Marketing Test 1
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
10 most common perceptions people have about marketing
marketing is advertising
marketing is sales
marketing is evil
great products don’t need marketing
marketing lies
marketing is just for large companies
marketing is a waste of money
marketing is a job of the marketing team
only creative people can do marketing
marketing is to create a customer
customer acquisition vs retention
acquisition- acquire a new customer
retention- getting an old customer to buy again
Consumer lifetime value
value of the entire stream of purchases that a customer would make over a lifetime or patronage
Ex: losing a customer could lose you $50,000 in future sales
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
process of building and maintaining profitable customer relationships by delivering superior customer value and satisfaction
Marketing
An activity, set of institutions, and processes for creating, communicating, delivering, and exchanging offerings that have value for customers, clients, partners, and society at large
value has to be something that has functional, experiential, symbolic, or emotional value
want
form that needs take as they shaped by culture and individual personality
things you do not need for survival
need
State of deprivation- physical, social, individual
demand
wants backed by buying power
marketing myopia
focusing on only existing wants and losing sight of underlying customer needs
ex: insurance sells safety, not a piece of paper
Feature, Advantage, Benefit
what a product has
what features do
why customers buy
Ex: Anti-aging lotion features collagen, an advantage is that it reduces wrinkles, and the benefit is more confidence in oneself
Process of marketing planing (know structure and components)
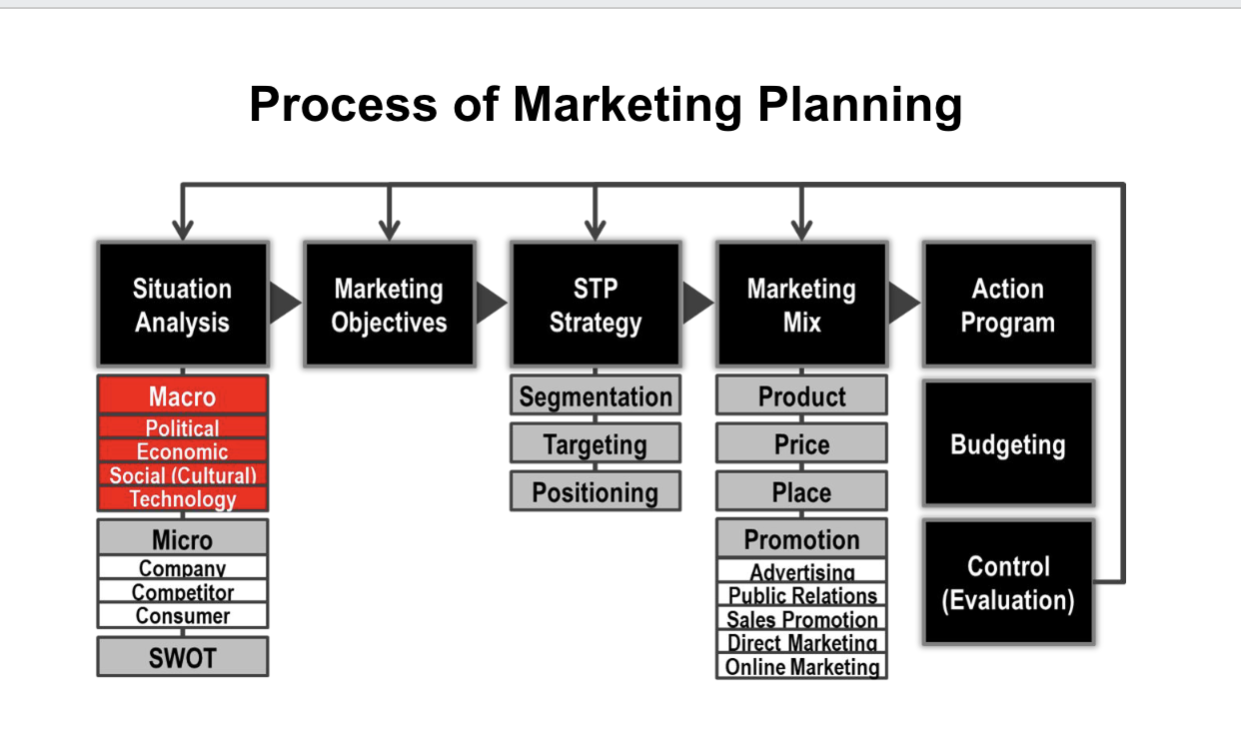
Macro factors- PEST
Political-laws and gov pressure can change marketing
Economic-impact businesses and expansion (2008 crisis)
Social- buying patterns of different groups and societies
Technology-automation and innovation (new products, dramatic changes in marketplace, concern for saftey for new products)
Micro factors- 3 C analysis
understand the….
