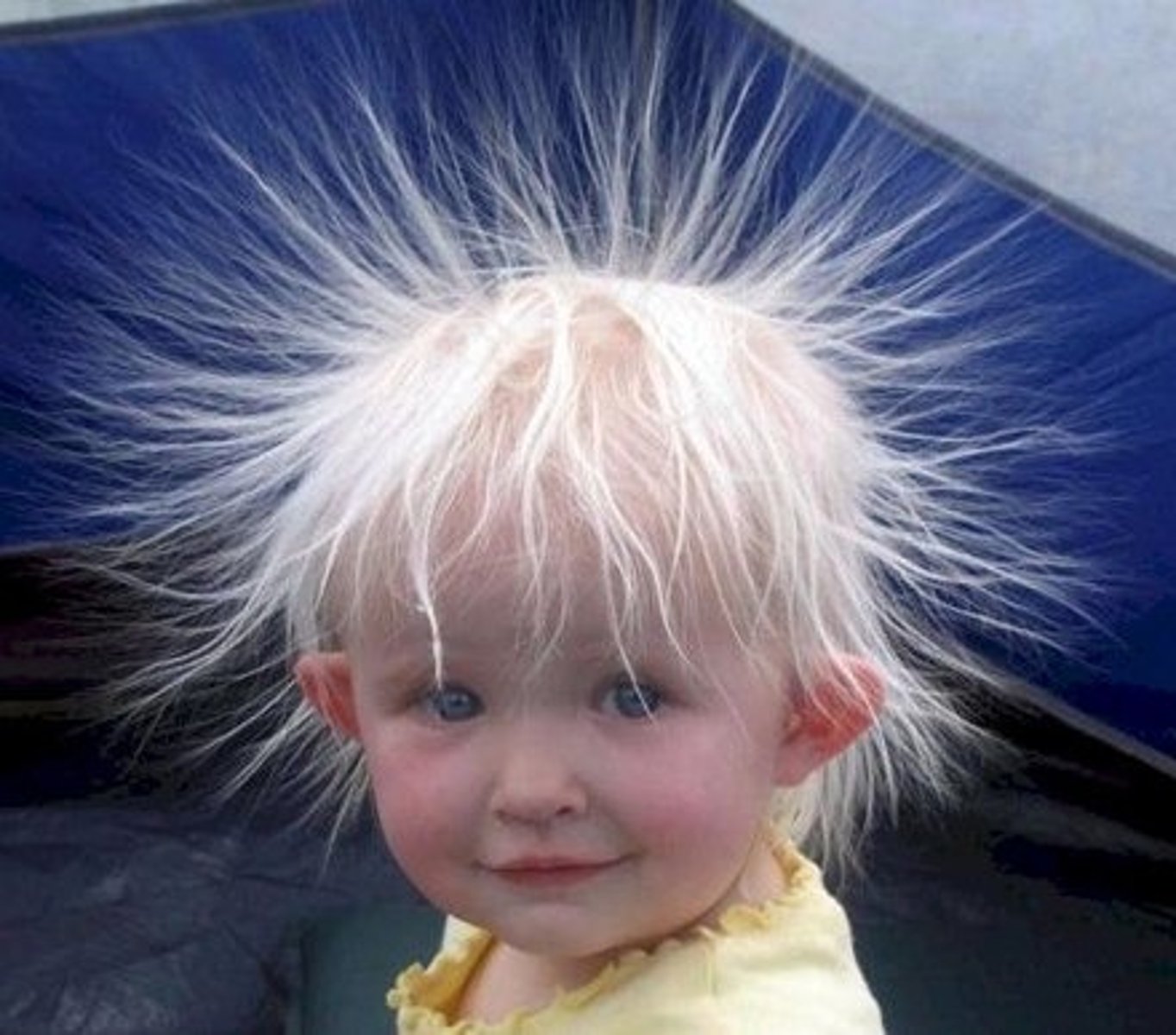
AQA GCSE Physics - Static Electricity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What is matter made of?
Atoms
What are the three types of electric charge?
Positive, negative and neutral
What particles have a negative charge?
Electrons
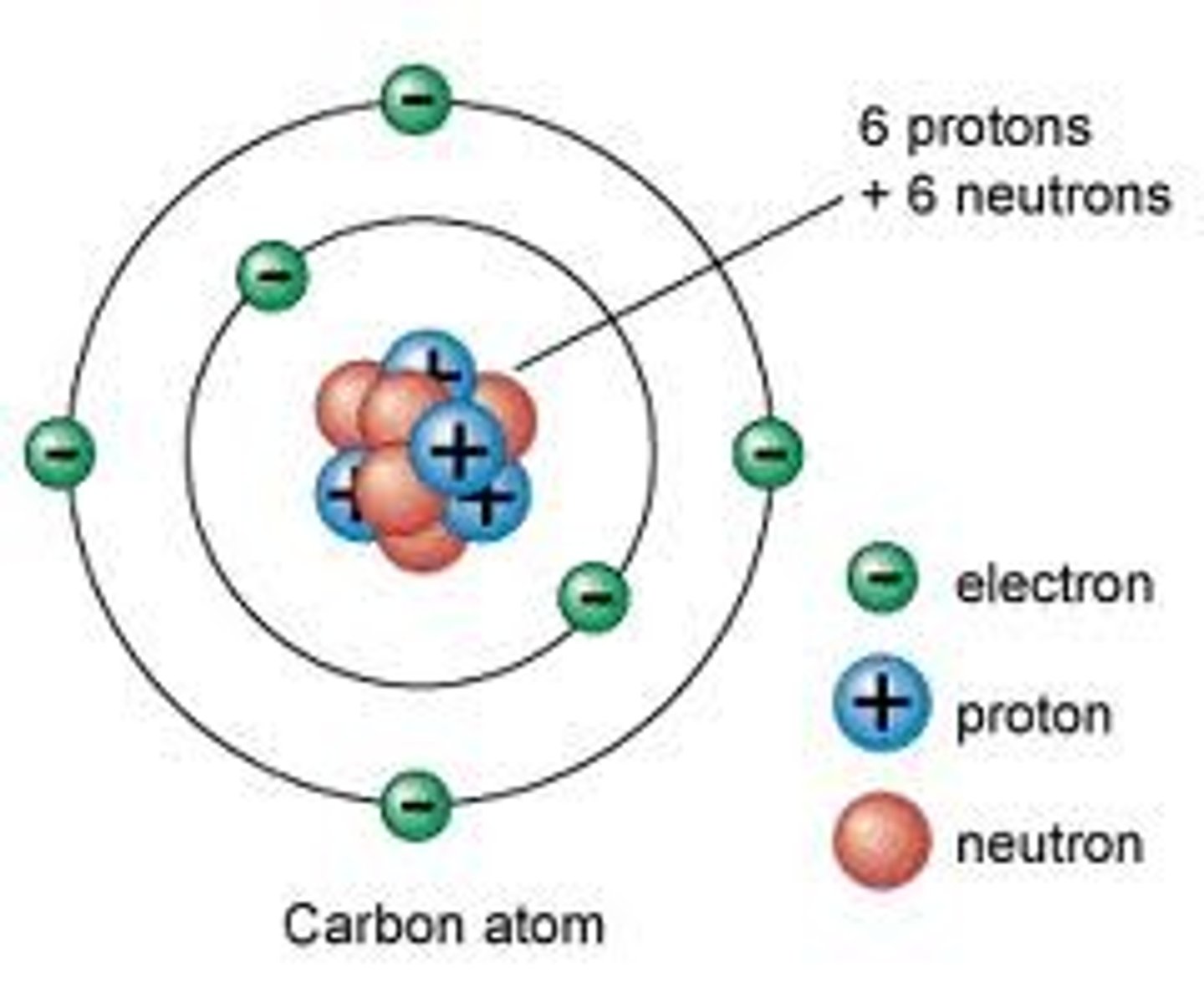
What particles have a positive charge?
