MICR5831 L4: Introduction to Bacterial Gene Regulation 8/12/25
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
Explain how a repressor and activator protein works to control gene expression. (slide 6)
-Activators/repressors bind to ligands called co-repressors or inducers
-Ligands: small molecules like amino acids, sugars
-Respond to environmental changes such as pH, temperature
Describe 4 ways a repressor can prevent transcription of a gene (slide 7)
1) Repressor protein binds to the promoter, blocks the Sigma Factor
2) Repressor binds upstream of Promoter
3) Repressor binds opposite of RNAPol
4) RNApol binds Promoter but Repressor proteins stops the initiation phase
Describe 2 ways that an activator can induce transcription (slide 8)
1) Activator proteins stabilize RNApol + the promoter
-Bending the DNA at the -35 and -10 sites
-Optimal distance for Sigma Factor
2) Activators bind a ligand that changes their conformation
-Enables them to bind the DNA operator
Explain how a regulatory protein can bind DNA? (slide 9)
1) Ligand binds to the EBD (Effector-Binding Domain)
2) DNA-Binding Domain (DBD) conformation changes
3) DBD will either release the DNA or bind to it more tightly
How does a regulatory protein sense environmental cues inside and outside the bacterial cell (slide 9 and 10)
1) Ligand enters cytoplasm to interact with the regulatory protein EBD
2) Histidine Kinase (HK) periplasmic domain binds ligands in periplasm, phosphorylates RR receiver domain
3) Response Regulator (RR) DBD domain is phosphorylated and acts as repressor/activator
Explain a simple two component circuit for gene expression (slide 10)
1) HK periplasmic domain binds ligands
2) His residue in HK dimerization domain is phosphorylated
3) HK phosphorylates Asp residue of the RR receiver domain, affecting DBD
4) DBD is phosphorylated and changes conformation into repressor/activator
Using an example, explain how a regulatory protein like AraC can be both an activator and repressor? (slide 11)
Without ligand arabinose (repressor):
-AraC forms an elongated dimer form
-Binds to ara02 and aral1, creates a loop
-Prevents RNApol from binding to the promoter
With the ligand arabinose (activator):
-Compact dimer forms that binds aral1 and aral2
-RNApol binds to the araB promoter
-Transcription = catabolism of arabinose for carbon
-Another regulatory protein, CRP, also binds and this inhibits araC expression
Explain how attenuation works to control gene expression (slide 12)
1) Binding of Trp to the aporepressor makes holorepressor
2) Binding of holorepressor to the trp operator inhibits but does not altogether prevent transcription
3) It lowers expression 100x fold but does not turn it off completely as the repressor binding is weak
What are the important features in the attenuator region? (slide 13)
2 Hairpin Loops:
Stem loop 1:2
-Contains a short ORF
-"Leader peptide coding region"
-Rich in Trp codons
Attenuator hairpin loop (stem 3:4)
-Ends in a U-rich transcriptional termination motif
-High Trp: Transcription elongation into trp operon cannot occur
-Low Trp: Entire operon is transcribed
How does coupling of transcription and translation result in attenuation (slide 14)
-Transcription is initiated
-First 140 bp of the 5'mRNA are synthesized
-Ribosome binds the Shine Dalgarno site
-Transcription and translation are coupled
-Attenuator loop stops Trp transcription during High Trp
-Anti-terminator loop helps elongate mRNA during Low Trp
Using an example, explain how mRNA stability can be used to control gene expression (either slide 16 or slide 19)
1) mRNA stability affects RpoH expression
Normal temperature:
-mRNA forms thermosensitive riboswitch
-Occludes SD site to prevent translation
-Triggers degradation, mRNA half-life of 40secs
-RpoH is low
2) sRNA stability affects succinate dehydrogenase expression
Low Iron:
-Fur repressor de-repressors Enterochelin (iron scavenger) and rhyB promoters
-SRNA rhyB binds to succinate dehydrogenase mRNA
-Enables the RNAase to bind the mRNA
-Rapidly degrade the mRNA, shutting down the expression of the enzyme
Explain how RpoH levels are controlled during normal growth conditions. (slide 16 and 17)
1) rpoH is transcribed from a sigma 70 promoter
2) RpoH binds DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE in the inner membrane
3) Associates with FtsH protease which degrades RpoH
4) Low RpoH protein levels
Explain how RpoH levels are controlled during heat shock (slide 16 and slide 18)
mRNA stability is determined by secondary structure and sensitivity to degradation:
1) mRNA structure unwinds
2) Allows ribosome access to the Shine-Dalgarno site
3) Half-life of mRNA increases to 4 min
4) Increased translation of RpоH
5) Proportion of RNApol association with RpoH increases
6) Induces genes encoding factors that protect from stress
De-repression during Heat Shock:
1) DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE chaperone preferentially recognizes misfolded proteins in the cytoplasm
2) Associates with ClpB foldase that refolds proteins to correct conformation
3) RpoH is released from DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE chaperone
4) RpoH associates with RNApol
5) Increased transcription from RpoH-dependent promoters
What is a sRNA (small RNA, anti-sense RNA) and what is one of its roles in controlling gene expression (slide 19)
-Encoded in intergenic spaces of the genome
-rhyB responds to low iron levels by binding to mRNA and shutting down succinate dehydrogenase
How does slipped strand mispairing occur in a bacterial cell?
