Exam 1 Psyc
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
psychologist
seek ways to use the knowledge that they discover through scientific research to optimize human performance and potential in many different fields
neuroscientist
study the structure and activity of the intact, living brain in increasing detail
psychiatrist
trained physicians who specialize in mental health. They evaluate, diagnose, and treat psychiatric disorders
neuropsychology
the branch of science that studies the physiological processes of the nervous system and relates them to behavior and cognition
neurologist
a medical doctor who diagnoses, treats and manages disorders of the brain and nervous system
Freud
uncovered causes of behavior that were unconscious, or hidden from the person’s conscious awareness. His school of though is called psychoanalysis. He was a neurologist.
Wundt
The Founder of Psychology. He used scientific methods to study fundamental psychological processes, such as mental reaction times in response to visual or auditory stimuli. He tried to measure how precisely how long it took a person to consciously detect the sight and sound of a bell being struck.
Titchener
He developed his own approach to psychology called structuralism. He trained his research participants in a procedure called introspection.
James
His ideas became the basis for a new school of psychology called functionalism. It stressed the importance of how behavior functions to allow people and animals to adapt to their environments.
Psychoanalysis
a personality theory and form of psychotherapy that emphasizes the role of unconscious factors in determining behavior and personality
Structuralism
holds that even our most complex conscious experiences can be broken down into component parts, of sensations and feelings
Introspection
a method where participants view a simple stimulus, such as a book, and then try to reconstruct their sensations and feelings immediately after viewing it
Functionalism
emphasized studying the purpose, or function, of behavior and mental experiences. it stressed the importance of how behavior functions to allow people and animals to adapt to their environments
Descriptive research
includes research strategies for observing and describing behavior, including identifying factors that seem to be associated with a particular phenomenon. Answers the who, what, where, and when kinds of questions about behavior. Correlational studies are a method of this
True experiment - Cause/effect
Although two factors may be very strongly correlated, correlational studies cannot be used to demonstrate true _____ relationships.
