ASCI 220 Midterm 2
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
What do we measure when we are using a new diet
Blood work, Body Mass, Food Intake(input), Digestion, Excretions(output), Length of time it take food to pass through GI tract
Digesta Passage: marker, transit time and mean retention time
Marker: not normally secreted, digested, or absorbed by the gut, not toxic
Transit Time(TT1): Time from marker administrations to first appearance in feces
Mean retention time (Rgit): average time the markers takes to be excreted after administration
Digestibility
Proportion of nutrients in a feed or diet that are observed from the GI tract, difference between the amount consumed and excreted.
Apparent digestibility (aDig), % calculation and ideal Digestibility (in vivo/in animal)
Intake(kg DM/day) - fecal or ileal outputs (kg DM/day) /intake x 100 = % aDig

Partial Tract Digestibility
Proportion of nutrients in feed or diet that are absorbed from the GI tract start at SI and end at anus

In situ Digestibility
Cannulated cow has a bag in rumen and measure the in situ digestibility in specific location (rumen)

In vitro Digestibility: process, species tested on
Study digestion in the lab. Tiller and Terry tested ruminant and keep the rumen fluid in body temp of cow, and shake it. Bodies and Fernandez’s created a 3 stage closed batch (stomach, SI, Hindgut) to emulated swine digestion. Lockhart tested it on horses. Animal donated fecal matter to get microbes. Easier to manage 10 tubes in a shaking water bath than 10 horses.

