Ch 20: Brain Structure and Function
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
87 Terms
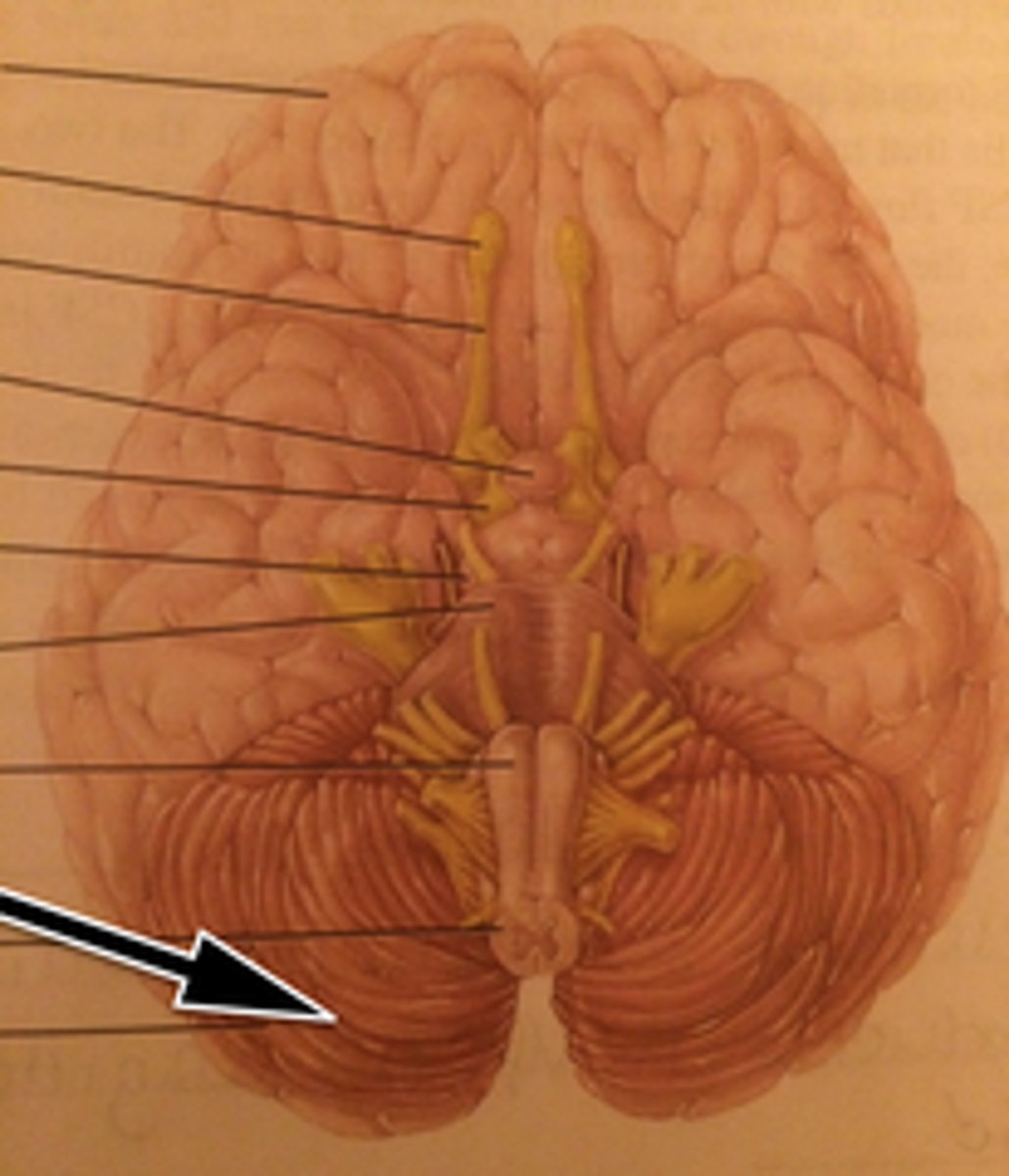
Brainstem
