Colligative properties of solutions
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
What are colligative properties of a solution ?
Properties determined by the number or the mole fraction of components in the solution and are independent of the nature of the solutes and their molecular weights
Factors of solvents in colligative properties
Vapor pressure lowering
Boiling point elevation
Freezing point depression
Diffusion
Osmotic pressure
What are supercritical fluids
liquids and gases at temperatures and pressures above their critical points
What is phase transition
the absorption or liberation of heat and/or by a change in pressure at a constant pressure
What is vapor pressure?
pressure exerted by vapour in thermodynamic equilibrium with the condensed phases ( solid or liquid ) at a given temperature in a closed system
Define volatile
A substance with a high vapour pressure at normal temperatures
How does vapour pressure increase
As the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules also increases,
and as the molecules’ kinetic energy increases, the number of molecules transitioning into a vapour also increases,
thereby increasing the vapour pressure
The equilibrium vapour pressure is an indicator of the
evaporation rate of the liquid and relates to the tendency of particles to escape from the liquid ( or a solid)
The vapour pressure of water is the pressure at which water
is in thermodynamic equilibrium with the condensed state
Define Raoult’s law
The vapour pressure lowering is directionally proportional to the mole fraction of the solute
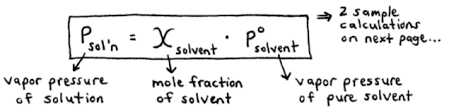
What kind of solution deviate from Raoults law ?
Non- ideal solutions
What is an ideal solution ?
No interactions between the components of the solution
Define boiling point
heat at which a liquid turns into a vapour when it is heated to its boiling point
Normal boiling point means ?
temperature at which vapour pressure of a liquid is equal to the atmospheric pressure
What does the Boiling point elevation depend on?
concentration of the solution
Define freezing point?
temp at which the solid and the liquid coexist and their vapour pressures are equal
Define Osmosis
A biophysical phenomenon occurring commonly in biological systems in which cells of a fluid compartment are separated by semipermeable membranes
Hydrostatic pressure equalizes solvent flow when there is a
net transfer of solvent molecules into a solution
Define Osmotic pressure
The pressure that must be applied to the solution side to stop fluid movement when a semipermeable membrane separates a solution from pure water
Osmotic pressure in an ideal solution is affected
temperature and volume
Why are the colligative properties of electrolyte solutions smaller
due to the formation of ion pairs at higher concentrations
Osmosis helps the internal environment of the organism by…
stabilising the internal environment and balancing the levels of water and intracellular fluids
Osmolarity
regulates solute concentration in and out of cells and aids in excreting excess water out of the body
Name the 3 types of solutions
isotonic
hypertonic
hypotonic
Isotonic
equal concentration