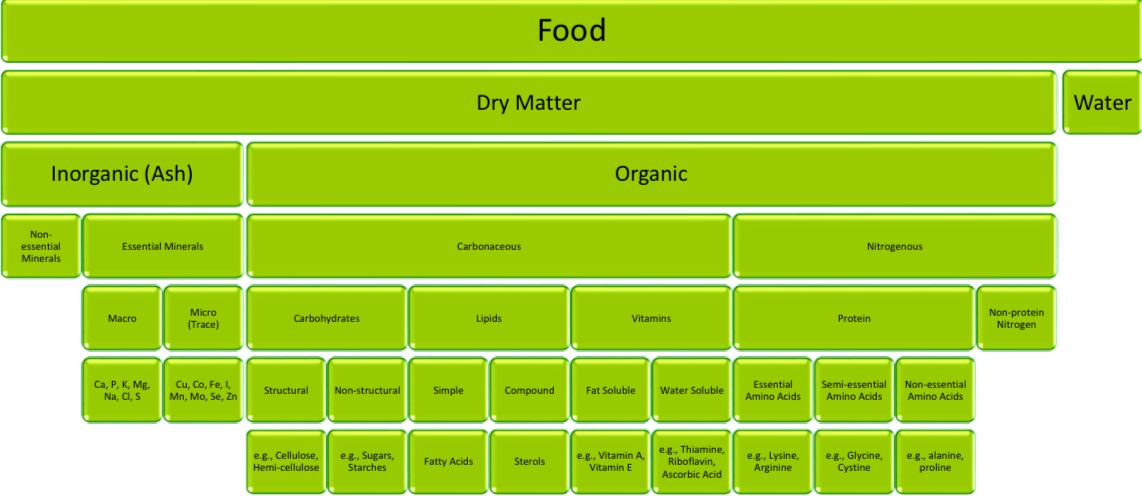
Nutrient Compsition of Food
Dry matter and water
Inorganic
Non vs Essential Minerals (Macro vs Micro)
Macro: Ca, P, K, Mg, Na, Cl, S
Micro: Cu, Co, Fe, I, Mn, Mo, Se, Zn
Organic
Carbonaceous
Carbs:
structural (Cellulose, Hemi-cellulose)
Non structural (Sugars, Starches)
Lipids
Simple (fatty acid) vs compound (sterols)
Vitamins
Fat soluble (A,E)
Water soluble (Thiamine, Riboflavin, Ascorbic Acid)
Nitrogenous
Protein vs non protein
Essential (lysine, arginine) semi (glycine, cystine) and non essential (alanine, proline) amino acids
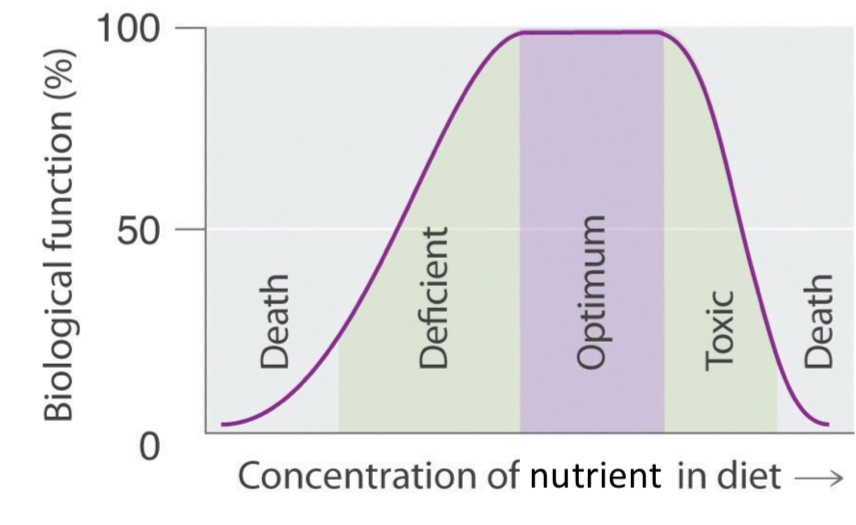
Biological Dose Response Graph (x/y axis) and areas
Biological function (%) y over Concentration of nutrient in diet, areas: death → deficient → optimum → toxic → death
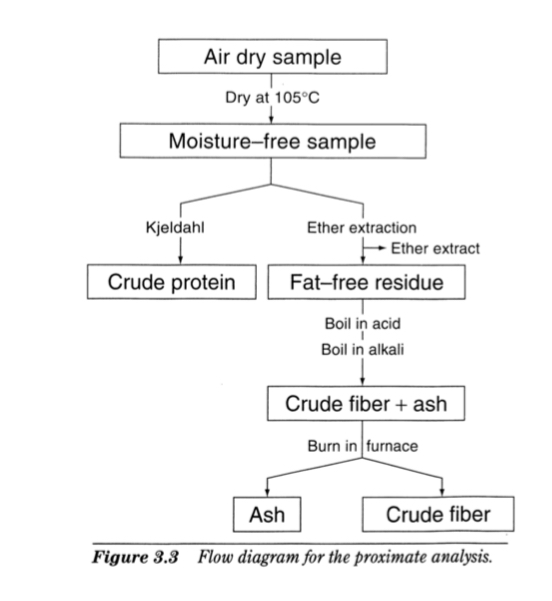
Proximate Analysis Process
Air dry sample -dry at 105C for 24 hours→ moisture free sample → crude protein → fat free residue → crude fiber + ash
Measure to Manage definition
Use data to confirm beliefs about management practices and strategies.
Water functions, percentage make up, if animals does have water?
Component of metabolism, solvent, transport medium, diluent, hydrolysis and oxidation. Regulation of body temp, lubrication, cushion, structural. 60% of animal body weight, if animals doesn’t have water it won’t eat
What parts of the body have more water? How do we find out how much of the body is water if they are living?
Blood, kidney, heart, lungs, spleen, brain, intestine, skin, muscle liver. Bioelectrical impedenle analysis: electrodes all of body send small electrical signals that detect resistance and electricity
Water Sources
Preformed water: in the food itself
Free water: water not in food, in a body of water (bowl)
Metabolic: water generated through chemical reactions in body
Metabolic Water: definition, breakdown of what nutrient produces the most water?
A byproduct of metabolizing energy-yielding nutrients from foods into carbon dioxide and energy, does not include water in foodstuff. Breakdown lipids produces more water per gram than carbs and proteins. Ex; hibernating bears build up fat as water storage.
Losses of water
Urine, fecal, perspiration, insensible (lactation) parturition
Water requirement factors
Dictated by need to balance intake and loss, influenced by: food composition, intake , metabolism, activity/production, environment. Ex: more sodium intake needs to drink more water and pass through urine
Relationship between dry matter intake (kg) and water intake (L)?
Very consistent across species, 2-3 times their dry matter intake
Water Dehydration vs Intoxication, hyponatremia?
Dehydration: water leaves in trace duller fluid into extracellular fluid via osmosis
Intoxication: water moves to intercellular fluid from extracellular fluid via osmosis and dilutes ions in intracellular fluid that are needed for processes such as sodium potassium pump, cells swell
Hyponatremia: low sodium levels in blood, cells swell
Three classes of nutrients that provide energy
Carbohydrates, Lipids and Protein
Short term vs long term sources of energy. Where does the energy come from?
Short: glycogen, Long term: adipose tissue (fat). The energy is in the bonds
How many more energy per gram in lipids compared to carbs and proteins
Lipids have 2.25 times more energy per gram than carbs and proteins
What do we use to measure how much energy in food in US? EU? Definition?
Calorie: the amount of energy (heat) required to raise 1 gram of water from 14.5 to 15.5 C
Joule: A unit of work or energy equal to the work done by force of one newton acting though a distance of one meter
Calories vs calories
Calories (kilocalorie) is 1,000 calories