Histopathology of Caries
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
caries affecting different dental tissues in different ways
-enamel: decalcification via acid
-dentin: decalcification and proteolysis (crown/root)
-cementum: resorption
-pulp: inflammation
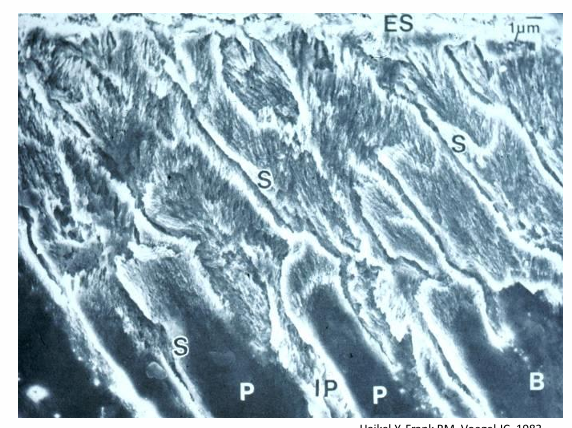
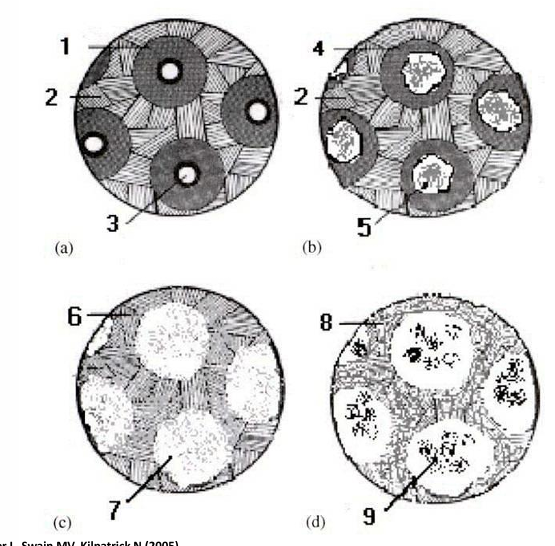
“pores” between hydroxy-apatite crystallites
-crystallites 200×40×40nm
-pores 2-10nm
-laminar pores in high caries risk group
-cylindrical pores in low caries risk group

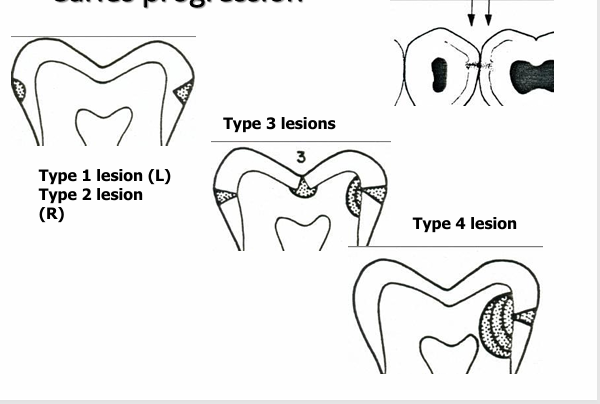
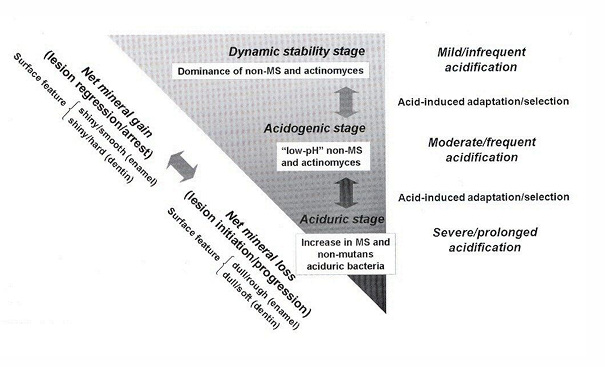
caries progression- type 1/2/3/4 lesions
-enamel lesions (pit and fissure)
fissures
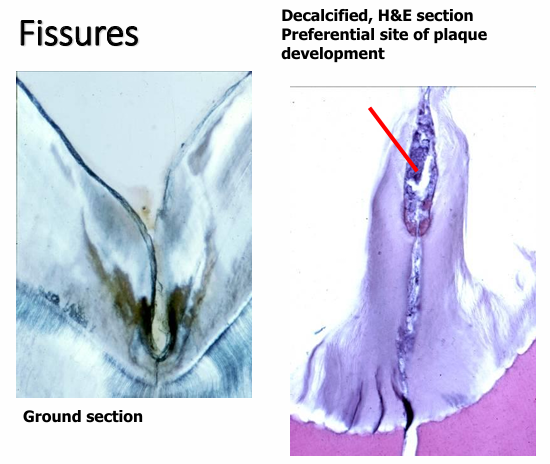
should a fissure be treated with fluoride?