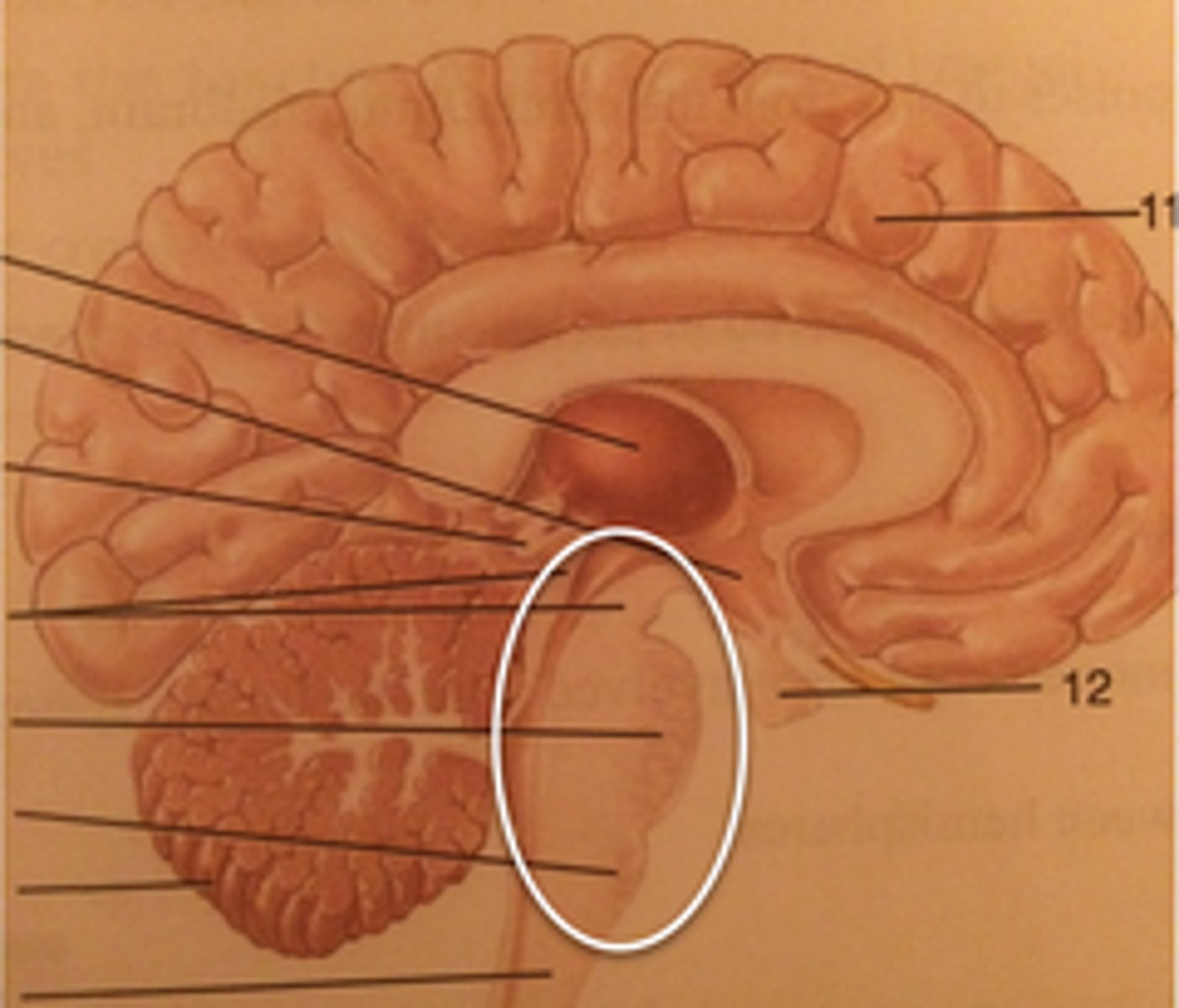
Cerebellum
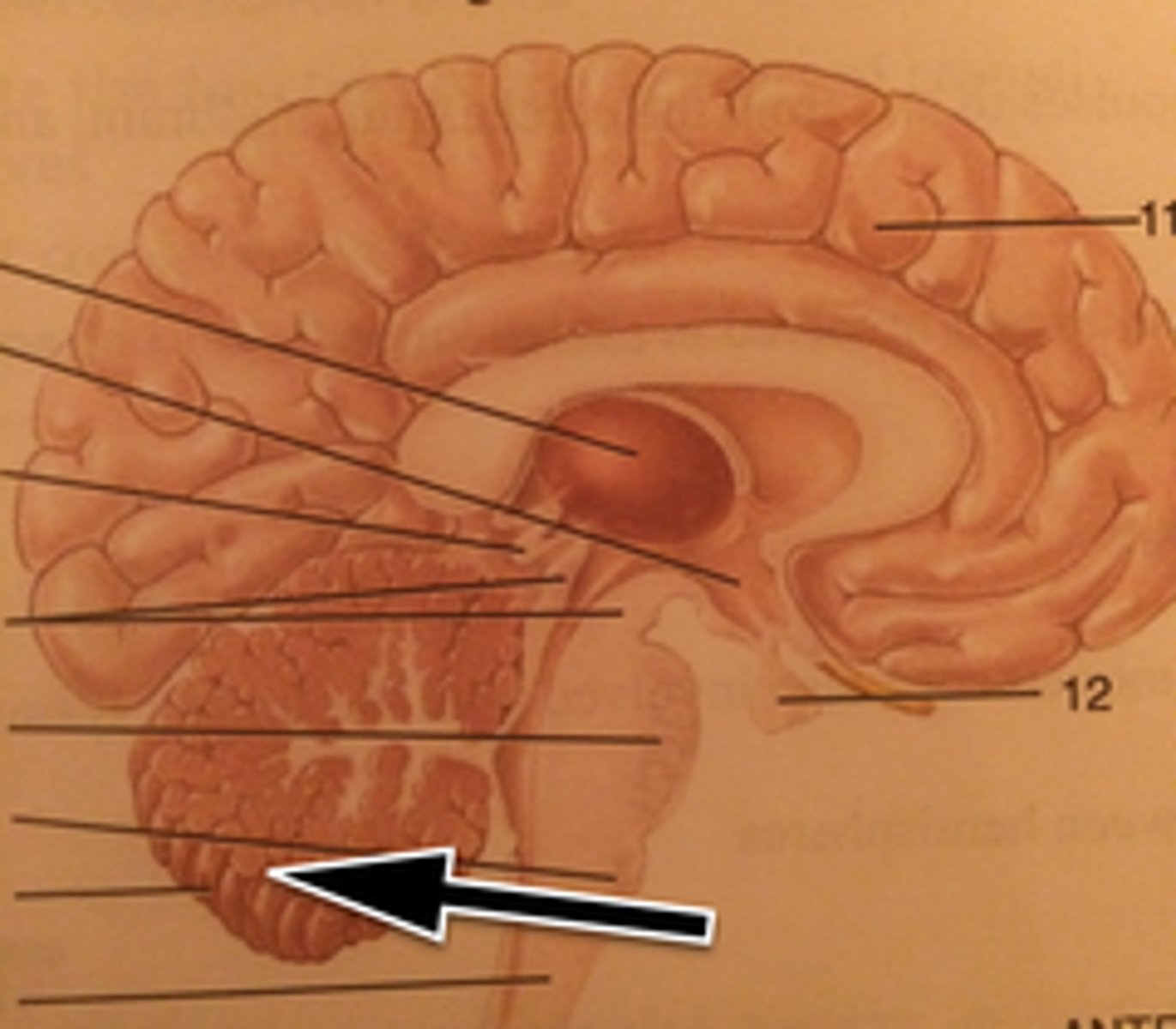
