microbio exam #1
1/358
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
359 Terms
which of the follwoing structures is found only in bacteria?
lipopolysaccharide
which of the following statements about viruses is true?
viruses that infect bacteria cannot infect humans
what are prions?
infectious proteins with no nucleic acid
taken together, the experiments of pasteur, tyndall, and koch demonstrated that…
as long as no living organisms enter a solution, it can be kept sterile indefinitely
there is much interest in using bacteriophage to kill the bacteria that cause infectious diseases in humans. which of the following is a valid concern about such theory?
the virus preparation might be contaminated with a few live bacterial cells
viroids are…
small pieces of RNA without a protein coat
archaea have …
a cell membrane
in pasteur’s famous experiment that finally disproved spontaneous generation, bacteria grew
only in the media that came in contact with other bacteria
tyndall repeated the same experiment, but got different results. this was because
the media he was trying to sterilize contained endospores
which of the following is currently believed to be a major difference between prokaryotes and eukaryotes
eukaryotes have a nucleus surrounded by a nuclear membrane
which of the following makes more copies of itself by acting as a template for protein folding?
prion
single-celled photosynthetic organisms with nuclei and without cell walls are …
algae
which of the following statements about bacteriophage is correct?
they have a protein coat
how do prions cause diseases like mad cow disease?
they act as a template to misfold native proteins
the three main branches in the phylogenetic tree of life are …
bacteria, archaea, and eukaryotes
which of the following is a hallmark of protozoa, but not of bacteria?
endocytosis to engulf nutrients
these viruses infect the bacterium E. coli. which of the follwoing must also be true?
they cannot infect humans
prions are infectious agents that contain
a protein only
we said in an early lecture that science should be “predictave”. what does this mean?
if you change a variable in an experiement, you know how the results will change
which of the following correctly describes comparaisons between bacteria, eukaryotes, and archaea?
only bacteria have peptidoglycan in their cell structures
last semester, when he was working with bacteriophage in the lab, a student came to me and said his doctor told him he had a viral infection. he was pretty sure he had aquired the infection from the bacteriophage in lab. what would you have told him?
bacteriophage cannot infect humans
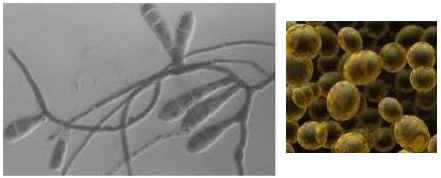
the pictures shown here represent the same organism in different stages in its life cycle. what is the organism?
a type of fungus
a structure that is 50 nanometers in diameter and is composed only of protein, RNA, and lipid would most likely be an example of which of the following?
an enveloped virus
which of the following is something that pasteur could have concluded logically after his swan necked flask experiment?
boiling destroys microbes in broth and they do not regrow from air
saying that microbes are “diffusion limited” is the same as saying that they…
lack an organized intracellular transport system
what are archaea?
a kingdom of prokaryotes that lack peptidoglycan
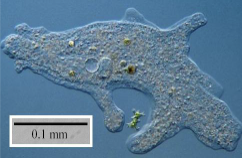
what is the organism that is depicted in the micrograph at the right?
a protozoan
you have discovered a new organism that is about 200 nm across its largest dimension. it contains DNA, RNA, protein, and lipid. it can replicate its DNA, but requires a host cell in which to do that. it appears to have no ATP generating mechanism. what is it? why?
a prokaryote because of its composition
the fact that bacteria lack an endomembrane system explains their …
small size
you are examining an organism under the microscope. it is about 15 micrometers (um) in diameter. a chemical analysis shows that it contains DNA< RNA, and protein, as well as other macromolecules. you grow it on a petri dish to get a pure culture, but this time when you look under the microscope, it consists of filaments 100 um long and 8 um wide. explain this.
you are looking at a fungal culture
we mentioned that viroids can infect and kill plant cells. how?
they inhibit protein synthesis by the plant cell
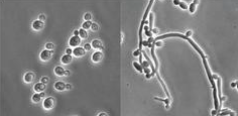
you inoculate a pure culture onto a petri dish, but when you look at the culture after it has grown, you find both of the organisms at the right. what is the explanation for this?
your pure culture was a fungus
eureka! you have discovered a new organism! you decide to analyze it chemically. finding which of the following would mean that your new organism cannot be a virus?