company
competitor
consumer
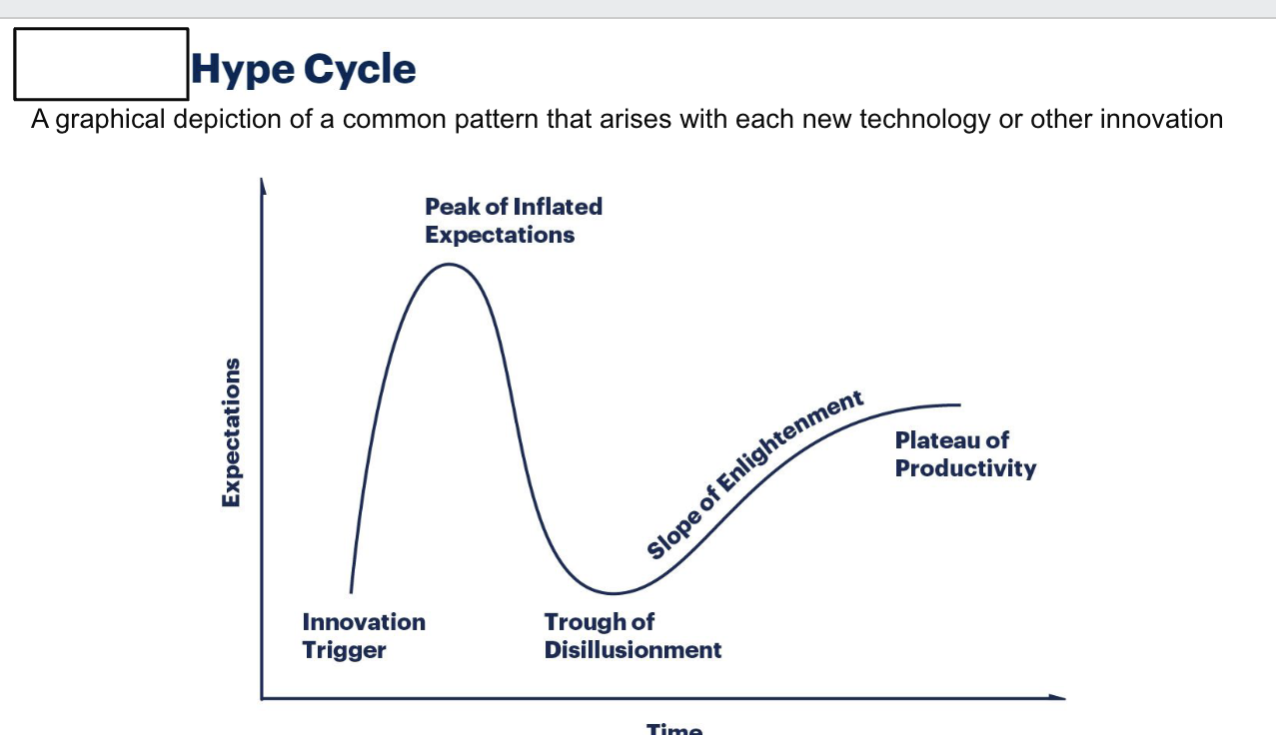
Gartner Hype Cycle
Age Brackets
Baby boomer: 1946-1964
gen x: 1965-1979
gen y (millennial): 1980-1994
gen z: 1995-2009
gen alpha: 2010-2024
market oriented mission statement
defines the business in terms of satisfying basic customer needs
core competency
harmonized combination of multiple resources and skills that distinguish a firm in the marketplace
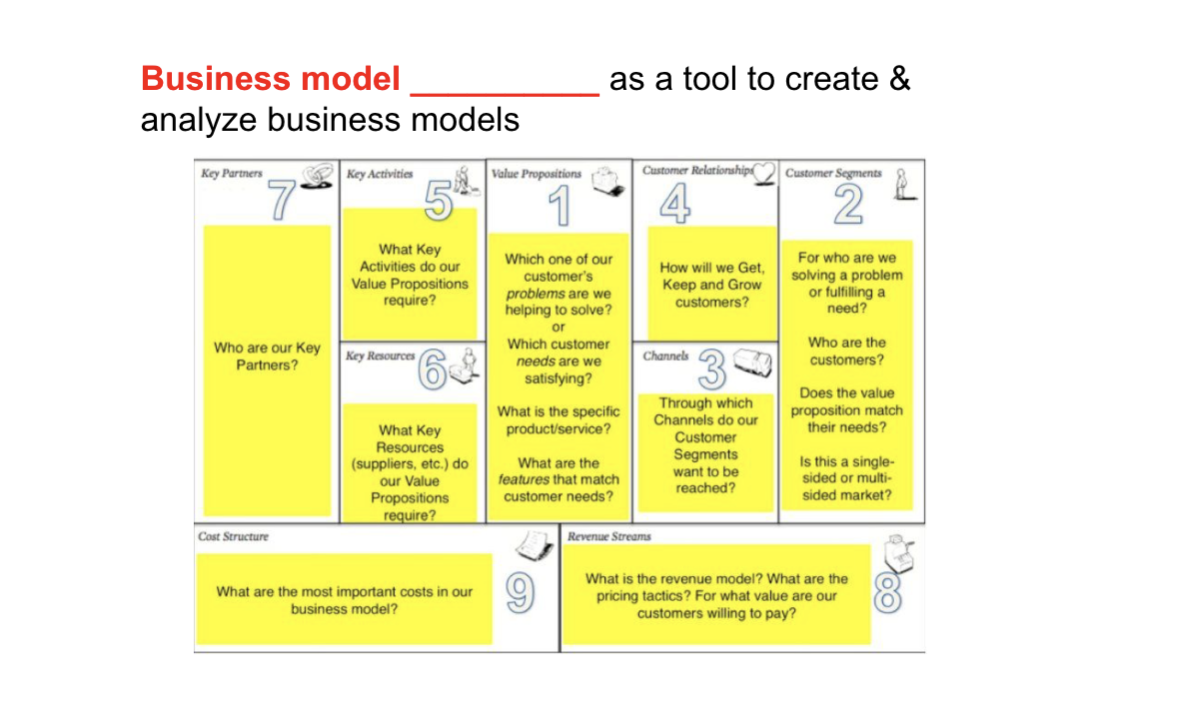
business model
describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers, and captures value
business model canvas
used as a tool to create and analyze the business model
Monetization strategies for digital products and services
one time transaction- pay to download an app
e-commerce- earn margins by selling-amazon
subscriptions
ads-supported-youtube
Freemium- charge users for premium features off a free product- Spotify
Boston Consulting Group (BCG) Matrix
