Instrument APRB
1/129
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
130 Terms
PERSONAL DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR FLIGHT
Pilot Certificate
Medical certificate
Photo ID
AIRCRAFT DOCUMENTS REQUIRED FOR FLIGHT
Airworthiness certificate
Registration certificate
Operating limitations
Weight & Balance data
How to get a BasicMed
Bring form 8700 to a licensed state physician
Must have held an FAA medical after July 14th, 2006
Who can exercise the privileges of BasicMed?
Private Pilots acting as PIC
required flight crew member (such as safety pilot)
Flight instructors
Pilot Examiners
66 HITS
Within the preceding 6 months a pilot must have performed and logged:
6 Instrument approaches
1 hold, interception, and tracking using navigational electronic systems
Mandatory VFR Reporting Points
Missed Approach
Airspeed change +/- 10kts or 5% of filed airspeed whichever is greater
Reaching a holding point/fix. Report time and altitude
VFR on top
ETA change =/- 3 mins
Leaving a holding fix/point
Outer marker
Unforecasted Weather
Safety of flight
Vacating an altitude
Final approach fix
Radio/nav failure
Compulsory reporting point
500- unable to maintain a 500 fpm climb/decent
What happens after those initial 6 months expire?
You have an additional 6 months to regain currency by performing the “6 HITS” with a safety pilot.
What are the safety pilot requirements?
Holds at least a private pilot certificate with the appropriate category and class
A valid medical/BasicMed.
Have adequate vision forward and to each side of the aircraft.
Aircraft must have a dual control system.
What happens if those additional 6 months expire?
An Instrument Proficiency Check (IPC) is required. Administered by a CFII or DPE
Proficiency vs currency
Proficiency is a pilot's ability to fly skillfully and safely beyond legal minimums
Currency is the bare minimum needed by the FAA that legally allows the pilot to act as PIC
What makes a plane airworthy?
If you keep up to date with it’s AD’s and inspections
How long are AD’s valid for?
Each AD is different and one must adhere to its compliance time.
How long is an aircraft registration good for?
7 years
What inspections are needed
Annual
VOR (30 days)
100 Hour
Altimeter (24 months)
Transponder (24 months)
ELT (if the battery was run for more than 1 hour or 12 months)
Static (24 months)
Types of VOR checks
VOT checks
Dual receiver checks
Airborne checks
Ground checks
VOT Check error allowed?
Plus or minus 4
Dual receiver check error allowed?
4 degrees total
Airborne VOR check error allowed?
Plus or minus 6
Ground VOR check error allowed?
Plus or minus 4
KOEL
Kinds of equipment list
Produced by our manufacturer & approved by the FAA
Minimum list of equipment must be working for certain operations
For all make/models
General aviation
MEL
Minimum equipment list
Produced by the owner/operator & approved by the FAA
List of what equipment can be inoperative and not ground the plane
Specific to serial # and registration
Comprehensive equipment list
A document, typically found in an aircraft's Pilot Operating Handbook (POH), that lists all the equipment installed in the aircraft, including both required and optional items
What are PIREPS?
Pilot Reports
How can you file a PIREP
through ATC
Flight Service Station
Online through Aviation Weather Center (AWC)
AIRMETS
Moderate weather advisory
What are AIRMETS and how long do they last?
AIRMETS warn of moderate weather and last 6 hours
What kind of AIRMETS are there?
AIRMET S, T, Z
AIRMET S
IFR conditions or mountain obstruction
AIRMET T
Moderate turbulence or surface winds of 30 kts or more
AIRMET Z
Moderate icing
What are SIGMETS and how long do they last?
SIGMETS warn of severe weather and last 4 hours
What kind of weather phenomena are associated with SIGMETs?
Dust storms
Sandstorms
Severe Icing
Severe turbulence
Volcanic Ash
What are Convective SIGMETS and how long do they last?
Warn of severe convective activity and they last 2 hours
What kind of weather is associated with convective SIGMETs?