Correlational Study
examines how strongly two variables are related to, or associated with, each other.
Independent Variable
a factor that is purposely manipulated to produce change
Dependent Variable
a second factor that is observed and measured for change in an experiment
Action Potential
a brief electrical impulse that transmits information along the axon of a neuron
Acetylcholine
a neurotransmitter that is the chemical means by which neurons communicate with muscles. Learning, memory, and muscle contractions.
Dopamine
a neurotransmitter involved in movement, attention, learning, and pleasurable or rewarding sensations
Serotonin
a neurotransmitter involved in sleep, sensory perceptions, moods, and emotional states
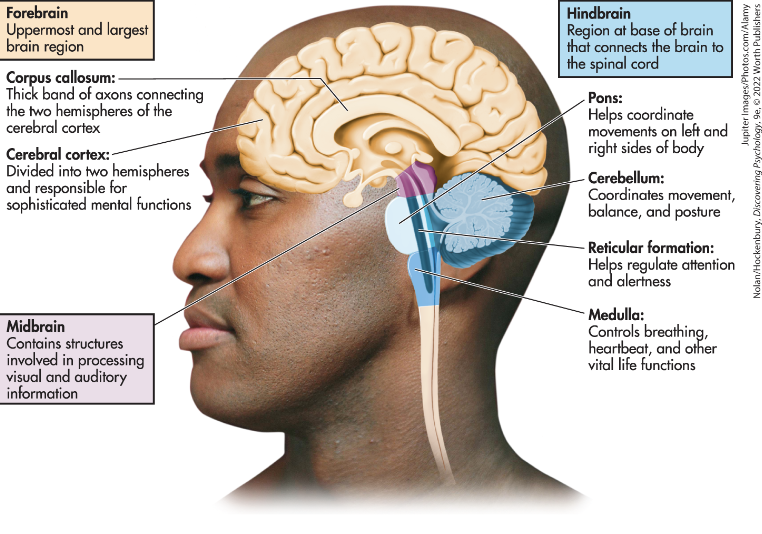
Cerebral Cortex
the wrinkled outer portion of the forebrain, which contains the most sophisticated brain centers
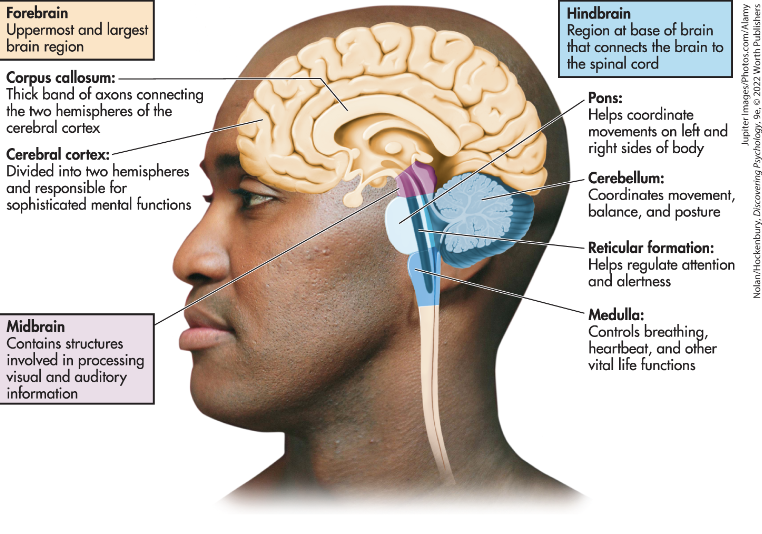
Corpus Callosum
the thick bands of axons that connects the two cerebral hemispheres and acts as a communication link between them
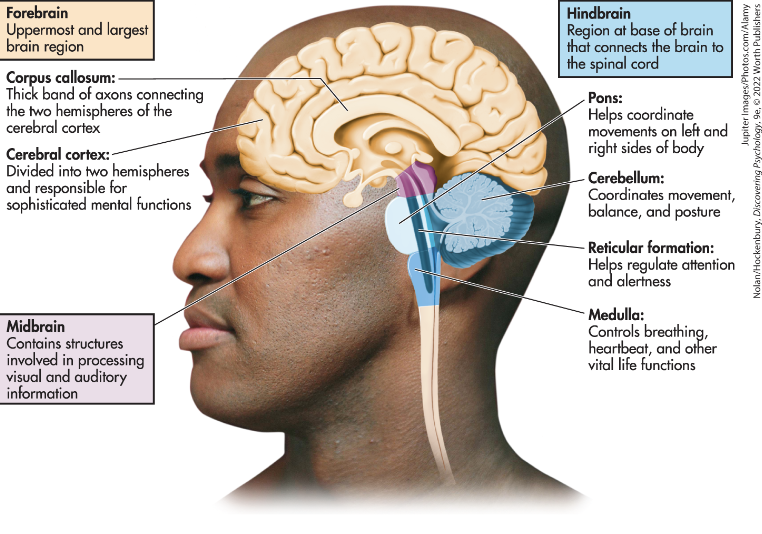
Midbrain
an important relay station that contains centers involved in the processing of auditory and visual sensory information
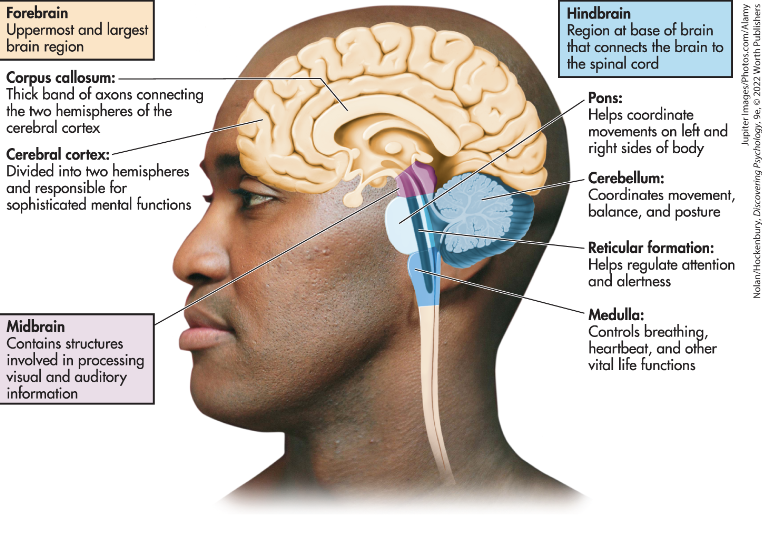
