Ap Hug: Unit 2 Vocab
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Economics
Production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services with a society or area.
Arithmetic Density
The distribution of a population living in a given area divided by the total land area.
Physiological Density
A measure of population density that considers the number of people divided by the arable land.
Agricultural density
The number of farmers divided by arable land.
Dependency Ratio
The number of people in a dependent age group divided by the number of people in the working age group times 100.
Fertility
Average number of live births accruing in one year per 1,000 people
Mortality
Number of children who die before age 1.
Rate of Natural a increase
How fast or slow a population is declining or growing.
Population doubling time
How long it takes for a population to double in size.
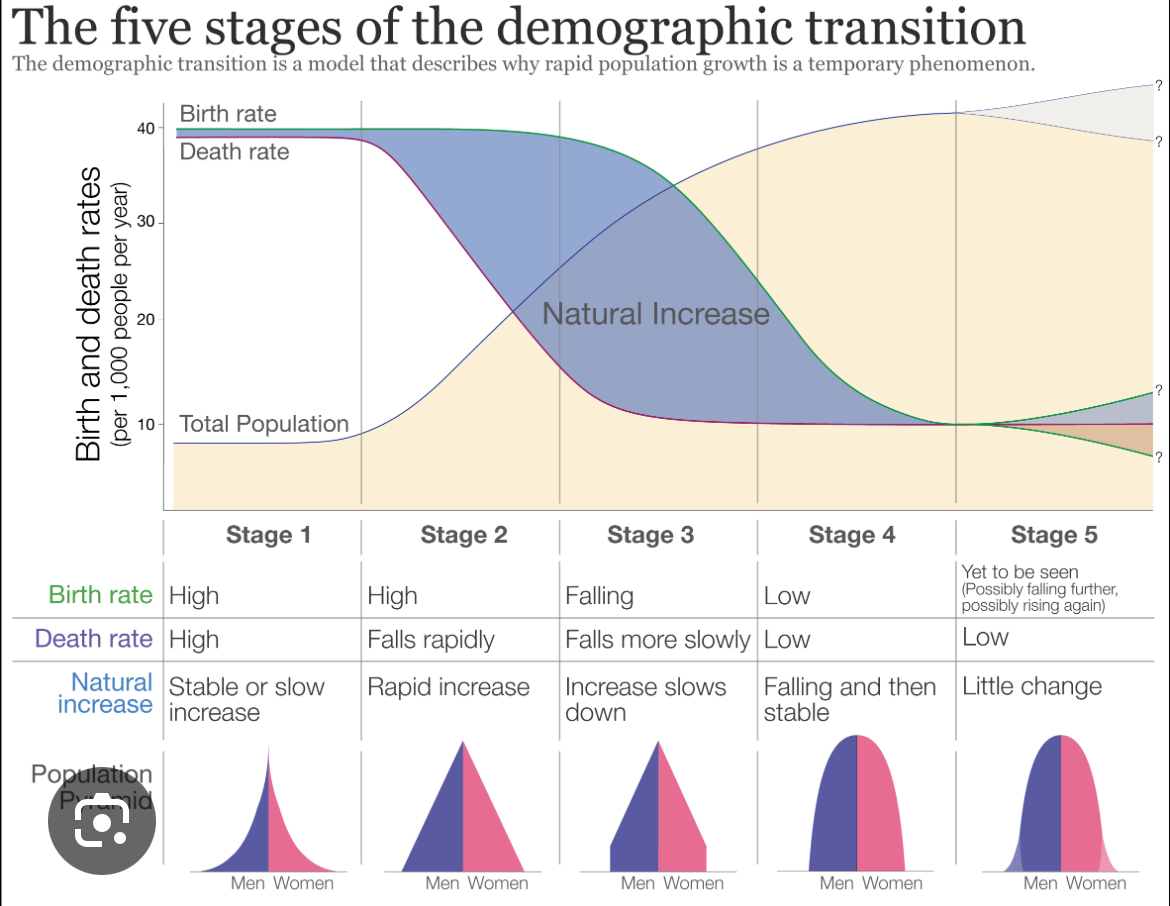
Demographic transition model
Used by geographers to analyze and predict trends in population growth and decline + patters of births, death and natural increase.