-no- use a sealant
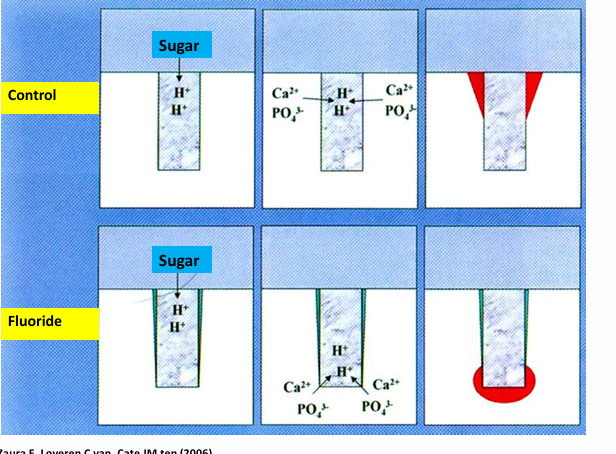
progression of plaque formation on enamel surface
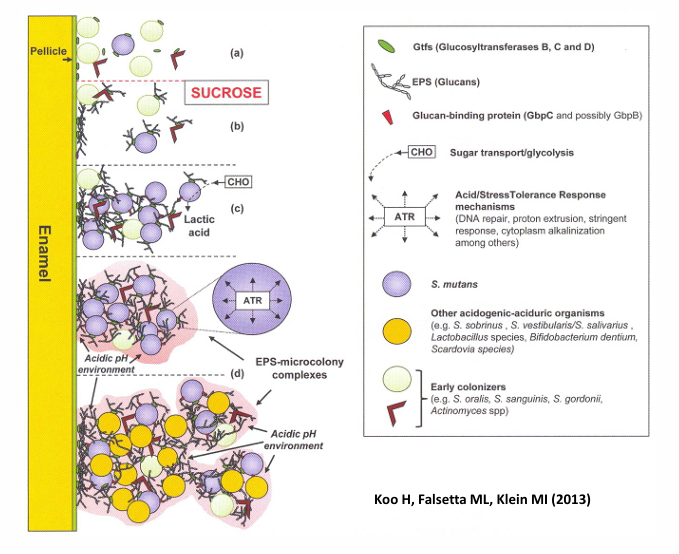
bacteria in dental biofilms- production of acid from carbohydrates
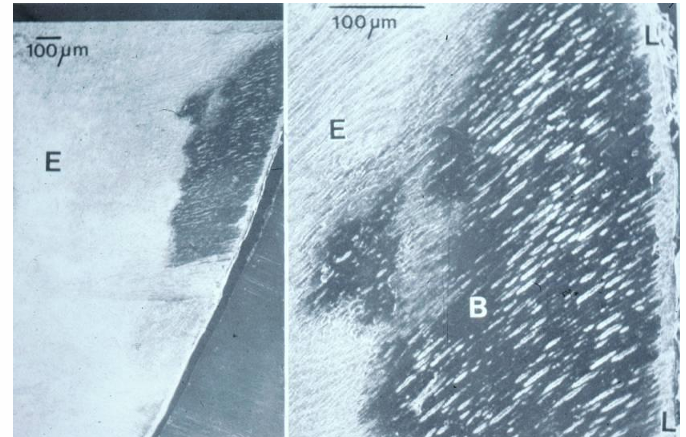
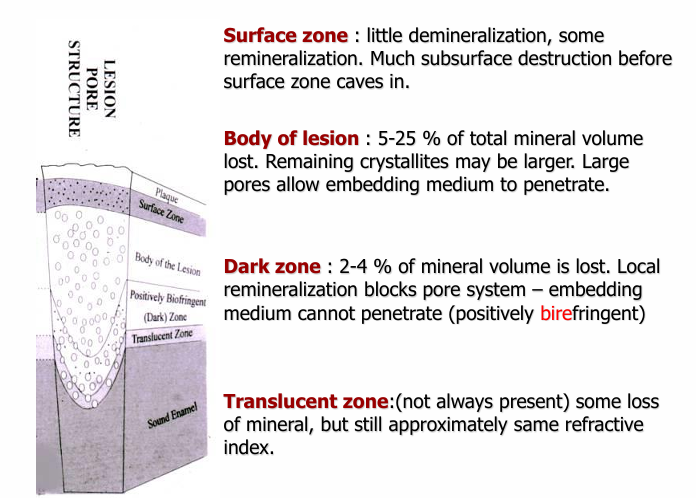
-enamel caries- white spot lesion
-early enamel lesion- loss of mineral
structure of enamel caries lesion
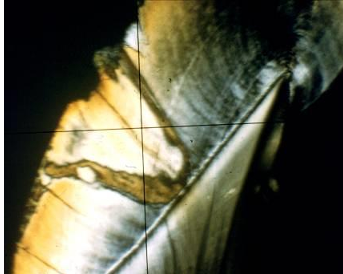
-lesion extending into dentin
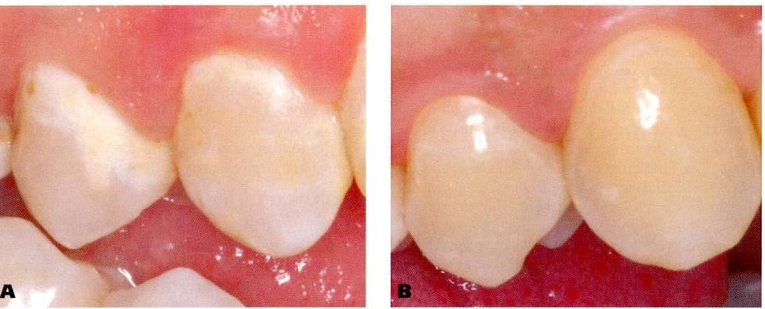
-white spot lesions- active and arrested
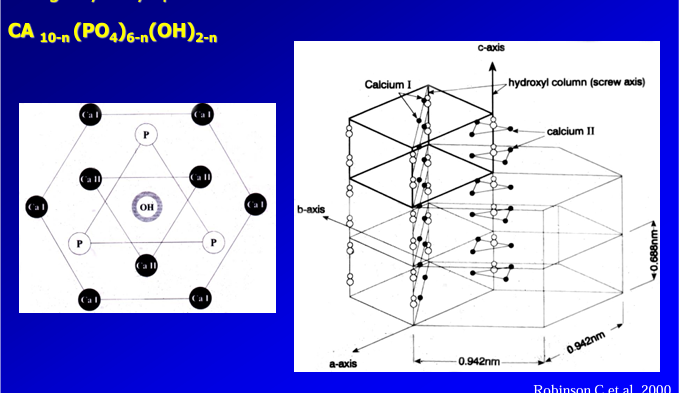
biologic hydroxy-apatite
demineralization generally starts in