star- new product wanted in fast growing industry (Apple watch or airpods)
cash-cow- well established and steady flow of money, hope is to get a lot of “milk” from here to fund other things (iphone)
question marks- have potential but require significant investment to increase market share and become stars (vision pros)
dogs- do not generate much profit and drain resources- try to phase these products out (IPod- old and outdated)

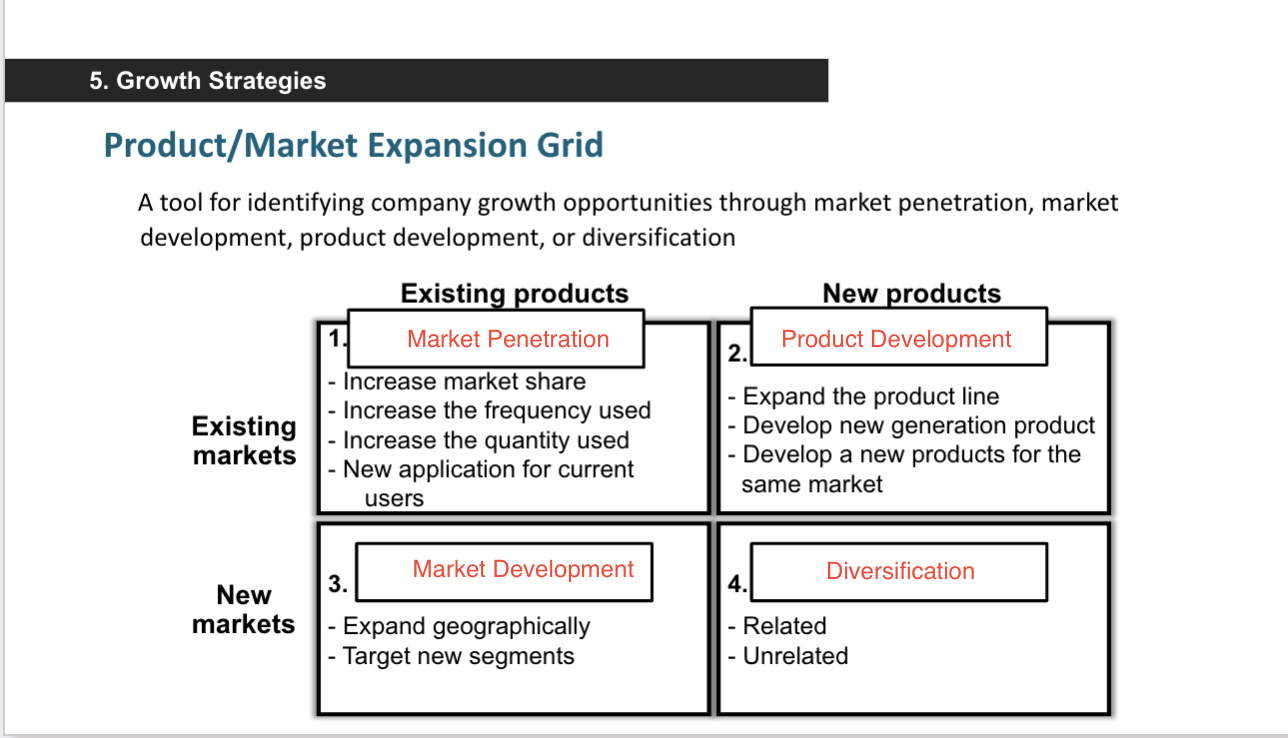
Product Market expansion grid
market penetration- toothbrush head
product penetration- electric toothbrush
market development- korean tooth brush
diversification- mouth wash
Growth Strategies (3)
compete more effictively
satisfy stakeholders
attract top talent
Marketing Return on Investment (ROI)
a measure of managerial effectiveness and efficency
Net Profit before income tax/total marketing investment
=1 is break even
You’re doing great Ethan and Patrick!
Halfway!