Protons

What particles have a neutral charge?
Neutrons

What particles are found in the center or nucleus of an atom?
Protons and neutrons
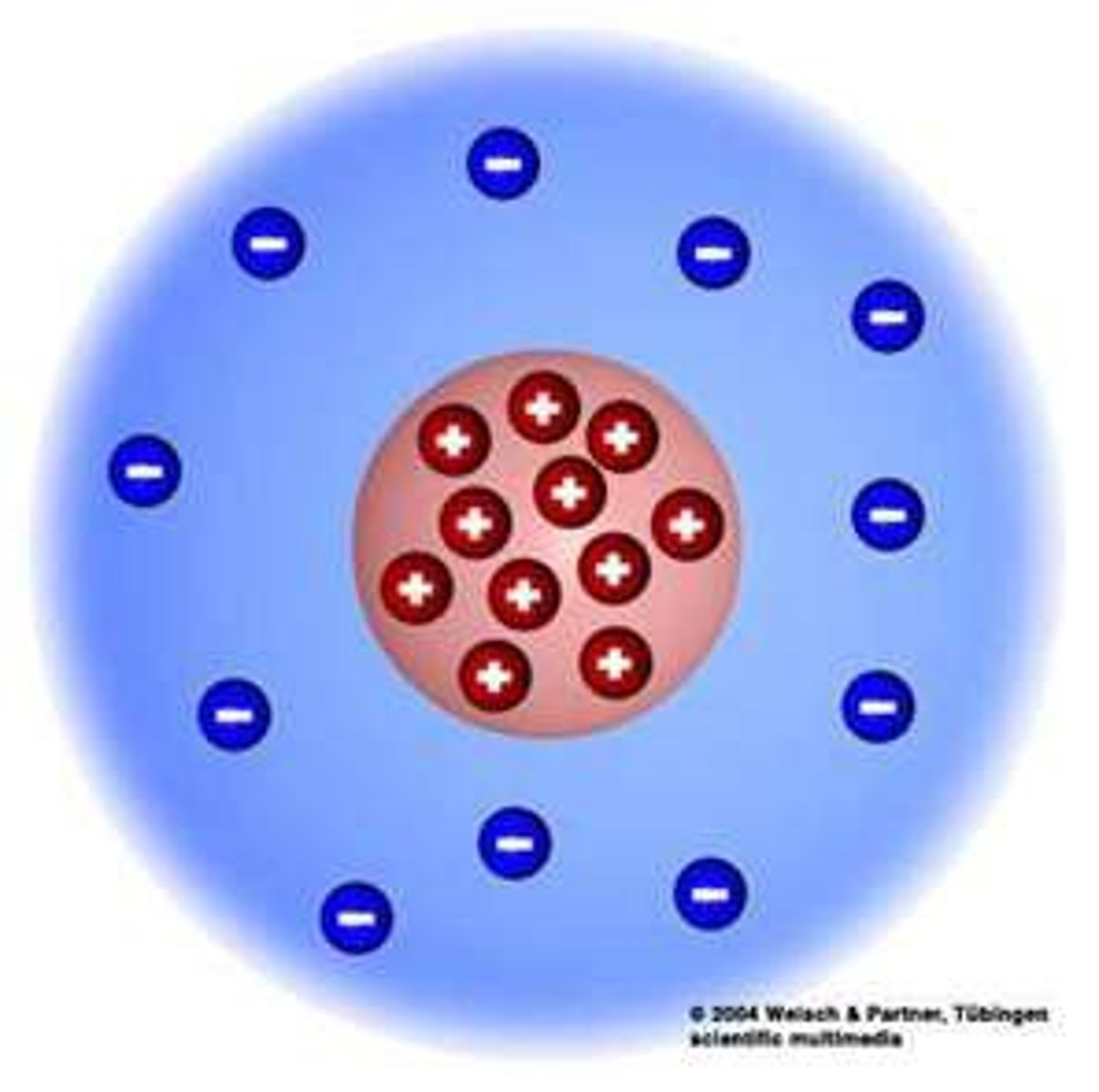
Where are electrons found?
In orbits surrounding the nucleus
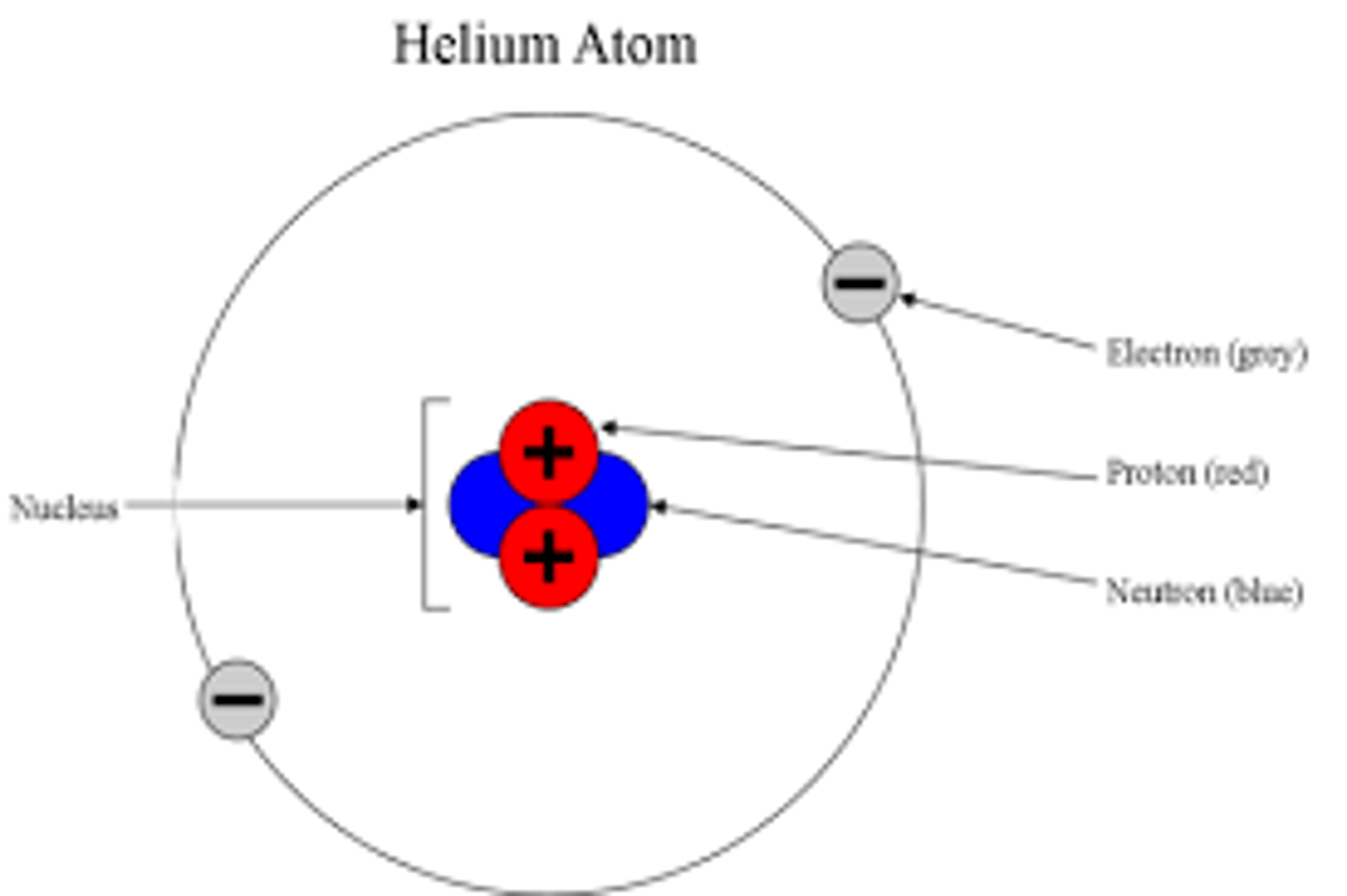
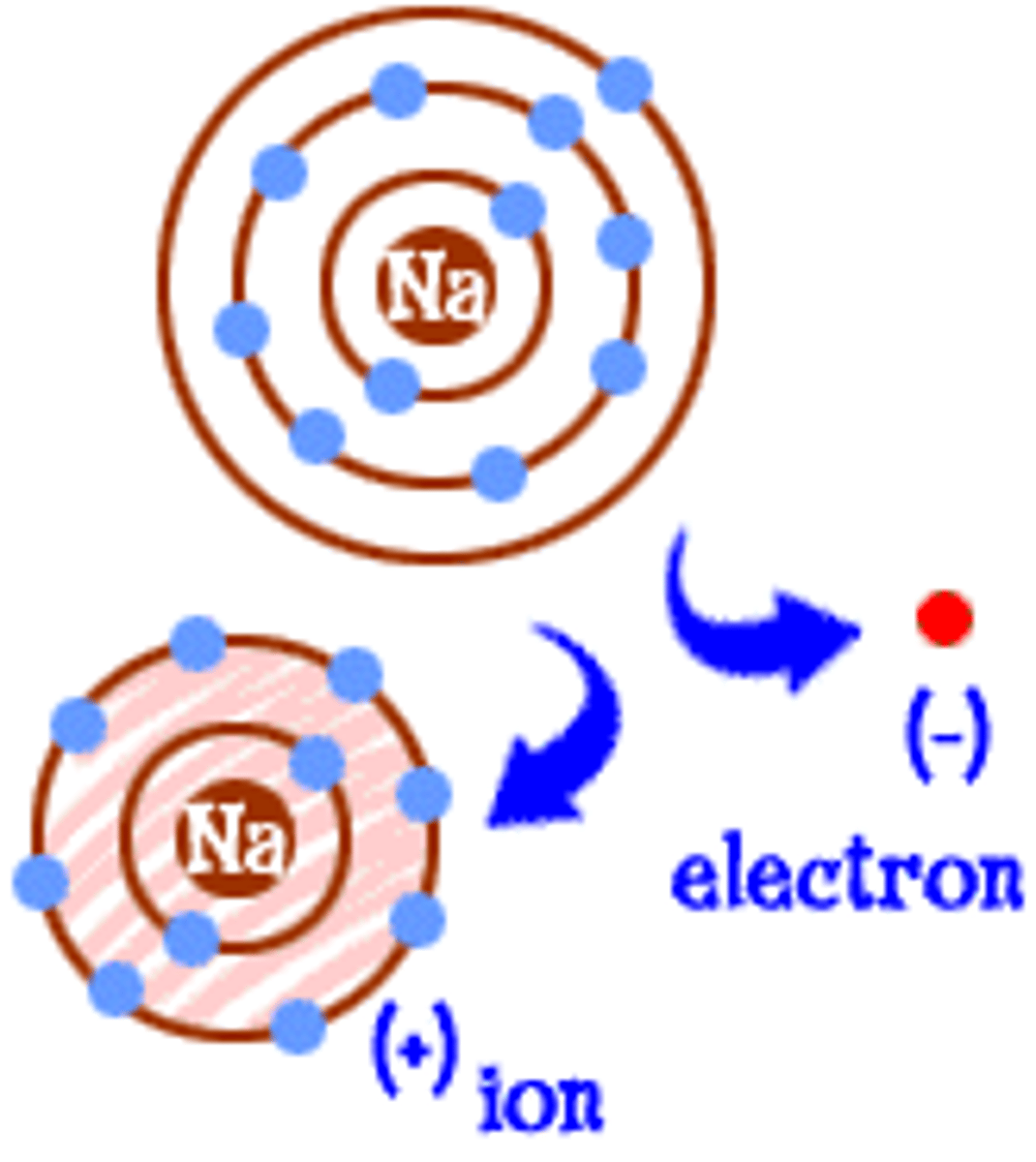