-the crystallite cores
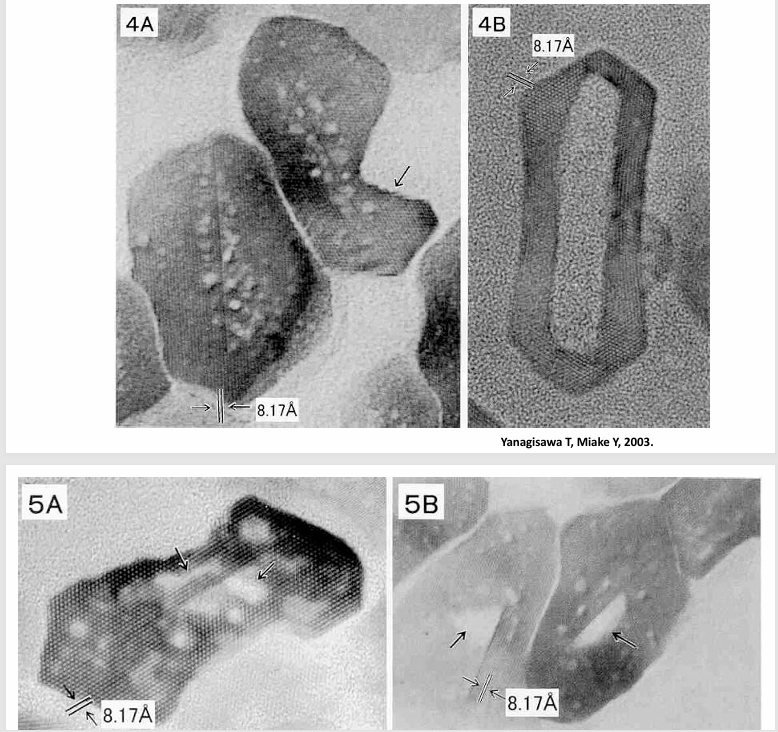
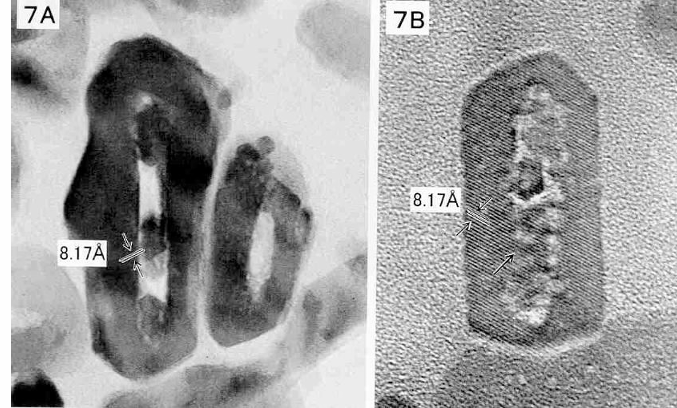
-remineralization
caries spreading into dentin
-initially a broad preferential spread along DEJ
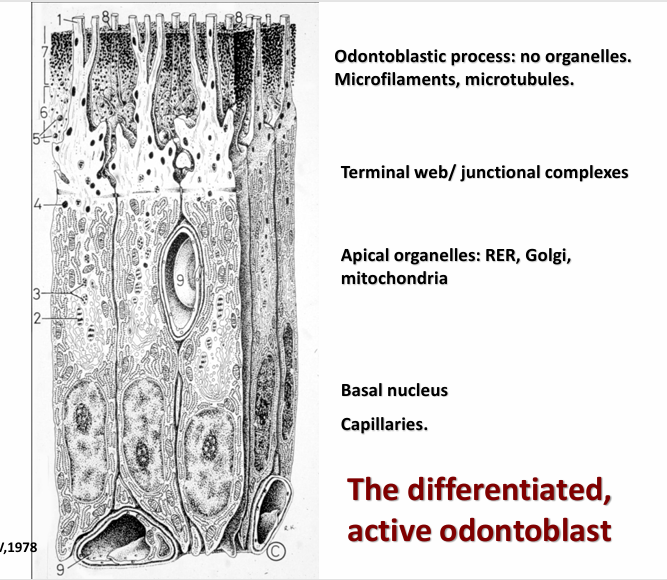
differentiated, active odontoblast
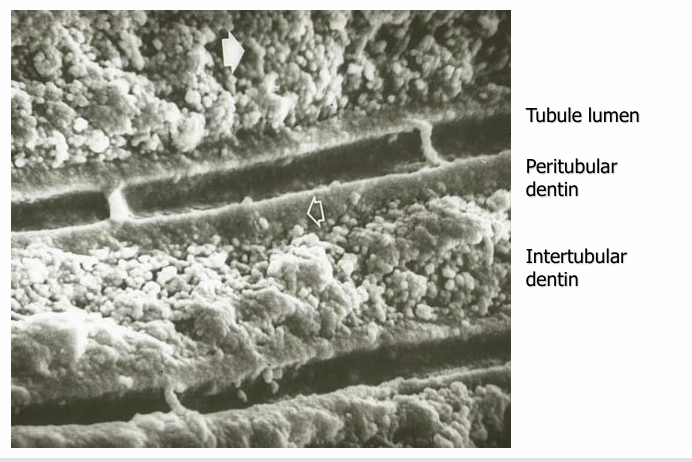
spread along dentinal tubules
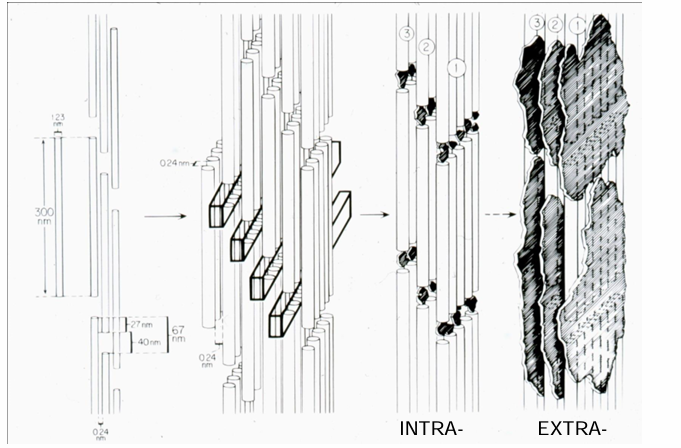
hydroxyapatite in collagen matrix
-intrafibrillar in “hole” zones
-extrafibrillar between fibrils
initial preferential spread along DEJ
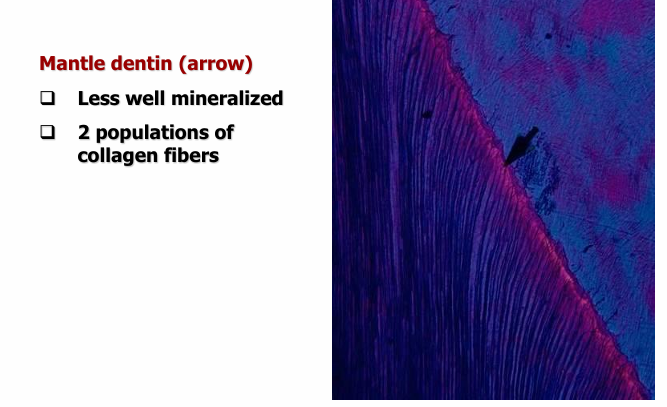
mantle dentin
-in mantle dentin (approximately 100um), two populations of collagen fibers exist:
-typical dentin collagen fibers parallel with DEJ
-thicker fibers perpendicular to DEJ
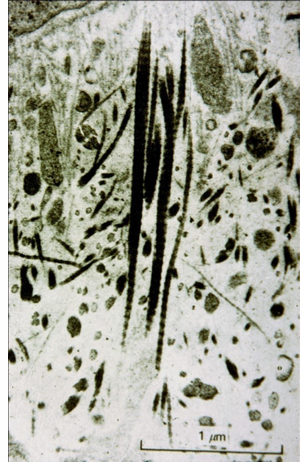
dentin caries
-decalcification plus:
-degradation of ECM by bacterial proteases
-invasion of degraded intertubular dentin by bacteria
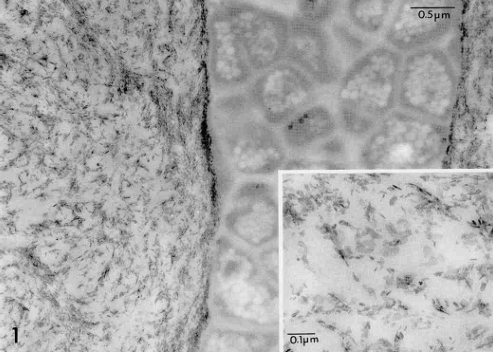
-bacterial invasion of tubules
-total absence of peritubular dentin
-demineralized dentin matrix with some reprecipitation of mineral along tubule wall
-advanced bacterial invasion
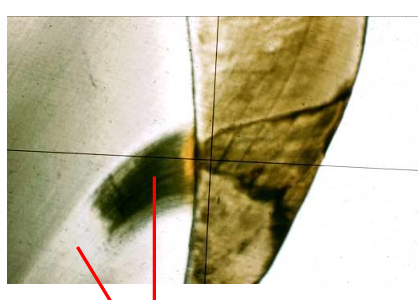
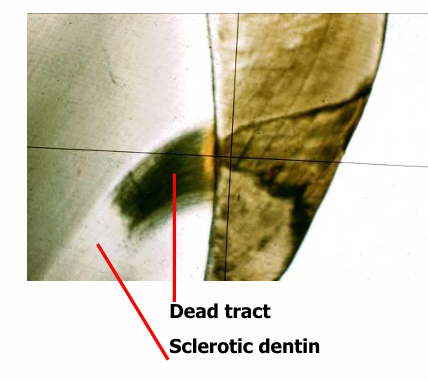
arrested dentin caries