Pioneer advantage
Pioneers get an advantage in being the first, but it is not gaurenteed they will be the best in the market
Indirect competition
competitors that offer different products or services but fulfill similar needs or solve similar problems for the target audience
Ex: Bookstores and Nintendo both compete for entertainment
3 competitive strategies
product leadership
operational excellence
customer intimacy
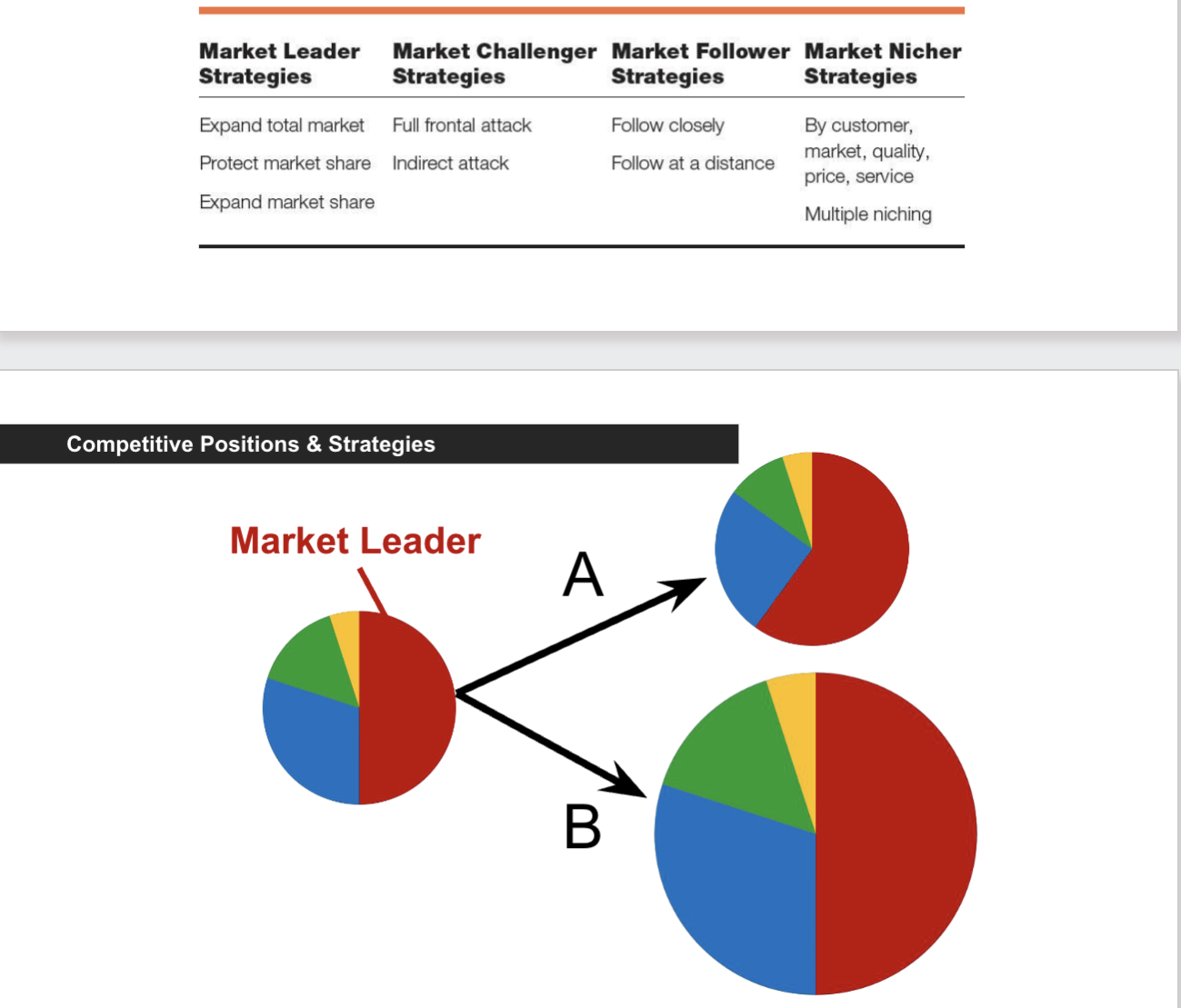
Market Leader
expand the market or customer range by adding products
Market challenger
Attack competitor
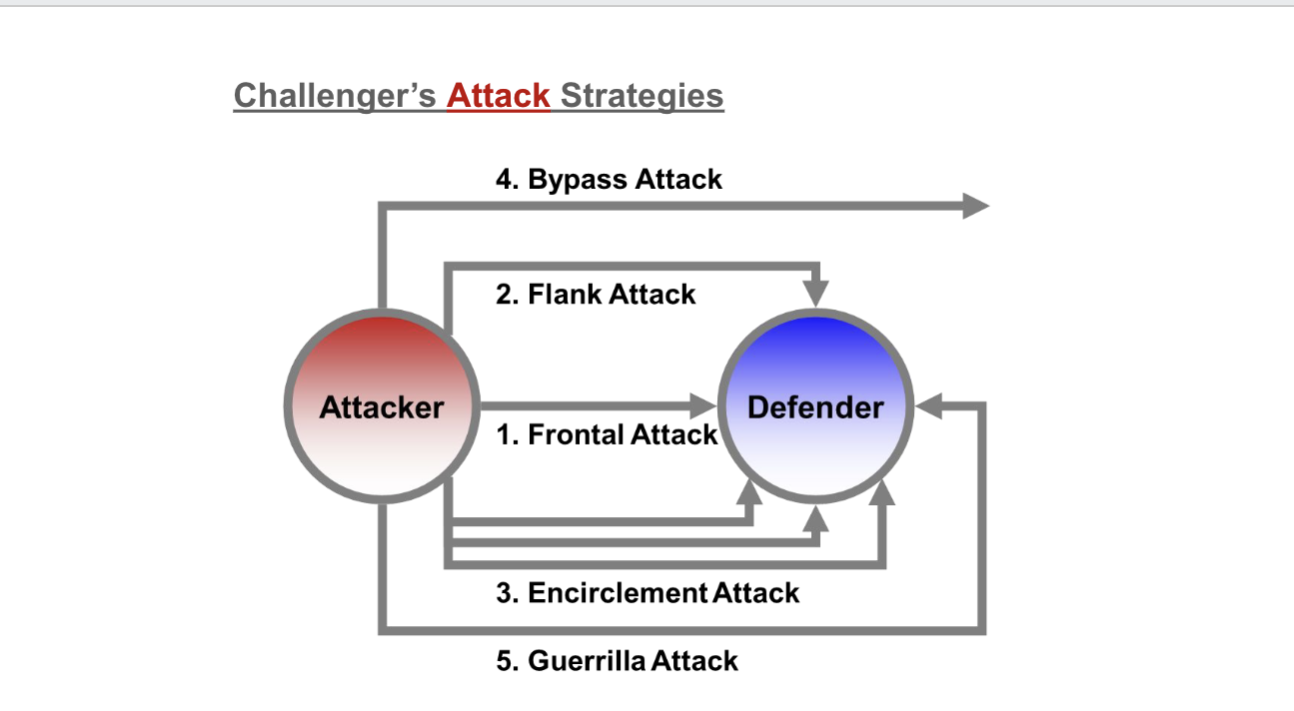
Challengers attack strategies (5)
1) Frontal-match opponent directly
2) Flank- attack weakness of leader
3)Encirclement attack- take a wide slice of enemy territory
