Hematology Final Exam Review
1/87
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Flashcards for Hematology Final Exam Review
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Total Count=
Formula for cell counts using a hemacytometer.
Cathode
Loading point of Patient sample during Hemoglobin Electrophoresis
Myelocyte
The last granulocyte to undergo mitosis
Primary Granules (Non-Specific)
First seen in Promyelocyte; examples includes Myeloperoxidase
Secondary Granules (Specific)
First observed in the Myelocyte; Contains lysozomes
Leukemia
Cells with high N/C ratio, multiple nucleoli, no granules and fine nuclear chromatin, may indicate:
Plasma Cells and Lymphocytes are found in both:
Peripheral blood and bone marrow.
Rubricytes are found:
Only in bone marrow
Hematocrit Value of 37% is:
Normal for an adult female: 35-49%
NOT typically part of a differential
Estimation of red cell number
Corrected WBC=
WBC X 100 / (#NRBC+100)
Normal for a newborn; abnormal for an adult
5 orthochromic normoblasts (metarubricytes) in the peripheral blood
Patient has a white count of 1,000/µL with 60% neutrophils:1,000 x 0.60 = 600 neutrophils per microliter
Absolute neutropenia
Absolute neutrophilia
Patient has a white count of 150,000/µL with 40% neutrophils:150,000 x 0.40 = 60,000 neutrophils per microliter
M:E Ratio
Myeloid to Erythroid Ratio, Includes Myeloid cells and Erythroid cells but not lymphoid ; Normal 3:1
Clinical presentation for all Myeloproliferative Chronic Myeloproliferative Disorders:
fatigue, malaise, bone pain, splenomegaly, and symptoms related to cell counts
low Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP) helps distinguish:
CML from a leukemoid reaction
Acute Myeloid Leukemia
have variable WBC with decreased platelet, Patient presents with bruising, Hypercellular BM, >30% Blasts in Bone Marrow, most common type of leukemia in adults; Incidence increases with age
Acute leukemia almost always has these blood counts?
Low platelet count
Acute Lymphocytic Leukemia
ALL (L1-L3)-Mostly blasts with one nucleolus and scanty cytoplasm, TdT, PAS, and CALLA positive, Best chance for survival for acute leukemias
Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia
CLL- Small, mature lymphocytes with smudge cells, High WBC with low/normal PLT - Best prognosis of all leukemias among adults
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Pancytopenia with hairy cells, Dry bone marrow type TRAP positive Tartrate Resistant Phosphatase
Multiple Myeloma
Malignant plasma cells with high serum immunoglobulins,Increased calcium and protein, Found in older adults, Observe punched-out bone lesions, Peripheral pancytopenia with rouleaux
Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Found in younger patients, Reed-Sternberg cell found in Bone marrow, Present with fever of unknown origin
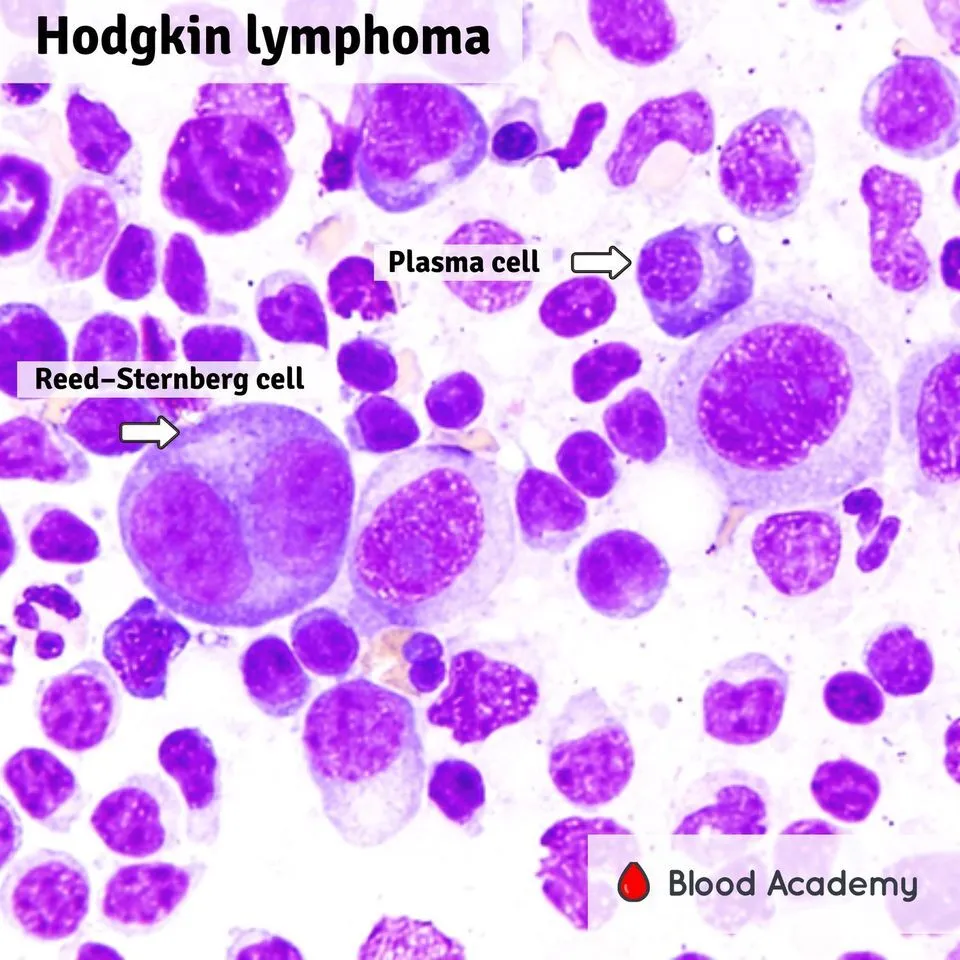
Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
Found in Older patients, Many different varieties, May see Butt Cells Immature Bizarre lymphoid cells
typical blood picture in lymphoma without bone marrow involvement:
Normal
Qualitative WBC disorders:
Toxic granulation, Dohle Bodies, Vacuoles
Reactive Lymphocytes:
Description for reactive (atypical) lymphocyte; Nucleus is often stretched out, May have granules, Ballerina skirt, Monospot and heterophile positive
patient has a hemoglobin value of 7.8 g/dL. The patient's MCH will be?
Could be low, normal, or high
Macrocytic Anemia
Megaloblastic Anemia; Defective DNA synthesis from B 12 or Folate poor diet, Bone marrow will show asynchrony, karryorhexis, giant metamyelocytes and bands, Hypersegmented Neutrophils, Pancytopenia
Macrocytic Anemia
Pernicious Anemia: Lack of intrinsic factor which is involved in the absorption of B 12
Microcytic Anemia
Iron deficiency (Hypo, Micro); Chronic blood loss the most common reason in adults, Poor diet ↓Serum Fe ↑TIBC ↓ Ferritin
Microcytic Anemia
Beta Thalassemia; Hypo,micro, Common in Mediterranean, South East Asians, and Black, Target cells, Basophilic stippling, increase in alpha chains, Electrophoresis ↑ A2 and F
Sports Anemia (march Hemoglobinuria)
loss of 10% of total blood from an acute bleed
Alpha Thalassemia 4 gene deletion
Serious life threatening disease
Which anemia would produce the most polychromasia on the blood smear?