-reprecipitation of mineral and some recalcification of decalcified dentin as the result of:
-growth of residual crystallites in intertubular dentin
-maturation of whitlockite into hydroxy-apatite inside tubular lamina
factors leading to neglect
-impaired cognitive skills
-impaired physical skills- resulting from arthritis, following a stroke
-caregiver does not contribute to oral health
-medicare does not cover dental
-lack of mobility limits visits to dentists
nursing homes
-required to do dental screening and help residents with oral hygiene
-does not always happen!
-people with well-maintained oral health throughout their lifetime: once in a nursing home, their oral health may decline in 6-8 months
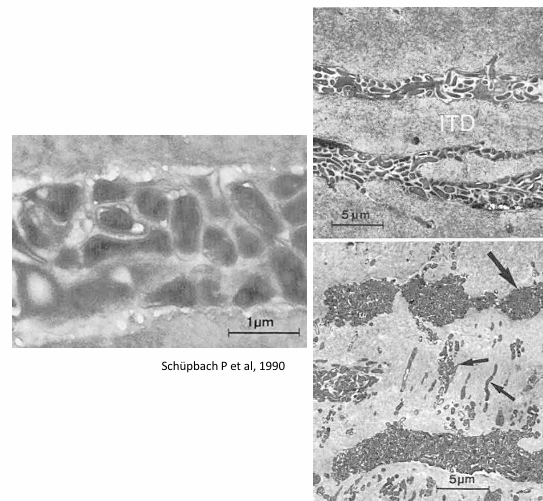
root caries
-in contrast to caries in the crown, bacterial invasion is a common feature in initial root cares

-resorption lacune in cementum
-some exposed dentin
-colonies of microorganisms in lacunae
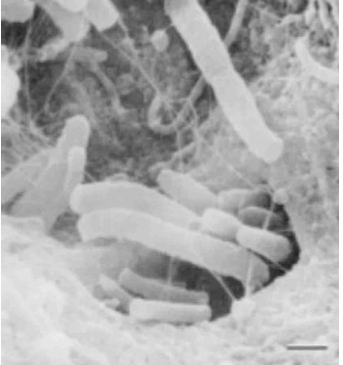
-invasion of orifices of dentinal tubules by filamentous bacteria
effects on cementum and dental pulp
-progression of infection along s-shaped tubules that are associated with the lesion
-tissue response in the corresponding pulp region
improve oral care
-single-use SDF
-provides easy, painless, and effective way to halt decay, strengthen compromised teeth, and prevent need for invasive treatments like RCT