Cerebrum
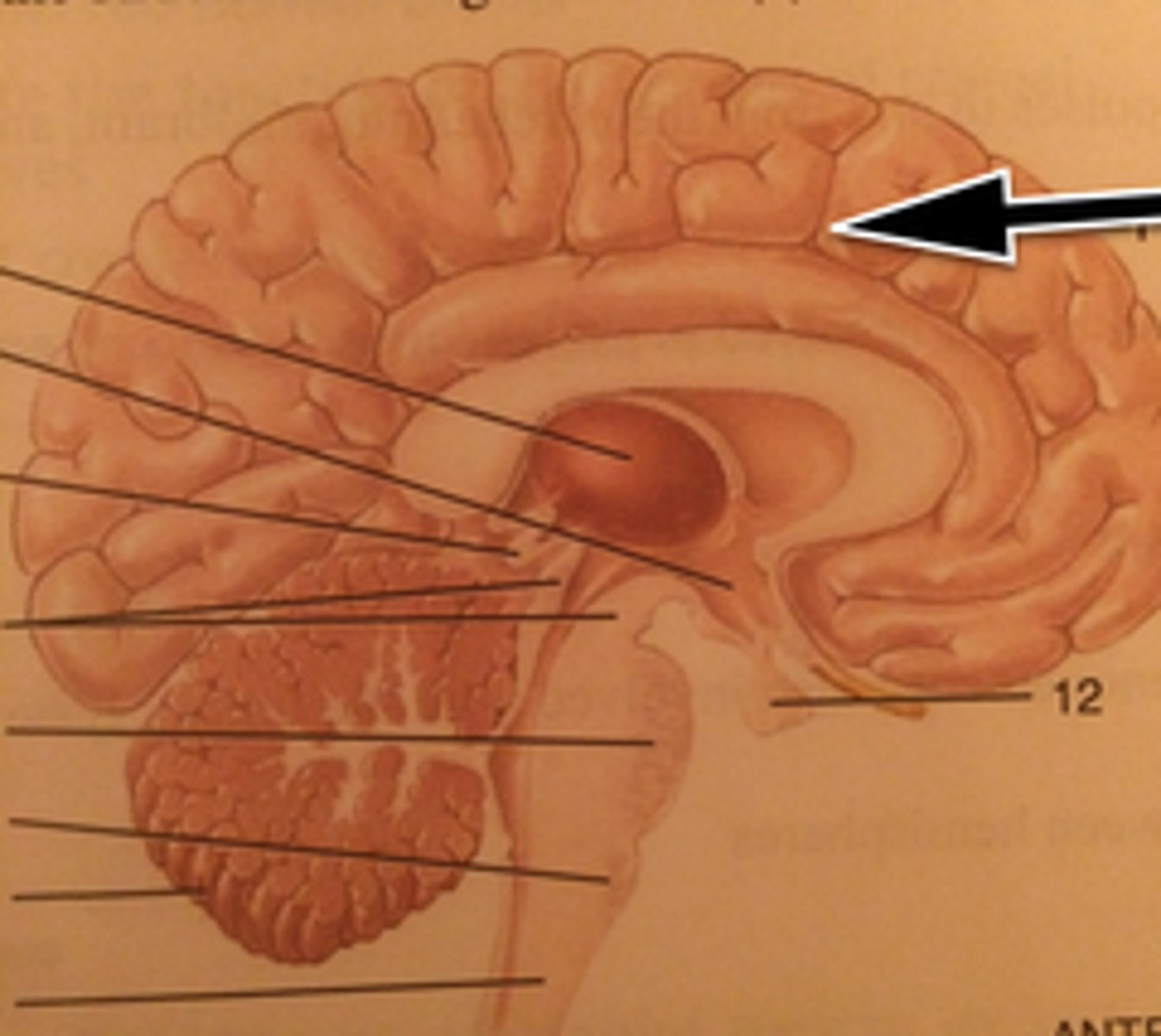
Diencephalon
