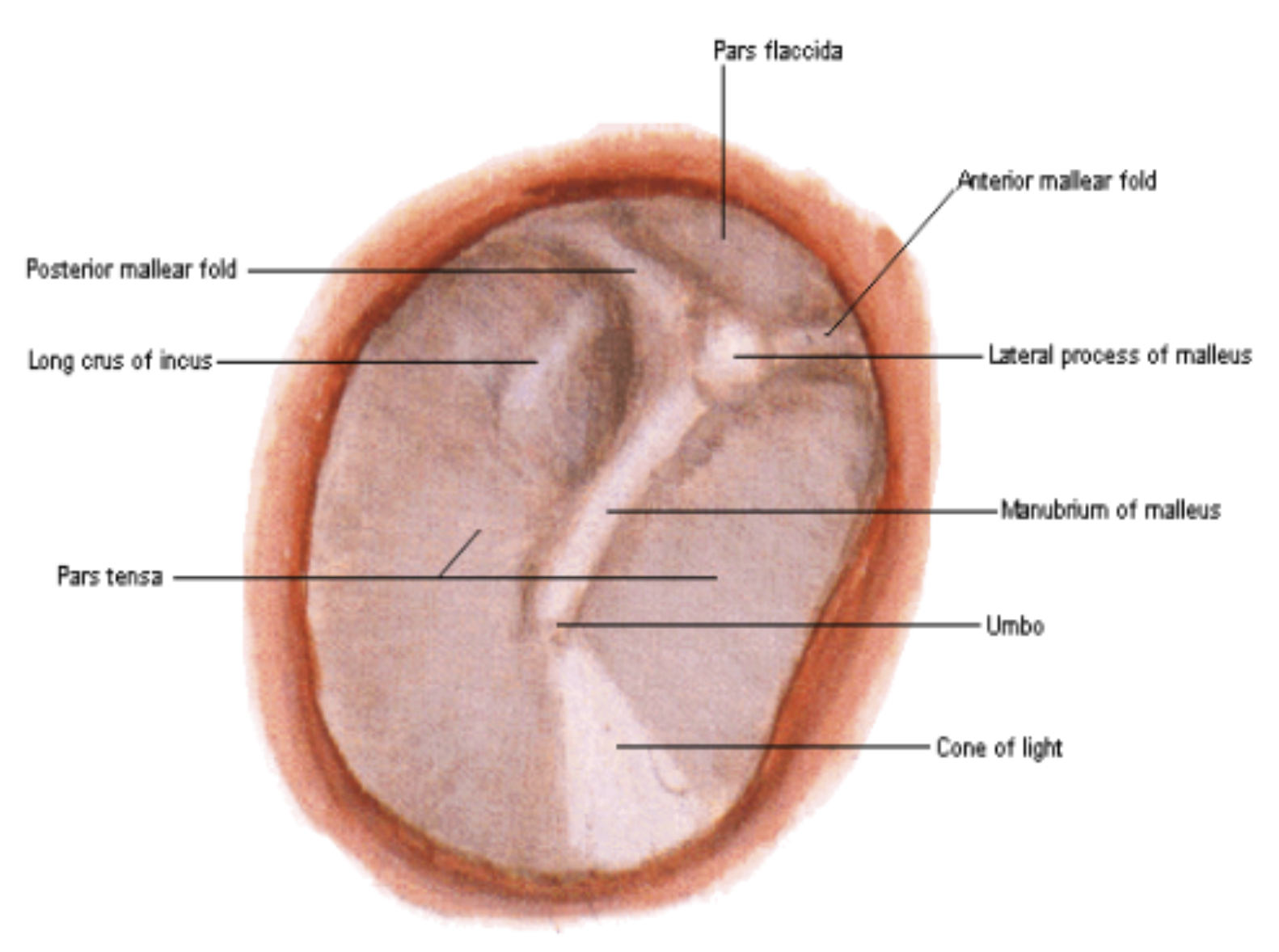
umbo = most depressed area at the center
anterior and posterior malleolar folds = separates pars flaccida and pars tensa
YOU CANNOT INCISE in which quadrant to avoid damaging the cone of light.
