Integumentary week 1
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
224 Terms
Largest organ
skin
Skin receives how much cardiac output?
1/3
Skin is made up of what percentage of water
15-25%
Skin renews itself every
28 days
thinnest skin
eyelids
thickest skin
palms and soles
Most dust in house is
dead skin
How long does a nail take to grow
6 months
How many strands of hair loss per day
50-100
One square inch of skin contains
0 19 million cells
0 20 blood vessels (8 feet)
0 78 yards of nerves
0 1,300 nerve endings
0 20k sensory cells
0 65 hairs
0 650 sweat glands
Sweat doesn't smell
bacteria does
Epidermis thickness
0.06-0.6mm
Dermis thickness
2-4 mm
Is the epidermis vascular
No, it is avascular
what tissue lies under the dermis
Subcutaneous fatty tissue (hypodermis)
Hair follicles start in the
dermis
How long does it take a cell to travel from the basal layer to the stratum corneum
15-30 days
keratinocytes form in the
basal layer
keratinocytes are important for
healing
Thickest layer of epidermis
stratum corneum
3/4 of epidermis is
stratum corneum
stratum corneum
the most superficial layer of the epidermis consisting of dead cells
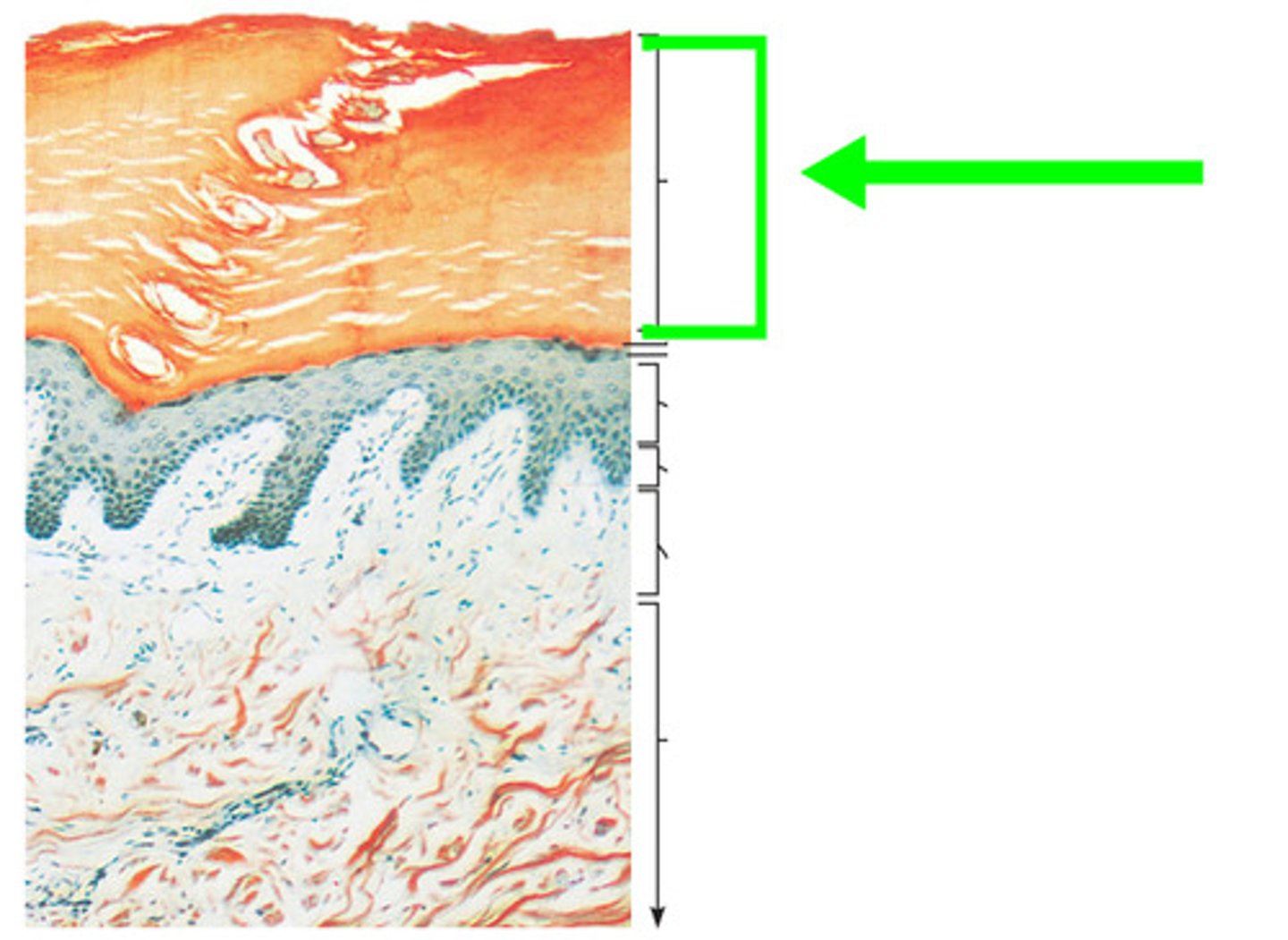
is the stratum corneum waterproof?
