biology honors - cell cycle: interphase, mitosis, & cytokinesis
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
adenine
thymine pairs with ________
cytosine
guanine pairs with _________
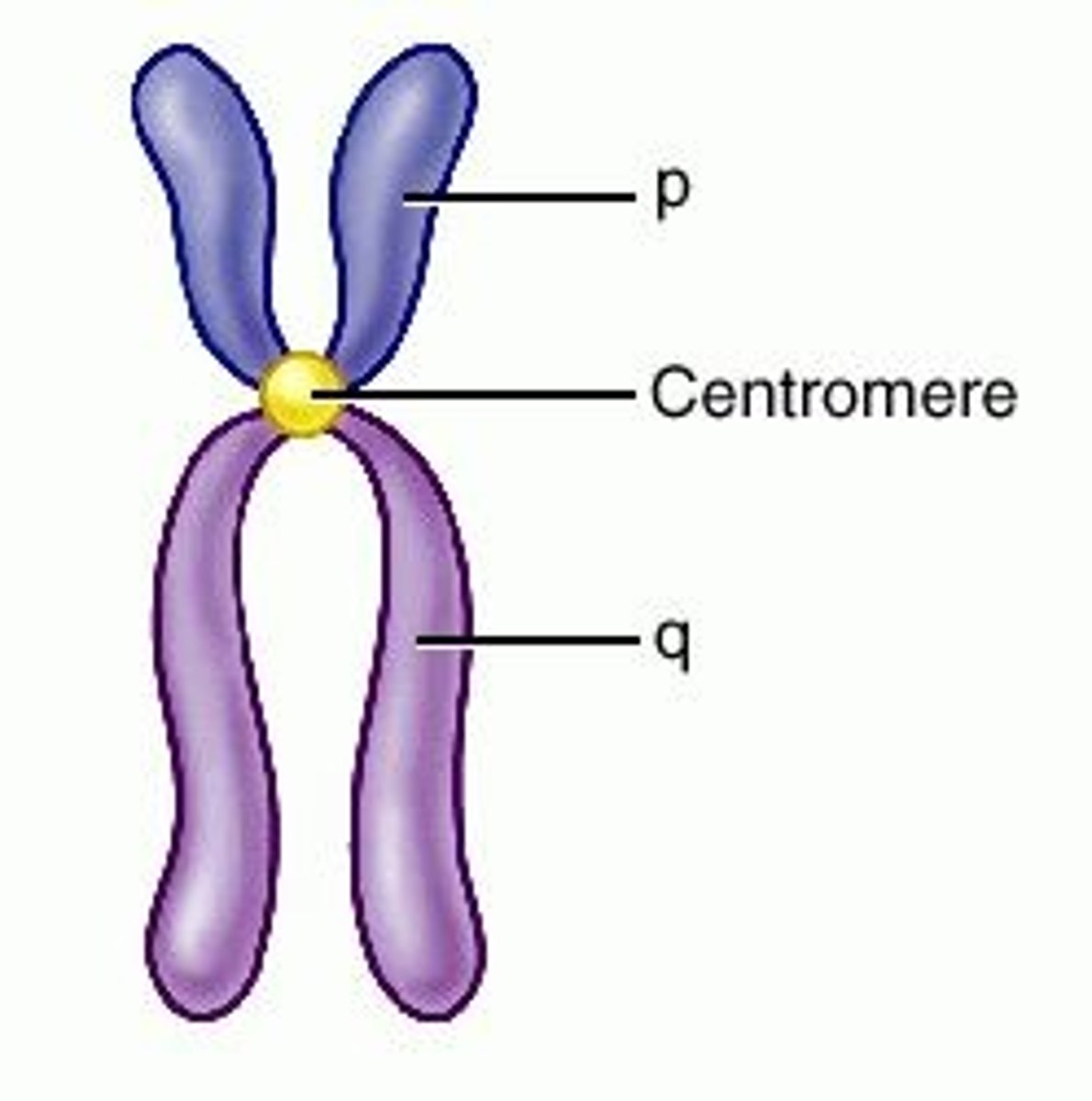
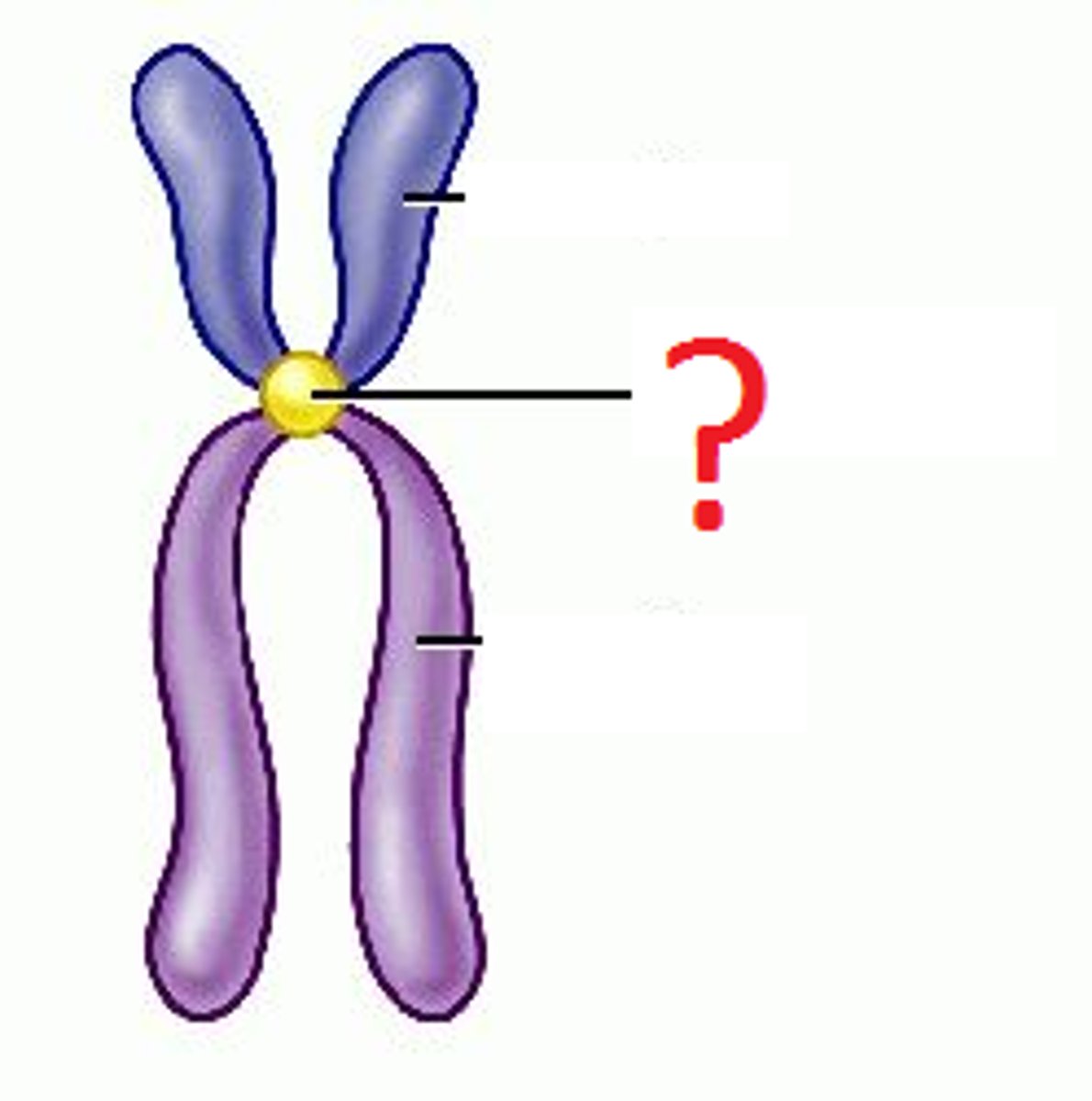
chromosome
DNA that is tightly coiled up for protection because the nucleus has disappeared
