Radiographic Contrast
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
Define Contrast
the difference between adjacent densities
5 ways to describe high contrast
few shades of gray
increased contrast
low kVp
short scale
less latitude
5 ways to describe low contrast
many shades of gray
decreased contrast
high kVp
long scale
greater latitude
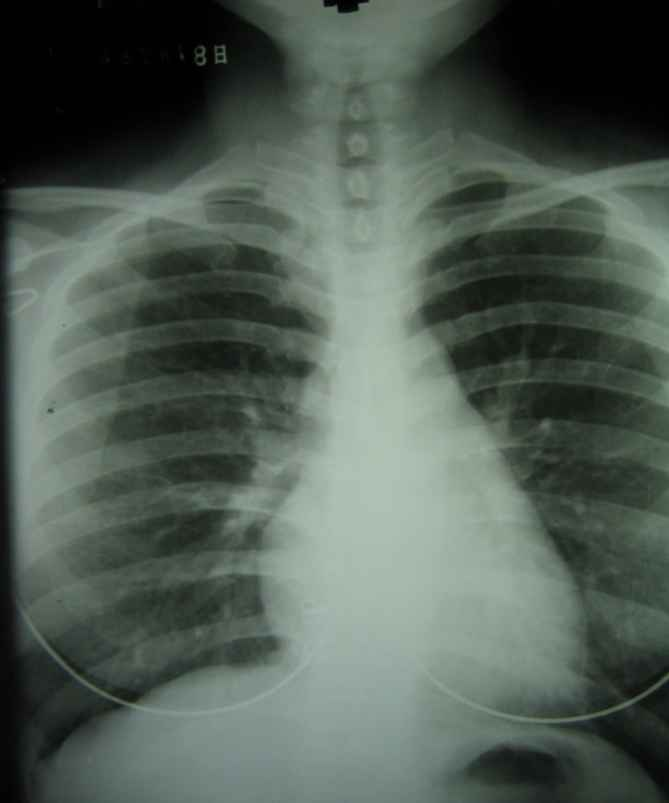
Does this radiograph have good or bad technique?
good
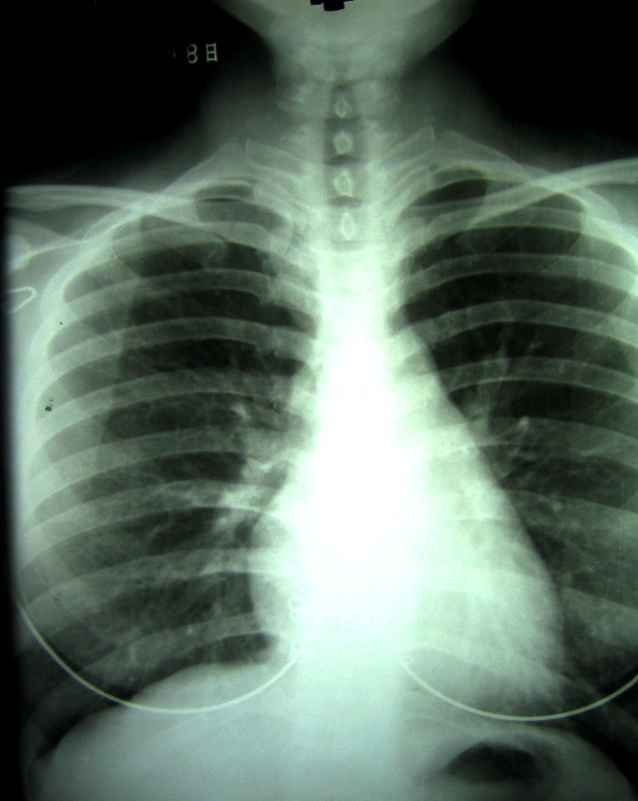
Does this radiograph have high or low contrast?