No, it is water resistant but not waterproof
stratum corneum permits
slow loss of water by insensible perspiration
Stratum lucidum
a layer of the epidermis found only in the thick skin of the fingers, palms, and soles
Stratum lucidum is
Clear, transparent layer of skin
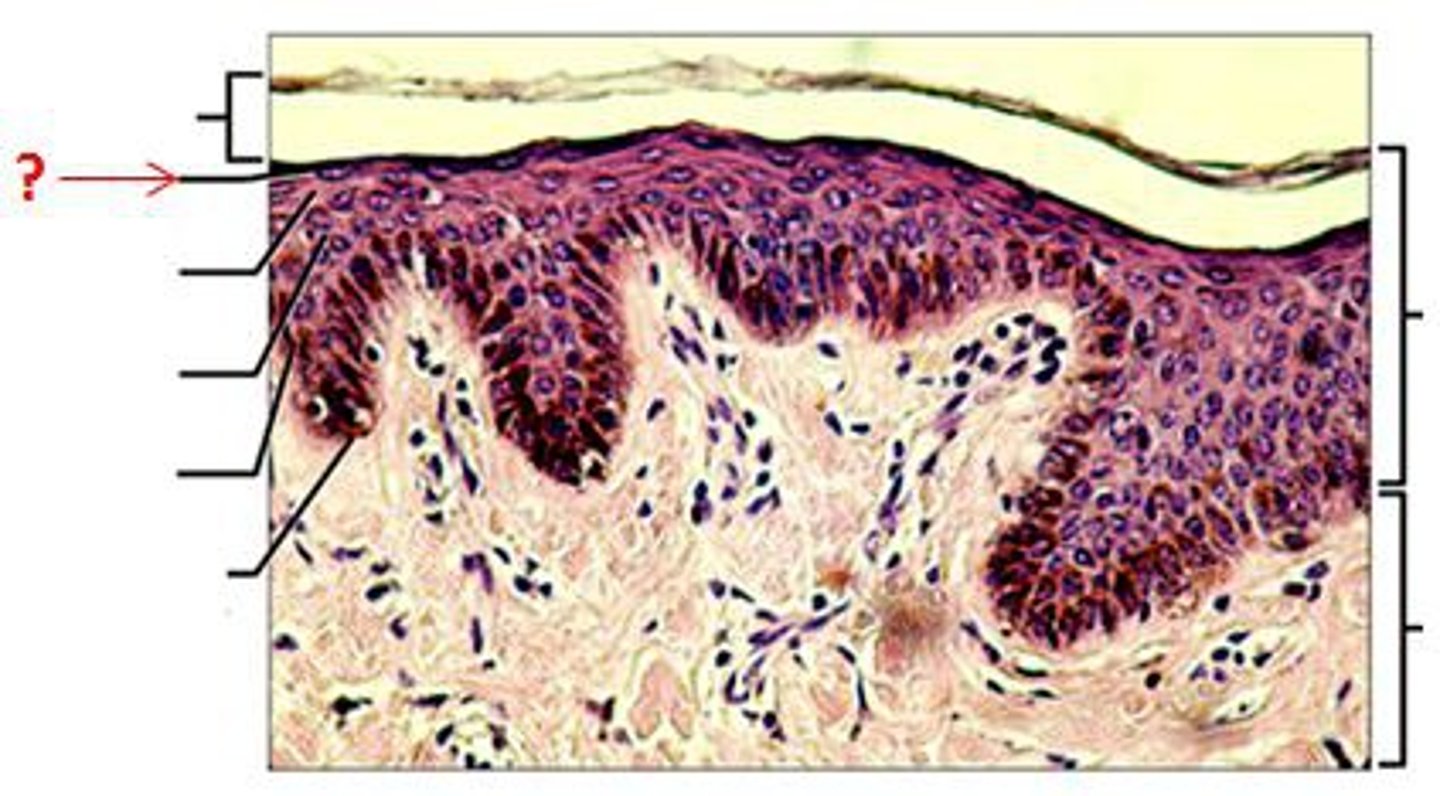
stratum granulosum
3rd layer of the epidermis
keratinocytes produce
kertohyalin and kertin in the granulosum
keratin fibers devleop as
cell becomes thinner and flatter
water resistant barrier is made where
Stratum Granulosum
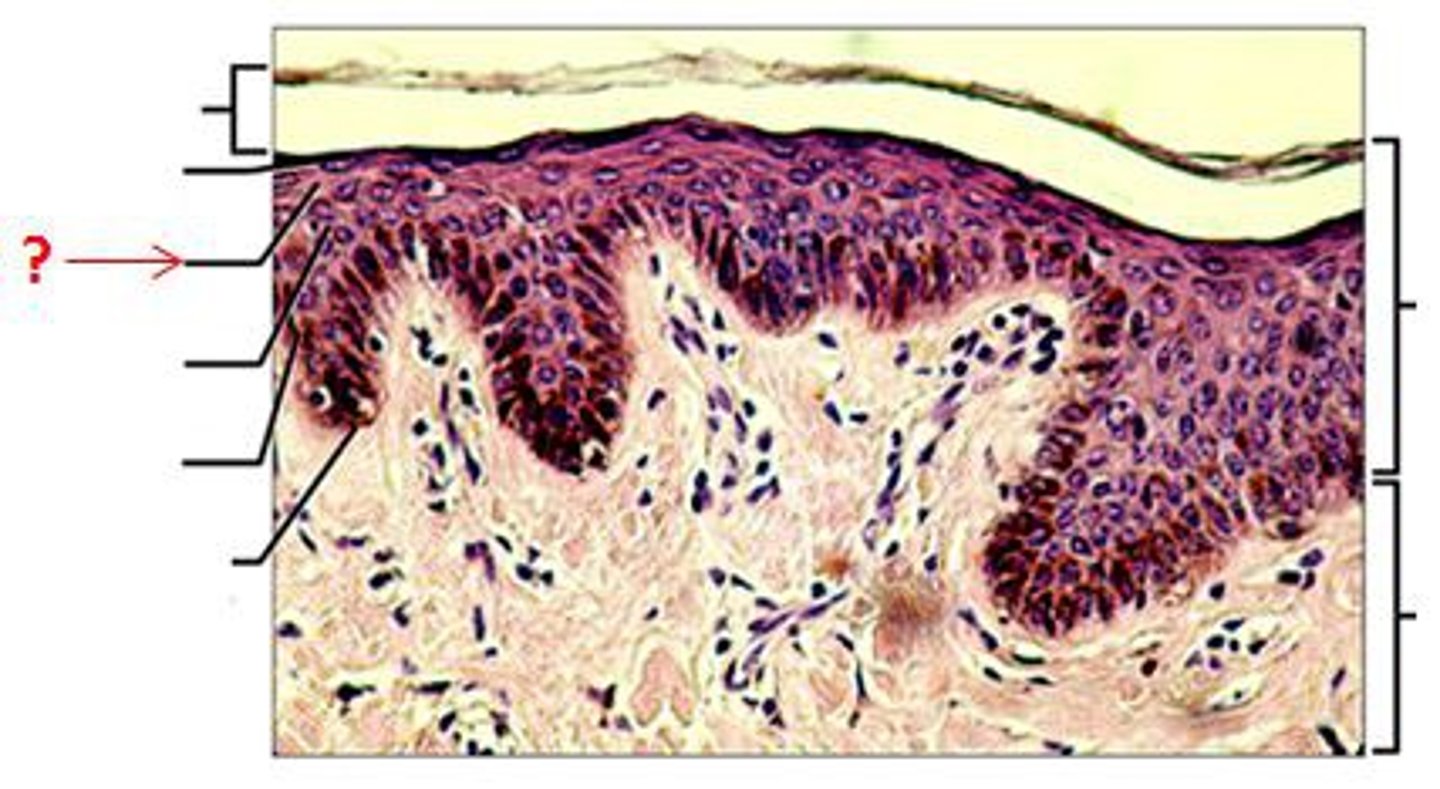
Stratum Spinosum
spiny layer
Stratum Spinosum contains
langerhans and melanocytes
langerhans cells
epidermal macrophages that help activate the immune system
melanocytes
cells that produce melanin
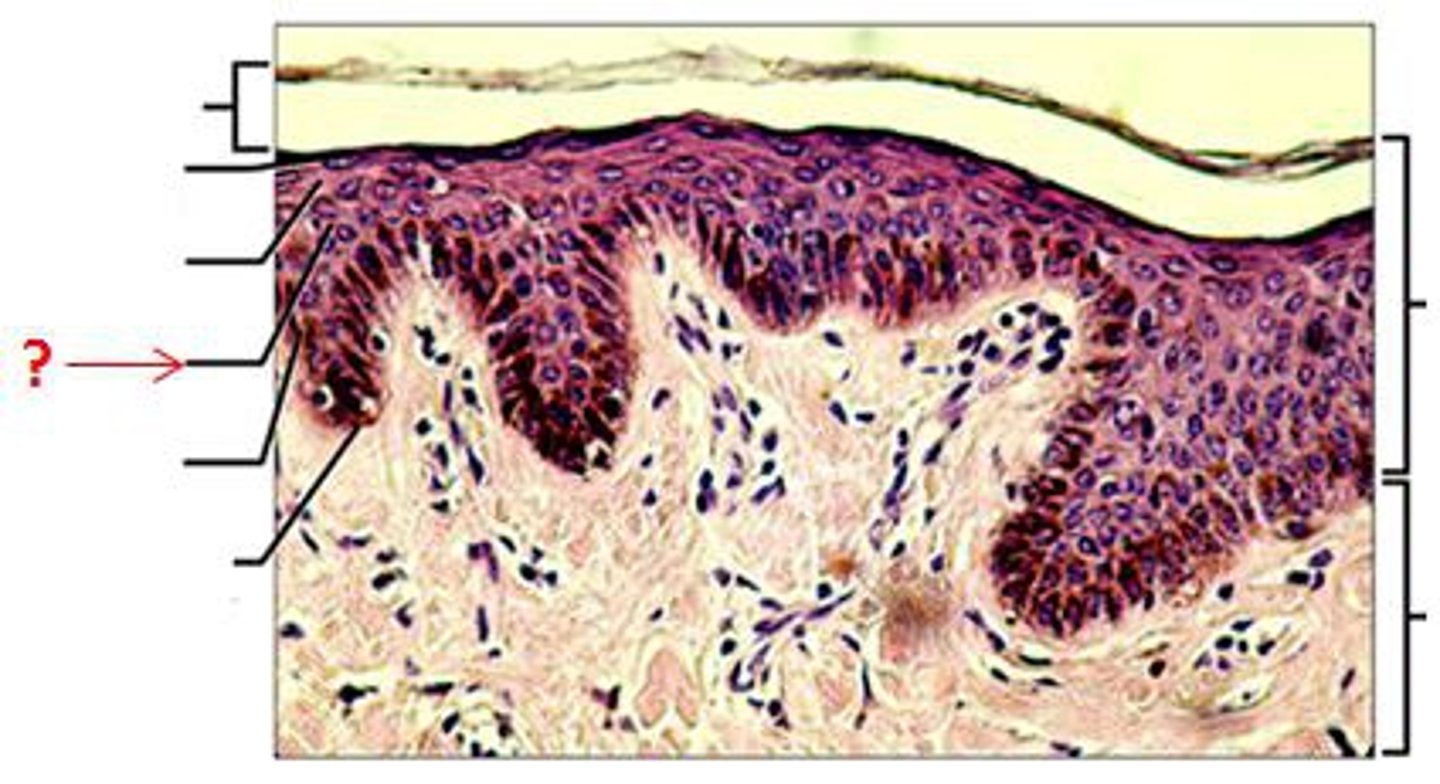