4) Bypass attacks- attack easier markets or broaden products
5) Guerrilla attack- small, intermittent attacks to secure footholds
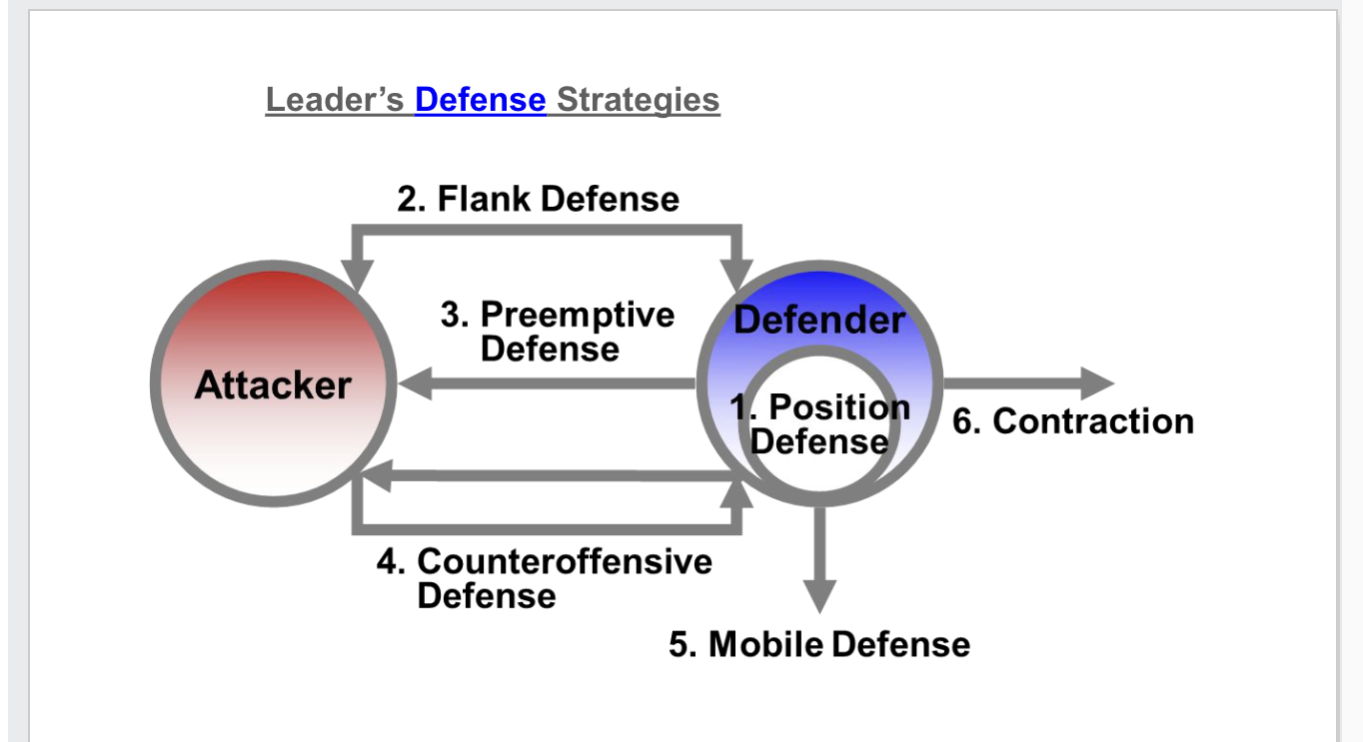
Defense Strategies
1) Position defense-ignore opponent
2) Flank defense- attack weakside (washmouth example)
3) Preemptive defense- leader attacks before enemy starts offense
4) counteractive defense- respond w/counterattack when attacked
5) mobile defense- stretch out domain over new territories for future defense
6) contraction- become smaller
Almost done 🙂
Utility Maximization
individuals and companies seek to achieve the highest level of satisfaction from their economic decisions
NOT FULL PROOF
Consumers do NOT gather all available information, make rational decisions, purchase best value, or have common traits and motivations
Types of consumers: influencer
