C. elegans
1/134
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
135 Terms
number of neurons
302
bleach treatment
kills everything but eggs
hermaphrodite genotype
XX
male genotype
XO
number of autosomal chromosomes
5
selfing
self-fertilization
DNC
dorsal nerve cord
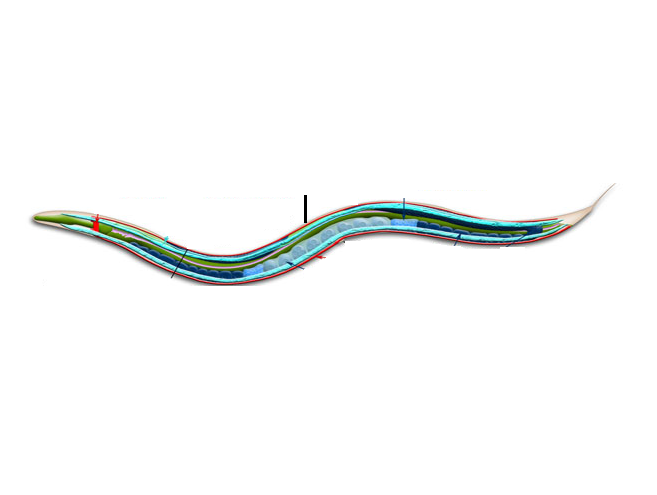
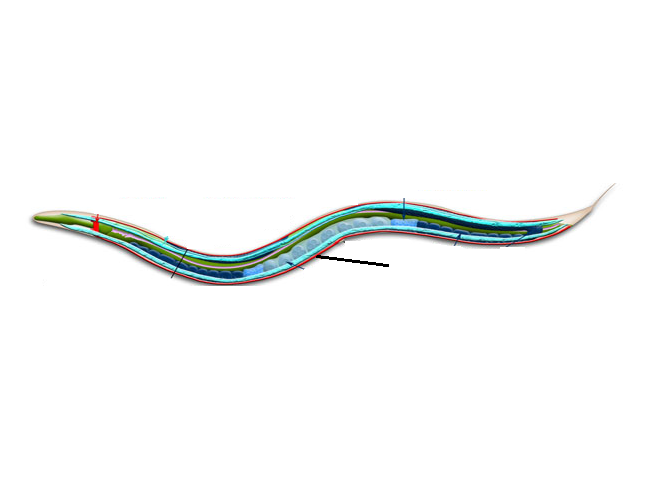
VNC
ventral nerve cord

L1 stage duration
16 hours
L2-4 stages duration
12 hours
lethargus
sleep-like period at the end of each L stage
end of the lethargus
the old cuticle molts
dauer
an alternative L3 stage triggered by stress or starvation
the cuticle surrounding the mouth
prevents eating and developing during dauer
N2
standard wild-type c. elegans strain
reverse genetics
causing a specific mutation then understanding the phenotype
foward genetics
undestanding the genetic basis of a known phenotype
axenic culture
single-species culture
coelomocyte
similar in function to macrophage
sodium action potentials in c. elegans
do not exist
neuron conductivity
very high
innexins
invertebrate equivalent of connexins in gap channels
worm bagging
the worm doesn't lay eggs and the larvae hatch inside, killing it
starvation
cause of worm bagging in nature
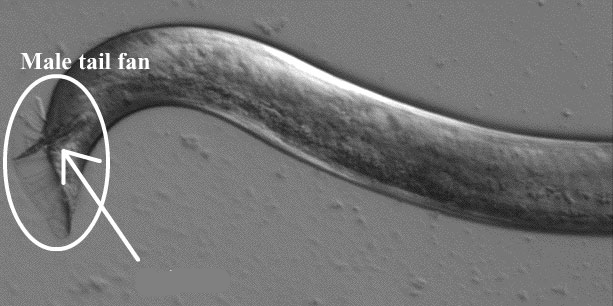
male size
smaller than hermaphrodite size
rays
support cells in the male tail
c. elegans genome size
100 Mb
operons
multiple genes that are expressed together
difference between operons in bacteria and c. elegans
in worms, different mRNAs are created for the different genes
trans-splicing
attaching an additional sequence to mRNA
trans-spliced leader sequences in c. elegans
aid in translation initiation
purpose of nictation
attaching to other creatures during dauer
factors affecting food pumping rate
food sensation by the motor neuron and serotonin signaling
