Parcial 1 - Economía II UFM
5.0(7)Studied by 68 people
Card Sorting
1/80
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:51 PM on 9/13/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
81 Terms
1
New cards
Monopoly
One seller. Organizations operating with the advantage of special privileges granted by the government.
2
New cards
Price taker
a seller that cannot affect the price by his own actions.
3
New cards
Price searcher
a seller that must choose a price.
4
New cards
Competitive markets
markets in which all buyers and sellers are price takers.
5
New cards
Optimal allocation of resources
no unit of the good is being produced whose marginal opportunity cost exceeds its marginal benefit. And every unit of the good whose marginal benefit exceeds its marginal cost is being produced.
6
New cards
Characteristics of perfect competition
* There is a large number of buyers and sellers so nobody possesses market power.
* Market participants possess full and complete information of alternatives.
* Sellers produce a homogenous product.
* There is costless mobility of resources.
* Economic actors are price takers.
* Market participants possess full and complete information of alternatives.
* Sellers produce a homogenous product.
* There is costless mobility of resources.
* Economic actors are price takers.
7
New cards
Mistakes with perfect competition
* It has overlooked the entrepreneur, which is the driving force of real-world markets.
* It also ignores the plan-adjustment process that characterizes real-world market activity.
* It also ignores the plan-adjustment process that characterizes real-world market activity.
8
New cards
Fair competition
Open entry and exit
9
New cards
Cartel
cooperative arrangement between companies intended to promote a mutual interest. Sellers agreeing not to compete with each other.
10
New cards
Problems of cartels
* How to prevent competition among its members, who will try to circumvent the agreement
* How to keep new competitors from trying to enter the market
* How to keep new competitors from trying to enter the market
11
New cards
Predatory price-cutting
reducing prices below cost in order to drive a rival out of business or prevent new rivals from entering with the intention of raising prices afterward to recoup all losses.
12
New cards
Distribution of income
the product of the supply and demand for *productive services*.
13
New cards
Capital
produced goods that can be used to produce future goods.
14
New cards
Human capital
productive capabilities generated by investment and embodied in human beings, such as knowledge and skills.
15
New cards
Three types of rights
Actual, legal, moral
16
New cards
Unions
Groups of organized workers that claim to compete against corporations, but in reality they want to exclude other workers who would do the same work for less.
17
New cards
Veil of ignorance
Imagine you would have to choose the laws of society, but before choosing, you forgot everything about yourself.
18
New cards
Externalities
costs or benefits that fall on bystanders.
19
New cards
Negative externalities
costs imposed on others that are not taken into account when making a decision.
20
New cards
Externalities are also called
Spillover cost or external cost
21
New cards
Positive externalities
benefits from an action that the decision-maker does not take into account.
22
New cards
Internalizing an externality
when the actor finds out about the consequences of his actions, takes the externality into account and chooses to alter his behavior.
23
New cards
We can reduce externalities through
Negotiation, adjudication, legislation, command and control, taxes, Coase theorem
24
New cards
Negotiation
work it out for ourselves, it produces mutual gains from exchange.
25
New cards
Adjudication
a process for discovering who has which rights. It aims at maintaining the continuity of expectations.
26
New cards
Legislation
The creation of new rules
27
New cards
Command and control
legislation of physical restrictions.
28
New cards
Bubble concept
permit factories to exceed the limits at one point if they could make it up at another point.
29
New cards
Rights to pollute
firms with more emissions can buy these rights, so the total amount of emissions stays the same.
30
New cards
Coase theorem
a solution to externalities through the creation of new markets.
31
New cards
Pigouvian tax
a tax on a good that produces negative externalities, in hopes to reduce it.
32
New cards
Network externalities
The value of a good or service increases the more people use it.
33
New cards
Externalities graph
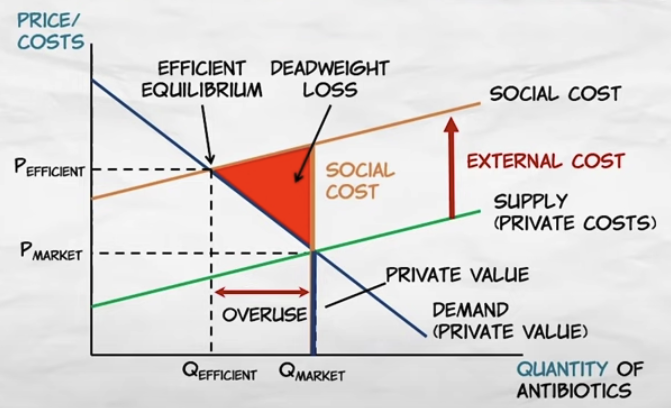
34
New cards
Structured individualism
el individuo carga con los beneficios y costos de sus acciones.