Antero inferior
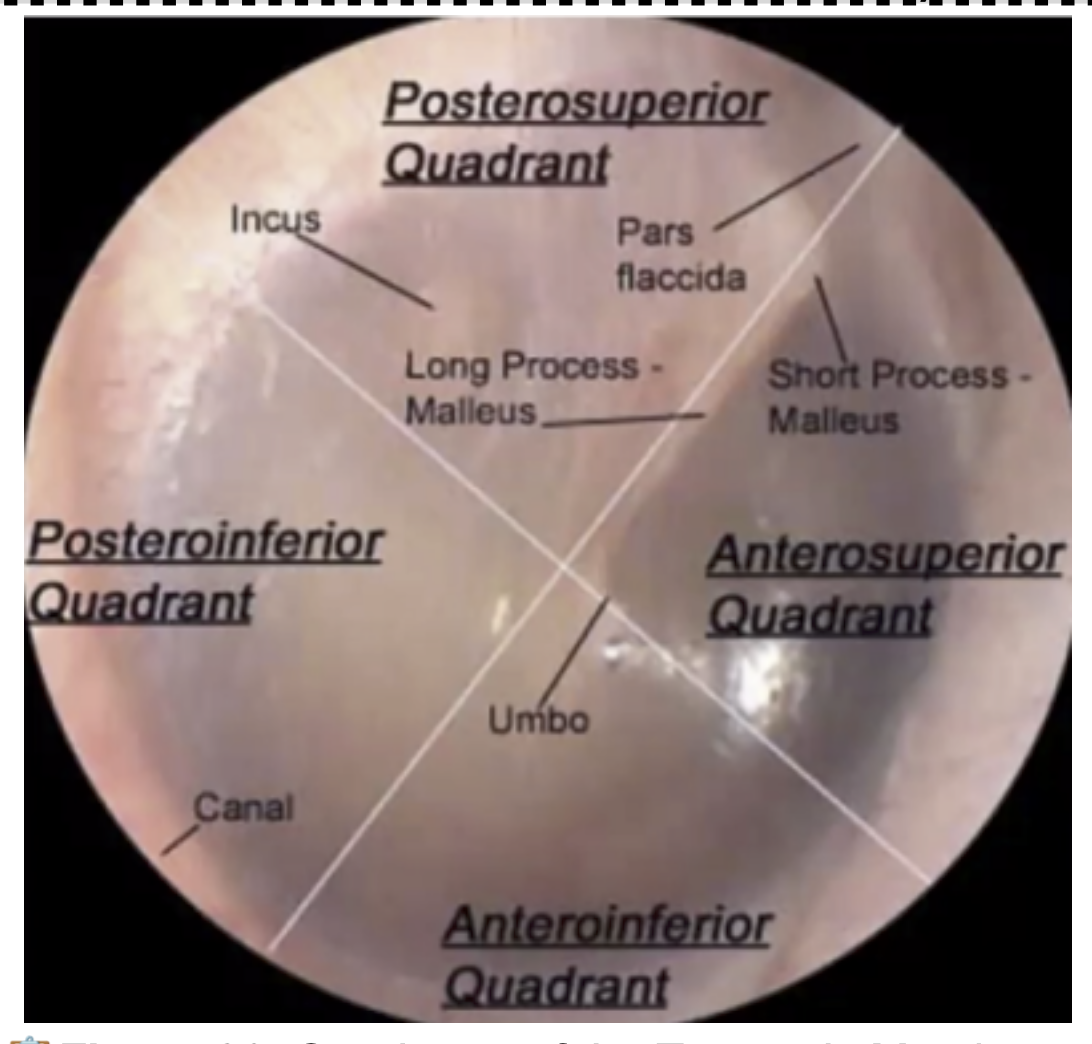
You CANNOT incise at the (?) or (?) quadrant to avoid damaging the Ossicles and Chorda Tympani.