Surface Winds equal or greater than 50kts
Hail
Tornadoes
Thunderstorms
What is Windshear?
Abrupt, drastic change in wind direction or speed.
Where are Windshear Reports found?
On PIREPS or METARs
Where can you find Winds Aloft?
On Aviationweather.gov
Read this Winds aloft.
2109
Winds from 210 at 9 kts
Read this Winds aloft.
1819+13
Winds from 180 at 19 kts and 13*C temp
Read this Winds aloft.
773350
subtract 50 from “77” and add 100 to “33”. This will read as winds at 270 at 133 kts with a temperature at -50*C
Read this Winds aloft.
783658
subtract 50 from “78” and add 100 to “36”. This will read winds at 280 at 136 kts with a temperature of -58*C
Fronts
Are transition zones between two air masses of different densities. Can extend both vertically and horizontally
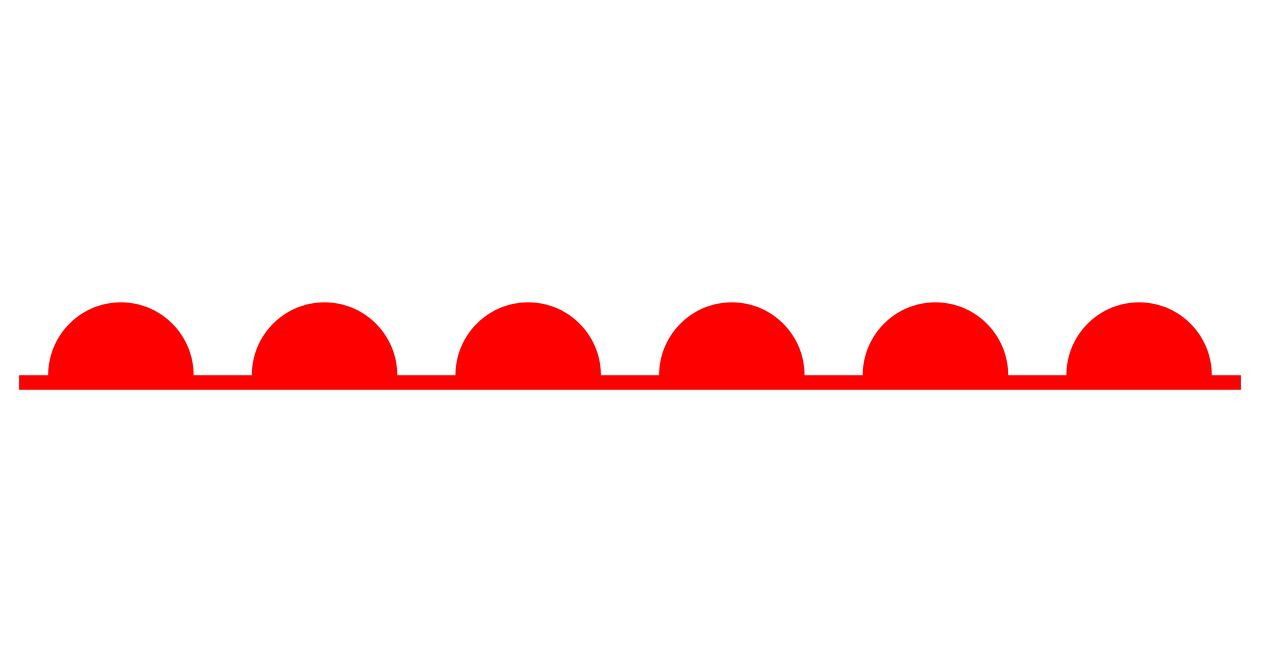
What is this and what weather is associated with this?
Warm front. Expect IFR conditions, steady precipitation, and overcast clouds (stratus clouds).