Buy it ASAP
Types of consumers: Initiator
I’ll buy it for my Dad
Types of consumers: Decider
Okay go buy it, but don’t overspend
types of consumers: buyer
Send the link I’ll use my card
types of consumers: end user
Looks good, I’ll use it
4 factors influencing consumer behavior
cultural
social
personal
psychological
culture
subculture
behaviors, values, perceptions from family or other important institutions
group of people within a culture
Each generation has slightly different core values shaped by events that occur in their lifetimes
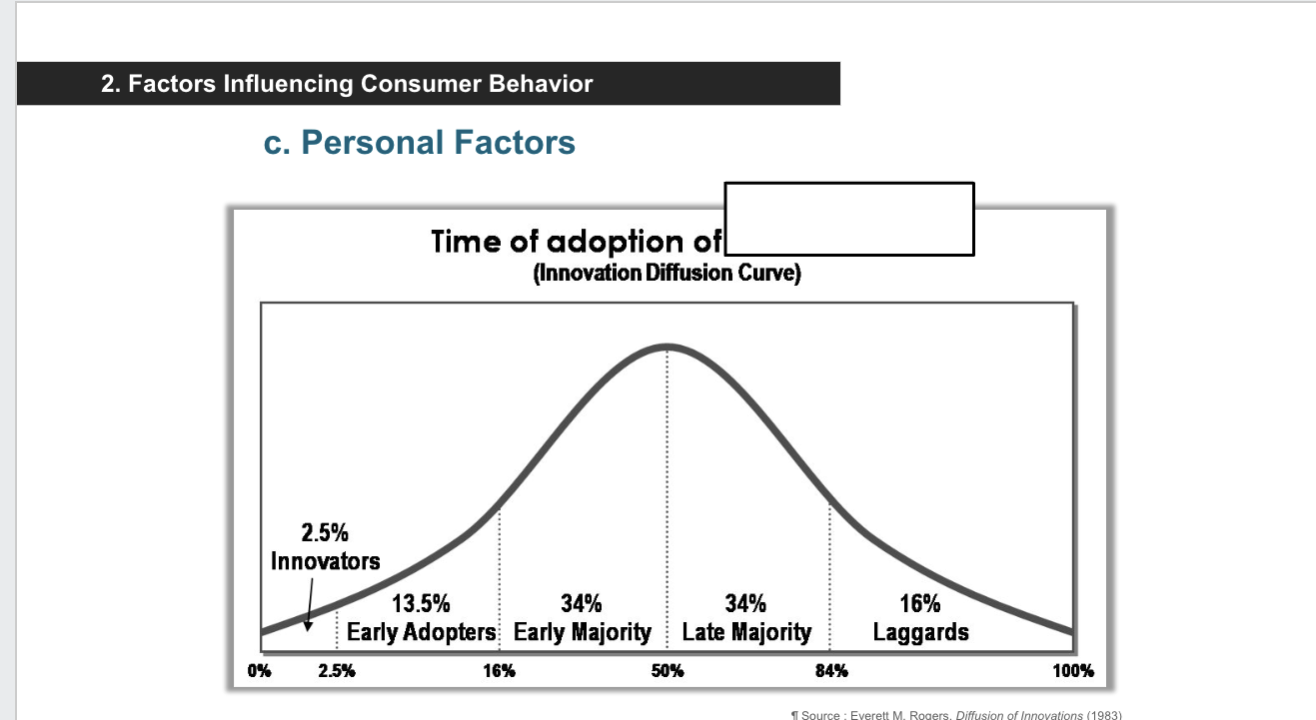
Innovation Diffusion Curve- know percentile and characteristics
Innovators 2.5%- venturesome and try new things
Early Adopters 13.5%- adopt new ideas carefully
Early Majority 34%- deliberate, adopt new ideas before average person