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Cells sensitive to lysis by complement
Cells fragmented by fibrin in vessels
Microangiopathic Anemia (DIC)
Product involved in heme synthesis
Hemosiderin
Hemosiderin in urine; Urine Free Hemoglobin
Intravascular Hemolysis
Inherited defect in spectrin, Decreased cell surface, Peripheral smear: Spherocytes (MCHC >36%), Polychromasia,↑ Osmotic fragility
Hereditary Spherocytosis
Pernicious Anemia
50-year-old white female who was experiencing shortness of breath on exertion, and numbness and tingling of her fingers. She is thin and pale with a slight yellow tinge to her skin. Her tongue is very smooth and slightly reddened. HGB= 4.7 g/dL HCT = 13.6% RBC = 1.1 x 10 6/µL WBC = 2.0 x 10 3/µL PLT = 87.0 x 10 3/µL
Hereditary Spherocytosis
At 0.55% NaCl there was a tinge of color in the supernatant and at 0.35% NaCl there was a dark red color with no red cell button. This osmotic fragility test is helpful for
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria
Red urine, Urine hemosiderin +, Sucrose + (Sugar Water), Ham’s test +
Auto Immune Hemolytic Anemia
Warm, Spherocytes, Polychromasia,+DAT
Sex-linked, decrease in enzyme Oxidant; drugs cause hemoglobin to denature and precipitate
G-6-PD; Heinz bodies seen with Methylene Blue
Pyruvate Kinase; Reduced ATP production results in alterations of RBC membrane
Peripheral Smear: Echinocytes
Lead Poisoning; Chronic exposure can lead to Hypochromic, Microcytic
Basophilic Stippling
Sickle Cell Beta Chain substitution ( β7[A3]Glu→Val)
Cells form rods at low O 2, Sickle Dex +
Significance of Reticulocytes:
Increased in our hemolytic anemias
Iron Deficiency Anemia
Low or normal reticulocyte count (untreated)
Pernicious Anemia
hypersegmented neutrophils; schilling test to diagnose
Seen with New Methylene Blue associated with decreased RBC survival/hemorrhage, erythroid hyperplastic marrow; Referred to as Polychromasia when seen on Wright Giemsa Stain
Reticulocyte-RNA
Heinz Bodies can only be seen with:
supravital stain
ESR A mechanism for cells falling (settling) A screening test
Factors affecting the ESR- Fibrinogen/protein, Rouleaux, Inflammation, infections, malignancies
All of the following cause an elevated ESR EXCEPT
Polycythemia
Platelet Impedence
are counted in same bath as RBC Anything between 2-20fL
RDW
red cell distribution curve width 12-15%
Which of the following would have a normal MCHC?
Macrocytes will have increased MCH, but normal MCHC.
Which of the following would have a low MCH?
Thalassemia trait
How is the hematocrit determined on most automated cell counters?
Calculated using red count and MCV: HCT= (RBC x MCV)/ 10
Which of the following measurements must have the red cells lysed?
Hemoglobin
Polychromasia would most likely be associated with:
Acute blood loss, a couple of days later
WBC Histogram R1 Lymphocyte population
does not begin at baseline (35fL)-Clumped or Giant Platelets, NRBC, Intracellular parasites
Interfering Substances for Cell Counters Interference
High Glucose
Which of the following will NOT affect the automated hematocrit?
Cold Agglutinin
What should be done before reporting these results?
Warm the sample to 37 degrees and rerun
the best course of action when hematocrit results dropped 5% after IV therapy
Report the results-it makes sense in view of the therapy
Anisocytosis
Variation in cell size
Poikilocytosis
variation of RBC shape
interfere with hemoglobin determination on the Coulter analyzer
Lipemia, High WBC, decreased RBC lysing reagent
What is the defect in Beta Thalassemia Major?
Rate of globin chain synthesis
What is the defect in Hemoglobin SC disease?
structural defect in globin chain
What is the problem in microangiopathic anemia?
Cells fragmented by fibrin in the vessels
What is the problem in PNH?
Cells are sensitive to lysis by complement
What is the best test to distinguish IDA from anemia of chronic disease?
Ferritin
What is the best test to distinguish PV from secondary polycythemia?
Oxygen saturation
M5 (monocytic)
a patient has peripheral smear containing blasts that react with the non-specific esterase stain, a positive murimadase, and bleeding gums, what is the most likely leukemia?
What cells are increased in Myeloid Hyperplasia?
blast
What would the M:E ratio be in myeloid hyperplasia?
Increased
a normal finding in adults?
an occasional echinocyte
Change their Shape
what must RBCs be able to do to escape the macrophages in the spleen?
Nuclear clumping.
What distinguishes a Myeloblast from a Lymphocyte? This image is of a myeloblast.
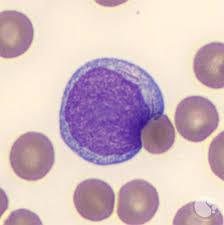
Distinguish from a left shift
Why should Pelguer-Huet anomaly be identified?
Administering Chloramphenicol
Often causes aplastic anemia?
Intravascular Hemolysis
What does urine hemosiderin indicate?
Why should Pelguer-Huet anomaly be identified?
Distinguish from a left shift
Which of the following is a product involved in heme synthesis?
Coproporphyrin