35
New cards
Private or competitive sector
The market sector
36
New cards
Public sector
Conformado por el gobierno
37
New cards
Coerce
induce cooperation by threatening to violently reduce people's options.
38
New cards
Persuade
induce cooperation by promising to expand people's options.
39
New cards
Free-riders
people who accept benefits without paying their share of the cost of providing those benefits.
40
New cards
Paternalistic argument
the widely held belief that the powerful will take advantage of the weak unless government regulates certain kinds of voluntary exchange.
41
New cards
Prisoners dilemma
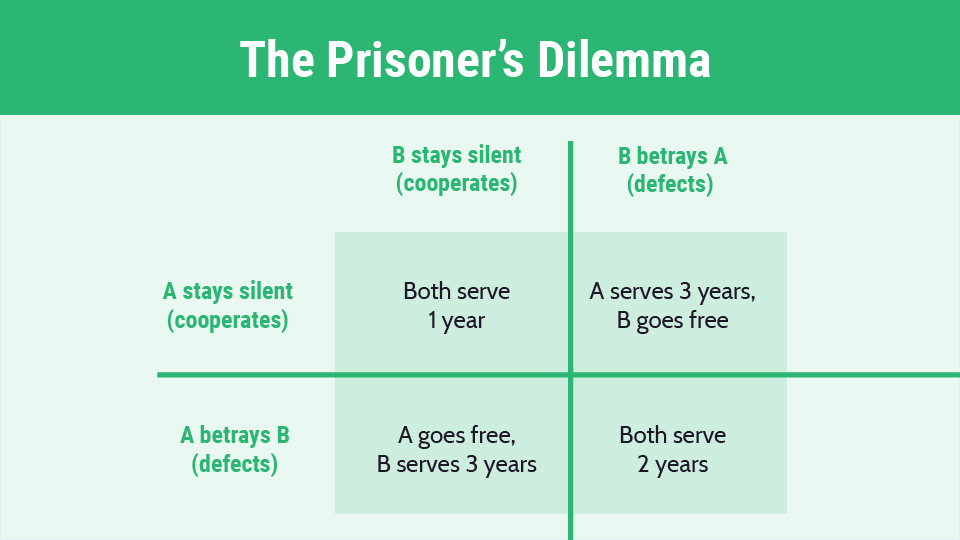
42
New cards
What the state is not
We are not the government
43
New cards
What the state is
Provides a legal, orderly, systematic channel for the predation of private property. it is the monopoly of violence.
44
New cards
Economic means of acquiring wealth
Production and exchange
45
New cards
Political means of acquiring wealth
seizure of another's goods or services by the use of force and violence.
46
New cards
Ways to raise government revenue
* Taxation
* Public borrowing or debt issue
* Money creation
* Public borrowing or debt issue
* Money creation
47
New cards
Neutral tax
aquel impuesto que no cambia la conducta.
48
New cards
Positive principles of taxation
analyze who bears the burden of taxes and what other economic effects can be expected to result from the imposition of taxes.
49
New cards
Normative principles of taxation
how tax policy can be used to design as desirable a tax system as possible.
50
New cards
Unit tax
a tax charged per unit of a good exchanged.
51
New cards
Ad valorem tax
a tax based on the dollar value of the goods sold.
52
New cards
Retail sales tax
taxes calculated as a percentage of retail sales, a type of ad valorem tax.
53
New cards
Excise tax
taxes placed on particular types of goods, can be either unit or ad valorem.
54
New cards
Tax incidence
the ultimate burden of the tax, after shifting has taken place.
55
New cards
Welfare cost of taxation is also known as
Excess burden or deadweight loss
56
New cards
Welfare cost of taxation
all the exchanges that could be made, but are not made, because of a tax.
57
New cards
Lump sum tax
a tax that completely eliminates the excess burden of taxation.
58
New cards
Ramsey rule
states that to minimize the excess burden of taxation, taxes should be placed on goods in inverse proportion to the elasticity of demand for the goods.
59
New cards
Compliance costs
the costs imposed on taxpayers to comply with the tax laws, such as collecting and keeping records.
60
New cards
Administrative costs
home by the government to collect taxes.
61
New cards
Political cost
home by the taxpayers and the government as a result of taxpayers trying to influence tax laws.
62
New cards
Earmarked tax
taxes whose revenues are designated to a particular spending activity.
63
New cards
General fund financing
the tax revenues are placed in the general fund, from which government programs are financed. The alternative to earmarking.