What is an ion?
An atom that has gained or lost electrons
What are charges that are the same called?
Like charges
What are charges that are different called?
Unlike charges
Which type of materials can usually become charged with static electricity?
Insulators

What do you have to do to insulators to charge them with static electricity?
Rub two different insulators together
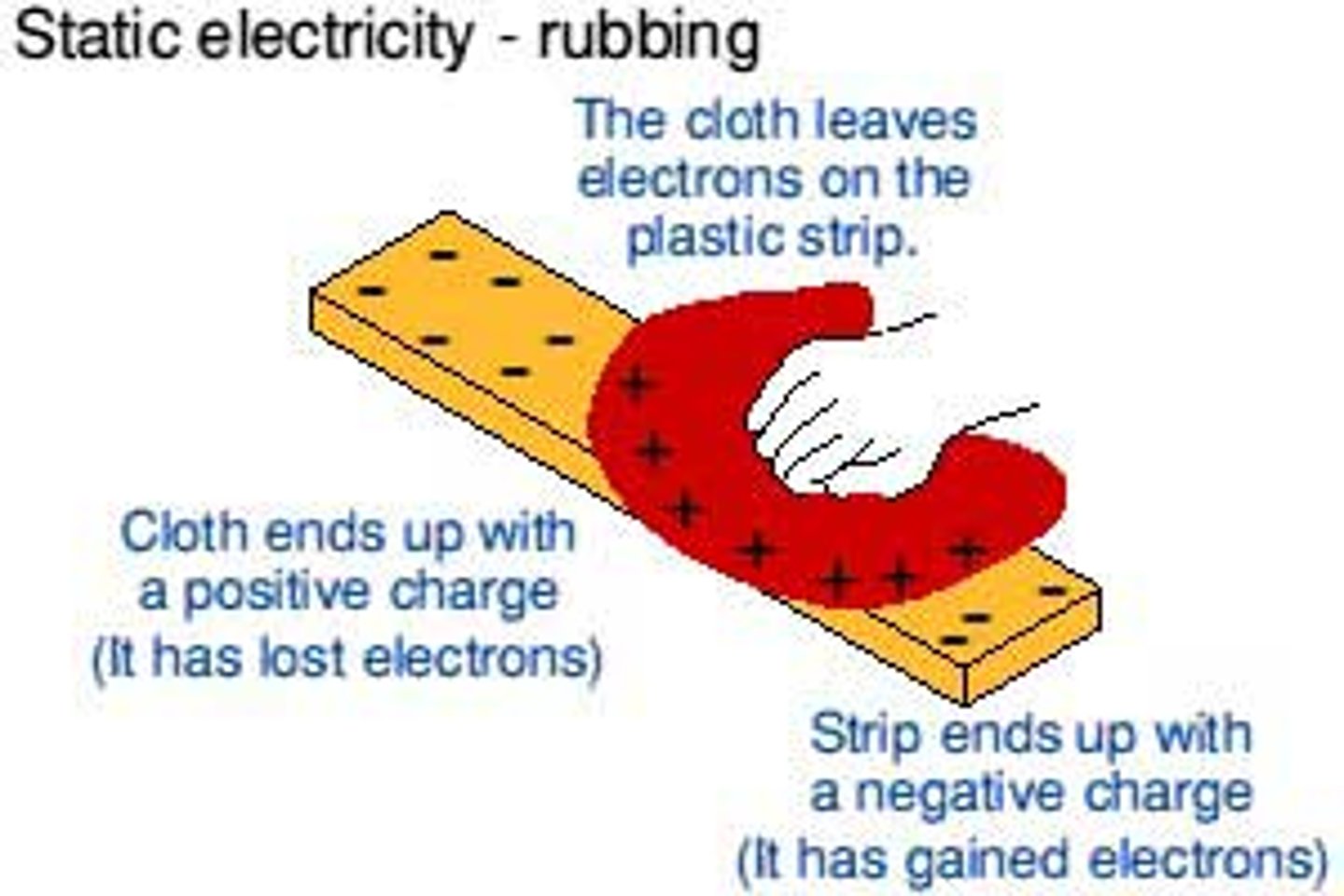
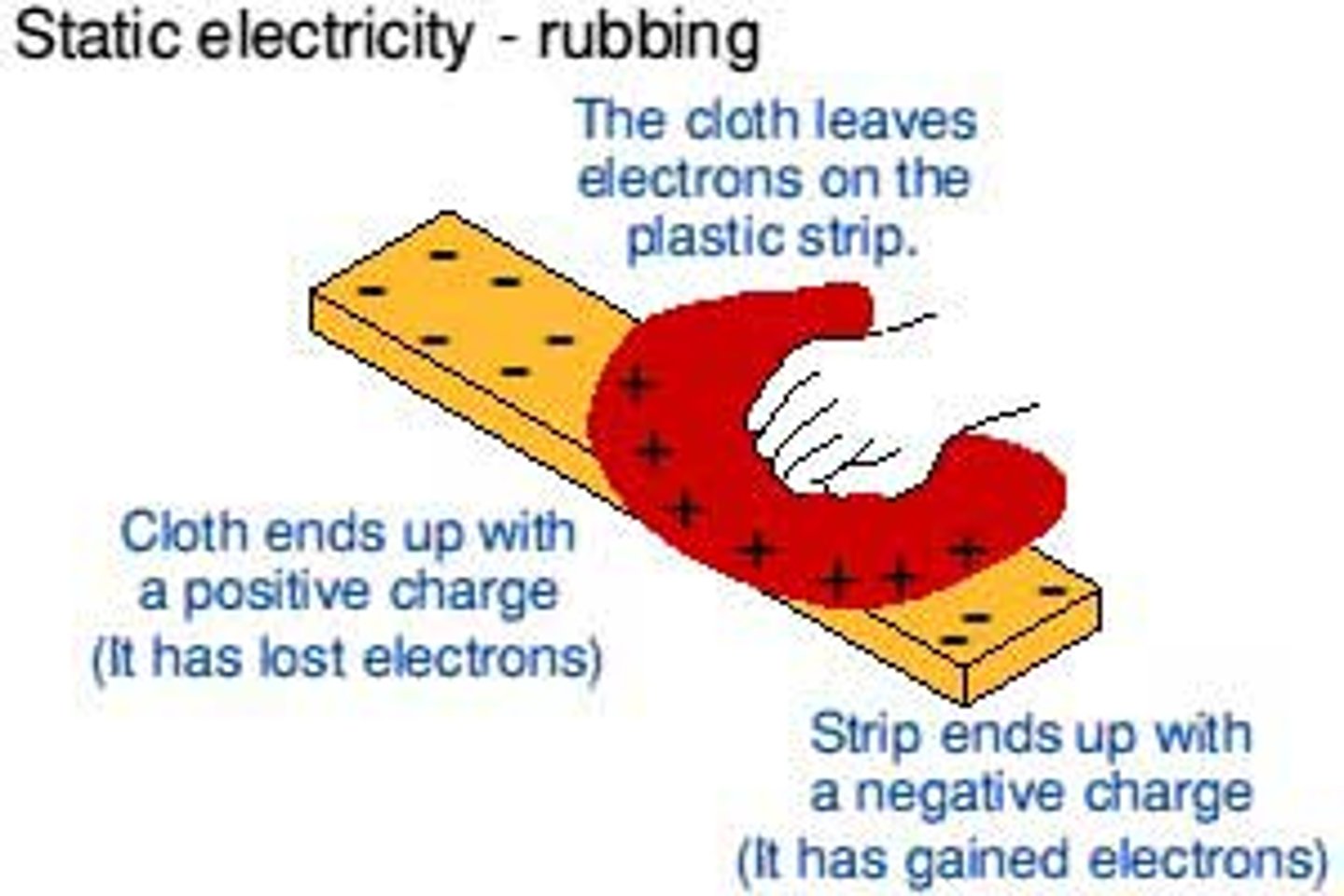
Which charged particle moves when insulators are rubbed together?
Electrons transfer from one insulator to the other
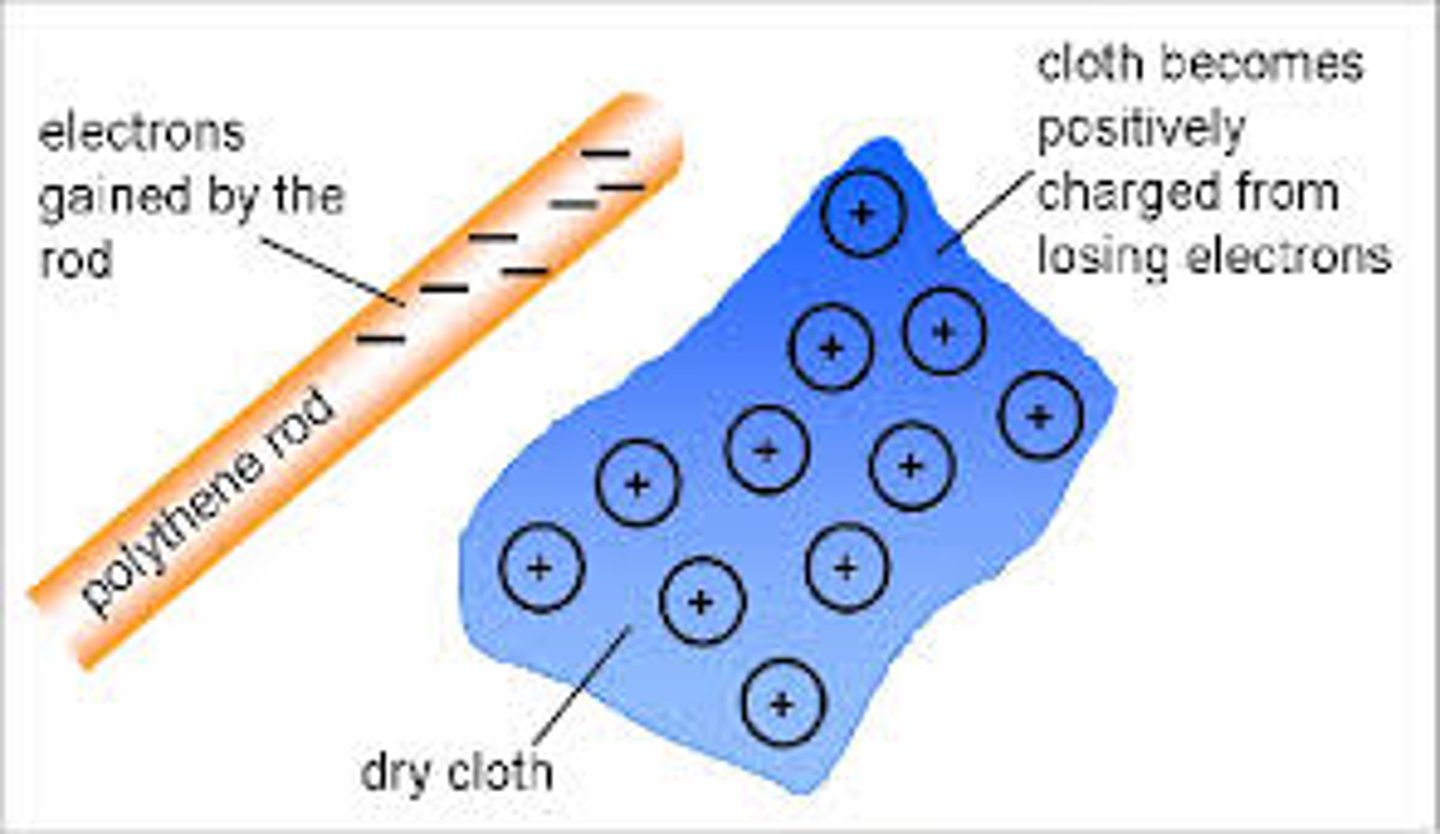
How do insulators become negatively charged?