stratum basale
the deepest layer of the epidermis consisting of stem cells capable of undergoing cell division to form new cells
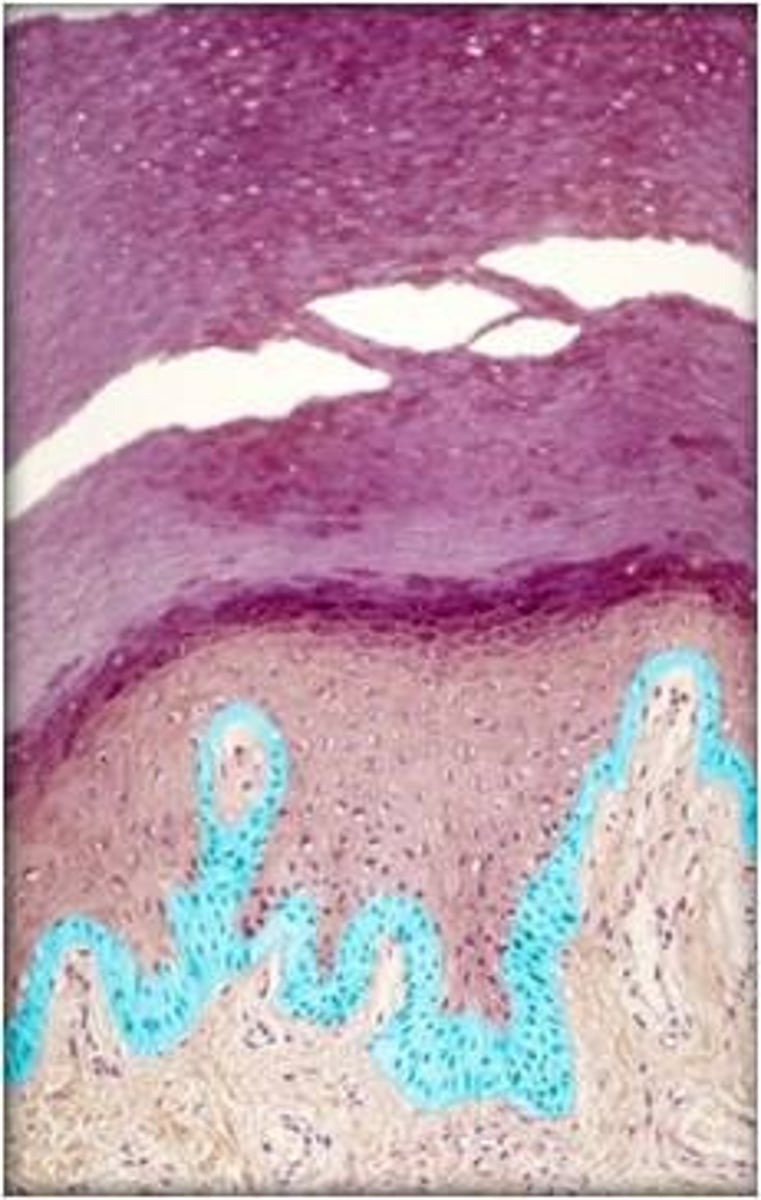
stratum basale attaches to
basal lamina
merkel cells are located in
stratum basale
where are keratinocytes born
stratum basale
keratin provides
waterproof covering
Number of melanocytes similar
Various skin colors
Size & activity of melanocytes differ and give
skin it's colors
freckles are
Concentrated groups of melanin
Cells of the epidermis
stem cells, keratinocytes, melanocytes, tactile cells, dendritic cells
Melanocytes protect from
UV radiation
Merkel cells
touch receptors in the skin
Epidermal appendages
hair, sebaceous glands, sweat glands, nails
Roles of the epidermis
Vitamin D production, regulates fluid, physical/chemical barrier, appearance, waste disposal
If a cut doesn't bleed
it's only in the epidermis
Epidermis thermoregulation
0 Hairs provide thermal covers and sweat glands cool skin
Epidermis and vitamin D
0 Makes vitamin D when exposed to sunlight
0 Critical for bone formation and calcium absorption from intestinal tract
Dermis layers
papillary and reticular
Basement membrane of the dermis
Attaches dermis to stratum Basale
dermis is
vascular
Dermis can withstand
large pressure
What provides the epidermis with nutrients
vasculature from the dermis
Dermis cell types
fibroblasts, macrophages, and occasionally mast cells and white blood cells
fibroblasts provide skin what
toughness and stretchability
Mast cells
Cells that release chemicals (such as histamine) that promote inflammation.