How does this affect gene expression? (slide 20)
-Occurs during DNA replication when one or the other strand, slips and mispairs with the wrong repeat on the other strand
-Can alter the number of repeat units in a gene and lead to variations in protein expression
Using an example, explain the principles behind our understanding of orthologous regulatory circuits in different bacterial species (slide 21-22).
-Orthologues of regulatory factors retain core target genes but have captured other species specific genes
-PhoPQ and PmrAB live in different environments where low Mg and low Fe occur separately or together and species have adapted their pathways of regulation to suit these situations
Why do bacteria regulate gene expression?
To express a subset of proteins to permit the bacterium to survive current conditions
What are some bacterial examples of Global responses?
-SOS response
-Starvation response
-Heat stress response
What bacterial gene expression does global DNA damage initiate?
SOS response
What are some bacterial examples of Specific responses?
-lac operon: Utilize lactose as an energy source
-trp operon: Synthesize tryptophan
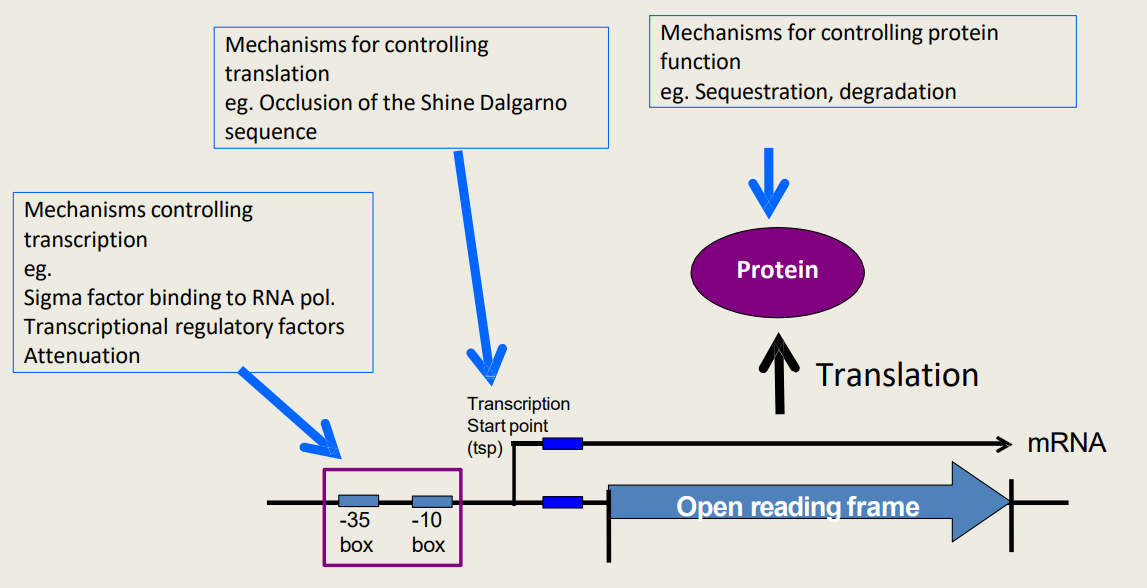
What are hierarchical control mechanisms for controlling transcription?
1) Sigma factor binding to RNApol.