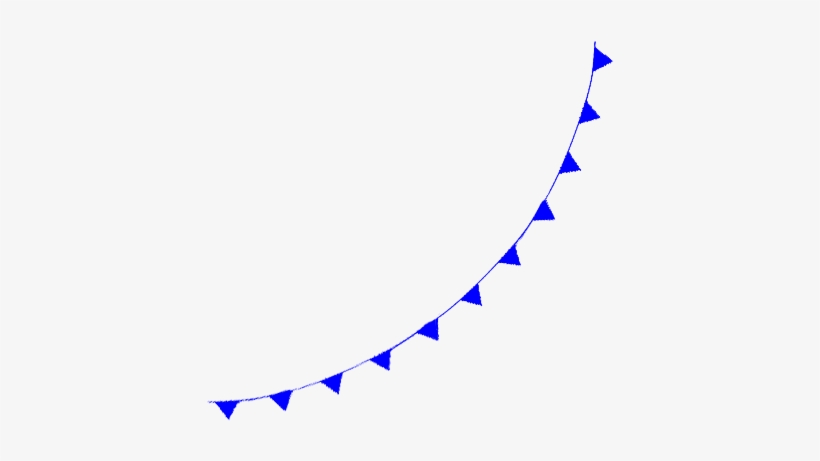
What is this, how does it move, and what kind of weather is associated with this?
Cold front.
It is fast moving, it shovels up the warm air and replaces it with cold air.
Expect bad weather, violent thunderstorms, and cumulonimbus clouds.
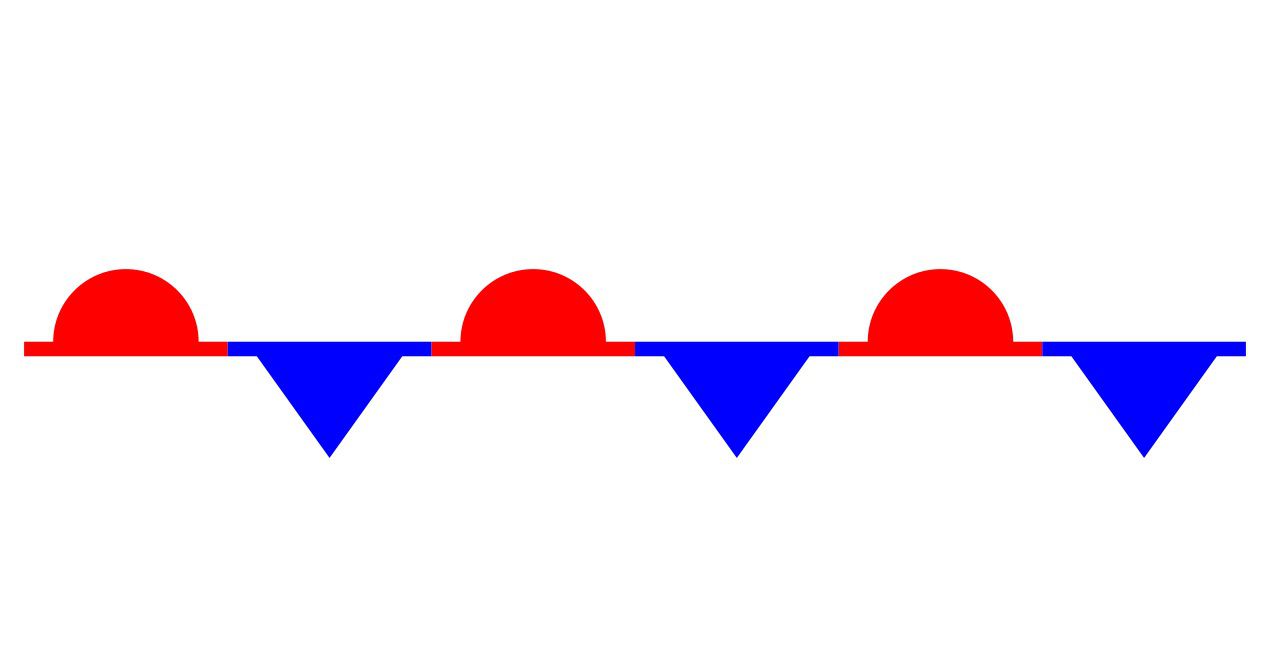
What is this and what kind of weather is associated with this?