the dermis should look
shiny, moist and pink
Can the dermis regenerate?
no
1 multiple choice option
large scars can't
sweat
functions of the dermis
thermoregulation, sensory reception, supports epidermis, nourishes epidermis
blisters occur from
friction between the dermis and epidermis
adipose tissue
0 Insulation and cushioning
0 Energy source
0 Can store Vitamins A, D, E ,K
0 Highly vascular
0 May be dark if dehydrated
0 Yellow if healthy
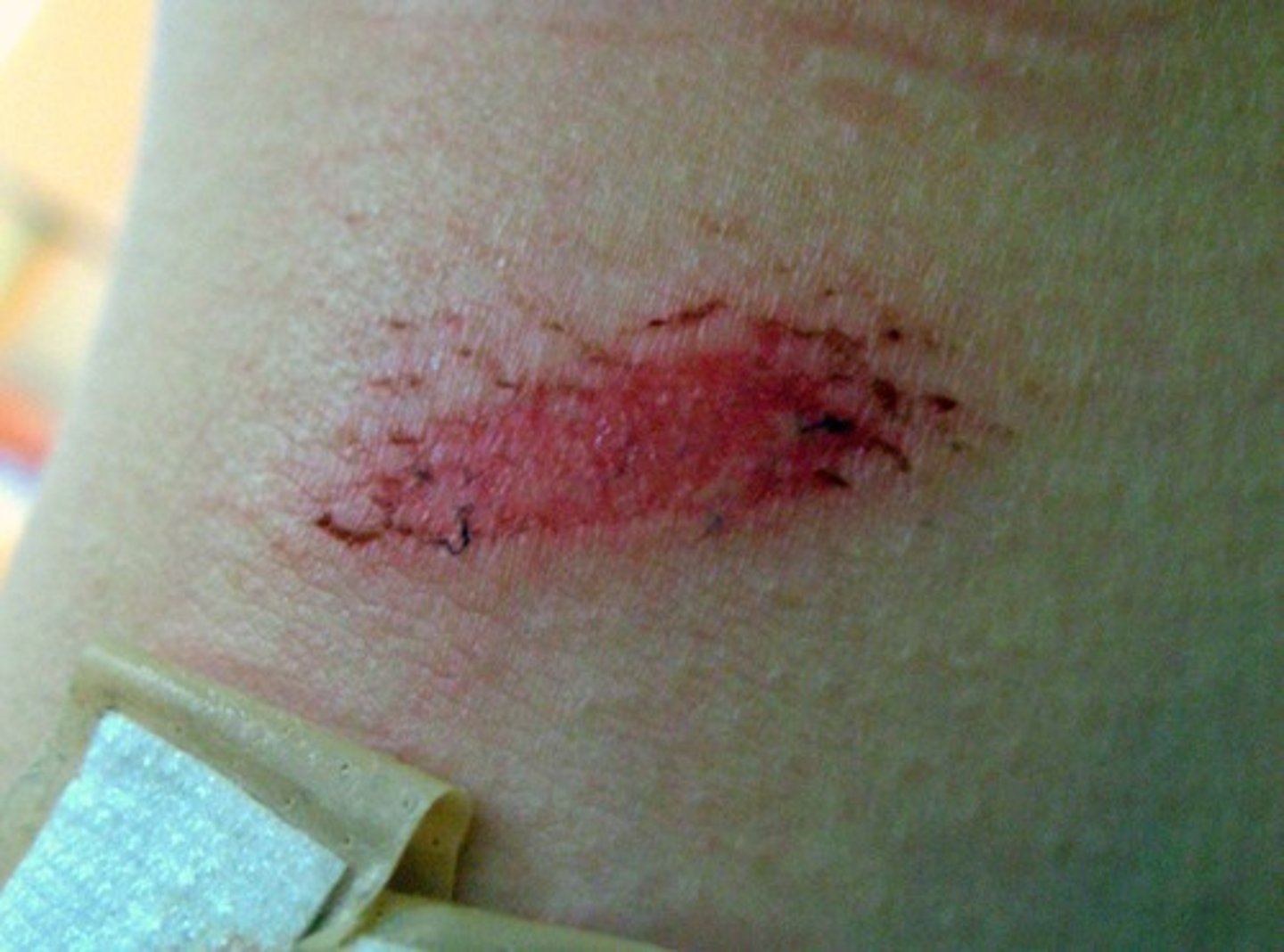
superficial wounds
involve only the epidermal layer of the skin
superficial wound examples
abrasions and 1st degree burns
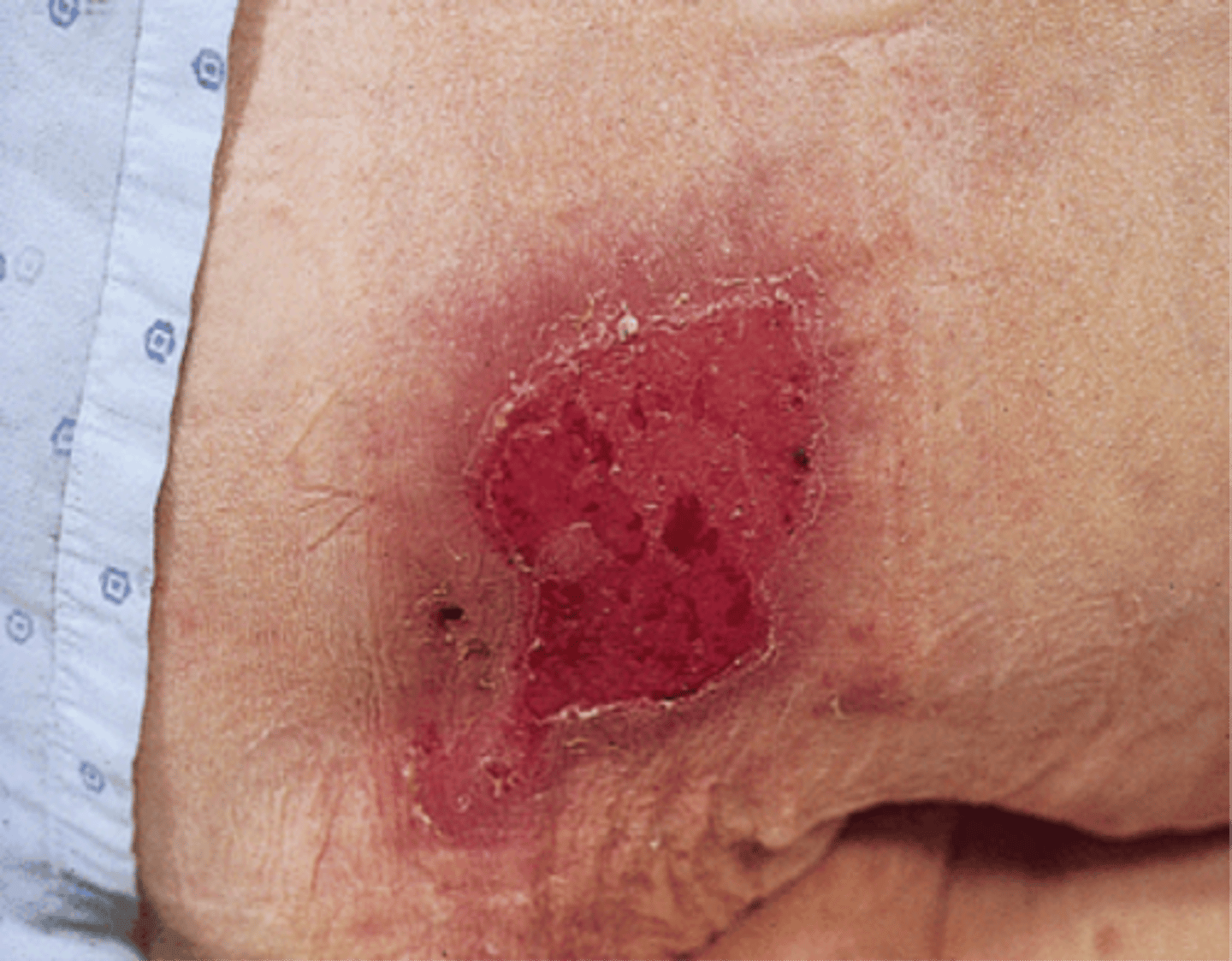
partial thickness wound
Involves the epidermis and the dermis but does not extend through the dermis to the subcutaneous layer
partial thickness examples
Superficial and deep partial thickness Blister