They gain extra electrons
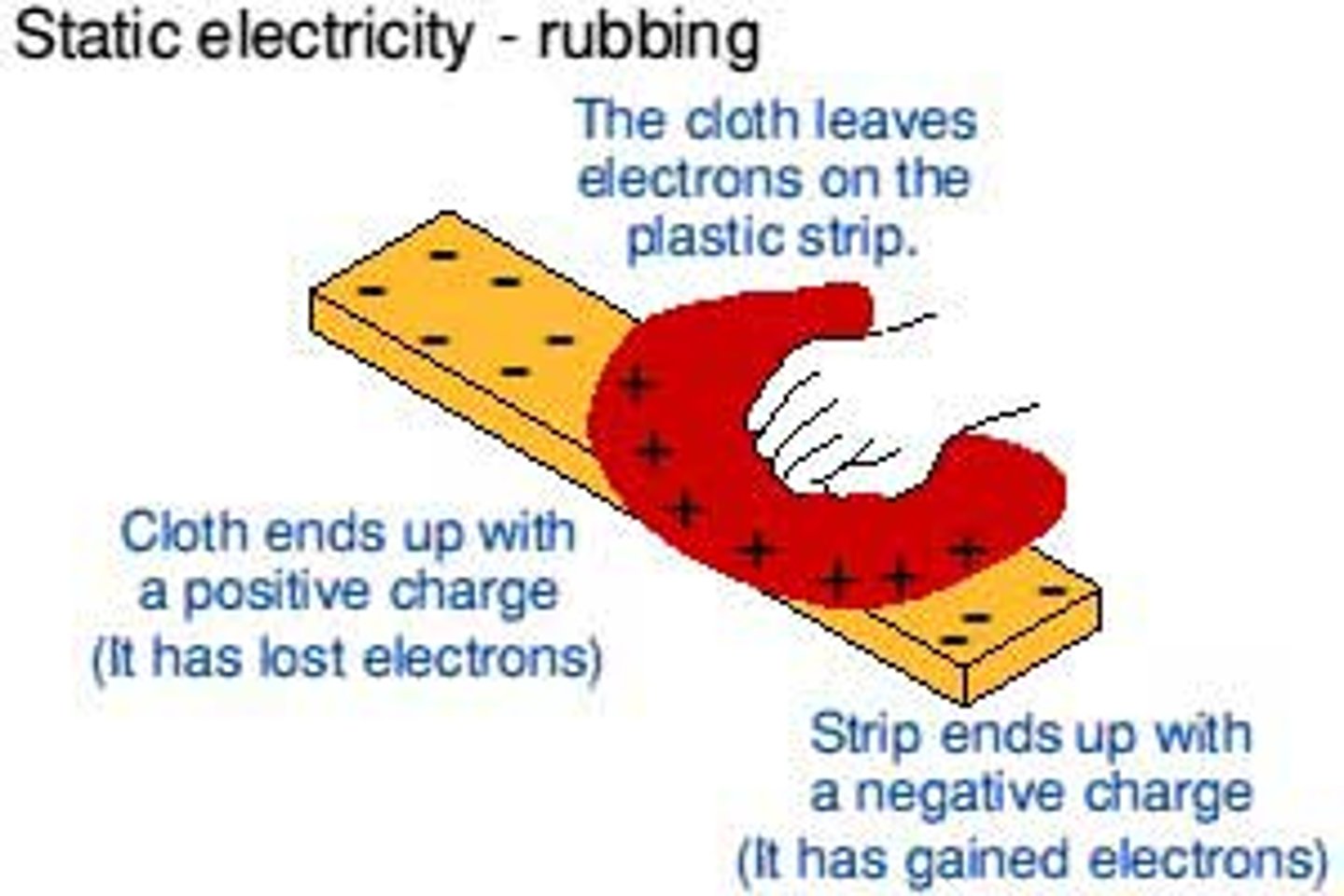
How do insulators become positively charged?
They lose some electrons
What charge is most matter?
Most matter is neutral.

What does neutral mean?
To have an equal number of positive and negative charges.

What is static charge?