64
New cards
Benefit principle
states that the people who benefit from the government's expenditures should be the ones who pay for them.
65
New cards
Ability-to-pay principle
states that individuals should pay taxes in proportion to their ability to pay.
66
New cards
Horizontal equity
individuals with an equal ability to pay should pay equal amounts of taxes.
67
New cards
Vertical equity
individuals with a greater ability to pay should pay more taxes.
68
New cards
Proportional tax
a tax that is the same percentage of a taxpayer's income no matter what the level of income.
69
New cards
Progressive tax
a tax that is a larger percentage of the taxpayer's income as income rises.
70
New cards
Regressive tax
a tax that is a smaller percentage of the taxpayer's income as income lowers.
71
New cards
Sumptuary tax
taxes designed to discourage the consumption of the taxed good.
72
New cards
Revenue-neutral carbon tax
el gobierno "devuelve" parte del impuesto sobre la contaminación
73
New cards
Tax graph
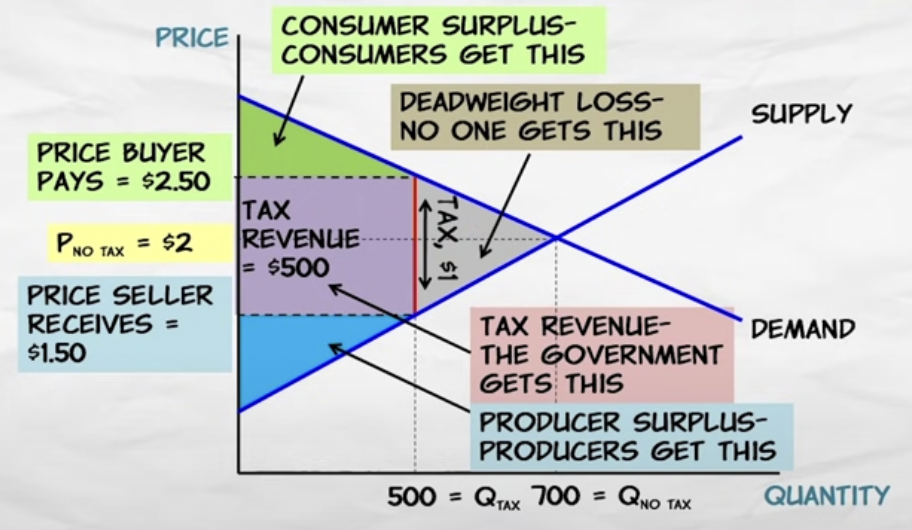
74
New cards
Laffer curve
belief that tax cuts generate additional revenue.
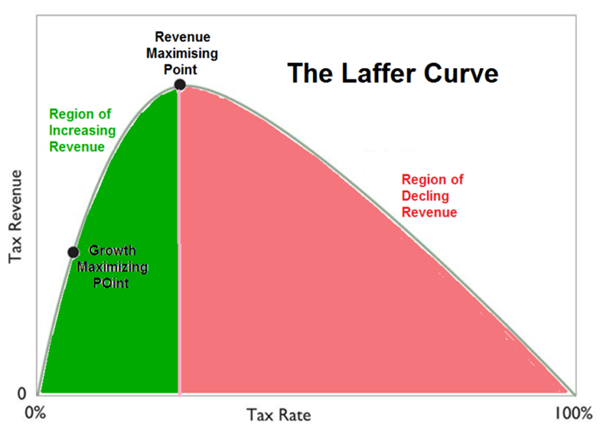
75
New cards
The old-time fiscal religion
*Deficits* emerged primarily during periods of war; budgets normally produced *surpluses* during peacetime, and these surpluses were used to retire the debt created during war emergencies.
76
New cards
Fiscal constitution
rules guiding fiscal choices
77
New cards
Multiplier effect
* By *creating jobs*, governments would save money that would have been spent on unemployment benefits.
* The increase in the number of emplyed people would create *additional spending power* and therefore boost the economy and tax receipts.
* Increased tax receipts would *pay off* the initial debt.
* The increase in the number of emplyed people would create *additional spending power* and therefore boost the economy and tax receipts.
* Increased tax receipts would *pay off* the initial debt.
78
New cards
Public choice theory
the application of economic methods to the study of political processes.
79
New cards
Market failure
There are certain areas where market forces do not opperate effectively and therefore we must have government corrective action.
80
New cards
Bifurcated view of human action
We know that people in markets are driven by self-interest, but we must also accept that people in government are driven by the same thing.
81
New cards
Public choice theory’s main question
What policy is likely to emerge from real-world democratic politics, and how does that compare to market alternatives?