2nd degree burn
Stage 2 pressure injury
Wagner grade 1 ulcer
Granulation occurs in
partial thickness wounds
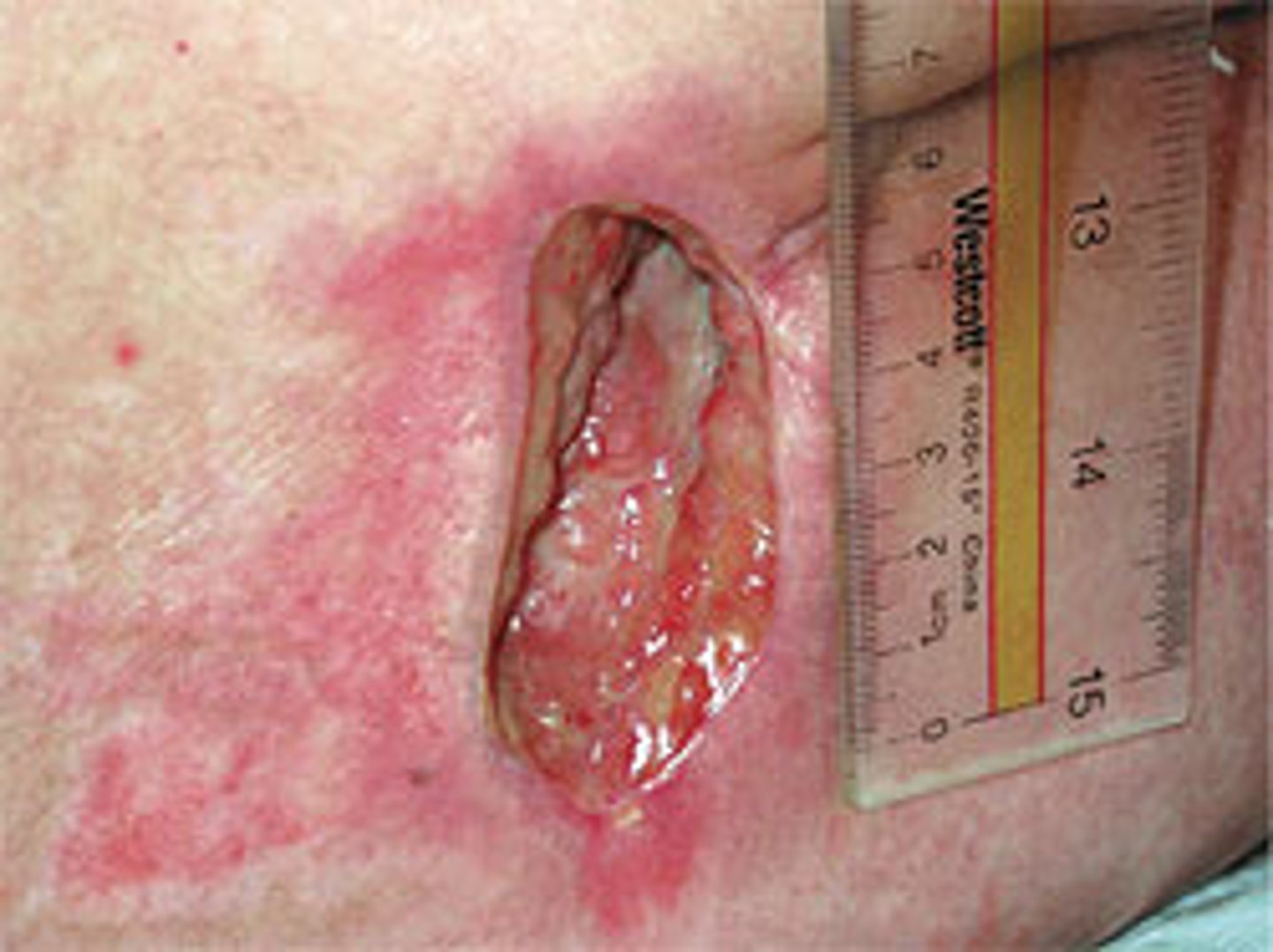
full thickness wound
the dermis, epidermis, and subcutaneous tissue are penetrated; muscle and bone may be involved
full thickness examples
Full stage thickness burn
Stage 3 pressure injury
Subdermal (4th degree burn)
Wagner grade 1-5 ulcers
full thickness wound
partial thickness wound
superficial wound
Phases of wound healing
inflammatory, proliferative, maturation
Inflammatory stage purpose
Control bleeding and fight germs and bacteria
inflammatory stage length
3-6 days
Vascular response
increase blood flow to site of an injury
cellular response
adaptation at the cellular level that involves a cell responding to signals in its environment
PNMs
polymorphonuclear leukocytes
Fibroblasts produce