Imbalance of electric charge
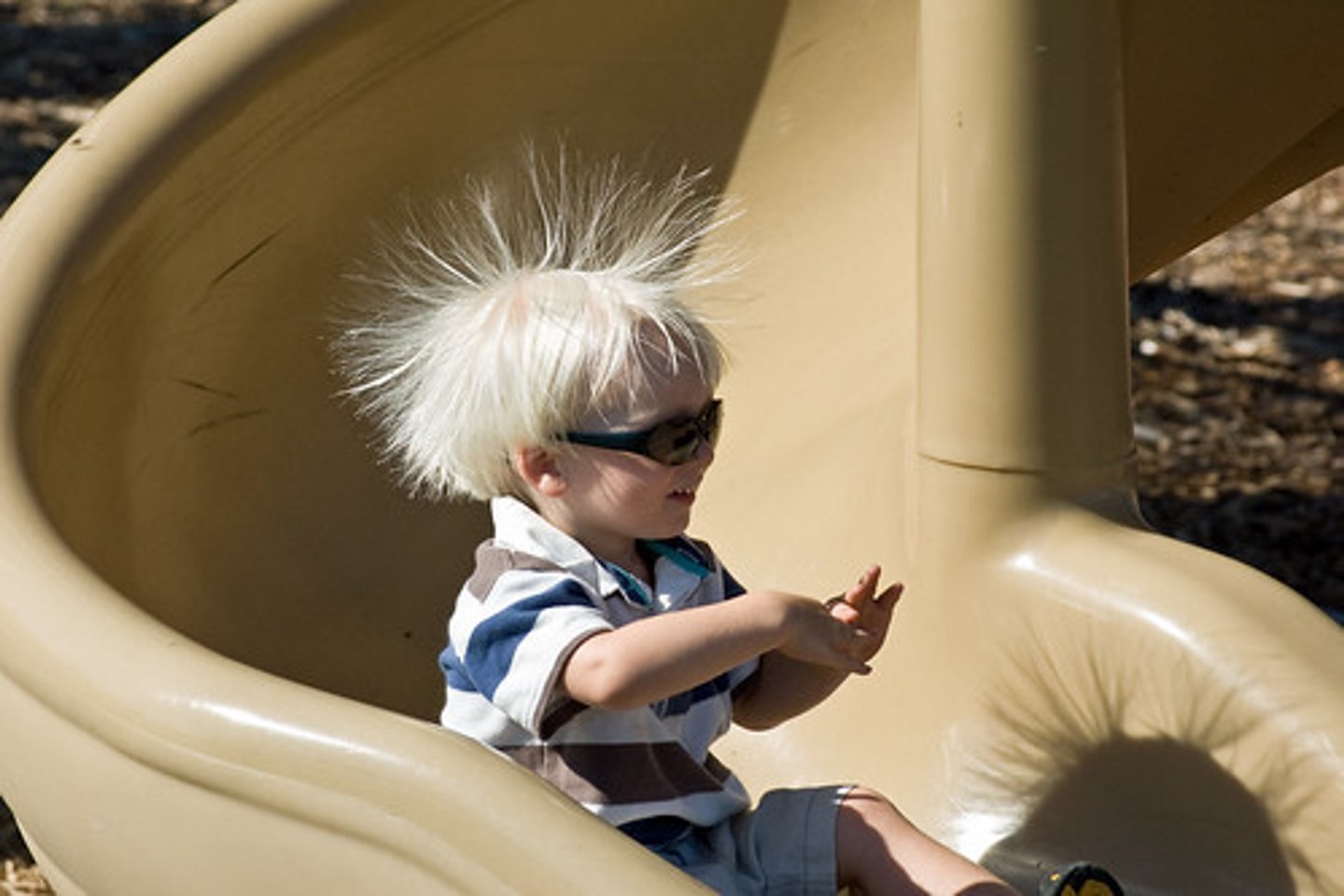

What is an electric force?
Attractive or repulsive force between charged objects
What causes objects to attract and repel each other?
Opposite charges attract
Like charges repel
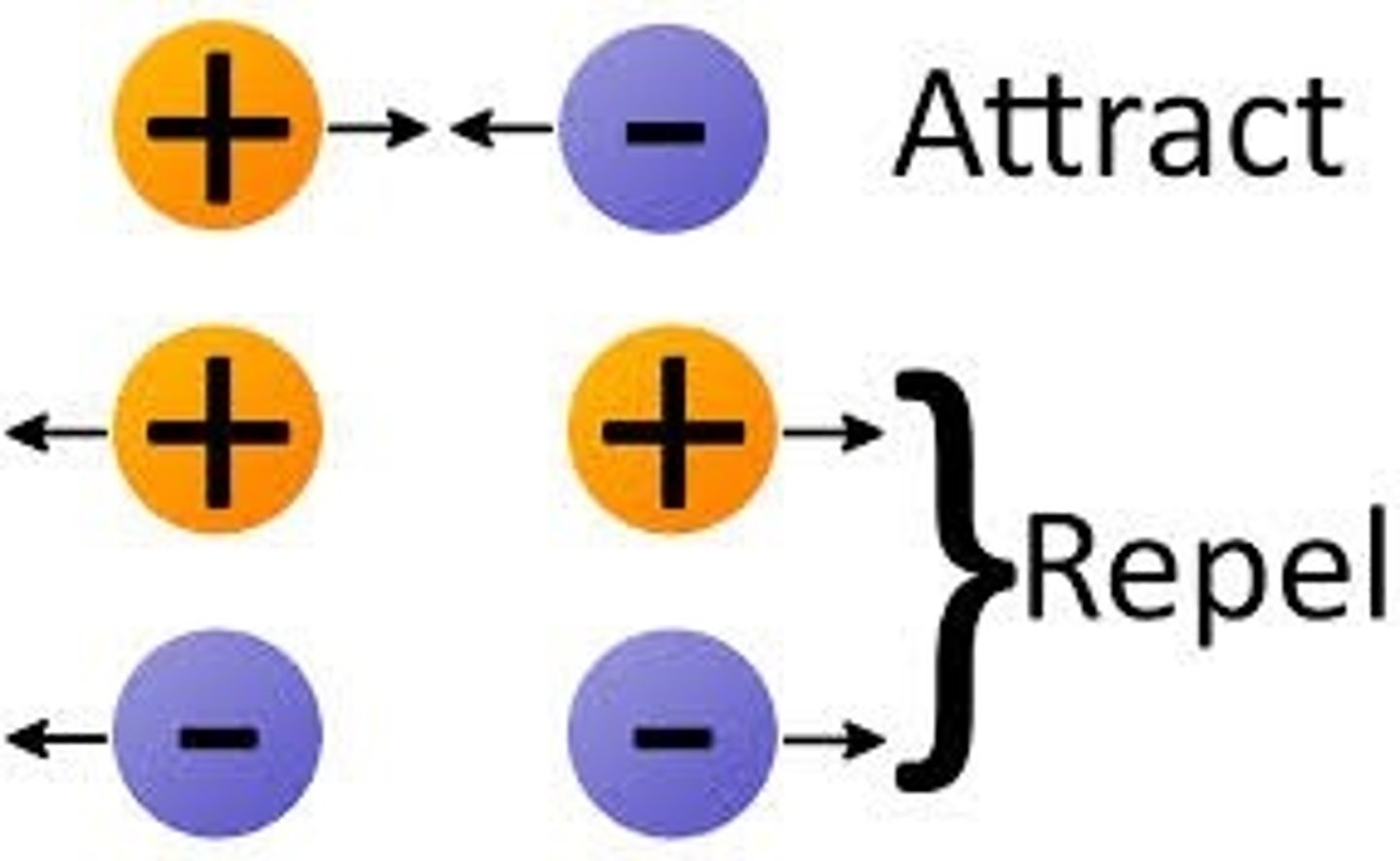
What happens to the size of the force as charged objects get closer together?
The force gets stronger
What happens when like charges are close together?
They repel or push away from each other.
