Biology Final Study Guide
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 9:44 PM on 5/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
1
New cards
What are Mendelian traits
dominant and recessive traits
2
New cards
Dominant alleles
The allele that is always shown
Ex. Rr R= the dominant trait
Ex. Rr R= the dominant trait
3
New cards
Recessive traits
Masked by dominant allele and is only shown when dominant allele is not present
ex.) Rr r= recessive rr= the recessive is shown
ex.) Rr r= recessive rr= the recessive is shown
4
New cards
Modes of Inheritance
co-dominance, incomplete dominance, multiple alleles, polygenic traits, sex-linked
5
New cards
co-dominance
both alleles contribute to the phenotype
Ex. BB x WW = BW → white chicken with black spots
→ spotted
Ex. BB x WW = BW → white chicken with black spots
→ spotted
6
New cards
Incomplete Dominance
One allele is not completely dominant over the other
* they blend together
RR x WW = RW → red x white= pink
* they blend together
RR x WW = RW → red x white= pink
7
New cards
Multiple alleles
More than 2 alleles can exist for a trait
* Ex. Blood A,B,O
* Eye color in fruit flies
* Rabbit coat color
* Ex. Blood A,B,O
* Eye color in fruit flies
* Rabbit coat color
8
New cards
Polygenic traits
Traits controlled by 2+ genes
* phenotypes exist in a gradient
Ex. Human eye color, hair color, and height
* phenotypes exist in a gradient
Ex. Human eye color, hair color, and height
9
New cards
Sex-linked
Genes located on either x or y
* x linked are more common because boys don’t have another x chromosome to dominate their diseased x
* Sex linked disorders: colorblindness, hemophilia, duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
* x linked are more common because boys don’t have another x chromosome to dominate their diseased x
* Sex linked disorders: colorblindness, hemophilia, duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
10
New cards
Punnett squares
shows the principle of segregation
* alleles are separated from their partner during meiosis
* alleles are separated from their partner during meiosis
11
New cards
Major events in meiosis
* Major Event 1 = Tetrads form
→ happens in prophase 1 where the homologous chromosomes pair up to form tetrads for crossing over
* Major Event 2 = Crossing Over
→happens in prophase 1 when the homologous chromosomes exchange sections
→ This increases genetic diversity
* Meiosis 1 =
→ Metaphase 1 : tetrads line up on metaphase plate → Anaphase 1 : tetrads separate and chromosomes move to opposite poles
→ Results in 2 non-identical haploid cells
* Meiosis 2 =
→ No DNA replication occurs before hand
→ process exact copy of mitosis
Results in 4 non-identical haploid cells
→ happens in prophase 1 where the homologous chromosomes pair up to form tetrads for crossing over
* Major Event 2 = Crossing Over
→happens in prophase 1 when the homologous chromosomes exchange sections
→ This increases genetic diversity
* Meiosis 1 =
→ Metaphase 1 : tetrads line up on metaphase plate → Anaphase 1 : tetrads separate and chromosomes move to opposite poles
→ Results in 2 non-identical haploid cells
* Meiosis 2 =
→ No DNA replication occurs before hand
→ process exact copy of mitosis
Results in 4 non-identical haploid cells
12
New cards
results of meiosis
Meiosis 1 = 2 non-identical haploid cells
Meiosis 2 = one diploid cell forms **4 non-identical haploid gametes**
Meiosis 2 = one diploid cell forms **4 non-identical haploid gametes**
13
New cards
Inheritance types observed in blood type
A , B , AB , and o
* inherited through co-dominance
* Blood is determined off 2 types of antigens : type A and type B
* type A = antigen A ; type B = antigen B ; type AB = both antigens ; type o= neither antigens
* inherited through co-dominance
* Blood is determined off 2 types of antigens : type A and type B
* type A = antigen A ; type B = antigen B ; type AB = both antigens ; type o= neither antigens
14
New cards
Homologous chromosomes
Pair of chromosomes with one paternal and one maternal
* same length, shape, and set of genes
* same length, shape, and set of genes
15
New cards
Homologous chromosomes involvement in crossing over
The homologous chromosomes, one set of maternal and one set of paternal, line up in the middle of the metaphase plate to form tetrads. They then exchange sections and increase genetic diversity.