Late Majority 34%- skeptical, majority of people must try it
Laggards 16%- tradition-bound and suspicious of change
Selective attention
tendency to screen out most info they are exposed to
selective distortion
people interact with info that will support what they believe
selective retention
remember good points made about brand they favor and forget good points about competing brands
Attitudes
a persons evaluations, feelings, and tendencies toward an object or idea
involvement
persons perceived relevance of the object based on inherent needs, values, and interests
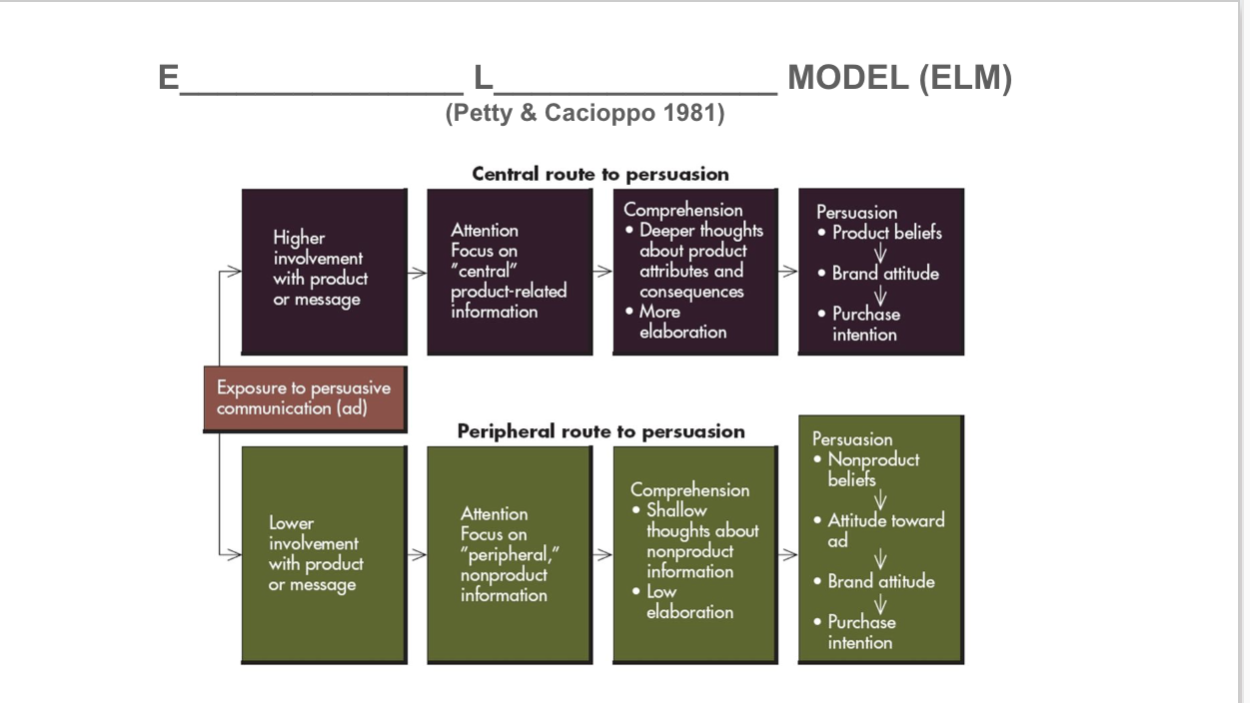
Elaboration likelihood Model (ELM MODEL)
Two forms for how people are persuaded
High involvement- pay attnetion to central product, elaboration, deep thought
