Cheat Sheet 9: Biotechnology and Microscopy
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
Cell Theory
All living organisms consist of one or more cells.
RNA World Hypothesis
Self-replicating RNA molecules were life's precursors.
Central Dogma of Biology
Genetic information flows from DNA to RNA to protein.
Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Amplifies DNA sample through denaturation, annealing, elongation.
Denaturation
High heat separates double-stranded DNA during PCR.
Annealing
Cooling allows primers to attach to DNA strands.
Elongation
Polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands during PCR.
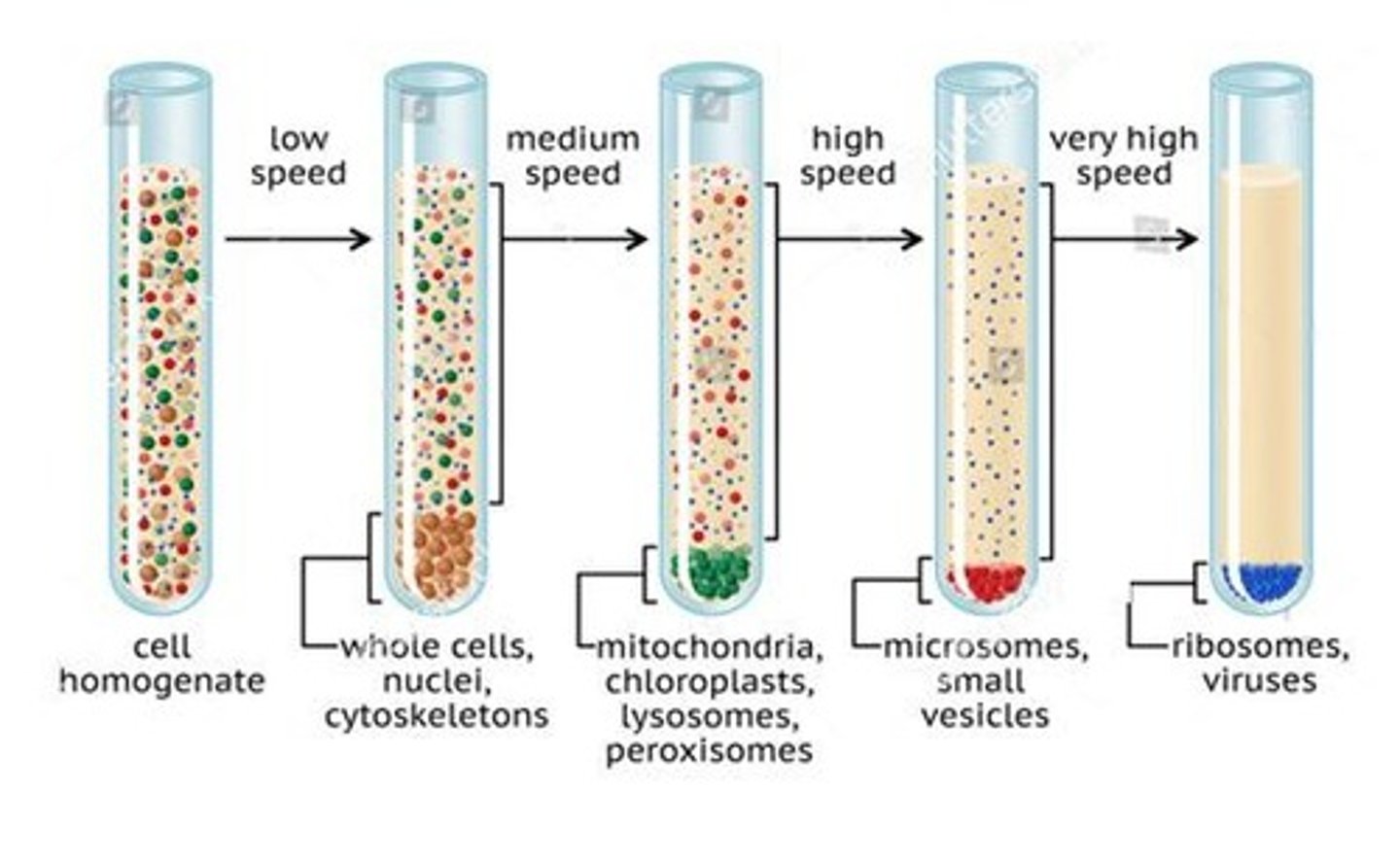
Centrifugation
Separates components of a liquid sample by spinning.