16
New cards
Karyotypes
a display of an individual’s complete set of chromosomes
* determine the gender by the last two set of chromosomes: if there are 2 X chromosomes, it is a girl. If there is 1 Y and 1 X chromosome, it is a boy.
* determine the gender by the last two set of chromosomes: if there are 2 X chromosomes, it is a girl. If there is 1 Y and 1 X chromosome, it is a boy.
17
New cards
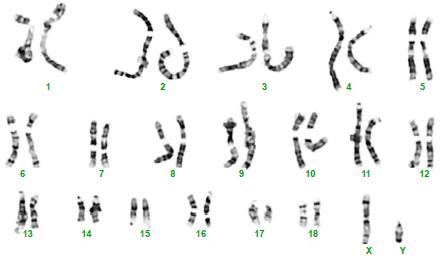
What gender is this:
Male
18
New cards
Nondisjunction
Chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis
* Leads to aneuploidy
* Leads to aneuploidy
19
New cards
aneuploidy
condition of having an abnormal amount of chromosomes in a haploid set
* monosomy
* Trisomy
* monosomy
* Trisomy
20
New cards
What is genetic engineering
Human manipulation of an organism’s DNA
* made possible by the ability to find particular sections of DNA
* Results in GMOs
* made possible by the ability to find particular sections of DNA
* Results in GMOs
21
New cards
What is a GMO
Genetically modified organism
22
New cards
What is selective breeding
* humans breed organisms with desired characteristics to produce the next generation
* “select” specific traits to pass on
* “select” specific traits to pass on
23
New cards
Types of selective breeding
Hybridization and Inbreeding
* DNA is not being messed with by humans
* DNA is not being messed with by humans
24
New cards
Hybridization
crossing of dissimilar individuals to bring best of both worlds together
* Ex.) Brangus cattle
* Ex.) Brangus cattle
25
New cards
Inbreeding
Continued breeding of individuals with similar characteristics
* ensures you know what the offspring looks like
* Can create serious problems as you bring together 2 recessive alleles
* ensures you know what the offspring looks like
* Can create serious problems as you bring together 2 recessive alleles
26
New cards
How do you increase variation
By introducing mutations
* using radiation or chemicals
* using radiation or chemicals
27
New cards
Why do scientists do this?
To study genes and to introduce new beneficial traits
* Critical in agriculture
* Critical in agriculture
28
New cards
Types of Genetic Engineering
1. PCR
2. Recombinant DNA technology
29
New cards
What does PCR stand for
Polymerase Chain Reaction
30
New cards
What does it do
Makes billions of copies of a target segment of DNA in a few hours
* Quick and doesn’t need large amounts of DNA
* Quick and doesn’t need large amounts of DNA
31
New cards
Why is this important?
* Allos for a particular section of DNA to be identified and studied
32
New cards
What is Recombinant DNA technology
Joining together DNA from 2 or more sources
* can change the genetic makeup
* can change the genetic makeup
33
New cards
Why is it important
Introduces new genes into another organism’s existing DNA
* DNA is cut, altered, and then put back together
* DNA is cut, altered, and then put back together
34
New cards
What are uses of recombinant DNA in bacteria
bacteria is used to produce many important substances for the pharmacies
* Produces insulin, growth hormone, and clotting factor in large quantities
* Produces insulin, growth hormone, and clotting factor in large quantities
35
New cards
What are transgenic organisms
Organisms that possess a useful gene from other organisms
* made by way of recombinant DNA
→ Meaning, the properties in the bacteria that are easily manipulated for beneficial traits are transferred into animals
* made by way of recombinant DNA
→ Meaning, the properties in the bacteria that are easily manipulated for beneficial traits are transferred into animals
36
New cards
Types of transgenic organisms
Transgenic bacteria, plants, and animals
37
New cards
Transgenic Plants- what are they important to? Why?