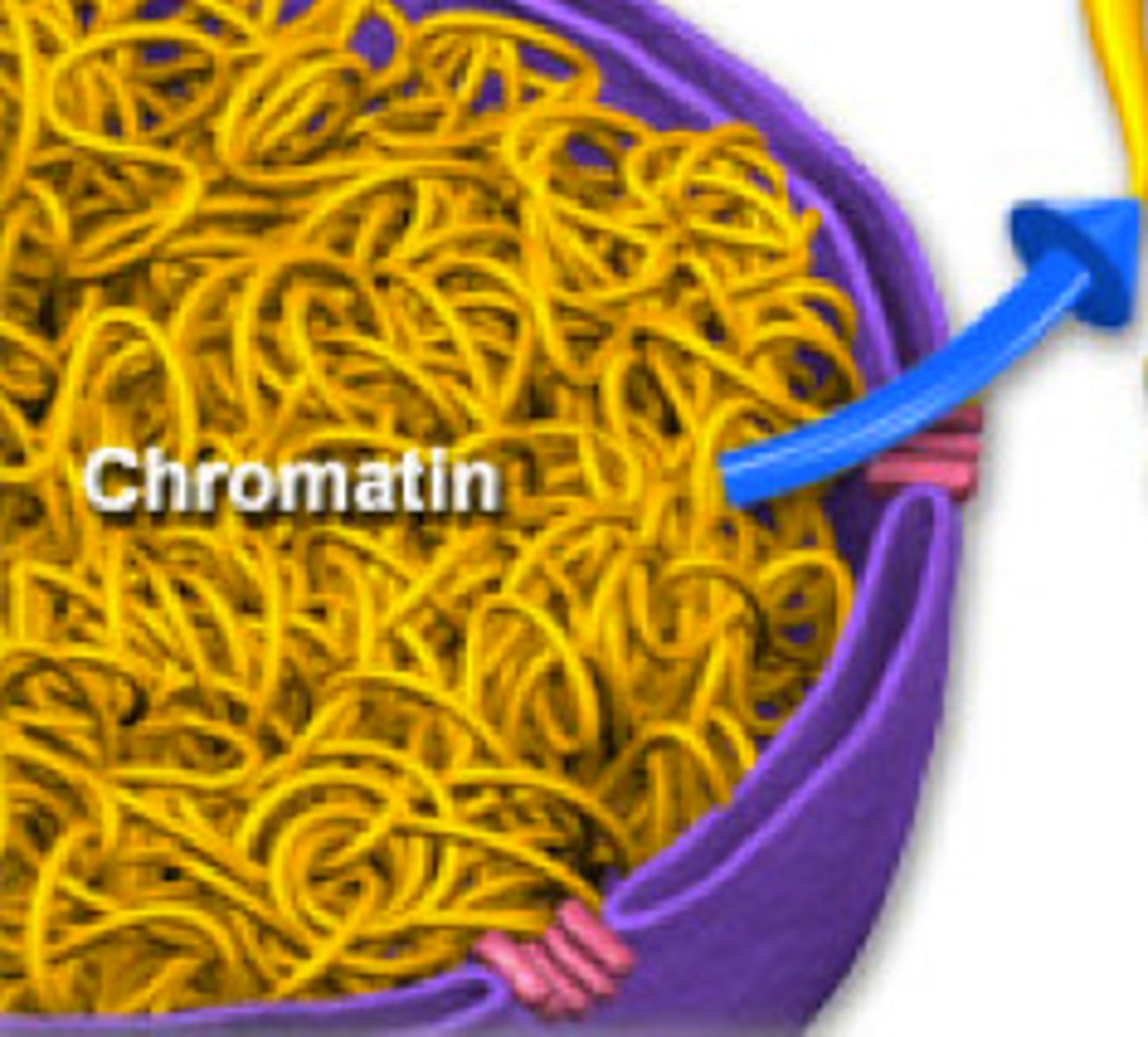
chromatin
when DNA is long and stringy; takes this form when there is a nucleus present
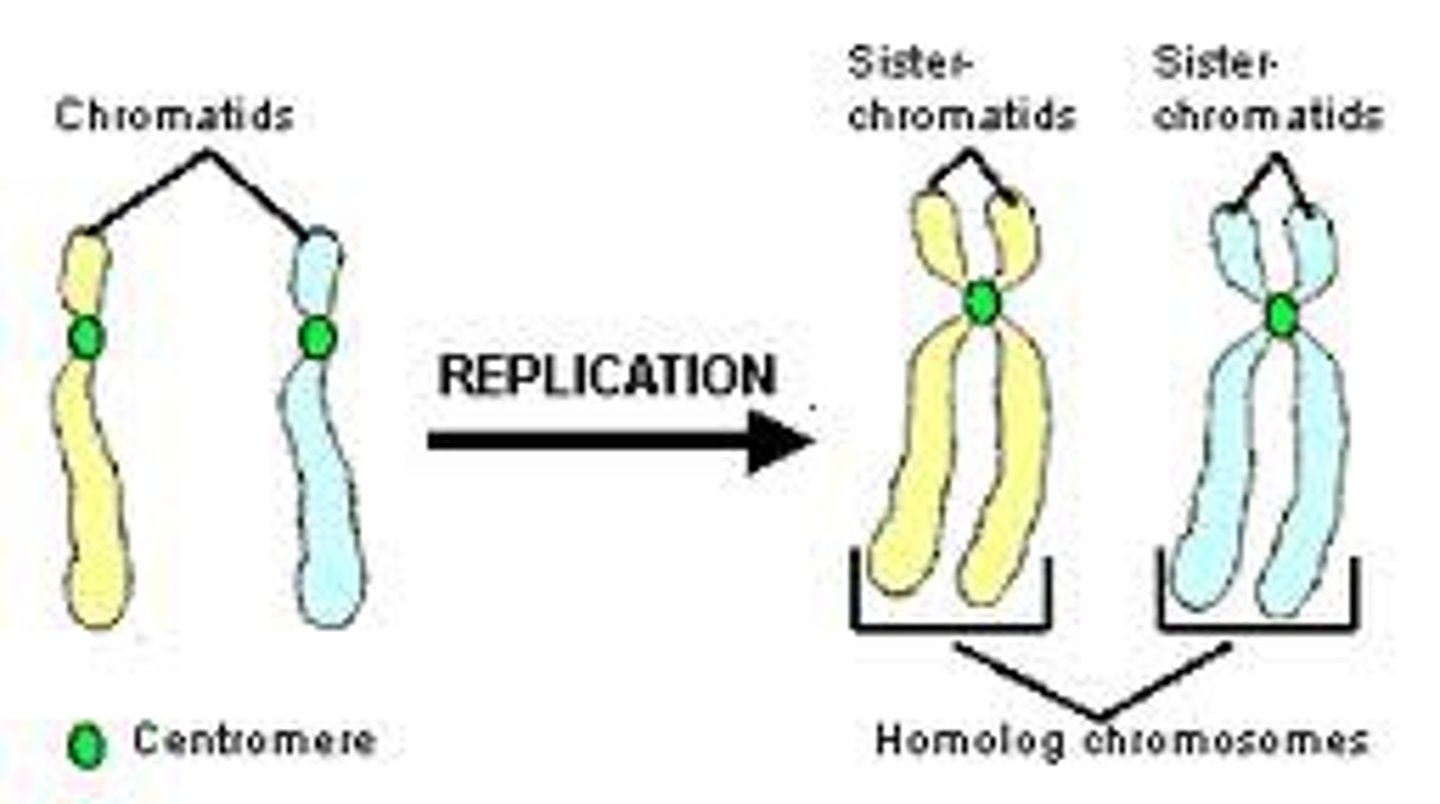
chromatid
1 strand of DNA; 2 sister chromatids together make up an X shaped chromosome
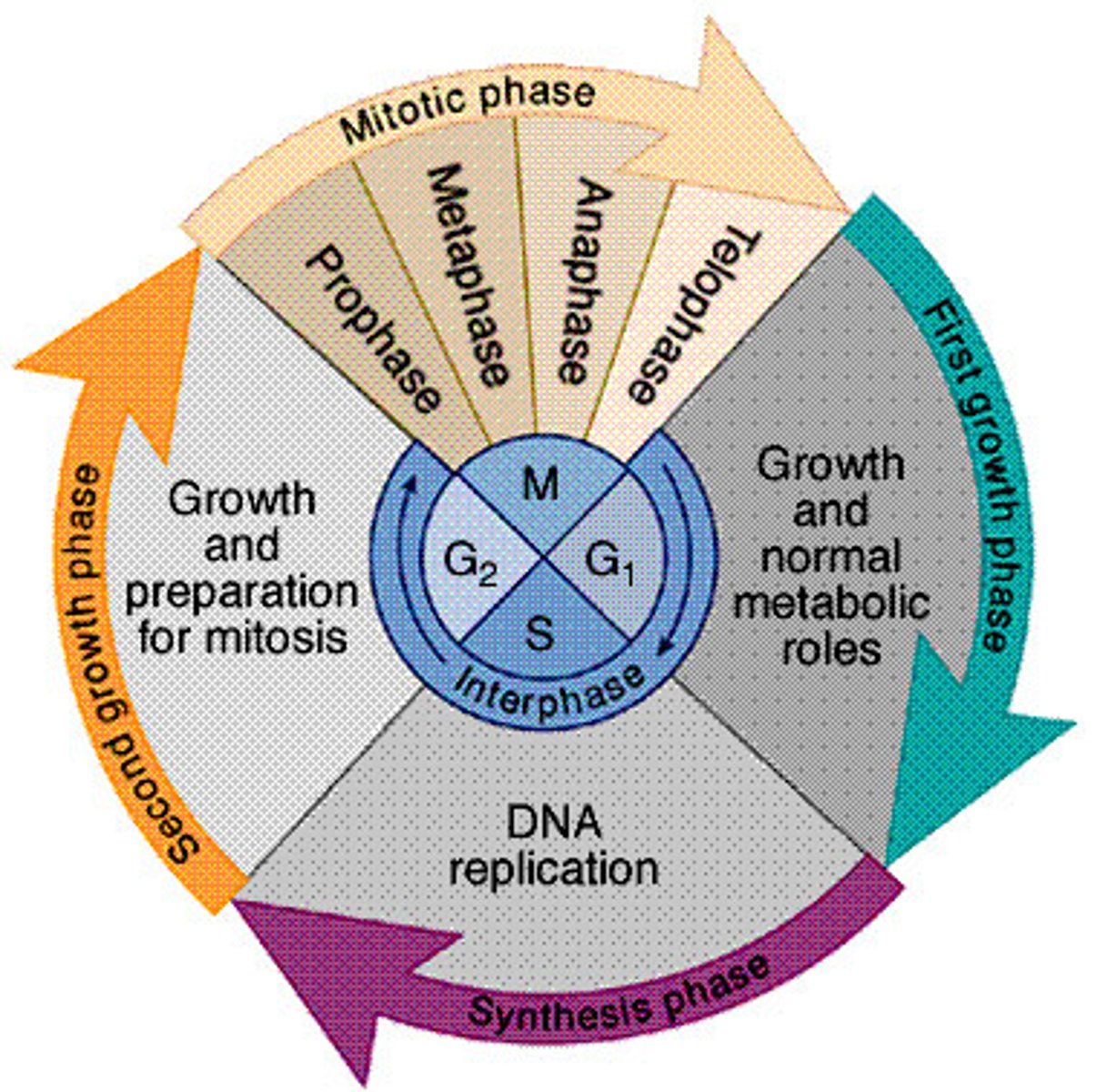
cell cycle
aka the cell's life span
somatic cells
the cell cycle happens to which type of cells?