-hardens decayed dentin, offers immediate relief from tooth pain, single-use format ensures precise, hygienic application (in-home, bedside tx with minimal discomfort)
angiogenic signaling by cariogenic bacteria
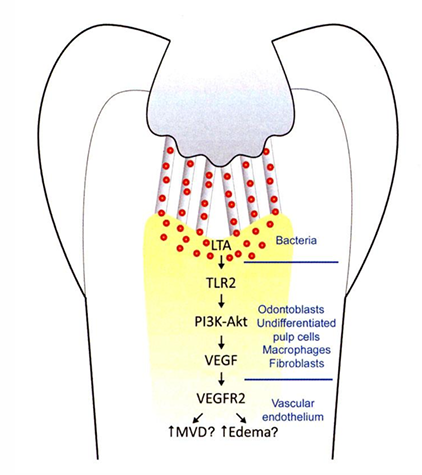
innate response of dentin-pulp complex to caries
-outward flow of dentinal fluid and immunoglobulins
-odontoblasts expressing IL-8
-neuropeptides and neurogenic inflammation
-innate immune cells (not Ag-specific): lymphocytes- NK cells, T cells; dendritic cells, monocytes, macrophages
-innate cytokines
-chemokines
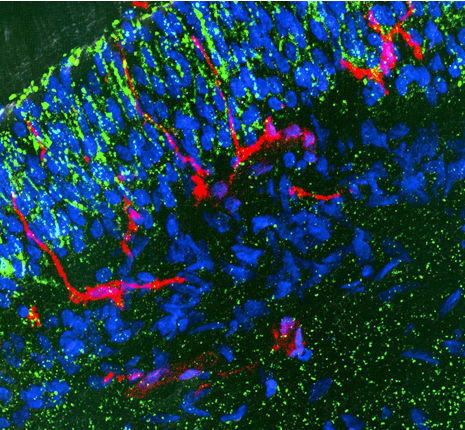
