POLYMERS OF LIFE
1/140
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
141 Terms
Between alcohol, c.acids and phenols, which is the most acidic?
C.acid
What would the observations be when u drop ethanoic acid on universal indicator paper?
Paper would turn red, indicating an acidic pH.
What type of acid is ethanoic acid?
Weak acid
Write the ionisation equation of ethanoic acid in water
CH₃COOH ⇌ CH₃COO⁻ + H⁺
Why are some acids ‘stronger’ even though they are in the same concentration?
Stronger acids dissociates more completely in solution, higher conc of H⁺ ions.
Write a balanced equation for ethanoic acid + NaOH
CH₃COOH + NaOH → CH₃COO-Na+ + H₂O
Write the ionic equation for ethanoic acid + NaOH (include state symbols)
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) → H2O (l)
What is the ionic equation for all acid + alkali reactions?
H+ (aq) + OH- (aq) → H2O (l)
Write the balanced equation for ethanoic acid + magnesium
2CH₃COOH + Mg → (CH₃COO-)2Mg2+ + H₂
Write the ionic equation for ethanoic acid + magnesium
2H+ + Mg → Mg2+ + H₂
Between alcohol, c.acids and phenols, which is the least acidic?
Alcohols
What does alcohol + NaOH make?
Nothing / no reaction
What is the main rule for naming esters?
Alcohol before C.acid
Name: CH3COOCH2CH2CH3
Proply-enthanoate
What are the 2 reactions of esters?
How to make them / how to break them
What are the 2 compounds that provides an -OH group to make esters?
Alcohol / phenol
What are the 3 compounds that provides an C=O group to make esters?
Acyl chloride / acid anhydride / c.acid
What is an important condition needed when using acyl chlorides in reactions?
Anhydrous conditions
How do you name acyl chlorides? (like what do the names end with)
__anoyl chloride
What does c.acids NOT react with to make esters?
Phenol
Why does phenol + c.acid not work?
Both reactants are too unreactive
What are the conditions for -OH + acid anhydride?
RTP
What are the conditions for alcohol + c.acid?
Reflux with c.H2SO4
State how would you break esters?
Hydrolysis with H2O
Why may hydrolysis of esters with H2O be an issue, and how could you fix it?
H2O alone is very slow (reaction), use acid / alkali catalyst
What is the concentration range of acid / alkaline catalysts in ester hydrolysis?
4-6 moldm^-3
What acid catalyst should you use in ester hydrolysis?
HCl
What alkali catalyst should you use in ester hydrolysis?
NaOH
What are the 2 conditions of ester hydrolysis?
4-6moldm^-3 acid or alkali catalysts / reflux
What is the first step of ester hydrolysis?
Break the bond
What is the second step of ester hydrolysis?
Add in H-OH
What is the third step of ester hydrolysis?
Consider if products will react with catalyst
What does c.acid + alkali make?
Carboxylate ion + H2O
What does alcohol + alkali make?
No reaction
What does alcohol + acid make?
No reaction
Describe a tertiary amine
Nitrogen atom bonded to 3 carbon atoms
What 2 compound is needed to make amines?
Haloalkane + NH3
What are the 2 conditions of making amines?
Heat / in a sealed tube
What is the scent of amines?
Fishy
What is a clear observation that an amine is present?
Fishy smell
What is the mpt / btp of amines? and explain why
Have IMF, so mpt / btp is low (but relatively high compared to other molecules due to H-bonding)
What is the solubility of amines in H2O? and why?
Is soluble, can form H-bonds with H2O molecules
Suggest when would the solubility of amines decrease?
Soubility deceases, as C chain length increase
What is the name of a phenol but with NH2 instead of the OH?
Phenylamine
Give the non-systematic name of CH3NH2
Methylamine
What does the non-systematic names of amines end in?
__yl-amine
What is the systematic way of naming amines?
Amino__ane
Give the systematic of CH3CHNH2CH2CH2CH3
2-aminopentane
Give the non-systematic name of CH3CH2CH2NH2
Propylamine
Give the systematic name of CH3CH2CH2NH2
1-aminopropane
What 3 things, amines can act as?