body cells that make up almost everything except those in reproductive organs
what are somatic cells?
- cells grow up, learn how to function, and carry out their functions
- cells decide whether or not to reproduce
what happens in G1?
they enter the G0 stage, which is where they stay the way that they are, get old and then die; can be reversed so that they can reproduce again
if cells do not decide to reproduce, what happens?
yes, they can decide to reproduce again even if they entered G0 originally
is the G0 stage reversible?
synthesis
what does the S stage stand for?
- DNA replication (DNA unwinds, unhooks, splits apart, and new nucleotides match in the correct order)
- in the nucleus
what happens in S?
2 new copies of DNA still stay attached to each other
what happens to the DNA after DNA replication occurs (in the S stage)?
centromere
the place where the 2 copies of DNA are attached together
- makes copies of organelles
- cell grows bigger
- reorganizes
what happens in G2?
prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
what are the steps of mitosis in order?
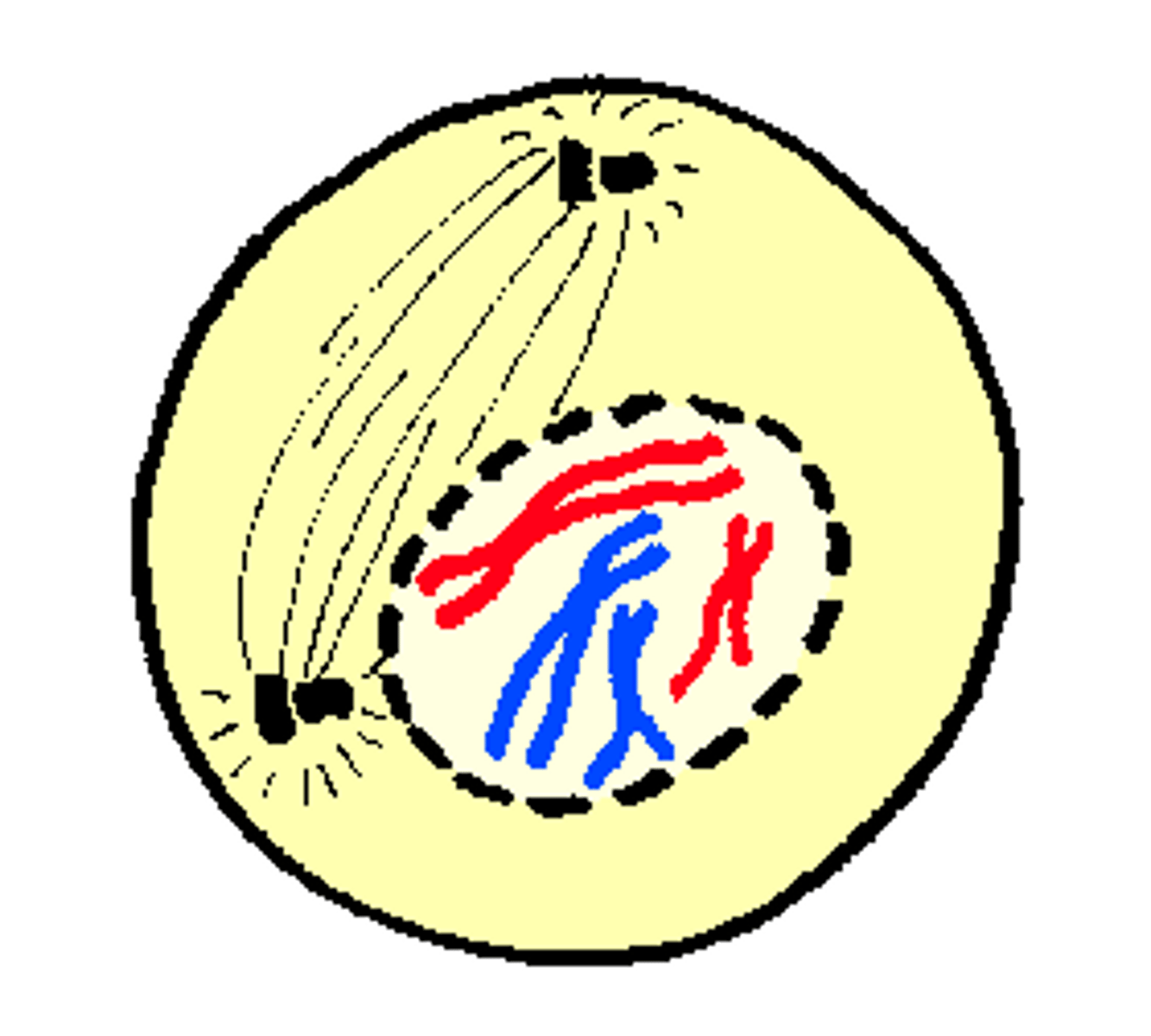
- centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell and start producing spindle fibers
- DNA coils up into a chromosome; nucleus dissolves
- spindle fibers attach to the chromosomes
what happens in prophase?
prophase
what stage of mitosis is occuring in this picture?
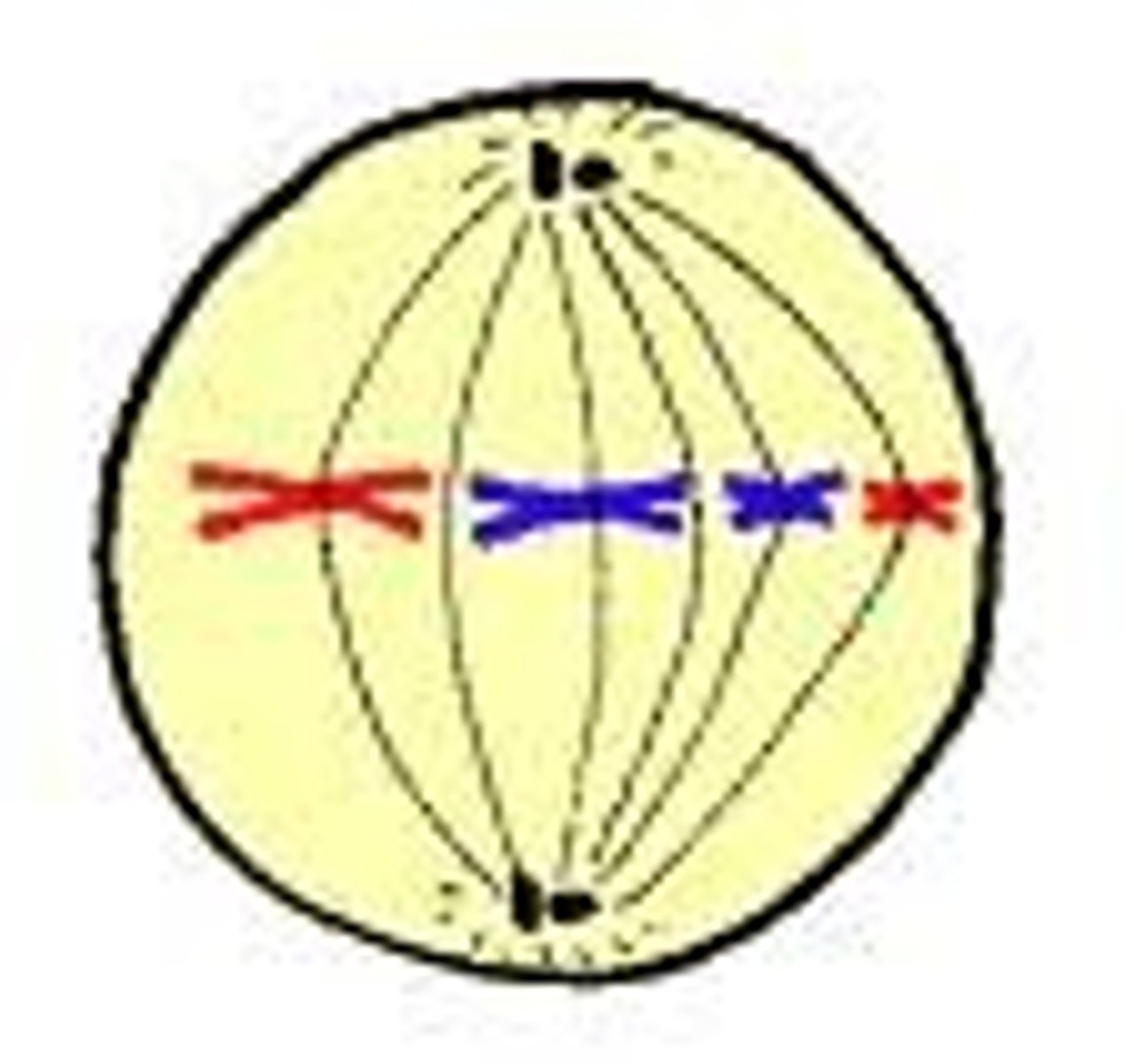
- chromosomes line up in a single file line in the middle of the cell