Stationary front. Expect cloudy and rainy weather for a prolonged period of time until the front passes. Where the cold and warm front meet head on.

What is this and what kind of weather is associated with this?
Trough lines. Expect cloudy, possible rain, and gusty winds

What is this, how does it move, and what kind of weather is associated with this?
Occluded front.
Both warm and cold fronts are moving in the same direction
Expect cloudy with some rainfall immediately followed by a thunderstorm.
METAR
Meteorological Aerodrome Report
How often are METARs issued?
on the 55th minute of every hour
Special METAR? (SPECI)
reports issued when conditions warrant a more frequent update than the hourly routine METARs
TAF
Terminal Aerodrome Forecast
How far can a TAF extend
5 NM from the airport
Rhime Ice
Milky white icing that forms when water droplets freeze immediately on impact with the aircraft. usually found on the leading edges of the aircraft
Clear Ice
Clear and glassy ice that forms on the airplane’s body and spreads unevenly, affecting its performance
Mixed Ice
A combination of rime and clear ice.
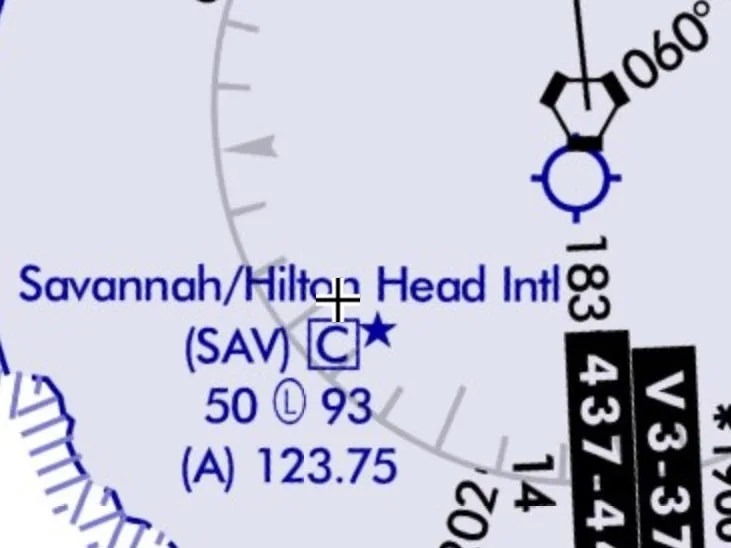
What is this?
OROCA (Off-route obstruction clearance altitude)
What is this?
Military Airport (Blue)
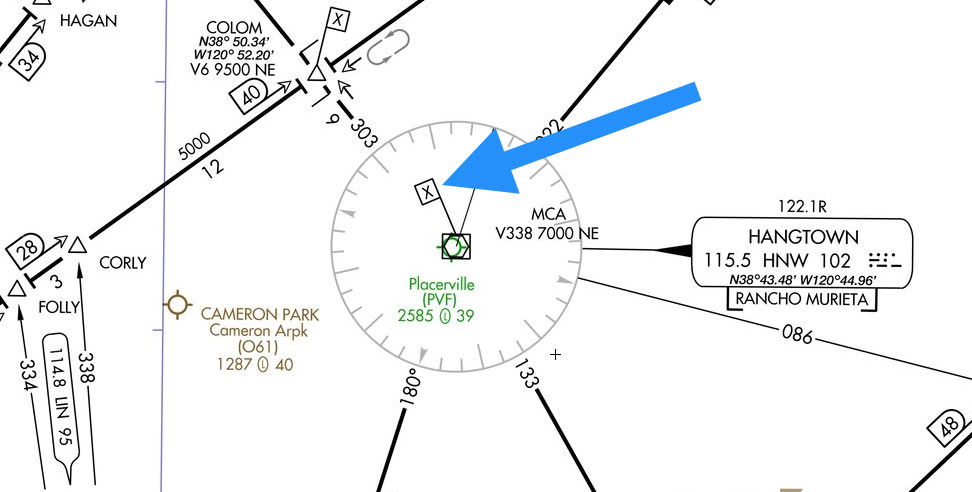
What is this?