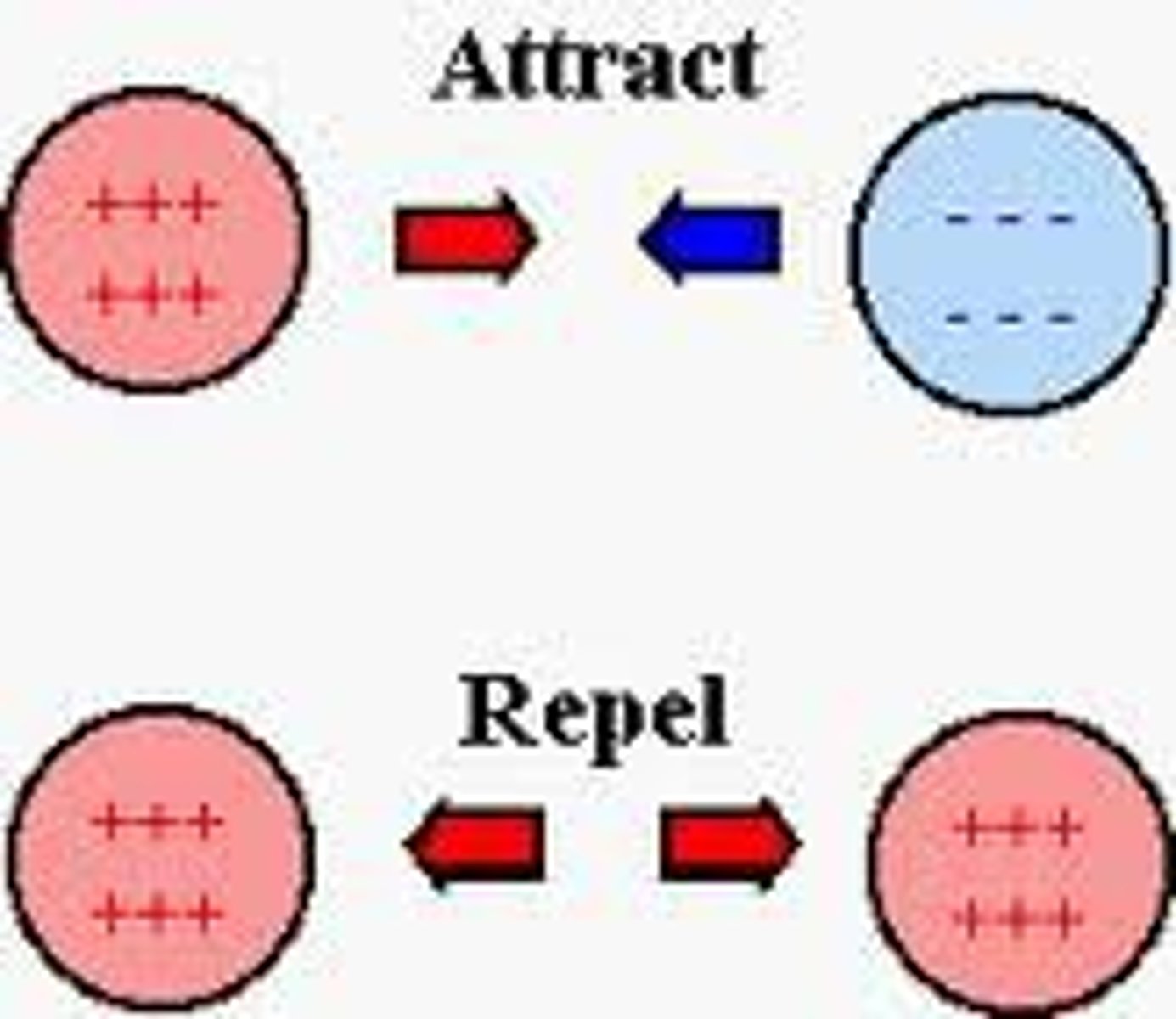
What happens when unlike (opposite) charges are close together?
They attract or pull toward each other.
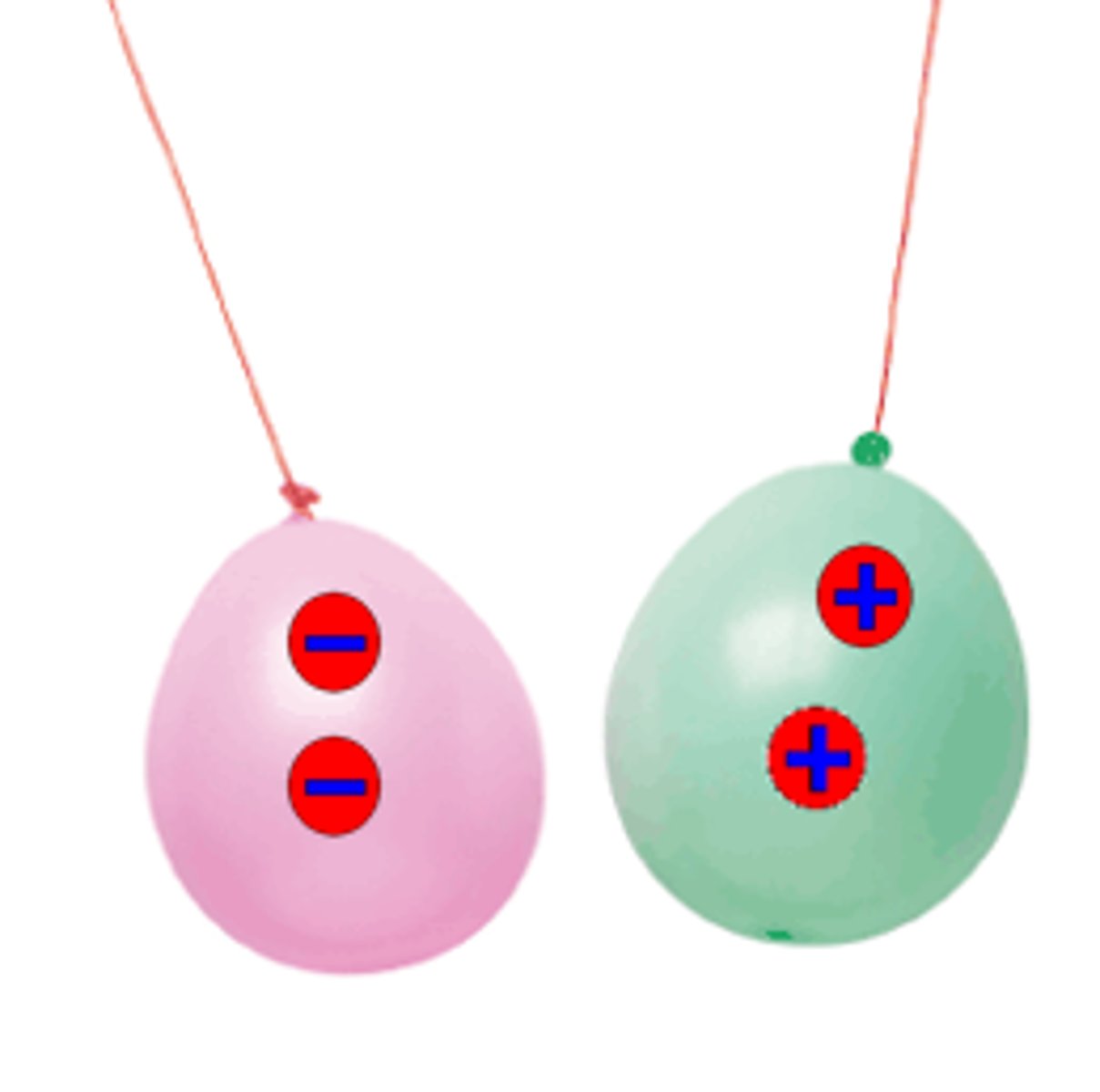

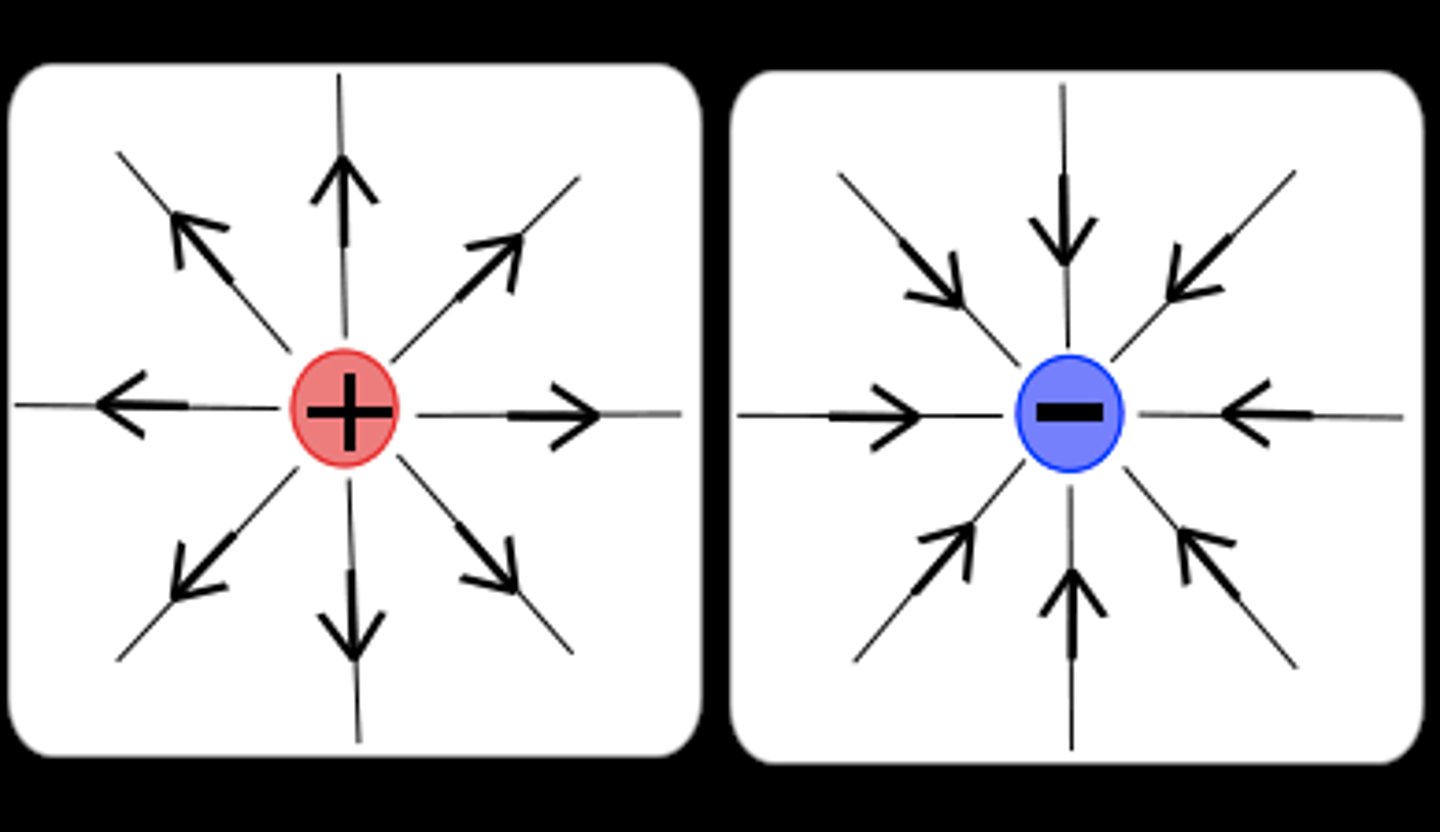
What is an electric field?