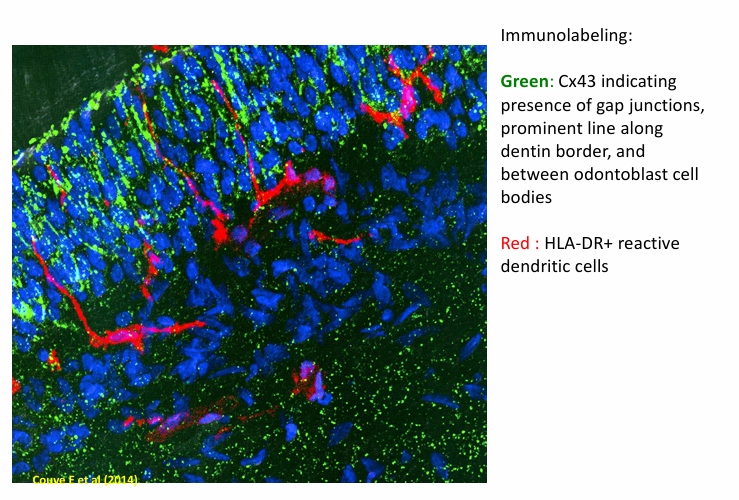

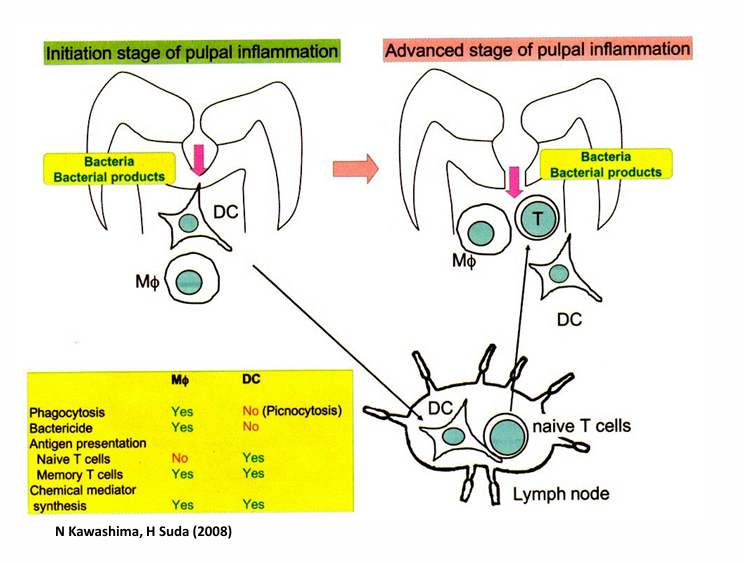
macrophages and dendritic cell actions in initiation stage and advanced stage of pulpal inflammation
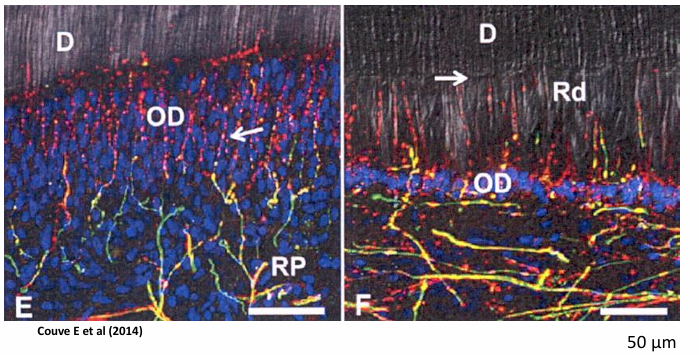
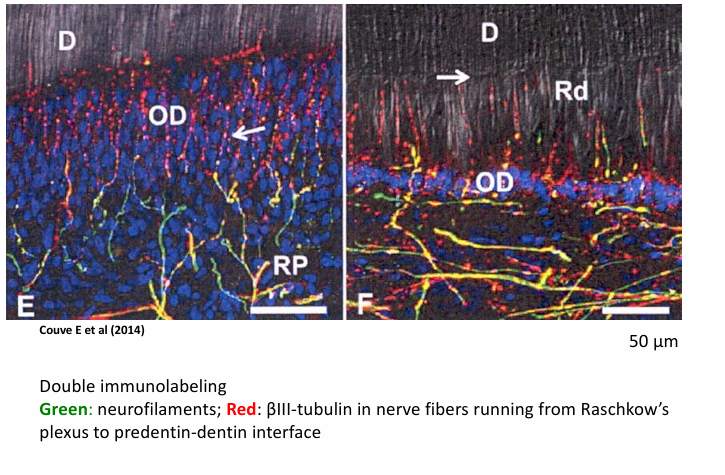
cellular events involved in reparative and in reactive dentinogenesis
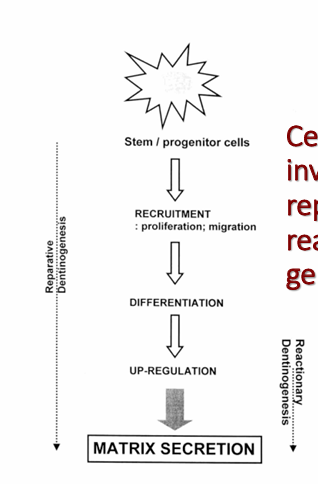
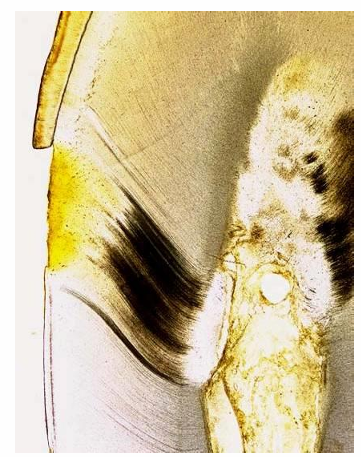
-progression of infection along s-shaped tubules that are associated with the lesion
-reactive tissue response in the corresponding pulp region
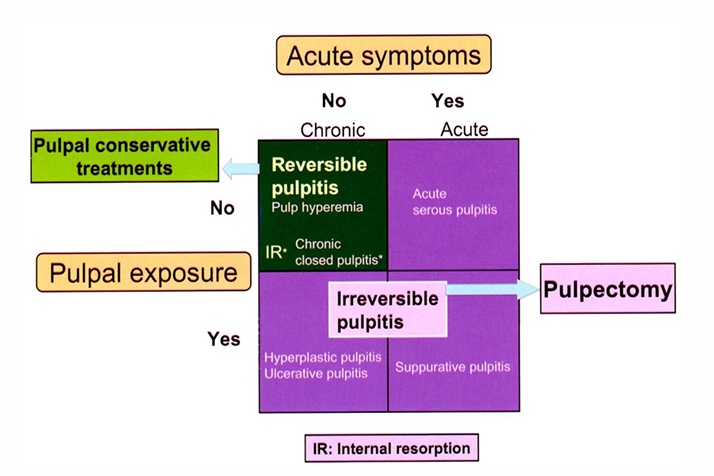
acute symptoms x pulpal exposure