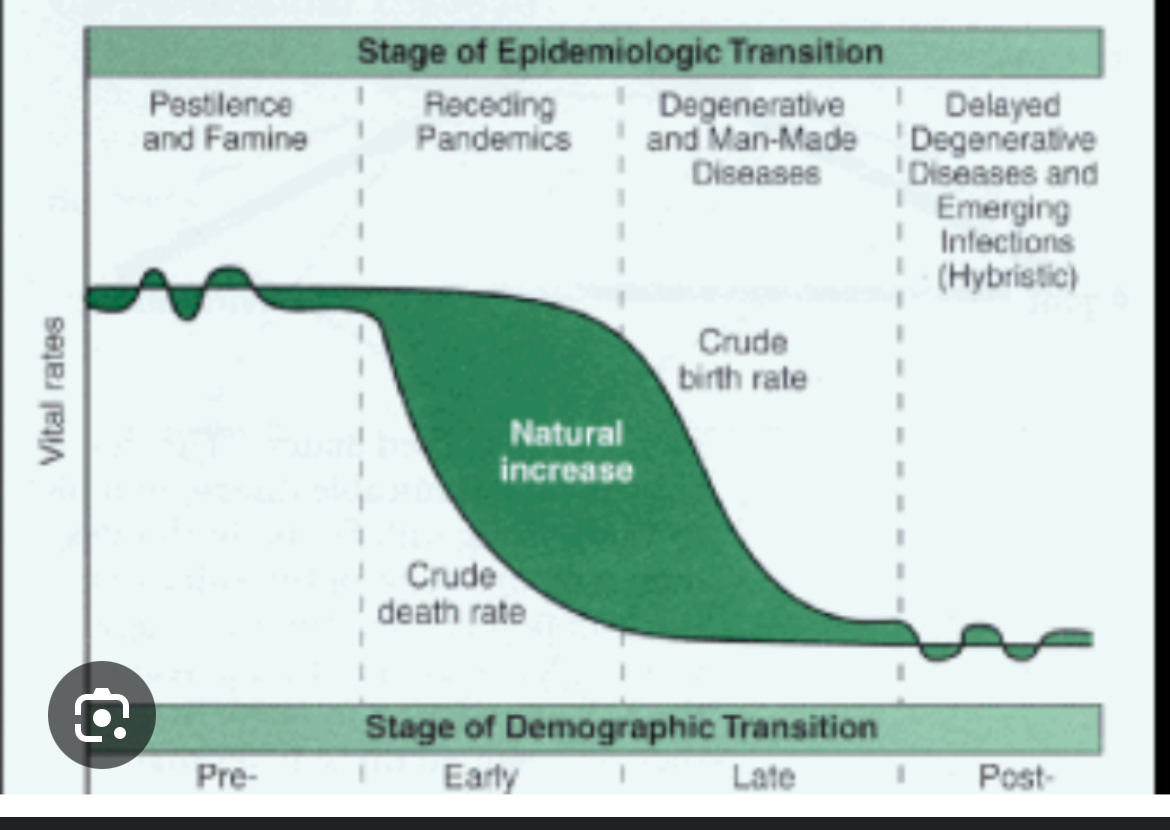
Epidemiological transition model
Predictable stages in diseases and life expectancy that countries experience as they develop.
Malthusian theory
Population growth will inevitably outpace food production, leading to widespread famine and other problems.
Neo-Malthusian Theory
Rides on and extends original theory to include concerns beyond food production, encompassing broader resources limitations and environmental issues.
Boserup Theory
Population growth is a positive force that stimulates agricultural innovation leading to increased food production per acre.
Erlich Theory
rapidly increasing population growth poses a significant threat to the environment and resource availability.
Push factors
Negative circumstances, events, or conditions present in a location that results in people moving away.
Pull factors
Positive conditions and circumstances of a location that drives people to move to a place.
Voluntary migration
Migrates or moves to a place that was their own choice.
Ravensteins Laws of Migration
Migrants move short distances that occur in steps, usually rural to urban areas.
(People usually travel short distances -nearby towns to cities and eventually metropolises rather than making long jumps- and long-range migrants usually move to urban areas)
Refugees
Someone who has been forced to flee from their country.
Exmpl: War, persecution, violence, and natural disasters.
Asylum seekers
People flee their county to seek sanctuary in another country.
Guest worker
Migrants who travel internationally to find work temporarily.
Internal migration
Migrants travel within country borders.
Internally Displaced Migration
Someone who has been forced to flee their home but never crossed an international border.
Transnational Migration
Migration from one country to another country.
Chain migration
Continuous flow of migrants to a location based of recommendation of or reunifying family members, friends, or community ties.
Step migration
A migration process where individuals move gradually through a series of stages or steps, often from rural to large urban centers, with temporary stays at each stage.
Transhumance
Traditional migration of nomadic herders that move livestock from high elevation in summer and lower elevation in winter.
Intervening opportunities/barrier
Barriers that hold migrants back from continuing travel / Opportunities that causes migrants to voluntarily stop traveling.
Exmpl: opportunity:Moved to Mexico to be eventually allowed to move to the USA but chooses to stay in Mexico instead.
Ecumene
Portion of lands earth that is inhabited by human beings.
Brain drain
Emigration of highly skilled and educated individuals from one country to another, often driven by better opportunities, living conditions, or political stability.