Area around electric charge where another charged object will experience a force
What is electric discharge?
Rapid movement of excess charge from one place to another e.g. a spark
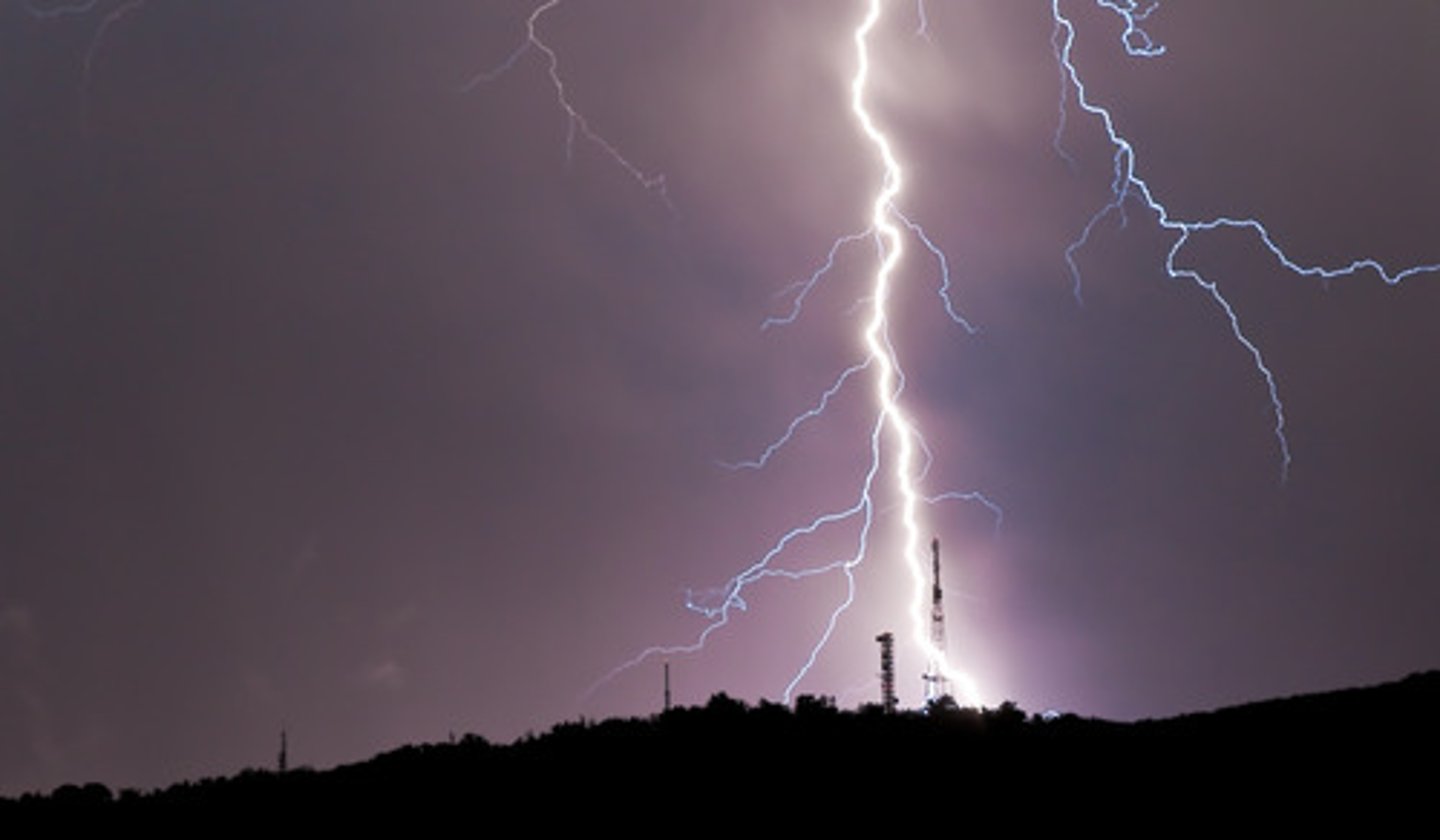

What is a build up of electric charge called?
Static electricity