MCA (Minimum crossing altitude)
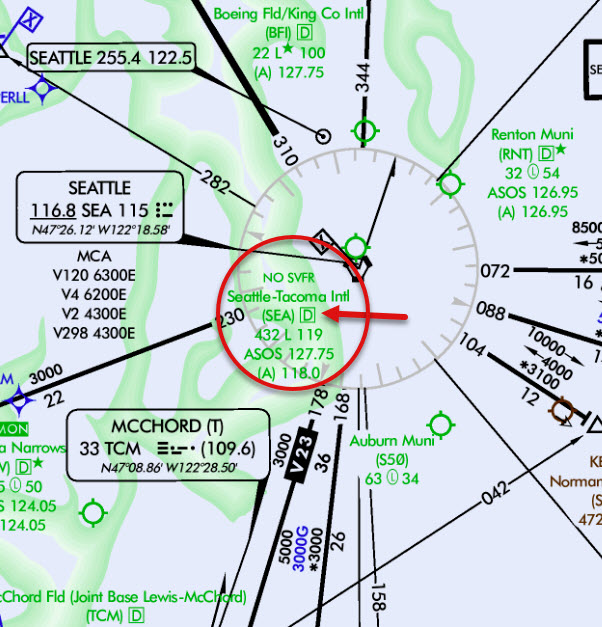
What does it mean when an airport is green on the IFR low enroute chart?
Has an FAA Instrument Approach
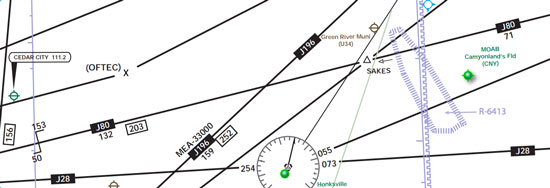
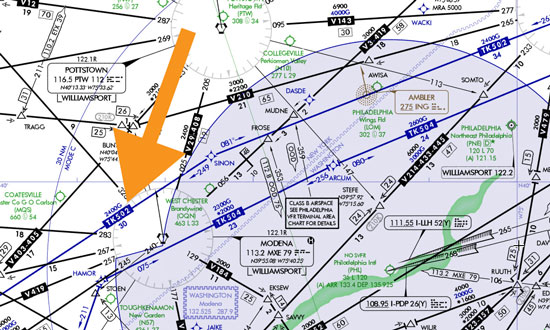
What are these?
V Airways; relay on VOR
What are these?
T Airways; relays on GPS
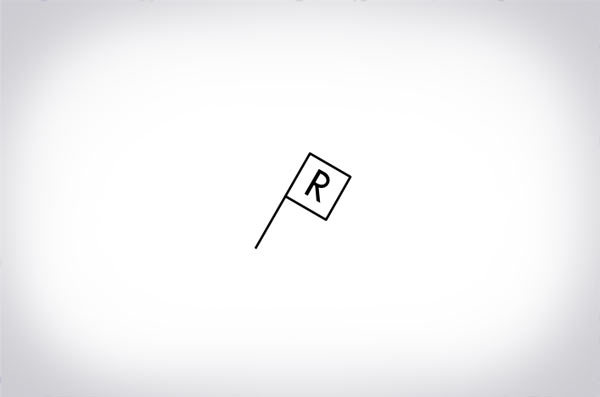
What is this?