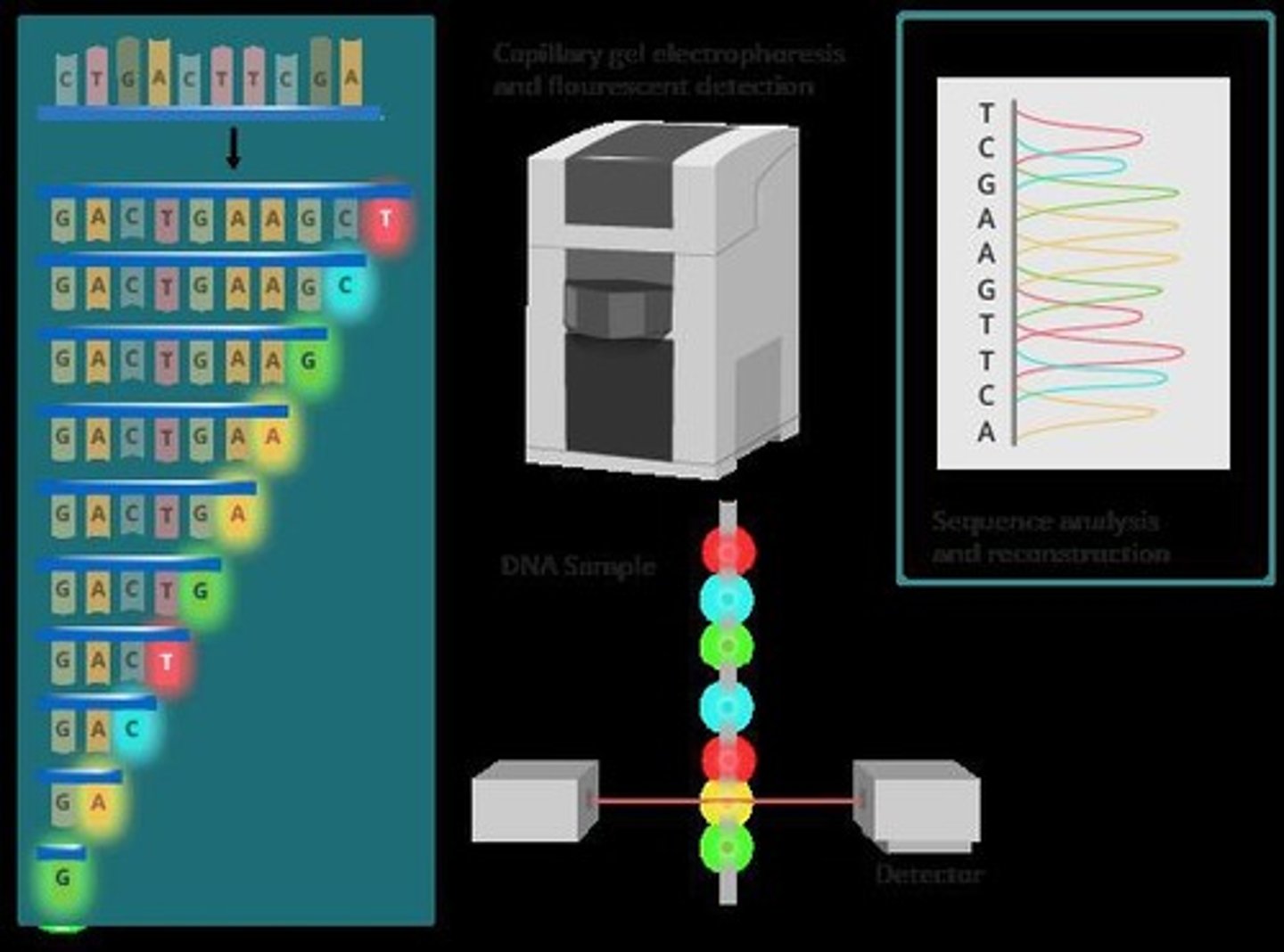
DNA Sequencing
Determines the sequence of base pairs in DNA/RNA.
Blotting Techniques
Identifies specific DNA, RNA, or protein fragments.
Southern Blotting
Technique for detecting specific DNA sequences.
Northern Blotting
Technique for detecting specific RNA sequences.
Western Blotting
Technique for detecting specific protein sequences.
Gel Electrophoresis
Separates DNA by size and charge using a gel.
Microarray Assays
Monitors expression of large gene groups in genomes.
Recombinant DNA
Contains DNA segments from multiple sources.
Restriction Enzymes
Cut DNA at specific sequences to create sticky ends.
DNA Ligase
Connects DNA fragments to form recombinant DNA.
Transformation
Introducing plasmid DNA into bacteria for cloning.
Gene Libraries
Collections of DNA pieces from a genome.
Dideoxy Chain Termination
DNA synthesis requires free OH group on 3' carbon.
Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope
Uses fluorescent tagging to observe specific cell parts.
Light Microscope
Uses visible light to view thin biological samples.
Scanning Electron Microscope
Views surfaces of 3D objects with high resolution.