2) Transcriptional regulatory factors
3) Attenuation
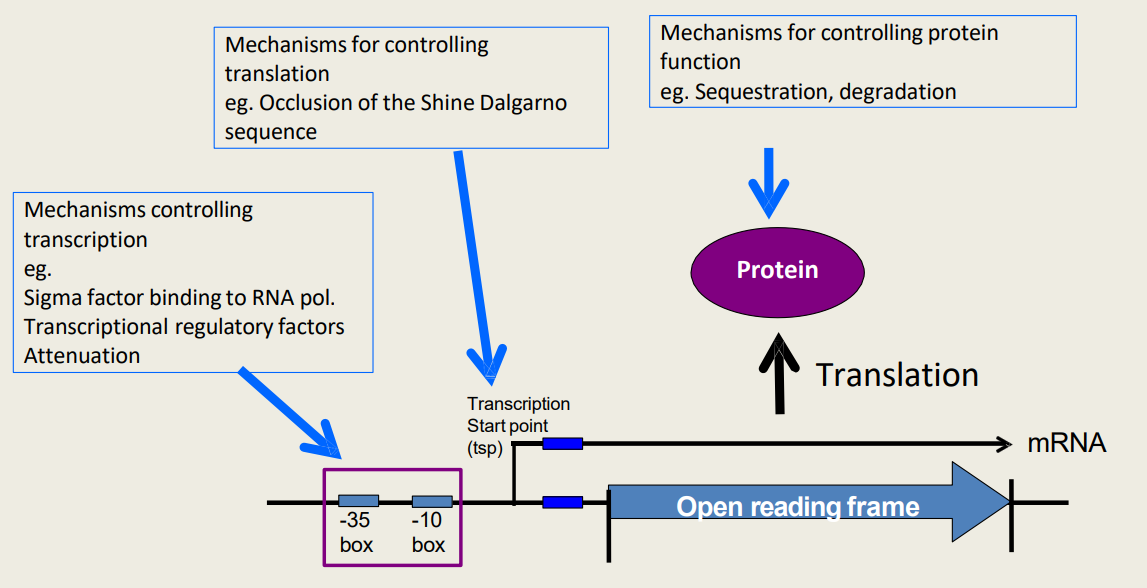
What are hierarchical control mechanisms for controlling translation?
Occlusion of the Shine Dalgarno sequencе
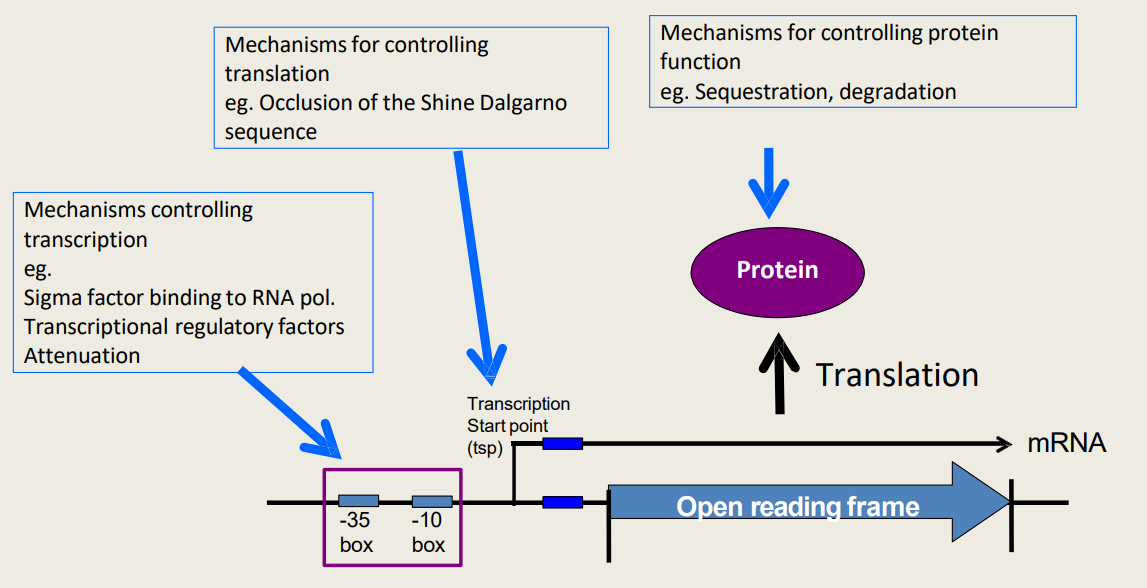
What are hierarchical control mechanisms for controlling protein function?
