Momentum and Newton's laws of motion (3.1)
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
What is mass? and what is its relation to motion?
Mass - the amount of matter in an object
Thus mass is a property of an object that resists change in motion
What is weight? and how does it differ to mass?
Weight - the effect of a gravitational field on mass
W=mg
Where W is in N
m is in Kg
g is in ms-2
Weight vs Mass
Weight can differ depending on the gravitational pull whereas mass is constant. E.g. on the moon someone will have a lower weight but the same mass
What is Newton’s first law?
1st law - a body will remain at rest or move with constant velocity if no resultant force acts on it
What is Newton’s second law?
2nd law - the rate of change in momentum is proportional to the magnitude of the force
FNET = ma
Where FNET is in N
Where m is in Kg
Where a is in ms-2
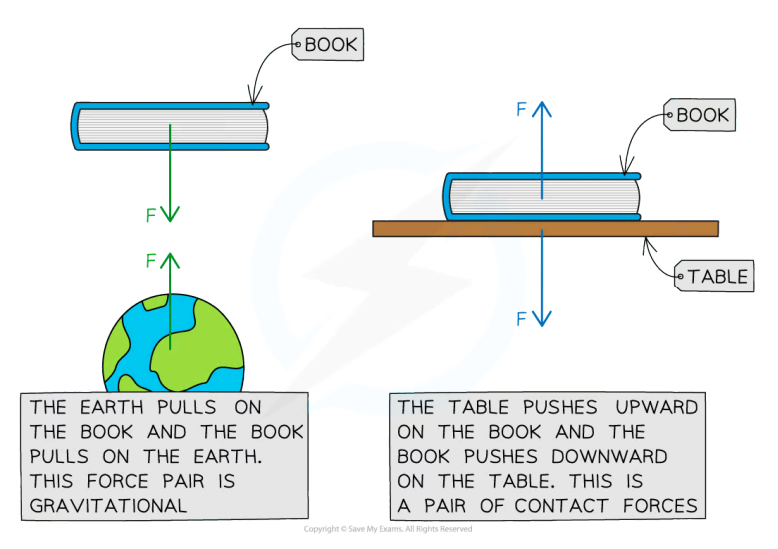
What is Newton’s third law?
3rd law - if one body exerts a force on another, it will experience a force by the other body, which is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction
Forces always occur in pairs
The force pairs must be:
The same type of force
The same magnitude
Opposite in direction
Acting on different objects
What is linear momentum?
Linear momentum - the product of mass and velocity
p=mv
Where p is momentum in kgms-1
Where m is mass in kg
Where v is velocity in ms-1
Momentum is a vector
How can force be defined in terms of momentum?
Force - the rate of change of momentum
F=Δp/Δt
Where F is force in N
Where Δp is change in momentum in kgms-1
Where Δt is change in time in s
Δp = pfinal - pinitial
F is the resultant force
Δp is also known as impulse