high pumping rate
caused by starvation
muscarinic receptor - MAPK pathway
promotes autophagy in response to starvation
food quality
ability to promote growth
large bacteria
low quality food
spoiled worms
experienced high-quality food and tend to leave lower quality food
satiety quiescence
occurs only with high-quality food
starvation before feeding
promotes satiety quiescence
abundance of food
increases egg-laying rate
salt solution and mechanical sensations
decrease egg-laying rate
egg-laying and movement
occur together
egg-laying pattern
short bursts separated by 20-minute rest
sexual reproduction in c. elegans
through internal fertilization
chemical released by hermaphrodites
attract males
cilated cells
chemo- and mechano-sensory cells
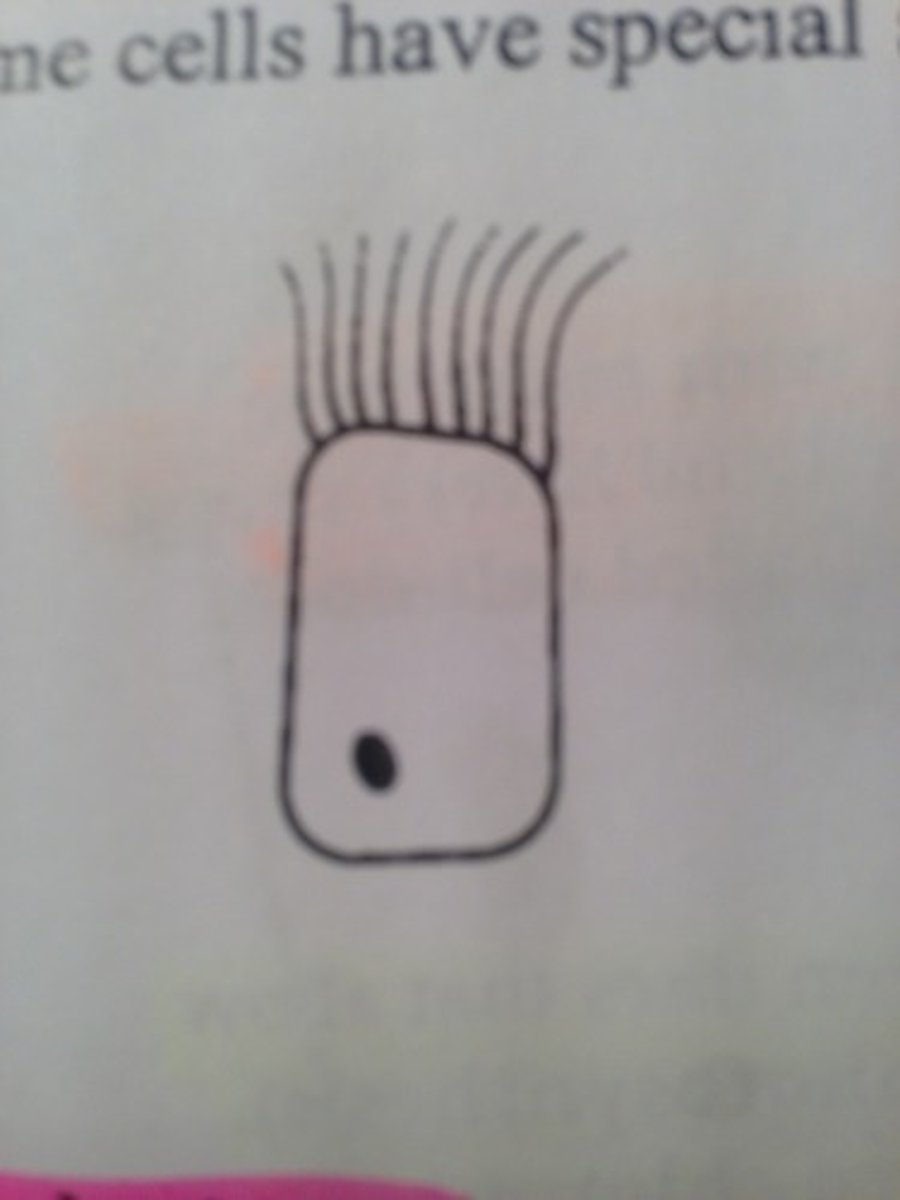
male ciliated cells
exist mostly in the tail
turning during mating
necessary to locate the vulva
spicules
assist penetration and anchor the male during mating
plugging
hinders other males from reaching the vulva after mating
plugging in N2 c. elegans
does not occur
number of somatic cells
959
cameleon
GFP derivative used as a calcium reporter
mechanism of c. elegans short-term habituation
decreased excitability of sensory cells by K channel autophosphorylation
TWR
tap-withdrawal response
c. elegans olfactory neurons
express receptors for multiple odorants
difference between habituation and sensory adaptation (receptor level)
habituation is reversed with new or malicious stimuli
the main transmitter in food-related contextual learning
serotonin
ASE
gustatory neurons
memory of cultivation temperature
stored in sensory neurons
aerotaxis
movement toward a specific oxygen level
usage of imprinting
predicting food in a specific environment
cis-regulatory element