Posterior Superior
Anterior Superior
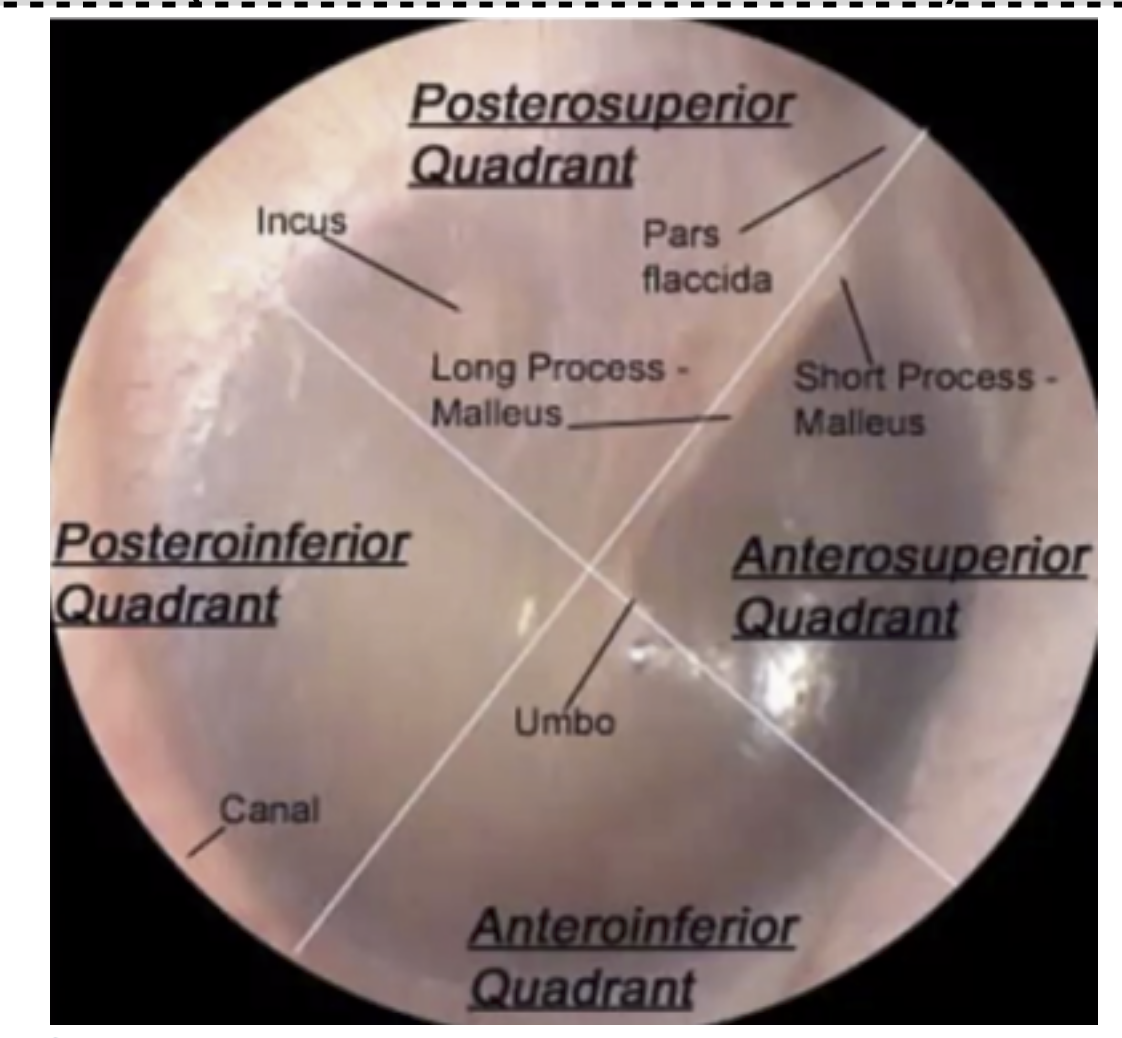
Where is the safest area to drain in the Tympanic Cavity?