1) Sequestration
2) Degradation
What ligands can activators and repressors bind to?
-Corepressors and Inducers
-Respond to pH and temperature changes
True or False: Co-repressors and Inducers are typically large molecules such as amino acids and sugars
False, they are small
True or False: Co-repressors and Inducers are typically small molecules such as amino acids and sugars
True
How does a repressor protein prevent Sigma factor from binding and initiating transcription?
Repressor protein binds to the promoter
How does a repressor protein prevent the elongation phase of transcription?
1) Repressor binds upstream of promoter
2) Repressor binds opposite of RNA polymerase
How does repressor protein stop the initiation phase?
Repressor blocks RNAPol after it binds the promoter
How do Activator proteins increase the frequency of initiation of transcription?
-Strong binding
-Stabilizes RNApol and promoter interaction
How do Activator proteins create a stronger bond between RNApol and the promoter?
-Conformational alteration of DNA
-Bend DNA so -10 and -35 are optimal distance apart
-Increases optimal binding by Sigma Factor
Why do Activators bend the DNA -10 and -35 sites in order to increase transcription initiation?
Bending the DNA creates an optimal distance for Sigma Factors to bind
True or False: Activators always bind a ligand that will change their conformation
True
Why do Activators always bind a ligand that changes their conformation?
Conformational change enables them to bind the DNA operator and bend the DNA
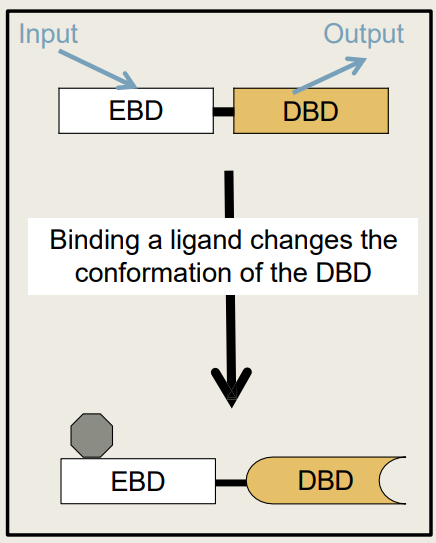
What are the 2 parts of a Regulatory protein's modular structure?
1) DNA Binding Domain (DBD)
2) Effector Binding Domain (EBD)
Which part of a Regulatory Protein is this?
-Very conserved
-Only 5 types
DNA Binding Domain (DBD)
Which part of a Regulatory Protein is this?
-Binds a small molecule ligand
-Very diverse
Effector Binding Domain (EBD)
What type of Regulatory Protein domain can bind to the following small molecule ligands?
-Sugars
-Amino acids
-Antibiotics
-Metals
-Quorum molecules
Effector Binding Domain (EBD)
Which Regulatory Protein domain undergoes a conformational change as a result of a ligand binding to its counterpart?
DNA Binding Domain (DBD)
What happens to the DBD when a ligand binds to the EBD?
1) Conformation changes
2) Releases or binds more tightly to DNA
True or False: Ligands must enter the cytoplasm to interact with the Regulatory Protein and bind to the EBD
True
What type of cues do Activators and Repressors (EBD and DBD) use?
What type of cues do Two-Component Systems use?
1) Regulatory Proteins (EBD and DBD) use internal cues
2) Two-Component Systems use external cues
What are the two parts of a Two-Component System?
1) Histidine Kinase (HK)
2) Response Regulator (RR)
Where are these Two Components found? Hint: External cues.
1) Histidine Kinase (HK)
2) Response Regulator
1) Inner Membrane
2) Cytoplasm
Which part of a Two-Component System is this?
-Periplasmic domain binds ligands in the periplasm
-Triggers phosphorylation of the conserved His residue in the Dimerization domain
-Donates phosphate group to a conserved Aspartate residue of the Receiver domain of a response regulator
Histidine Kinase (HK)
What triggers phosphorylation of the conserved His residue in a Histidine Kinase's Dimerization domain?
Periplasmic domain binds a ligand in the periplasm
What happens when the conserved His residue of the Dimerization domain of a Histidine Kinase is phosphorylated?
HK phosphorylates the conserved Receiver Domain of Response Regulator
Which residues are phosphorylated in a Histidine Kinase and Response Regulator?
HK: His residue, Dimerization Domain
RR: Asp residue, Receiver Domain
Which part of a Two-Component System is this?