high
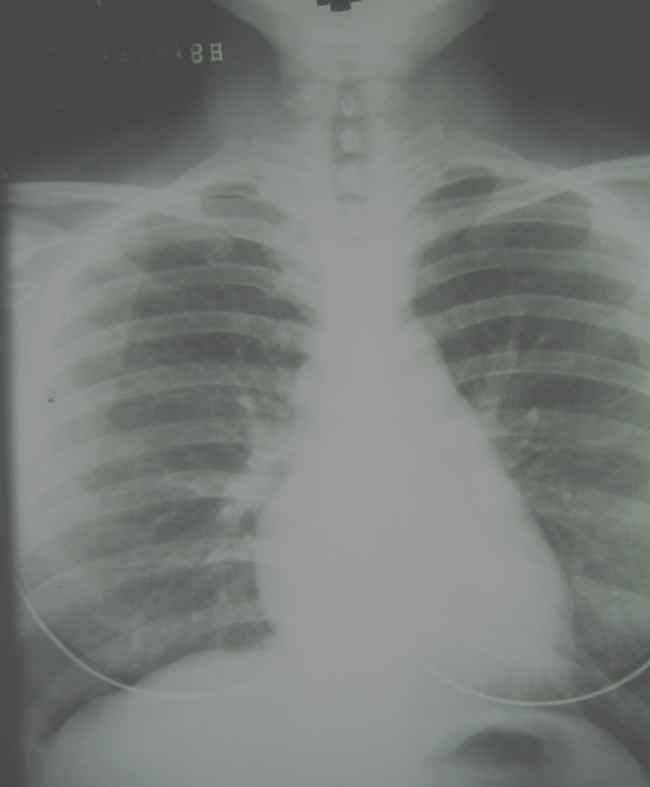
Does this radiograph have high or low contrast?
low
What are the two types of contrast?
Image Receptor (Film) Contrast
Subject Contrast
The range of densities that the image receptor is capable of recording is determined by:
1) Intensifying Screens
2) Film Density
3) D log E curve
4) Processing
Intensifying screens create an inherently _____ contrast image.
The higher the speed of the screen, the ____ the contrast.
BUT, this difference is ______.
higher
greater
negligible
Within the diagnostic range, film density has ____ effect on contrast.