Postero- INFERIOR quadrant
remember PIQ

Which is the space directly behind the tympanic membrane
Mesotympanum
Epitympanum

Mesotympanum
What is the space that house portions of the Ossicles ( Malleus + Incus)
Mesotympanum
Epitympanum
Epitympanum
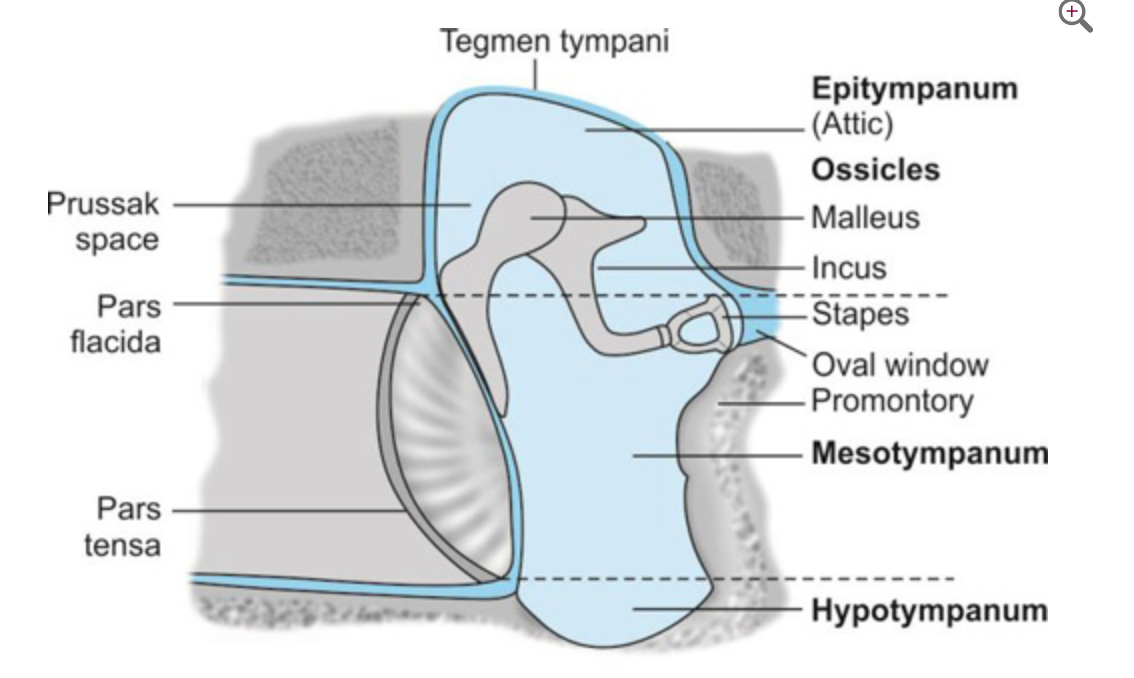
Which structure closes the Fenestra cochleae (round window) on the Labyrinthine (Medial) wall of the middle ear cavity?
Secondary tympanic membrane
In the event of an untreated middle ear infection (otitis media), erosion of the Tegmen tympani (roof) poses the immediate risk of spreading infection to the:
A.
Internal jugular vein
B.
Dura mater that covers the temporal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere.
C.
Cochlea and semicircular canals.
D.
Internal carotid artery
Dura mater that covers the temporal lobe of the cerebral hemisphere.