non-coding DNA sequence that regulates neighboring genes
trans-regulatory element
DNA sequence that encodes a transcription factor
endotokia matricide
worm bagging
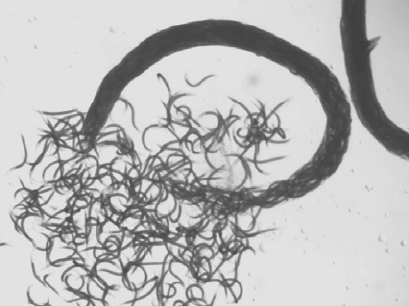
nictation
terminal selector
a regulatory element that determines the identity of neurons
synaptobrevin
SNB-1
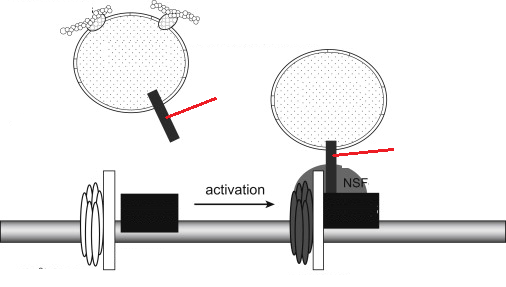
en-passant synapse
c. elegans synapse type
terminaux synapse
periactive zone
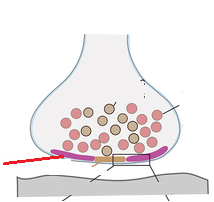
number of glia
56
nerve ring
amphid
the primary sensory organ
sheath glia
socket glia
low serotonin level
increased dauer entry
axon myelination in c. elegans
does not exist
trophic support
neurons surviving only when receiving signals from glia
glial trophic support in c. elegans
does not exist
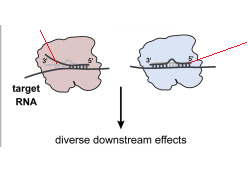
argunaute
determines the effect
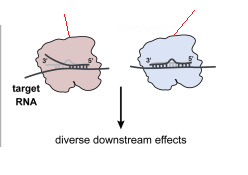
small RNA
determines the specificity
miRNA size
21-2 bases
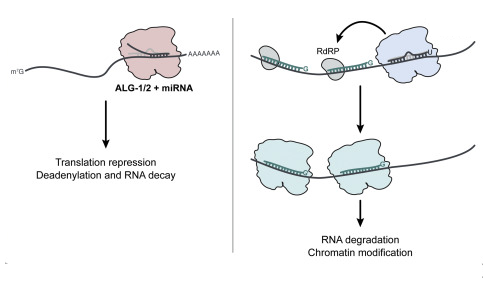
miRNA effect
repression of translation, deandenylation and mRNA degradation
seed sequence
miRNA region that determines binding to the argonaute
purpose of miRNA
regulation of gene expression
purpose of non-miRNA small RNAs
immunity against viruses and transposons
difference between miRNA and sRNAs
site specificity
primary argonaute
binds the primary sRNA
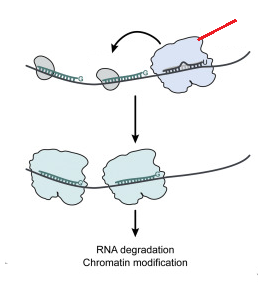
RNA-dependent RNA polymerase
RdRP
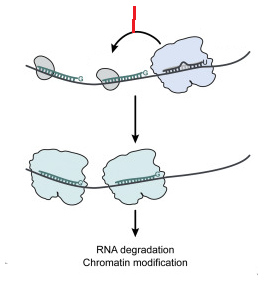
secondary argonaute
WAGO
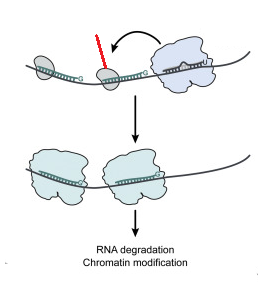
22G-RNA
sRNA bound by WAGO
miRNA source
the genome
Piwi
family of argunautes
piRNA
sRNAs bound to piwi argonautes
21U-RNA
piRNA in c. elegans
siRNA source
external dsRNA
mutator proteins
bind 22G-RNA and are necessary for transposon silencing
RNAe
RNA-induced epigenetic silencing