26 - Nuclear Physics
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
what are two conclusions drawn from E=mc²
- mass is a form of energy
- energy has mass
for a simple nuclear decay equation, how do you calculate the energy released, what are the steps?
mass of initial unstable nucleus - mass of nuclei produced = mass defect
△m x c² = △E
for annihilation or creation of particle and antiparticle pair, how do you calculate the energy of each photon emitted, or the mass of each particles
△m = final - inital mass
so initial is 2 x mass of one particle and final mass = 0
△m x c² = △E
divide △E by 2 as 2 photons are emitted to get the energy of each photon
define mass defect
difference between the mass of a nucleus and the mass of its individual nucleons
Define binding energy
The minimum energy required to completely separate a nucleus into its constituent nucleons
how do you get binding energy per nucleon?
why do we use it?
BE/num of nucleons
- useful to compare the stability of different nuclei
binding energy per nucleon graph
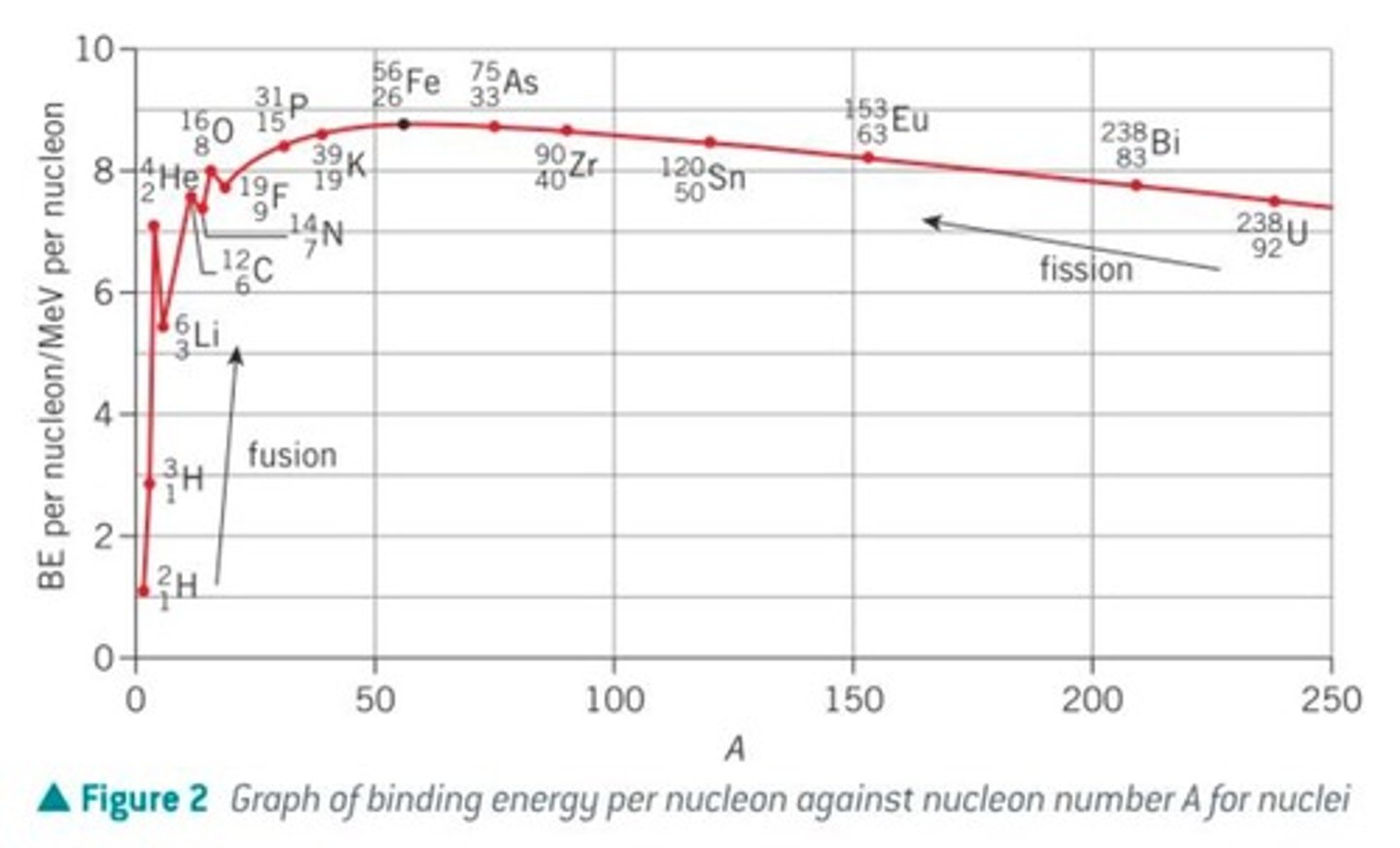
conclusions from the BE graph:
- what happens to BE per nucleon throughout the graph?
- what is the most stable isotope?
- what area is fusion, how does this graph show what the fusion process is?
- what area is fission, how does this graph show the fission process?
- for A < 56, BE per nucleon increases as A increases
- for A > 56, BE per nucleon decreases as A increases
- Iron-56 has the greatest BE per nucleon ∴ most stable isotope in nature
- in the fusion process, two low A num nuclei join to produce a higher A num nucleus that has much higher BE. Therefore, energy is released
- in fission process, high A num nucleus splits into two low A num nuclei, which have higher BE than parent nucleus so energy is released: process used in fission reactors
what is nuclear fission?
fission - a large nucleus splits into smaller nuclei causing a mass defect and energy to be released
explain the process of induced fission inside a nuclear reactor and its possible deathly dangers.
state what can be done to stop these deathly dangers (don't explain how)
- occurs when a thermal neutron is absorbed by a fissile nucleus
- the nucleus absorbs the nucleon, becoming an isotope in an excited state
- the excited state is highly unstable and quickly undergoes nuclear fission
- as well as producing 2 daughter nuclei, 3 fast-moving neutrons are also produced
- The total mass of the particles after fission is always less than the total mass of the particles before the reaction
- △m x c² = △E
- 3 fast-moving neutrons slowed down can lead to triggering more fission, causing a chain reaction leading to an explosion = danger
- to stop this in a nucelar reactor, we ensure that on avg one slow neutron survives between nuclear fission reactions
what is the moderator for in a fission reactor?
why do we need a moderator?
what are good moderators?
the moderator is to slow down the fast neutrons produced in fission reactions
- fast-moving neutrons bounce off uranium nuclei but when they collide with protons in water or with carbon nuclei, they transfer kinetic energy and slow down
- water or carbon = good moderator
what is the purpose of control rods in a fission reactor?
how would you stop fission in the reactor using the control rods?
how do the control rods carry out their purpose?
- control rods are there to ensure exactly one slow neutron survives per fission reaction by absorbing neutrons
- The position of the control rods is automatically adjusted
- to slow down or stop fission, rods are pushed into the reactor core
what are fuel rods inside a fission reactor ?
fuel rods contain fissile material
what is done with high level radioactive waste?
high-level radioactive waste, like spent fuel rods, has to be buried deep underground for many centuries because isotopes with long halflife must not contaminate our water and food supplies