food supply
GMO crops help farmers to be more productive while reducing overall costs
* pest resistant
* heat resistant
* higher nutritional content
GMO crops help farmers to be more productive while reducing overall costs
* pest resistant
* heat resistant
* higher nutritional content
38
New cards
Transgenic Animals
Genes for better meat, resistant to disease, faster growing animals
39
New cards
What is a spider goat
Goat given a gene to produce spider silk
* produces milk with silk protein
* can be spun into spider silk = bio steel
* produces milk with silk protein
* can be spun into spider silk = bio steel
40
New cards
What is biosteel
7-10x stronger than steel
Resistant to extreme temperatures
→ Can make bulletproof vests
Resistant to extreme temperatures
→ Can make bulletproof vests
41
New cards
Cloning
Creating a genetically identical organism
42
New cards
Example:
Scottish scientists were the first to clone a mammal in 1996
* Created a sheep named Dolly who suffered from lung cancer and arthritis
* Put down by lethal injection in 2003
* Created a sheep named Dolly who suffered from lung cancer and arthritis
* Put down by lethal injection in 2003
43
New cards
Cloning steps
1. obtain an egg cell
* Remove the nucleus
2. Obtain a somatic (body) cell from the “mother”
* Dolly’s cell came from an udder
3. Place the somatic cell into an empty egg
* Grow the embryo
* Implant into a surrogate mother
4. Genetic identity equal to the somatic cell donor
44
New cards
Cloning issues
Less than 2% embryos result in live birth
* Dolly was a 1/276
* Of those, many had serious health problems
* Dolly was a 1/276
* Of those, many had serious health problems
45
New cards
Benefits of cloning
1. if improved, could reproduce animals with specific benefits
* Mass produce these animals
2. Repopulation of endangered species
3. Produce whole human organs from a couple of cells
4. Stem cell research using cloned embryos
46
New cards
Gel electrophoresis
A strand of DNA is partially replicated using PCR
* electrophoresis separates DNA pieces by size to create a unique gel of bands unique to individuals
* used in DNA fingerprinting
* electrophoresis separates DNA pieces by size to create a unique gel of bands unique to individuals
* used in DNA fingerprinting
47
New cards
What are the two types of rate of evolution
Gradualism and punctuated equilibrium
48
New cards
Gradualism
* Slow, steady change over time
* slowly see change in fossils
* slowly see change in fossils
49
New cards
Punctuated Equilibrium
Stable periods interrupted by rapid change of species
* when changes happen quickly
* when changes happen quickly
50
New cards
Who is Charles Darwin
An english naturalist in the 1800’s who changed the way we viewed the world
51
New cards
What theory did he develop and what did it do
The theory of natural selection
* Gave scientific principles to what people observed (that things change over time)
* Gave scientific principles to what people observed (that things change over time)
52
New cards
Who was Lamarck
A scientist who created the original theory of evolution before Darwin, but was incorrect in many ways
53
New cards
What did he believe?
Individual organisms could change __in their lifetime__ by selectively using or not using organs
* These __acquired traits__ were then passed on to the offspring
* These __acquired traits__ were then passed on to the offspring
54
New cards
Who was Malthus
Another scientist before Darwin who came up with the idea that overpopulation lead to disease, famine, and war
55
New cards
How did Darwin apply Malthus’ theory?
The overwhelming majority of offspring die, so only the fittest survive
56
New cards
What did Hutton and Lyell come up with
They observed since the earth is extremely old. Processes that change Earth are the same ones today.
57
New cards
How did Darwin apply this
If Earth changes over time, why can’t life change too
58
New cards
Fitness
How likely you are to survive and reproduce
59
New cards
Adaptations
Things that increase ability to survive/reproduce
60
New cards
Where was natural selection proposed
in Darwin’s book - On the Origin of Species
61
New cards
What is it?
