Energy from fuels
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
combustion of metals
general equation: metal + oxygen —> metal oxide
reducing agent is the metal
combustion of non metals
general equation: non-metal + oxygen —> non metal oxide
reducing agent is the non-metal
complete combustion of organic compounds
they don’t spontaneously combust because their reactions have high activation energy - this is useful
general equation complete combustion: fuel + oxygen —> CO2 + water
general equation hydrocarbon combustion: CxHy + (y/4)O2 —> xCO2 + (y/2)H2O
incomplete combustion
limited supply of oxygen, produces water
produces CO or C (if oxygen supply very limited)
from carbon present in the organic compound
the higher the carbon content in a fuel, the more likely it is that incomplete combustion will occur, as more oxygen is required for complete combustion
a sooty yellow flame is indicative of incomplete combustion
CO is toxic gas that binds irreversibly to haemoglobin in blood, preventing it from carrying oxygen
coal
advantages
relatively safe
abundant
long life span
disadvantages
combustion produces lot of pollution
global warming and acid rain
not readily transported
oil
advantages
easy to store and transport
impurities easily removed
disadvantages
combustion produces lot of pollution
global warming and acid rain
limited lifespan
natural gas
advantages
cheapest
easy to store and transport
large energy per unit mass
disadvantages
combustion produces lot of pollution
expensive to store
global warming
greater risk of explosions
limited life span
burning fossil fuels
specific energy is energy stored in a subtance
as hydrocarbon chain increases
increased carbon content, production of more carbon dioxide/monoxide/carbon
stronger london forces, hydrocarbon is less volatile
releases less energy per unit mass of fuel (so methane makes the most)
specific energy of a fuel equation
energy released from fuel / mass of fuel consumed in kJ kg -1
carbon dioxide levels
CO2 levels are rising due to human activities such as
combustion for electricity
deforestation
CO2 and methane contribute carbon levels and raise temperature
increased use of fossil fuels is main reason for increase
greenhouse effect
GH gases absorb radiation emitted from earth and trap it so its not lost to space
radiation from sun strikes earth, is absorbed, and re emitted from earth as IR radiation
some IR radiation passes through the atmosphere, some is absorbed by GH gases
this reduces thermal energy lost in space and traps it within earth
why GH gases absorb IR radiation
molecules can vibrate as the bonds in them stretch and bend
energy associated with bond vibrations is IR
if stretching and bending involves a change in dipole, then vibrations are IR active
biofuels
made from organic compounds which are produced by biological carbon fixation
renewable, reduce pollution from combustion of fossil fuels
general photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12OH + 6O2
bioethanol
glucose made from photosynthesis converted into ethanol by fermentation
C6H12O6 —> 2C2H5OH+2CO2
carbon neutral because CO2 absorbed during photosynthesis = CO2 produced by combustion of biofuel
ethanol is then burned to produce energy
ethanol can be combined with gasoline, gasohol is produced, used by cars
biofuels in combustion
direct combustion of waste material from plants or animals
biogas
fuel released when organic matter is broken down by microorganisms anaerobically
pros and cons of biofuels
pros
carbon neutral, renewable, sustainable
reduce GH emissions
safer to produce
cons
expensive
many developed countries don’t have space to produce enough plants for biofuels
lower specific energy than fossil fuels
fuel cells
electrochemical cell where fuel gives electrons at one electrode and oxygen gains electrons at the other electrode
as fuel enters cell it becomes oxidised, which sets up voltage within the cell
hydrogen oxygen fuel cell equations
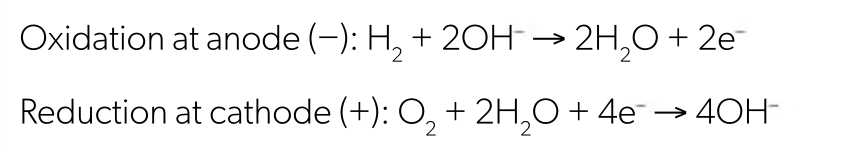
methanol fuel cell equations
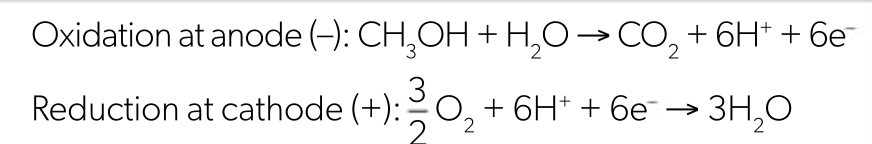
hydrogen oxygen fuel cell pros and cons
pros
water is the only reaction product, so better for environment
no harmful oxides of nitrogen produced
cons
hydrogen is highly flammable so dangerous to store
expensive
methanol fuel cell pros and cons
pros
easier to store than hydrogen
has greater energy density than hydrogen
cons
toxic gas
commonly made from non renewable fossil fuels
fuel cell produces lower voltage