low involvement- peripheral, non-product info, shallow thoughts, brand attitude
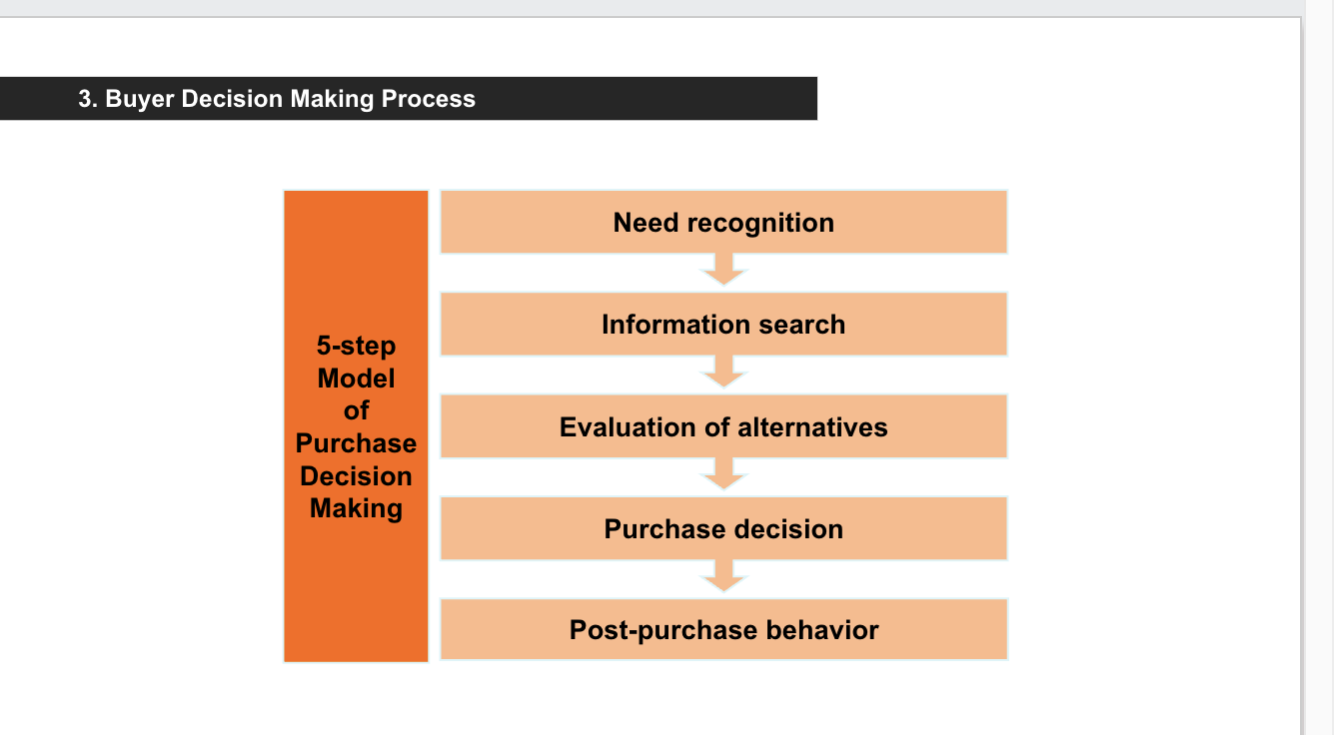
5 model of purchase making decision
needs-recognition- consumer wants and needs
information search- personal, commercial, public, experiential sources
evaluation of alternatives- “consideration set”- brands must be included in consideration or customers won’t be bought
purchase decisions- what, where, when, how much
post purchase behavior- satisfied/dissatisfied
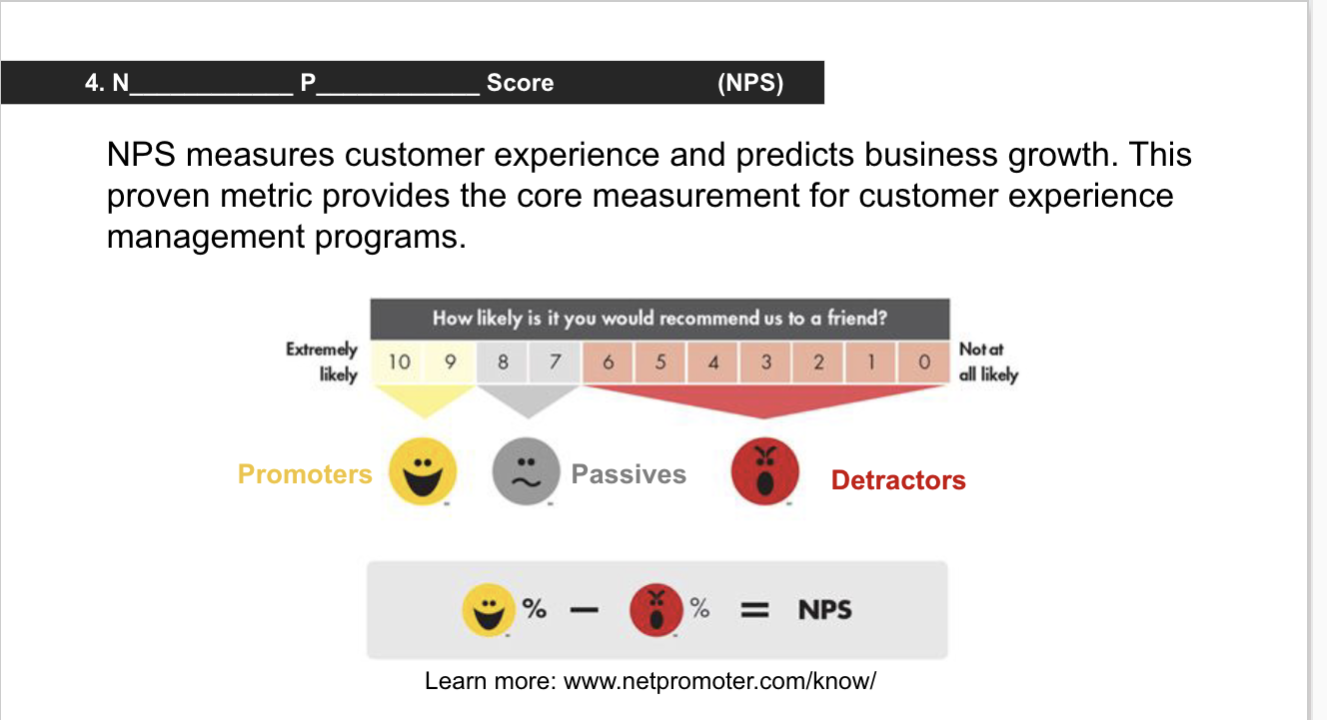
Net promotor score
Subtract the total of positives (10/9) from negatives (0-6) for total. NUMBER CAN BE NEGATIVE
ex: 25 happy, 15 not happy
nps= 25-15=10
Consideration set

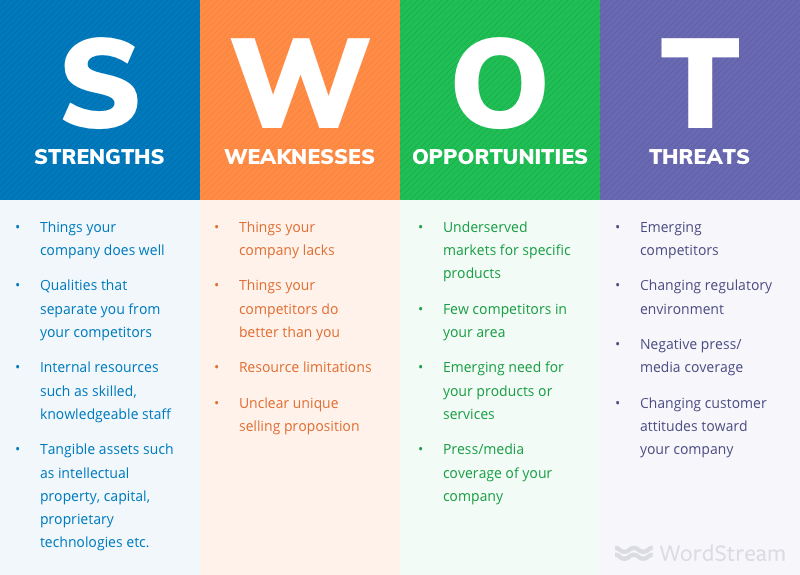
SWOT
strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, threats