MRA (Minimum reception altitude)
Preferred route?
Expeditious movement of traffic during heavy demand periods and the reduction of traffic management initiatives and coordination.
TEC route
Standard IFR routes within designated areas, allowing pilots to fly within approach control airspace without needing to contact air route traffic control centers.
IFR cruising altitude rules
West even thousands and East Odd thousands
How do you close a flight plan at a towered airport?
Tower will close the flight plan for you
How do you close a flight plan at a uncontrolled airport?
Call Flight Service Station or appropriate ATC facility (i.e. departure)
What are NOTAMS
Notice to Airman
types of NOTAMs
NOTAM D
NOTAM FDC
Military NOTAM
NOTAM D
Domestic NOTAM. Airports and navigation facilities.
NOTAM FDC
Changes in procedures, regulations, and airspace. I.e. TFR
Military NOTAM
NOTAMs specific to military navigational aids and airports
Types of Departure Procedures
Obstacle Departure Procedure (ODP) and Standard Instrument Departure (SID)
Standard Instrument Departures (SIDs)
pre-planned routes that pilots follow from takeoff to the en-route phase of their flight
Obstacle Departure Procedure
Provides obstacle clearance only.
CRAFT
Clearance
Route
Altitude
Frequency
Transponder code
STAR
Standard Terminal Arrival. A transition between the enroute structure to a point where an approach to landing can be made
Types of approaches
ILS, LOC, RNAV, VOR,
What are the different kinds of RNAV approaches
LNAV, LNAV+V, LP, LPV, LNAV/NAV,
What approaches are non-precision approaches?
VOR, LNAV, LOC, LP,
What approaches are precision approaches?
LNAV/VNAV, LNAV + V, LPV, ILS,
What is clearance void time?
IFR clearance issued by ATC for departures from non-towered airports, specifying the latest time the aircraft must be airborne
What is a composite flight plan?
It is a flight plan that allows both IFR and VFR with specified points on which flight rules change.
When are alternate airports required?
if the destination airport 1 hour before and 1 hour after has less than 2000 ft ceilings, and less than 3SM visibility.
What requirements need to be met to list an airport as an alternate (Precision approach)?
600ft ceiling and 2SM visibility
What requirements need to be met to list an airport as an alternate (Non-precision approach)?
800ft ceiling and 2 SM visibility
What requirements need to be met to list an airport as an alternate (no instrument approach available)?
Ceiling and visibility must allow descent from MEA approach and landing under VFR
Weight and Balance
The distribution of an aircraft’s weight, crucial for safe flight. Must remain within limits for CG and total weight.
Forward CG
increases stall speed but enhances stability
Aft CG
Decreases stall speed but reduces stability and makes spin recovery more difficult.
Spins
An aggravated stall (both wings) resulting in autorotation.
Spin Recovery
Power idle, Ailerons neutral, Rudder opposite, Elevator forward.
Different kinds of Lost Com Procedures
Altitude (MEA) and Route (AVEF) and squawk 7600
Route - AVEF
Follow last Assigned, Vectored, Expected, or Filed route in that order.
Altitude - MEA
Fly the highest of: Minimum enroute, Expected, or Assigned.
Oxygen Requirements
Part 91.211
Above 12,500 ft to 14,000 ft MSL: Crew needs oxygen after 30+ minutes.
Above 14,000 ft: Crew must use oxygen
Above 15,000 ft: Passengers must be provided oxygen
Precision Approach
An instrument approach with vertical and lateral guidance, such as an ILS. Ends at a DA (Decision Altitude).
Non-Precision Approach
Provides lateral guidance only (no glide slope). Ends at an MDA (Minimum Descent Altitude).
Missed Approach
Procedure followed if approach cannot be completed. Follow published missed approach instructions or ATC directions.
Circling Approach
A maneuver to align with a different runway after a non-precision or precision approach. Requires maintaining visual contact and staying within protected airspace based on aircraft category.