NADH
how do prions cause infectious disease?
they misfold, and then cause other proteins to misfold, eventually damaging host cells
which of the following is not caused by hydrogen bonding
hydronium ions form in water
van der waals (hydrophobic) interactions occur when
a random charge fluctuation sets up a transient dipole in a non-ionic molecule
two molecules with polar covalent bonds are attracted to each other. the resulting bond could be a
hydrogen bonds
weak bonds are caused by
charge interactions
why is it important that most intermolecular interactions in cells are weak bonds
they are more easily reversible
what happens when water hydrates itself
H3O+ and OH- ions form
which of the following cannot participate in hydrogen bond formation?
the H in C-H
the pH inside a bacterial cell is 7. the pH outside is 6. what is the size of the H+ gradient?
there are 10 times as many protons outside the call than inside
which of the following can serve as a hydrogen bond donor?
the H in an N-H bond
weak bonds are caused by
charge interactions
a C-C bod in molecule A undergoes a random charge fluctuation. as molecule A comes close to a C-C bond in molecule B, what will happen to molecule B?
a dipole will be induced which will weakly attract molecule B to A
the hydrophobic effect is used to explain
how micelles form in an aqueous environment
which of the following pairs of atoms may be involved in hydrogen bond formation, either as donor or acceptor
P=O
a difference between strong bonds and weak bonds is that
weak bonds involve charge attraction between two molecules or within a large molecule
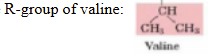
proteins with the amino acid valine on their surface often stick together when placed in water. why?
due to the hydrophobic effect, H2O forms a network of H-bonds around collected valines
the pH of bacterial cytoplasm is 7, and the pH of the environment where the bacterium is growing is 5. how much difference is there in the H+ concentration between the inside and outside of the bacterial cell?
the outside of the cell has 100 times as many protons as the inside
which of the following statements is true about polar covalent bonds?
electrons in a polar covalent bond spend more time around one of the bond atoms than the other
what advantage is it for biological systems to use hundreds of weak bonds rather than one strong bond to hold two molecules together?
weak bonds can be broken with less energy input than strong bonds
which of the following is a consequence of water forming hydrogen bond networks?
water dissolves polar molecules and ions easily
an acidiphilic bacterium lives in an environment with an external pH of 3. there are approximately
10000 times as many H+ outside than inside the cell
which of the follwoing could be a hydrogen bond acceptor?
the N in a C-N bond
what makes a biological strong bond?
electron sharing between atoms in the bond
how can the R-group of leucine interact with the R-group of valine?
a temporary dipole in leucine’s R-group can induce another dipole in valine’s
which of the following is a consequence of the unique structure of water molecules?
there are a small number of ions even in pure water
two molecules are composed of the same atoms, but the molecules have different molecular weights. this can be explained by the existence of
isotopes
in a biological context, which of the follwoing describes a strong bond
electron sharing between atoms with an electronegativity difference less than 1.6
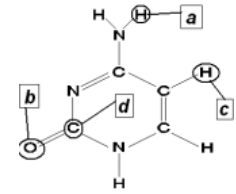
which of the atoms in the structure at the right could be a H-bond donor? a H-bond acceptor?
donor = a; acceptor = b
which of the following is most important in the formation of micelles from a collection of phospholipids? why?
the hydrophobic effect since without water the micelle will fall apart
in order to make ATP, bacterium needs a change in pH of 2. assume ions can pass through porins freely. if the bacterium is growing in a neutral solution, what must the proton concentration in the bacterial cytoplasm?
10^-9 molar
what can you say about the element phosphorus from its entry in the periodic table
with a full outer energy shell it would be a (-3) ion
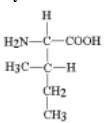
the amino acid depicted at the right can participate in what sort of tertiary interactions
van der waals interactions
which of the following is not a description of the hydrophobic effect
a transient interaction betweem temporary dipoles
enzyme X has the amino acid threonine in its active site. a mutation that replaced threonine with valine would likely have what effect on enzyme X?
it would cause the active site to become partially denatured
we can’t digest cellulose, though bacteria can, because …
we cannot digest B-glycosidic bonds but bacteria can
nucleic acids are put together from their monomers, nucleotides, with ___ bonds.
phosphodiester
rank the following lipids in order from most solid to least solid at room temperature:
1) saturated lipids
2) cis-unsaturated lipids
3) trans-unsaturated lipids
most solid (1) > (3) > (2) least solid
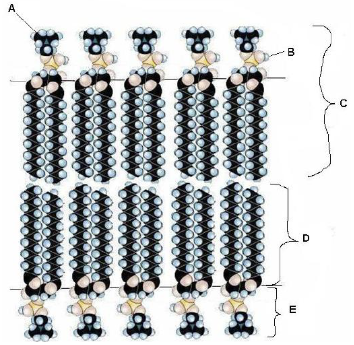
in the following depiction of a phospholipid membrane, what represents the fatty acid component of the membrane?