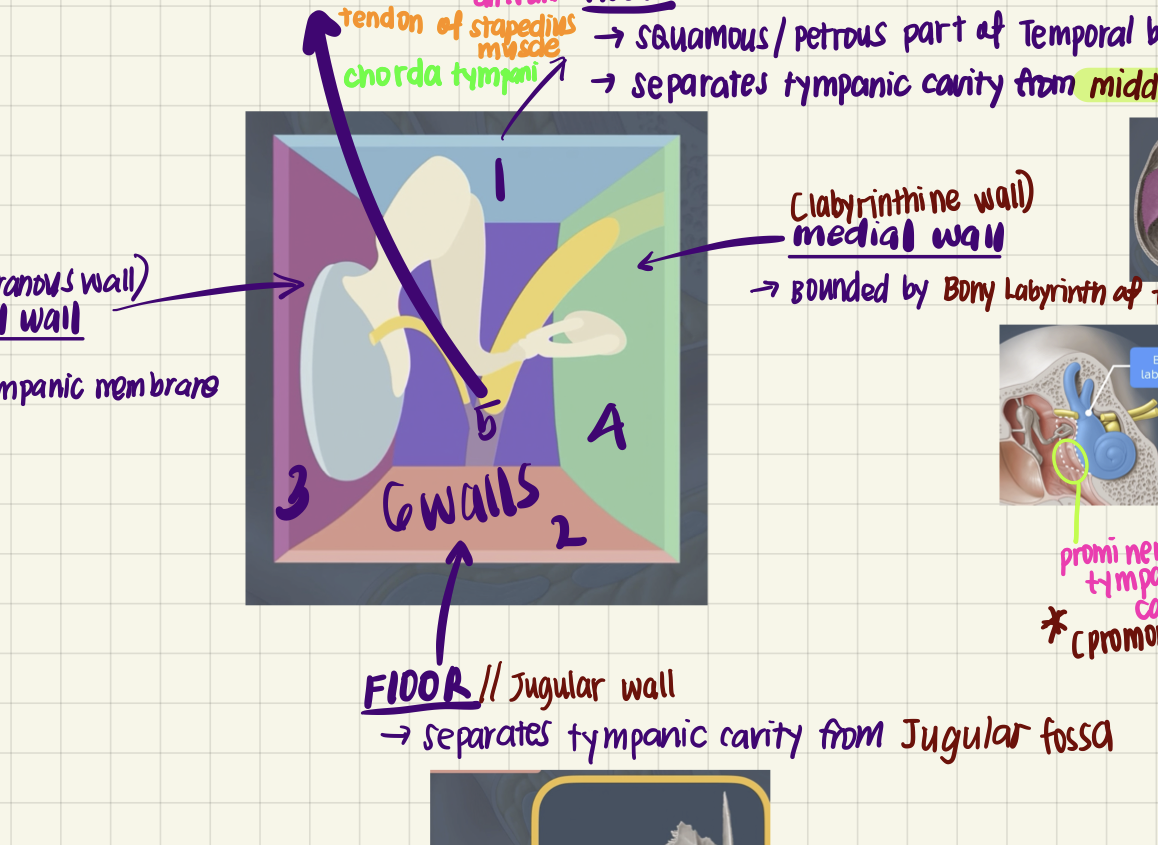
The Jugular Wall (Floor) of the middle ear cavity is formed by the fundus tympani and separates the middle ear from which major structure?
A.
Temporal lobe
B.
Superior bulb of the internal jugular vein
C.
Facial nerve canal
D.
Internal carotid artery
Superior bulb of the internal jugular vein
Infection that spreads from the middle ear to the mastoid antrum can cause which clinical condition?
A.
Meningitis
B.
Mastoiditis
C.
Vertigo
D.
Labyrinthitis
Mastoiditis
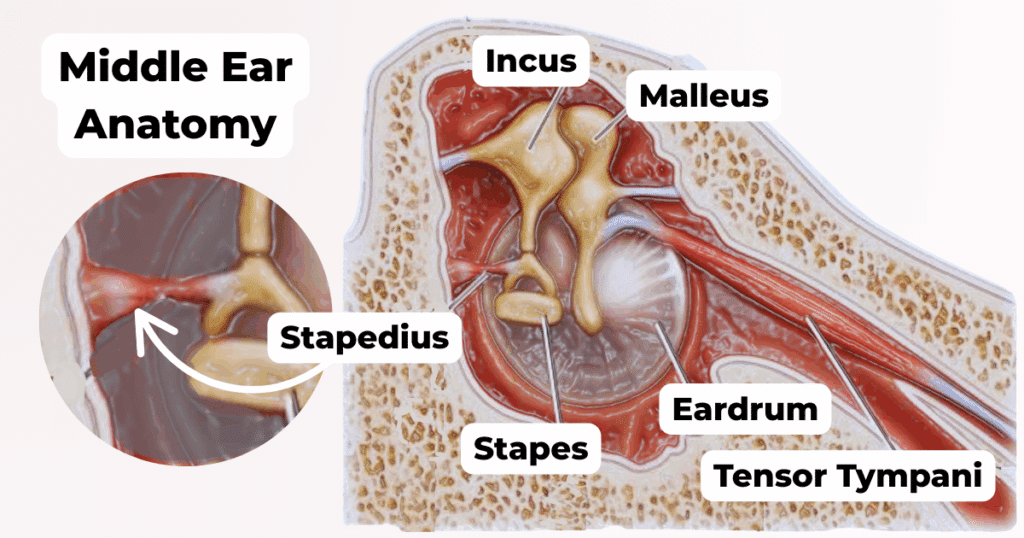
The Mastoid (Posterior) Wall of the middle ear cavity houses the stapedius muscle in a structure known as the:
A.
Pyramid
B.
Prominence
C.
Aditus ad antrum
D.
Fossa incudis
Pyramid

The Carotid (Anterior) Wall is characterized by two openings above it. One is for the Auditory Tube, and the other is for the:
A.