Pons
a hindbrain structure that connects the medulla to the two sides of the cerebellum and helps coordinate and integrate movements on each side of the body
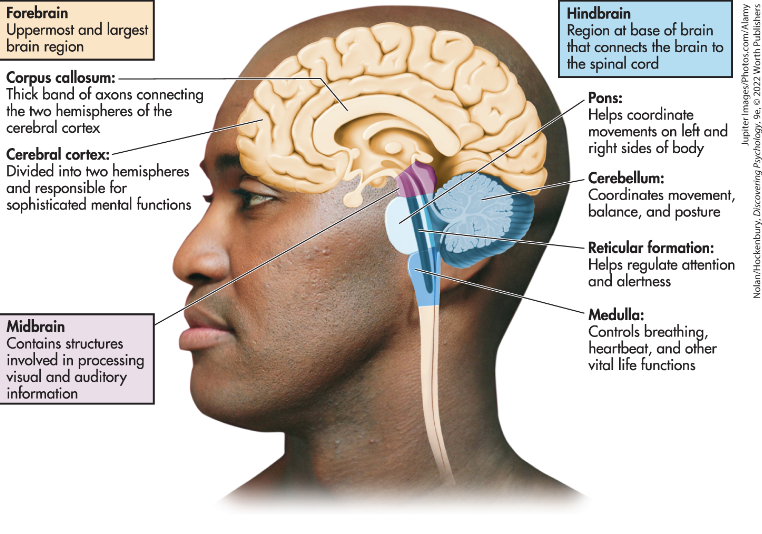
Medulla Oblongata
a hindbrain structure that controls vital life functions
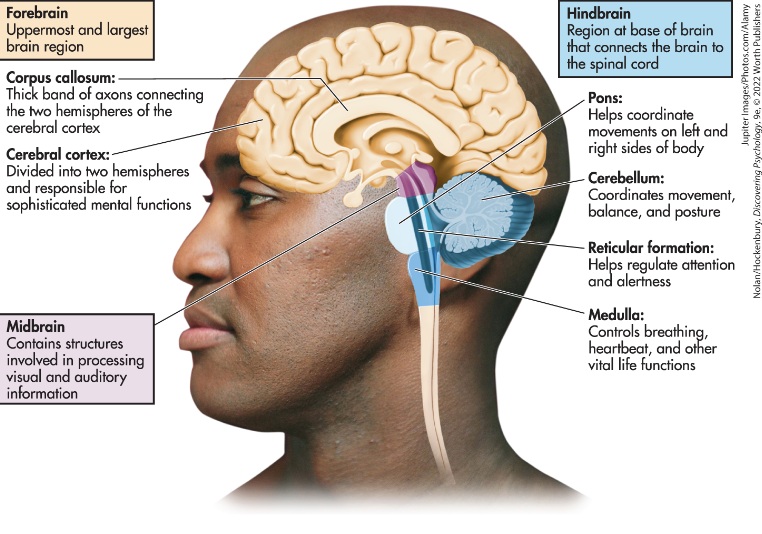
Cerebellum
located behind the pons, a large, two-sided hindbrain structure at the back of the brain that is responsible for muscle coordination and equilibrium
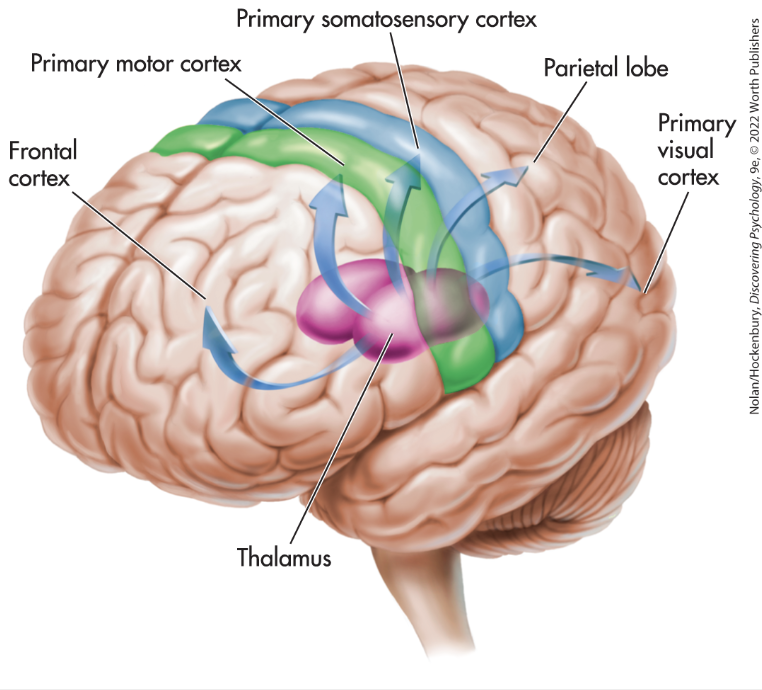
Primary Motor Cortex
sends signals to body regions. this is where the initiation of movement for different parts of the body occurs
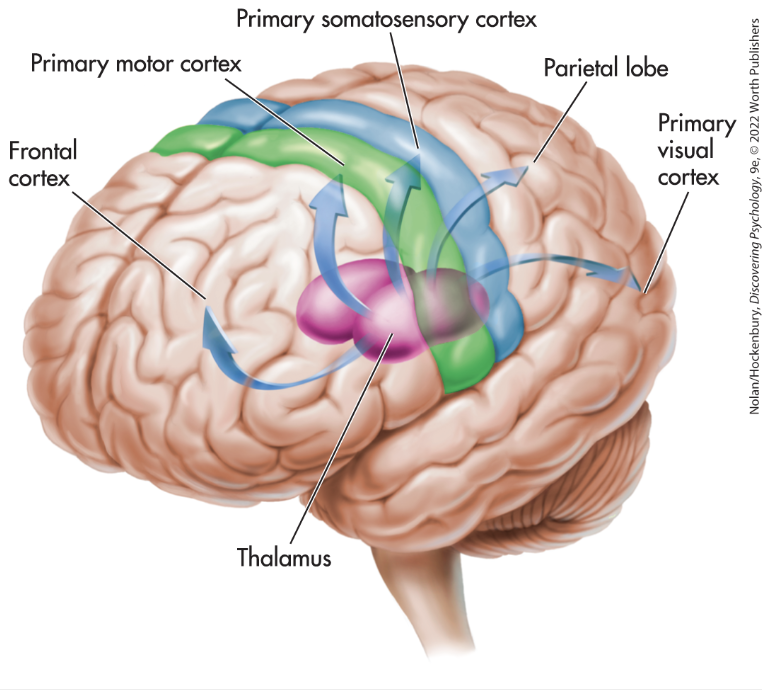
Somatosensory Cortex
signals sent to this part of the brain from body regions. touch, temperature, pressure, and pain sensations for different areas of the body occur at distinct locations here
Primary Auditory Area
receives the basic auditory information from the ears
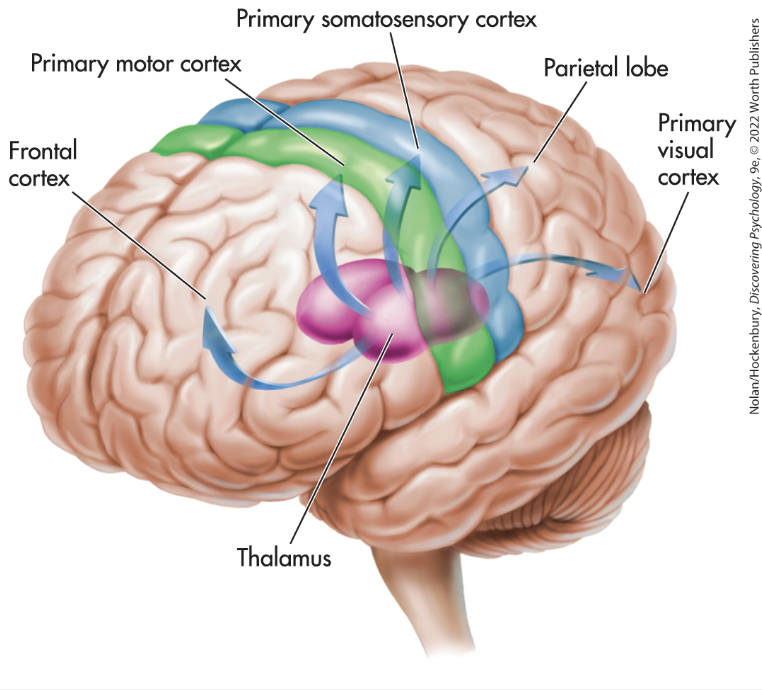
Primary Visual Area
visual information received by the eye is processed here
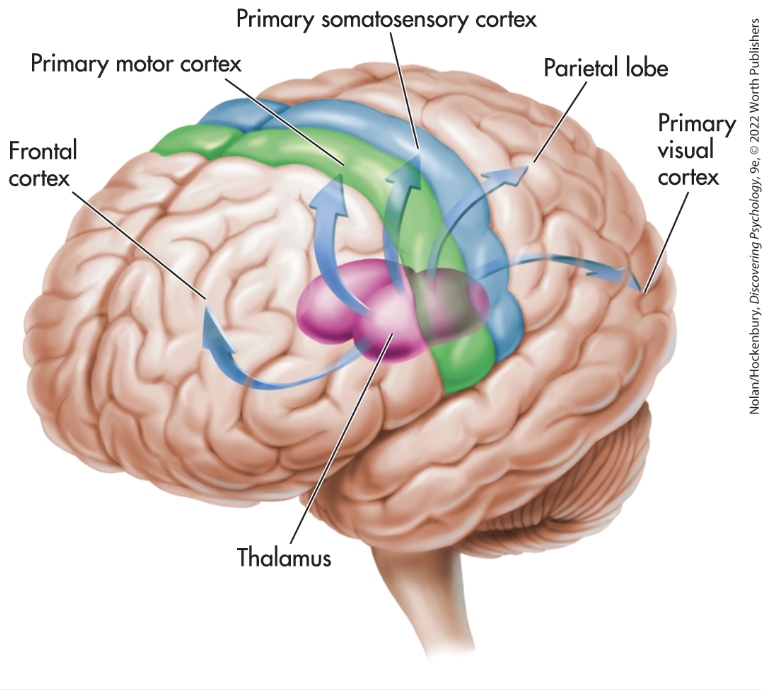
Broca’s Aphasia
difficulty speaking but able to comprehend written or spoken language
Wernicke’s Aphasia
difficulty understanding spoken or written communications