D
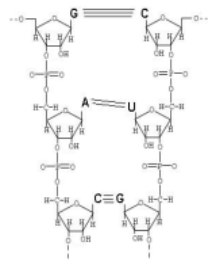
what is wrong with this model of a nucleic acid molecule?
the model is not antiparallel
which of the following is not true of cellulose?
it is branched
bacteria can vary the lipids they use in their membrane, depending on the temperature. the goal is to keep the membrane from melting, but not allowing it to get so solid that proteins can’t move around. How would the membrane of a psychotroph growing at 28 C compare to the membrane of the same organism growing at 5 C?
it would have more cis-unsaturated lipids at 5 C
amphipathic phospholipids form a membrane bilyer if placed in water. what would happen if the membrane were placed in a nonpolar solvent?
it would turn inside out
in a protein tertiary structure, the side chains of the amino acids valine and isoleucine could interact by …
van der waals interactions
which of the following does not involve hydrogen bonding?
lipids form from fatty acids and glycerol
which of the following describes the hydrophobic effect?
hydrogen bonding of water around hydrophobic molecules
in a protein alpha helix, hydrogen bonds form between …
atoms in the peptide bonds that join amino acids together
a great deal of the structure of a a bacterium is composed of carbohydrates. which of the following structures does not involve carbohydrates?
carboxysomes
a nucleic acid polymer is formed by …
phosphodiester bonds between 5’ and 3’ carbon atoms
which of the following lipids would be the most fluid at room temperature?
lipids with 3 cis-unsaturated fatty acids
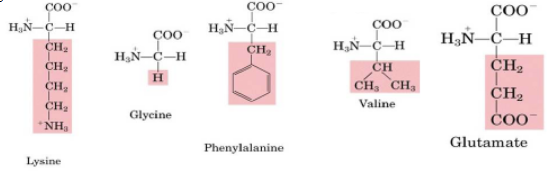
which of the following amino acids does not have D- and L- stereoisomers?
glycine
alpha helices and beta pleated sheets …
are both considered to be protein secondary structures
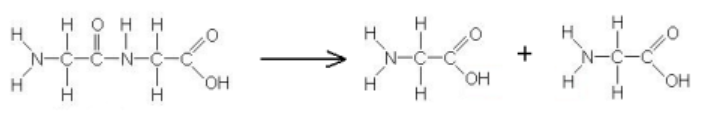
this reaction is an example of …
hydrolysis
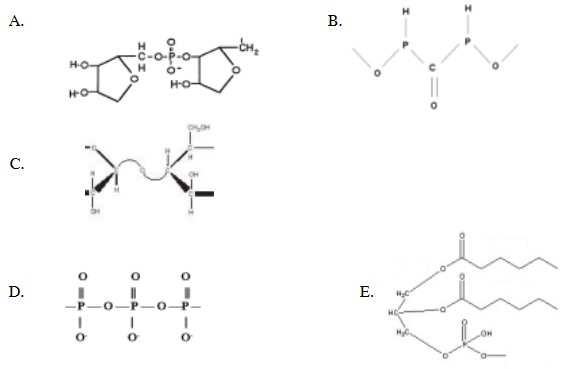
which of the following shows a phosphodiester bond?
A
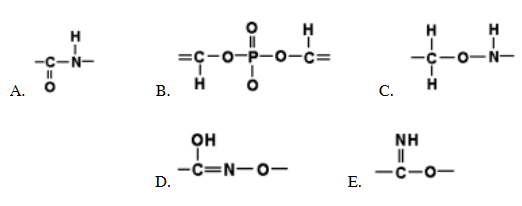
which of the following represents the structure of a peptide bond correctly?
A
why is it important to understand that glycosidic bonds can have both alpha and beta anomers (that there can be a and B glycosidic bonds)?
it is much harder to digest B-glycosidic bonds. only bacteria can do it
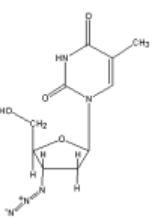
this is the structure of the DNA synthesis inhibitor and antiviral drug AZT. how does AZT interfere with the structure of nucleic acids so much that it can be used as an antiviral?
its 3’ end cannot participate in a dehydration synthesis reaction
condensation reactions …
usually require energy input
how is hydrogen bonding involved in the structure of cellular lipid molecules?
H-bonding is not involved in the structure of a lipid molecule
which of the following is true about a condensation reaction
it generally requires energy output
what is a disulfide bond?
a covalent bond that is involved in forming protein tertiary structures
in which of the following polymers would you find alpha glycosidic bonds?
starch
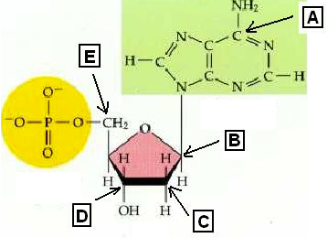
which of the carbon atoms in the nucleotide could be the 3’ end of a DNA molecule?
D
which of the following is a correct reference to a hydrolysis reaction?
carrying it out releases energy
beta sheets …
involve peptide bond amino groups as H-bond donors
we now know that trans-unsaturated fatty acids contribute to heart disease, but they were formerly in widespread use in the food industry. what was the advantage in using them?
they could be synthesized cheaply by heating cholesterol-free natural oils
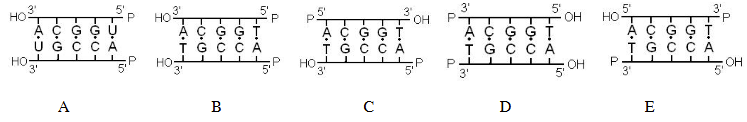
which of the following most accurately represents the structure of DNA?
C
which of the following would not require enzyme catalysis?
folding of a protein into an alpha helix