- spindle fibers are fully attached to the chromosomes
what happens in metaphase?
metaphase
what stage of mitosis is occuring in this picture?
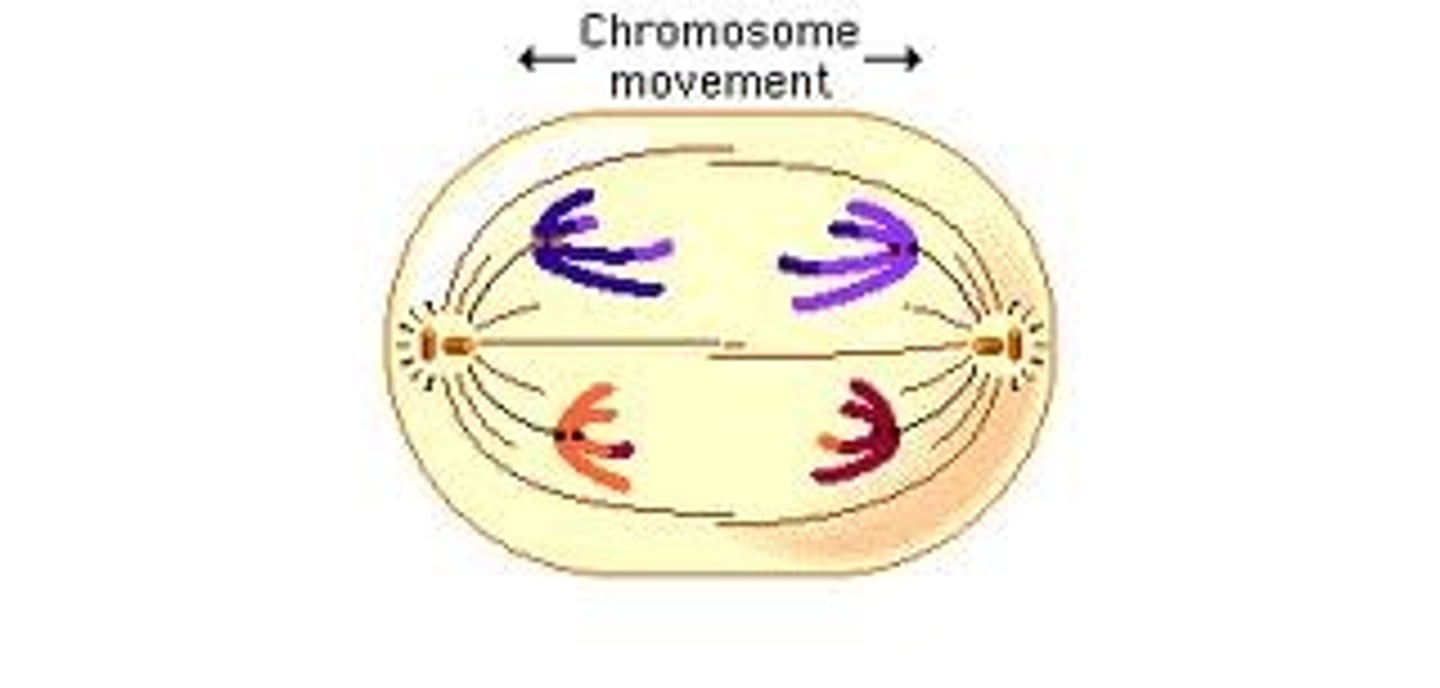
- DNA copies are pulled apart (centromere breaks) and move to opposite ends of the cell
- organelles are divided up and sent to opposite ends
what happens in anaphase?