-Modular organization: DBD attached to a Receiver domain
-Conformation of the DBD is determined by phosphorylation state of Receiver domain
-Acts as a Repressor or Activator of gene expression
Response Regulator
What affects the conformation of the DBD in a cytoplasmic Response Regulator (RR)?
Receiver Domain phosphorylation status
What is this?
-Regulatory protein that regulates araBAD degradation operon
-Normally elongated dimer form binds araO2 and aral1
-With arabinose, forms compact dimer that binds ara1 and ara2
AraC
What is this?
-Arabinose degradation operon
-Transcription = arabinose catabolism
-Regulated by AraC and CRP regulatory proteins
-Includes araB promoter
araBAD
What is this?
-Promoter found on araBAD degradation operon
-Blocked by AraC in the absence of arabinose
-Increases arabinose catabolism when RNApol binds to it
araB
What happens to AraC in the absence of its ligand, Arabinose?
-AraC forms an elongated dimer form
-Binds to ara02 and aral1
-Creates a loop that prevents RNApol from binding to the araB promoter of araBAD operon
What happens to AraC in the presence of its ligand, Arabinose?
-Compact dimer forms binds aral1 and aral2
-Allows RNApol to bind to the araB promoter
-araBAD operon is transcribed, arabinose is degraded
-CRP also binds and this inhibits araC expression
True or False: If arabinose is present, RNAPol will bind to araB promoter and increase catabolism of arabinose for carbon
True
What is this?
-Repressor protein that regulates tryptophan biosynthesis
TrpR
What is this?
-Co-repressor in the trp operon
-Binds to TrpR repressor, helps it bind DNA operator sequence
-Inhibits transcription of the trp operon
Tryptophan (Trp)
What is this?
-Inactive form of TrpR
-When Corepressor (Trp) is absent, cannot bind to operator site
-RNAPol can bind to promoter and initiate transcription
Aporepressor
What is this?
-Aporepressor + Corepressor complex
-Binds operator of Trp operon to prevent transcription
-Lowers expression 100x but has weak bond
Holorepressor
What happens when the Holorepressor binds to the operator of the Trp operon?
-Lowers expression 100x fold
-Does not turn it off completely
-Repressor binding is weak
How much does attenuation decrease the rate of trp transcription?
10x decrease
How much is the modulatory range of a holorepressor and attenuation on Trp operon?
100x10 = 1000x
What parts would you find upstream of the Attenuator site/region?
1) Promoter
2) Operator that TrpR binds
3) Leader sequence, first 140 bp of mRNA
What is this?
-First 140 bp of the mRNA
-Transcribed upstream of the start codon of trpE
Leader sequence
What part of the DNA sequence does TrpR bind to?
Operator
What is this?
-Two hairpin loops: Stem and Attenuator Hairpin
-High Trp: Transcription elongation into trp operon can't occur
-Low Trp: Entire trp operon is transcribed
Attenuator region
What hairpin loop found in the Attenuator region is this?
-Contains a short ORF called "leader peptide coding region"
-Rich in Trp codon
Stem loop (1:2)
What hairpin loop found in the Attenuator region is this?
-Ends in a U-rich transcriptional termination motif
Attenuator hairpin loop (stem 3:4)
What happens once transcription is initiated and the Leader sequence (first 140 bp of the 5' mRNA) have been synthesized?
-Ribosome binds Shine-Dalgarno site
-This means transcription/translation are coupled
True or False: Transcription and translation are coupled
True
What happens if there is High Trp?
1) Ribosome completes LP synthesis
2) Pause at the stop codon
3) Attenuator loop (3:4) forms, binds to RNApol
5) RNAPol pauses/releases DNA
6) Terminates transcription
What happens if there is Low Trp?
1) Ribosome pauses inside LP ORF due to lack of tRNA-Trp for translation
2) Anti-terminator looр (2:3) forms
3) mRNA elongation continues into trp operon.
What is this?
-mRNA secondary structure
-Signal for degradation and Thermostat
-Low protein/transcription at normal growth conditions
-High transcription during heat shock
rPOH
What happens to RpoH mRNA during normal temperature?
-mRNA forms a tertiary structure
-Thermosensitive riboswitch blocks Shine-Dalgarno site
-Prevent translation, triggers degradation
-mRNA half-life of 40secs, low RpoH
What happens to RpoH during normal growth conditions?