all 3 types of fibers (collagen, reticular, elastic fibers) through synthesis and secretion of protein subunits that combine or aggregate within the matrix
Vasodilation occurs when
vascular smooth muscle tissue relaxes to increase the diameter of the lumen
exudate
fluid that accumulates in a wound; may contain serum, cellular debris, bacteria, and white blood cells
transudate
The fluid component of blood that normally passes through the endothelial cell walls of the microcirculation
histamine
short term vasodilation
Prostaglandin
long-term vasodilation
Signs of inflammation
redness, heat, swelling, pain, loss of function
proliferation stage purpose
Growth and production of cells to produce tissues required to close wound
length of proliferation stage
Can start 48 hrs after injury but may start days after
Health of wound determines how long it lasts and when it starts
events in proliferation
angiogensis, granulation formation, wund contraction, epithelialization
Angiogenesis
formation of new blood vessels
Granulation formation
Temporary lattice of vascularized connective tissue that allows for contraction and epithelialization across the wound
granulation is replaced by
scar tissue
wound contraction
process whereby the borders of a wound are physically drawn together
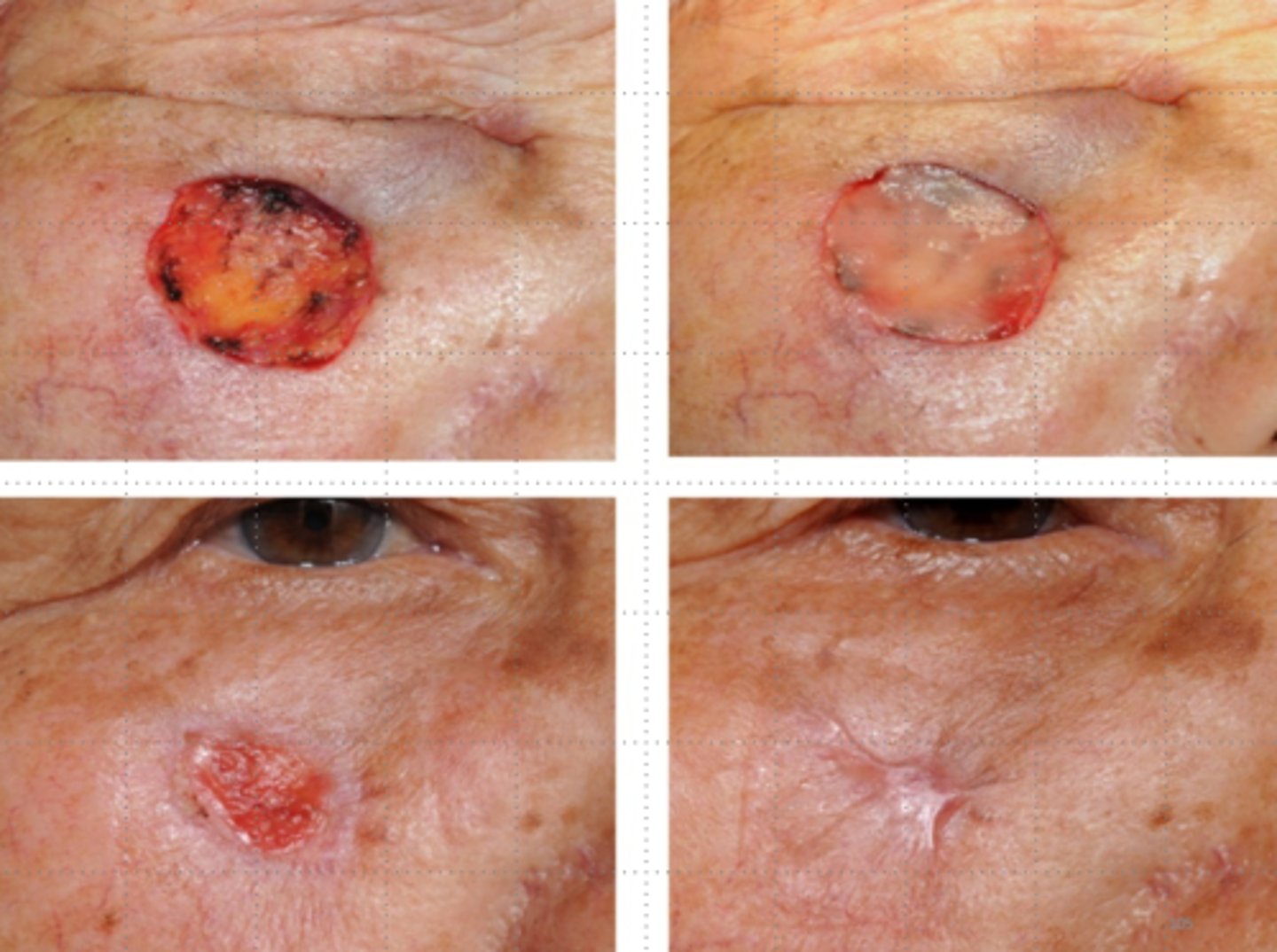
Amount of contraction affected
by shape & depth
what wounds heal the slowest
circular
which wounds heal the fastest
straight
Deeper wounds contract more
than partial thickness wounds
wounds heal from
bottom up, sides in
epithelialization
stage of wound healing in which epithelial cells form across the surface of a wound; tissue color ranges from the color of "ground glass" to pink