Says that organisms with variations most suited to their environment will survive and have offspring
62
New cards
What are natural selection’s 3 conditions
1. there is a struggle for existence
2. variation and adaptation are found within a species that is heritable
3. survival of the fittest occurs
63
New cards
Artificial selection
selecting the best traits that are heritable and producing them to the next generation
64
New cards
what are the 3 types of selection
directional
stabalizing
disruptive
stabalizing
disruptive
65
New cards
Directional selection
an extreme phenotype is favored
* causes allele frequency to shift over time in that direction
* causes allele frequency to shift over time in that direction
66
New cards
Stabilizing selection
Eliminates the extremes of a phenotype
* the intermediate is favored
* the intermediate is favored
67
New cards
Disruptive selection
favors the extremes and eliminates the middle phenotype
* can lead to speciation
* can lead to speciation
68
New cards
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism
69
New cards
Phenotype
Observable characteristics
70
New cards
Gene pool
The possibilities for the species
* species share a common group of genes
* species share a common group of genes
71
New cards
Gene/ allele frequency
Number of times an allele shows up in a gene pool
72
New cards
Reproductive isolation
When gene flow between 2 groups stops, so they can no longer reproduce
73
New cards
What are the 3 types of speciation / reproductive isolation
behavioral
geographical
temporal
geographical
temporal
74
New cards
Homologous structures
Structures with the same origin, but different function
* Animals that are related (have a common ancestor) but live in different environmens
* Animals that are related (have a common ancestor) but live in different environmens
75
New cards
Analogous structures
Different origin, same function
* They aren’t related but use their structures the same
* They aren’t related but use their structures the same
76
New cards
Vestigial structures
Structures that no longer have a function but were onced used in the ancestor
77
New cards
Vestigial examples
* whale pelvic girdle
* Human appendix and tailbone
* Eyeballs in blind creatures
* Human appendix and tailbone
* Eyeballs in blind creatures
78
New cards
Divergence
Evolutionary process where a species separates resulting in related species becoming more and more dissimilar
79
New cards
Convergent Evolution
Unrelated organisms evolving similar traits due to similar niches
* Ex. penguins and dolphins
* Ex. penguins and dolphins
80
New cards
Co-evolution
When a species evolving affects the evolution of another species
Ex.) if an animals gains better camouflage, its predator might gain better eyesight
Ex.) if an animals gains better camouflage, its predator might gain better eyesight
81
New cards
Adaptive radiation
A single species diverges into multiple different species
ex.) Darwin’s finches
ex.) Darwin’s finches
82
New cards
Morphological change
appearance that benefits an organism’s survival
83
New cards
behavioral adaptations
a behavior that benefits an organism’s survival
84
New cards
Physiological adaptation
internal change that benefits an organism’s survival
85
New cards
Genetic Drift
When an allele becomes more or less common in a population due to chance
* Meaning, it is random
* Meaning, it is random
86
New cards
What are the two types
Bottleneck effect
The founder effect
The founder effect
87
New cards
Bottleneck effect
An external event (natural disaster) kills off many in the population → the new population has different allele frequencies than previously
* Ex.) Pingelap when a typhoon and starvation hit
* Ex.) Pingelap when a typhoon and starvation hit
88
New cards
The founder effect
A few individuals colonize a new habitat
* can cause major changes in allele frequencies
* Ex. the Amish founders with polydactyly and dwarfism
* can cause major changes in allele frequencies
* Ex. the Amish founders with polydactyly and dwarfism
89
New cards
Human evolution
come back to
90
New cards
what were the 3 major mass extinctions
1. Snowball earth (caused by glaciation)(increase of oxygen levels)
2. Pangea forms (upsets ocean currents) (the Great Dying)
3. Meteor hits Earth (meteor that kills the dinos)
91
New cards
What did the snowball earth usher in
Cambrian explosion
92
New cards
The Great Dying
Pangea forms, volcano erupts, Earth temp rises, 96% of all life goes extinct
93
New cards
What does this usher in
The Mesozoic: Age of the reptiles
94
New cards
Meteor
wipes out dinos and 76% of life
95
New cards
What does this usher in
the Cenozoic: Age of mammals
96
New cards
What is a half-life
Time required for half of the radioactive atoms to decay
* how long something takes to decay by 50%
* how long something takes to decay by 50%
97
New cards
Characteristics of first life
* unicellular bacteria (prokaryotes)
* 3.6 BYA
* a billion years after Earth’s formation
* Fossil evidence through cyanobacteria’s stromatolites
* 3.6 BYA
* a billion years after Earth’s formation
* Fossil evidence through cyanobacteria’s stromatolites
98
New cards
Absolute dating
More precise than relative dating
* relies on radioactive isotopes which break down at a steady rate
* relies on radioactive isotopes which break down at a steady rate
99
New cards
Relative dating
Generic method of dating fossils using layers
* uses index fossils to give an approximate date for other things
* uses index fossils to give an approximate date for other things
100
New cards
Importance of fossils
1. Show evolution
2. Reveal different species
3. Can be used for dating