anaphase
what stage of mitosis is occuring in this picture?
- the cell squeezes in the middle and starts to split in half
- nuclei begin to reform, DNA goes back to looking like chromatin
what happens in telophase?
telophase
what stage of mitosis is occuring in this picture?
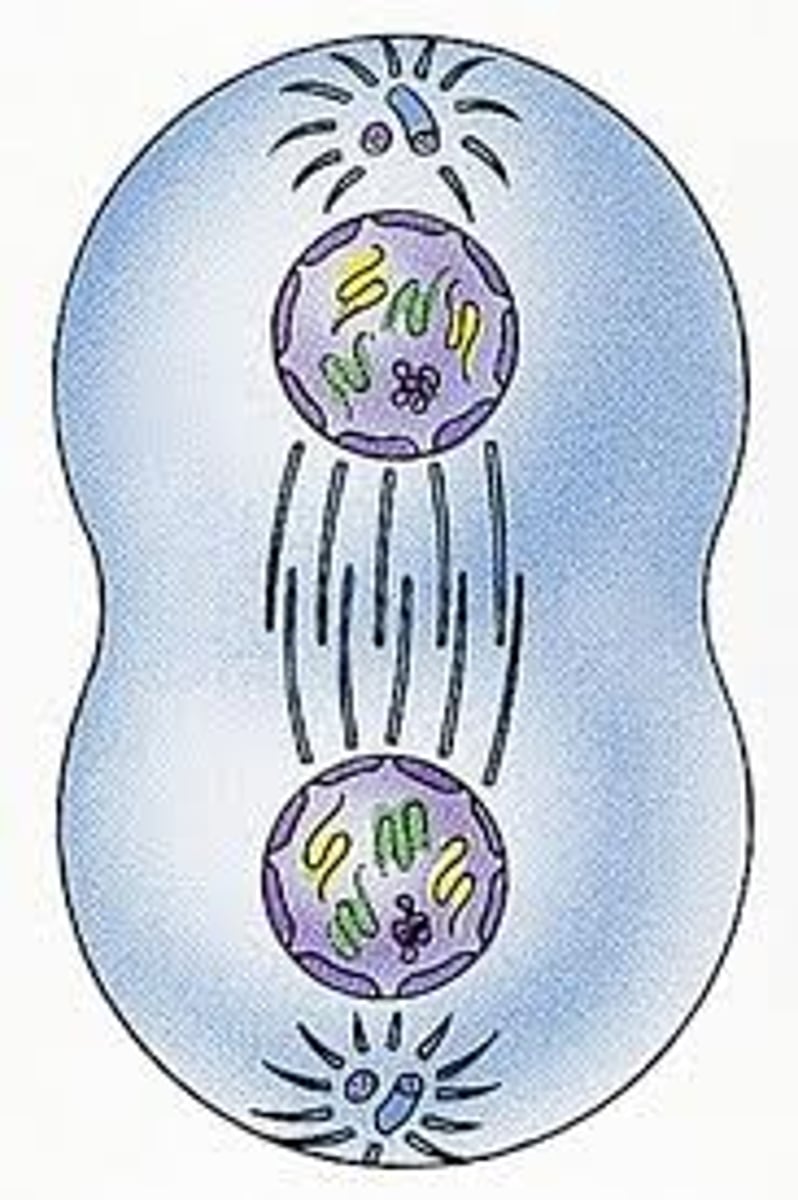
- the 2 cells completely separate
what happens in cytokinesis?
- 2 identical cells
- 46 pieces of DNA
what is the result of cytokinesis (and the cell cycle as a whole)?
starts off with 46 and ends with 46
how many pieces of DNA does the cell cycle start off with? how many in the end result?