Fenestra vestibuli
B.
Canal for the facial nerve
C.
Canal (or Semicanal) for the tensor tympani muscle
D.
Aditus ad antrum
Canal (or Semicanal) for the tensor tympani muscle
Which of the following describes the most lateral portion of the Auditory Tube/Eustachian Tube?
A.
Vascular
B.
Membranous
C.
Osseous (bony)
Osseous (bony)
A patient experiences vertigo and dizziness following an upper respiratory tract infection. Based on the notes, this is most likely a complication known as:
Labyrinthitis, inflammation of the inner ear, affects the vestibular system and causes vertigo/dizziness.
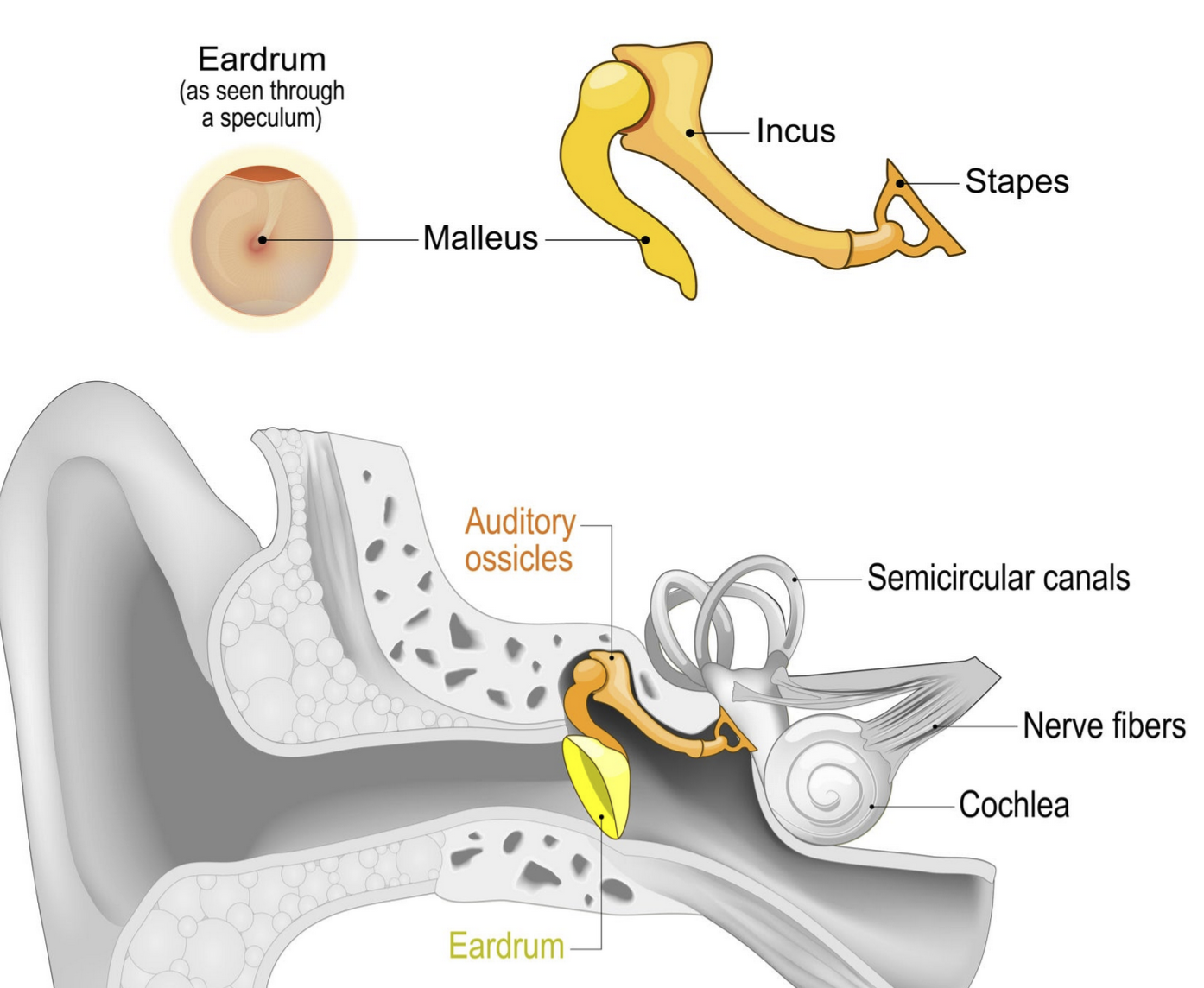
What is the Small muscle that dampens the vibrations from the malleus called?