1) rpoH is transcribed from a Sigma 70 promoter
2) RpoH protein is bound to DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE in the inner membrane
3) Complex associates with FtsH protease
4) FtsH degrades RpoH
Normal growth conditions. Name the following:
1) Promoter that rpoH is transcribed from
2) Inner Membrane complex that RpoH protein is bound to
3) Protease that associates with RpoH and degrades it
1) Sigma 70
2) DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE
3) FtsH
True or False: High levels of RpoH transcription is required to make the DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE complex for protein refolding
False, very low levels of transcription from operons with RpoH-dependent promoters are needed
What happens to mRNA during heat shock?
-mRNA structure unwinds
-Allows ribosome access to the Shine-Dalgarno site
-Half-life of mRNA increases to 4 min
-Increased translation of RpоH
-Proportion of RNApol association with RpoH increases
-Induces genes encoding factors that protect from stress
What structure does the ribosome need access to in order to increase translation of RPOH and half-life of mRNA?
Shine Dalgarno Site
What is the mRNA tertiary structure that blocks the SD site at normal temperature, resulting in low RpoH and a short mRNA half life?
-Thermosensitive Riboswitch
-Triggers degradation
True or False: RpoH is high during normal temperatures and low during heat shock
False
True or False: RpoH is low during normal temperatures and high during heat shock
True
What happens to RpoH repression during heat shock?
1) DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE chaperone recognizes misfolded proteins in the cytoplasm
2) Associates with ClpB foldase that refolds proteins to correct conformation
3) RpoH is released from DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE chaperone
4) RpoH associates with RNApol
5) Increased transcription from RpoH-dependent promoters
Heat shock conditions apply. Name the following:
1) Chaperone that preferentially recognizes misfolded proteins
2) Enzyme that associates with chaperone and refolds proteins
3) What type of transcription is increased when RpoH associates with RNAPolymerase?
1) DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE
2) ClpB foldase
3) DnaK/DnaJ/GrpE, GroES/EL, ClpP and other heat stress genes from RpoH-dependent promoters
True or False: Chaperones are expressed less during heat shock conditions and deal with misfolded proteins to restore normal function
False
True or False: Chaperones are expressed more during heat shock conditions and deal with misfolded proteins to restore normal function
True
What is this?
-Anti-sense RNA
-Highly versatile regulatory functions
-Encoded in intergenic spaces of the genome
sRNA (Small)
What are some functions of small sRNA?
1) Plasmid/Viral Replication
2) Transposition
3) Response to Environmental Cues (rhyB)
What is this?
-Iron regulator
-Binds co-repressor Fe if high iron levels present
-Represses Enterochelin and rhyB
Fur
What is this?
-Scavenger protein, needed to scavenge iron
-Repressed by Fur iron regulator during high iron levels
Enterochelin
What is this?
-sRNA or anti-sense RNA
-Binds to mRNA of succinate dehydrogenase during low iron
-Repressed by Fur iron regulator and Fe co-repressor if high iron
rhyB
What is this?
-Uses iron for function
-Decreased expression when iron is low
-rhyB sRNA will bind to it so RNAase can degrade it
Succinate dehydrogenase
What environmental response does sRNA initiate during high levels of iron?
-Fur iron regulator binds its co-repressor Fe
-Enterochelin is repressed, rhyB is suppressed
-Succinate dehydrogenase (which uses iron for function) is expressed
What environmental response does sRNA initiate during low levels of iron?
-Fur repressor releases the promoters of enterochelin and rhyB
-SRNA rhyB binds succinate dehydrogenase mRNA, creates complex
-RNAase binds and rapidly degrades mRNA
-Succinate dehydrogenase expression shut down
What is this?
-Phase variation resulting in stochastic expression of a gene in a population of daughter cells
-The progenitor cell may be "on," but progeny could be either "off" or "on" randomly
Slipped strand mispairing
When does mispairing occur in DNA replication?
One or the other strand slips and mis-pairs with the wrong repeat on the other strand
True or False: Mispairing repeats can be homopolymeric (single nucleotide repeats) or heteropolymeric (repeats of dimers, trimers, tetramers, etc)
True
What determines the frequency of slippage/slipped strand mispairing?
Length of the tract
-Longer tract, higher frequency of slippage
-Can be as high as 1 in 100 daughter cells
Name an example of a highly heterogeneous population that can be controlled/maintained by cell replication
-N. gonorrhea
-Has over 100 genes
-Gene expression controlled by slippage