BUT, excessive or inadequate density _____ contrast.
little
decreases
What represents the physical composition of the film?
D log E curve
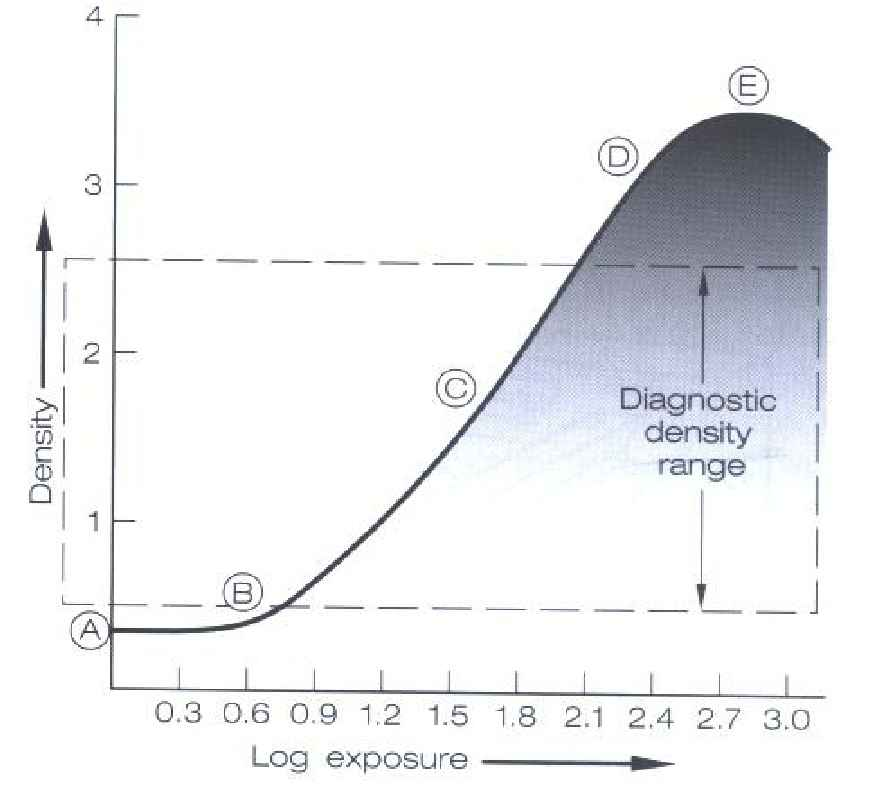
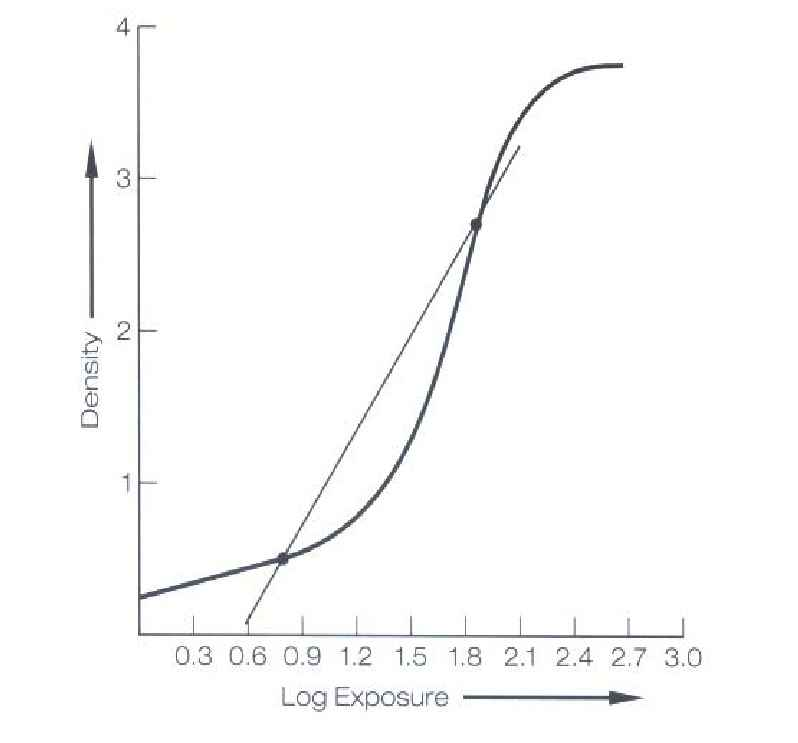
D log E Curve
The steeper (more vertical) the slope of the curve, the ______ contrast.
The steeper the slope, the _____ the range of exposures that will produce densities within the diagnostic range.
The greater the contrast, the ____ the latitude.
greater
narrower
less
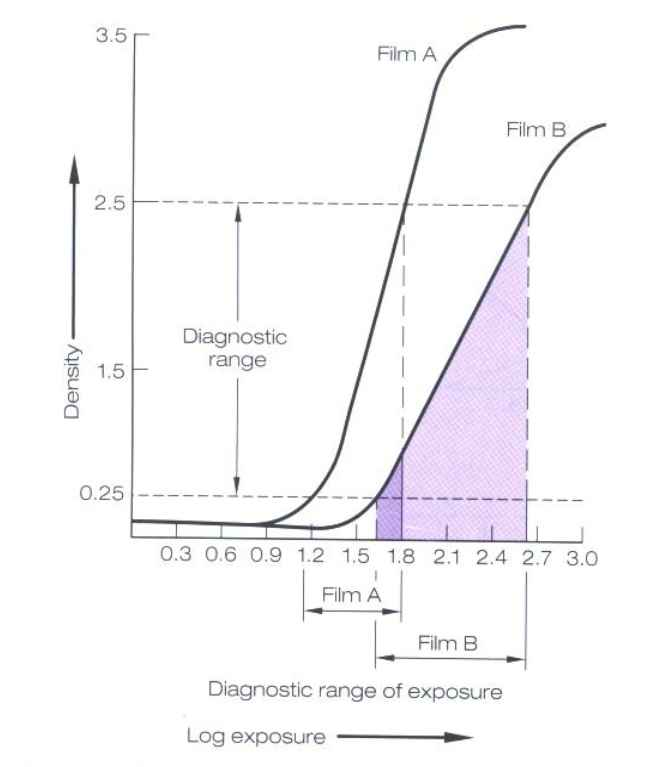
Which film has greater contrast, greater latitude, greater speed, and less detail?