Tensor Tympani
What nerve innervates the tensor Tympani?
Trigeminal Nerve → mandibular branch (V3)
The Chorda Tympani is a branch of which nerve?
facial nerve
The incudomalleolar joint is what type of Joint?
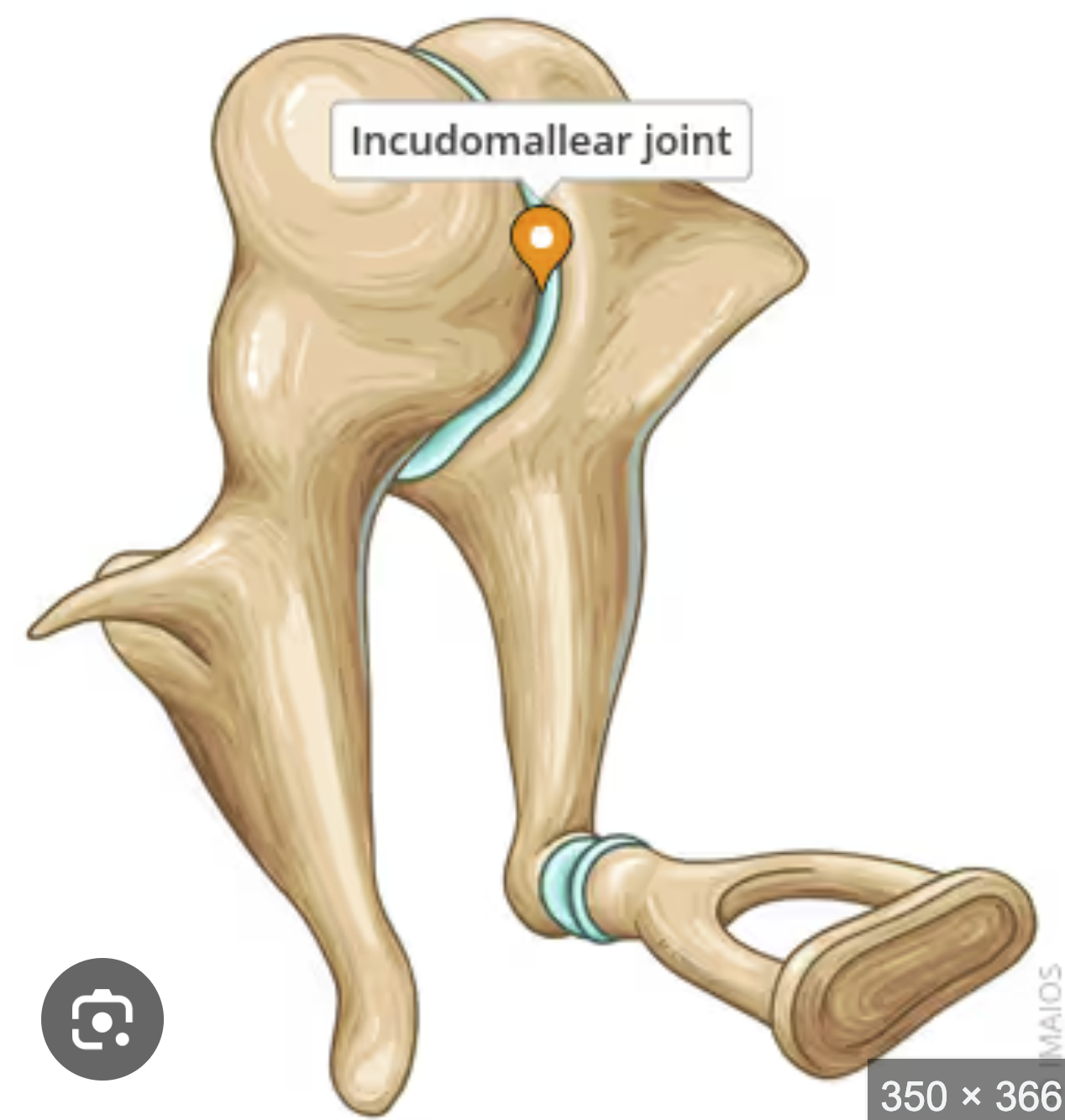
Saddle Joint (Synovial Joint)
What type of joint is the Incudostapedial joint?