Ligands / nucleophiles / base
What are the 4 reactions of amines?
Can act as ligands / Can act as nucleophiles (L.P donor) / Can act as a base (H+ acceptor) due to L.P / Can form amides in condensation rxn with acyl chloride
What could be used in replace of acyl chloride while making amides from amines in industry?
C.acid
What happens to an amine, when reacted with an acid?
Amine is protonated
Give the products of CH3CH2NH2 + HCl →
CH3CH2NH3+ Cl -
What are the 2 reactions of amides that we need to know?
How to make / How to break them
What is the name of the reaction that makes amides?
Condensation reaction
What are the conditions for the reaction [ amide + acyl chloride → amide + HCl ]
RTP / anhydrous
In the reaction [ amide + acyl chloride → amide + HCl ] , what are the 2 possible observations?
Amide= white solid / HCl= steamy white fumes
What are the 2 compounds needed to make amides at RTP?
Amines + acyl chloride
What is the name of the reaction for breaking amides?
Hydrolysis
What are the 2 conditions for amide hydrolysis?
4-6moldm^-3 acid or alkali catalysts / reflux
Amine + acid catalyst would make… ?
Protonated amine
What are the products for the hydrolysis of amides with H2O?
Amine + c.acid
What are addition polymers?
Monomers joined with no loss of atoms
What are condensation polymers?
Monomers joined with loss of a small molecule
What are the 2 main condensation polymers?
Polyesters / Polyamides
What are the 2 monomers needed to make polyesters?
Diol + dicarboxylic acid
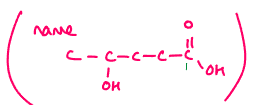
4-hydroxy pentanoic acid
What are the 2 monomers needed to make polyamides?
Diamine + Diacyl-chloride
What is the alternative name of polyamides?
Nylons
What does the numbers in ‘nylon 5,4’ mean?
5= 5C’s in the diamine / 4= 4C’s in the dicarboxylic acid
What catalyst do you usually use for the hydrolysis of condensation polymers?
NaOH
What IMF’s are in polyesters?
PdPd forces between the ester groups on different chains
What IMF’s are in polyamides?
H-bonding between the amide groups on different chains
Suggest 2 circumstances that increases the strength of IMF’s of polyesters / polyamides
When chains are closer together / when the functional groups are closer together
How many naturally occurring amino acids are there?
20
Which amino acid distrupts the a-helices & B-pleated sheets?
Proline
What happens to amino acids in acidic conditions?
The amine (group) becomes protonated
What happens to amino acids in alkali conditions?
The c.acid group becomes a carboxylate ion
What happens to amino acids in neutral conditions?
Becomes charged at both ends (zwitter ion)
What is the state of amino acids at RTP in neutral conditions? and why?
Solids at RTP due to ionic bonding (caused by zwitter ion)
When amino acids join through condensation reaction, they form a….?
Secondary amide group
What is it called when 2 amino acids are joined together?
A dipeptide
What is the name of the functional group of amino acids?
Secondary amide group
What are the 3 steps in identifying which amino acids were joined?
Hydrolysis / chromatography / use ninhydrin to visualize the spots
Which amino acid does not have optical isomers?
Glycine
What are the 2 types of isomers?
Structural / stereoisomers
How many different dipeptides can you make when 2 different aa’s joined?
2 different dipeptides
What are the 2 stereoisomers?
E/Z isomers / optical isomers
What are E/Z isomers?
Have C=C which restricts rotation / have 2 different groups on each C of C=C
What do optical isomers need?
4 different groups around a C (chiral C)
What is a chiral C atom?
A C atom with 4 different groups attached to it
What are enantiomers?
Mirror imagines of each other, which cannot be superimposed
2 ways which 2 enantiomers can differ (1/2)
They rotate plane polarised light in different directions
2 ways which 2 enantiomers can differ (2/2)
They interact with other chiral molecules differently
What are proteins made from?
Amino acids
How are the monomers of proteins joined?
By secondary amide links
What is the primary structure of a protein?
The order of amino acids
What is the tertiary structure of a protein?
The overall 3-D shape given by the folding of the secondary structure