film A
List the 4 processing factors that affect contrast
developer time
developer temperature
replenishment rate
contamination of the chemicals
Changes in any of the processing factors will result in ___ contrast on the film.
decreased
(Subject Contrast) The range of difference in the intensity of the x-ray beam after it has passed through the patient is dependent upon:
kVp
amount and type of irradiated material
What is the primary controller of subject contrast?
kVp
The higher the kVp, the ___ the range of energies in the beam.
This produces a ____ range of densities on the film (____).
greater
wider, (grays)
High kVp = ___ contrast
low contrast
With low kVp, dense structures (bone) will absorb most of the x-rays while x-rays will pass through structures with ____ density (soft tissue or air).
Low kVp will ____ differential absorption.
little
enhance
Low kVp = ____ contrast
high contrast
Define the Compton Effect
higher kVp will cause more scatter
(T/F) Scatter causes fog on the film.
true
What is fog?
What will fog do to contrast?
an overall unwanted density on the film
any kind of fog will decrease contrast
The thicker the body part, the ____ x-rays are absorbed and the ____ x-rays are transmitted.
Smaller body parts absorb ____ x-rays.
Great difference in adjacent body part thicknesses will cause ____ subject contrast.
more, less
less
high
(T/F) When the overall thickness of the body part increases or the field size increases, the amount of scatter decreases.
False, the amount of scatter increases
More scatter = ____ contrast
less contrast
Two factors that affect subject contrast:
1) atomic number
2) density (mass per volume)
The higher the atomic number, the ____ x-rays are absorbed.
The greater the difference in average atomic number of adjacent tissues, the _____ the contrast.
Barium = Soft tissue =
more
greater
56, 8
The greater the density of a tissue, the ____ x-rays are absorbed.
When the difference between adjacent densities is great, the subject contrast is ____.
Bone vs. ____ tissue
more
high
lung
What is the major controller of radiographic contrast?
kVp
An increase in kVp will cause a ____ in contrast.
decrease
It takes a change of at least ___% in kVp to see a visible difference in contrast.
4%
mAs controls _____
density
If the density is too much or too little, the contrast is _____.
reduced
What affect does focal spot size have on contrast?
little or no effect
What effect does anode heel effect have on contrast?
very little effect
What does SID affect?
density
OIDs over ____” will reduce the amount
less scatter = ____ contrast
10 inches
higher
more filtration = ____ contrast
less contrast
tighter collimation (increased beam restriction) will result in ____ scatter
less scatter = ____ contrast
less
higher
the thicker the part, the _____ scatter
more scatter = ____ contrast
higher the atomic number of the part = the ____ the contrast
more
less
higher
Grids absorb scatter which creates ____ contrast
higher contrast
What is the contrast improvement Factor (K)
K = average gradient w/grid/average gradient w/o grid
Most grids have contrast improvement factors between ____ and ____.
the contrast is ___ to ___ times higher than if a grid is not used.
the higher the contrast improvement factor —- the _____ the contrast
1.5 and 3.5
1.5 to 3.5
higher
screens create _____ contrast
the faster the screens, the _____ the contrast
higher
higher
Changes in temperature, developer times, replenishment rate, or chemical contamination will ____ contrast
decrease