Ball and Socket Joint (Synovial Joint)
Nerve supply of the Middle Ear?
Typanic Plexus
The Osseous or Bony Labyrinth contains what fluid?
Periplymph
The Membranous labyrinth contains what type of fluid?
Endolymph
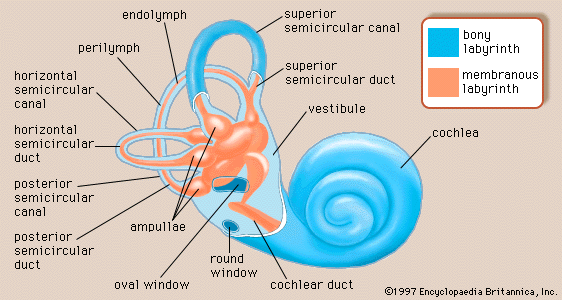
The Bony labyrinth has what 3 parts
Vestibule
Semicircular canals
Cochlea
**T or F? The semicircular DUCTS are part of the Bony labyrinth.
False!
The membranous labyrinth is suspended within
endolymph
perilymph
Perilymph!
*remember that membranous labyrith contains endolymph inside
What detects horizontal acceleration?
Utricle
What detects vertical motion?
Saccule
What detects angular motion (rotational)?
Crista ampulllaris
What detects linear acceleration and tilting of the head?
Maculae
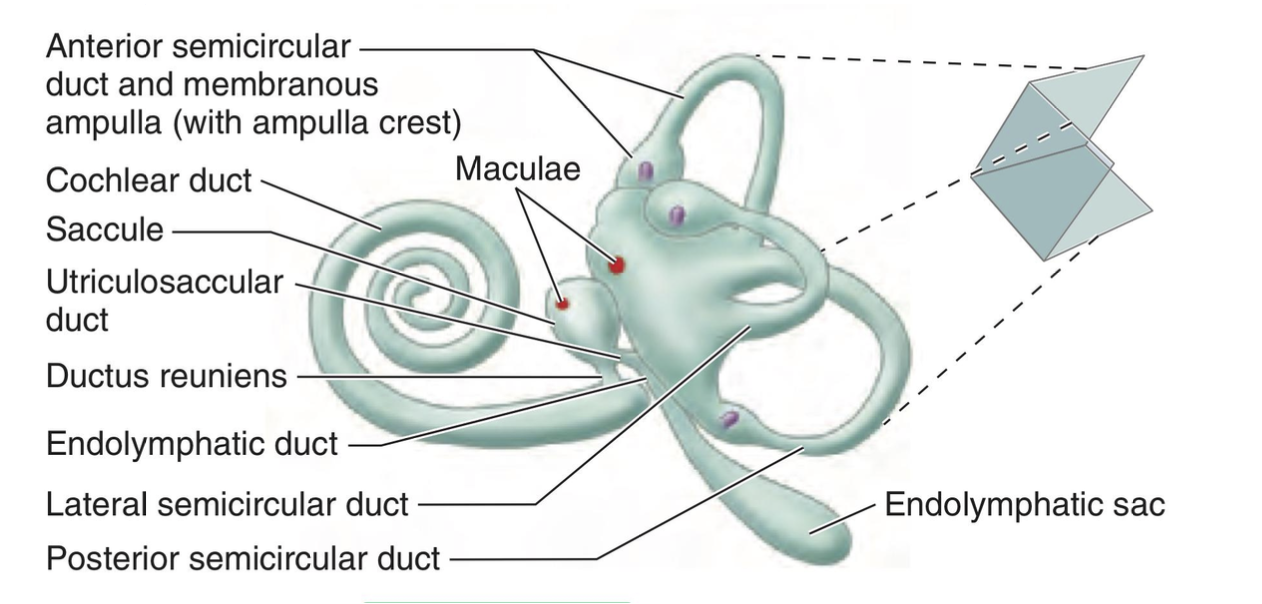
(?) is concerned with hearing …
hint… the snail in ur ear is whispering something to u
Cochlear labyrinth