IDSC topic 4
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/15
Earn XP
Last updated 7:30 PM on 2/12/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
1
New cards
enterprise resource planning (ERP)
tightly integrated software used to automate back-office functions in a single management information system
* “one source of truth"
* stores data so that **all departments** of a business **can share information**
* All financial transactions **flow to the general ledger** (if we change something in the business, we need to change it in the system as well!)
* “one source of truth"
* stores data so that **all departments** of a business **can share information**
* All financial transactions **flow to the general ledger** (if we change something in the business, we need to change it in the system as well!)
2
New cards
ERP basic processes
* Procure to pay
* Order to cash
* Plan to produce
* Field to fork
* Hire to retire
* Order to cash
* Plan to produce
* Field to fork
* Hire to retire
3
New cards
challenges with ERP
* software may **not support all** business functions
* Risks in vendor lock-in, **switching cost**
* Vendors **continually updating software**, companies **need to stay current** for support
* Risks in vendor lock-in, **switching cost**
* Vendors **continually updating software**, companies **need to stay current** for support
4
New cards
estern digital (example with ERP)
* A merger of Western Digital, SanDisk, and HGST was a big challenge for the company.
* After the merger, Western Digital wanted to centralize ERP so that all three companies could work together.
* After the merger, Western Digital wanted to centralize ERP so that all three companies could work together.
5
New cards
clour based (example with ERP)
* TTI Inc., a specialty distributor of electronic components based, needed to go beyond replacing its legacy system.
* “This technology gives us the guardrails to do things in a standardized, simplified way around the world. “
* That foundational process, with the help of technology, allows us to look globally, act locally.
* “This technology gives us the guardrails to do things in a standardized, simplified way around the world. “
* That foundational process, with the help of technology, allows us to look globally, act locally.
6
New cards
supply chain management (SCM)
* management of the flow of goods and services
* Includes the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption.
* Includes the movement and storage of raw materials, work-in-process inventory, and finished goods from point of origin to point of consumption.
7
New cards
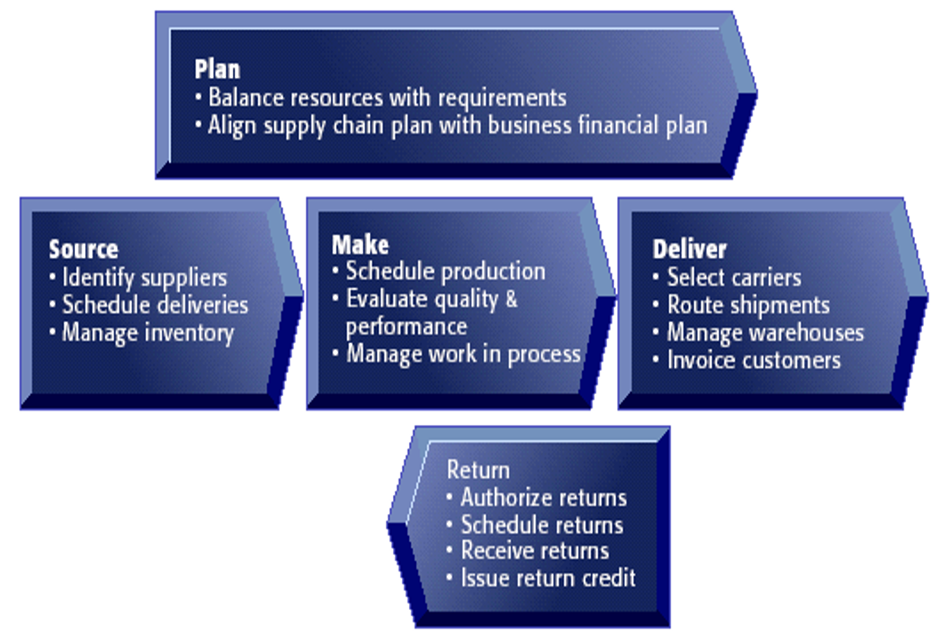
5 processes of SCM
* plan
* source, make, deliver
* return
* source, make, deliver
* return
8
New cards
==WHAT IS ERP ARTICLE:==
\
what is ERP?
\
what is ERP?
ERP systems collect and organize key business information and help organizations run lean, efficient operations, even as they expand.
* Each module pulls information from and pushes information into the central database that is a key component of an ERP system.
* Each module pulls information from and pushes information into the central database that is a key component of an ERP system.
9
New cards
two main approaches:
1. to purchase software that can handle each of these core business functions like accounting, sales, inventory and manufacturing from different vendors. -> then integrate with a central database (ERP)
2. to buy all the modules you need from the ERP vendor and avoid integrations since the applications are already designed to work together. (best option for the large majority of businesses thanks to its simplicity)
10
New cards
the 13 ERP modules:
1. finance
2. procurement (manages purchasing raw or made materials)
3. manufacturing
4. inventory mgmt
5. order mgmt
6. warehouse mgmt
7. supply chain mgmt
8. CRM
9. project service resource mgmt
10. workforce mgmt (keeps track of attendance and payroll)
11. HRM (keeps track of PTO and performance reviews)
12. ecommerce (websites)
13. marketing automation
11
New cards
how does ERP help businesses
* access data from everywhere
* Information is always up-to-date
* Business decisions based on the same data
* Information is always up-to-date
* Business decisions based on the same data
12
New cards
benefits of ERP
1. **Cost savings**
2. **Workflow visibility**
3. **Reporting/analytics**
4. **Business insights/intelligence**
5. **Regulatory compliance & data security**
6. risk mgmt
7. data security
8. collaboration
9. **Scalability**
10. flexibility
11. customization
12. **Customer & partner management**
13
New cards
dissadvantages of ERP
1. system cost
2. need for training
3. data conversion cost
4. complexity
5. maintenance
6. doesn’t solve process and policy issues
14
New cards
==What Is Supply Chain Management ARTICLE:==
\
what is the main goal of SCM?
\
what is the main goal of SCM?
make the most of the resources involved in a supply chain and be as productive as possible
15
New cards
what is the SCM process?
1. planning
2. sourcing
3. making
4. delivering
5. returning
16
New cards
benefits of SCM
* Keeps Businesses Competitive & Paces with Technology
* Creates Productive Environments
* Proactive Strategy (leads to creative thinking)
* Satisfies Customers While Reducing Operating Costs
* Creates Productive Environments
* Proactive Strategy (leads to creative thinking)
* Satisfies Customers While Reducing Operating Costs