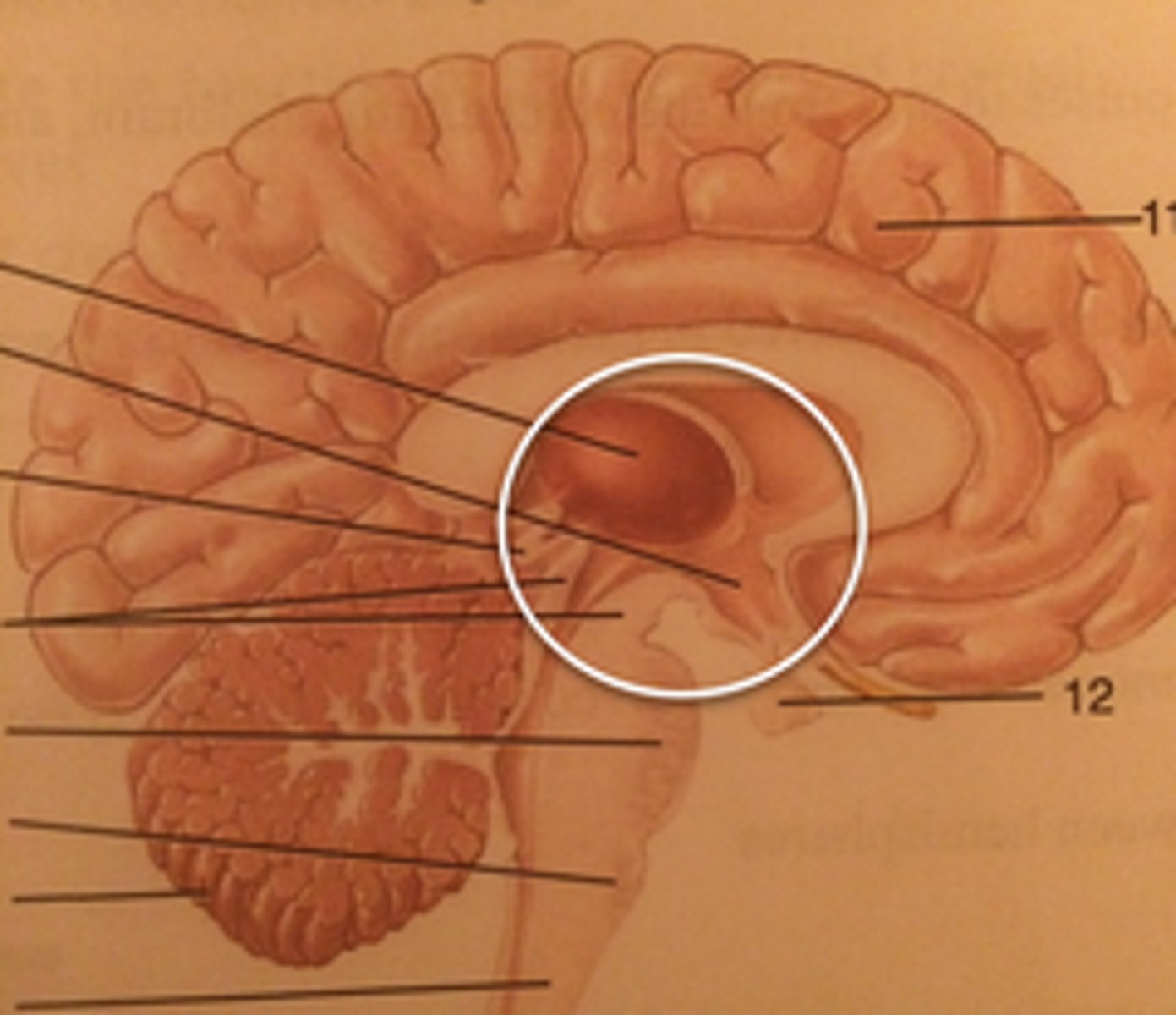
Folla
Hypothalamus
Medulla Oblongata
Medulla Oblongata
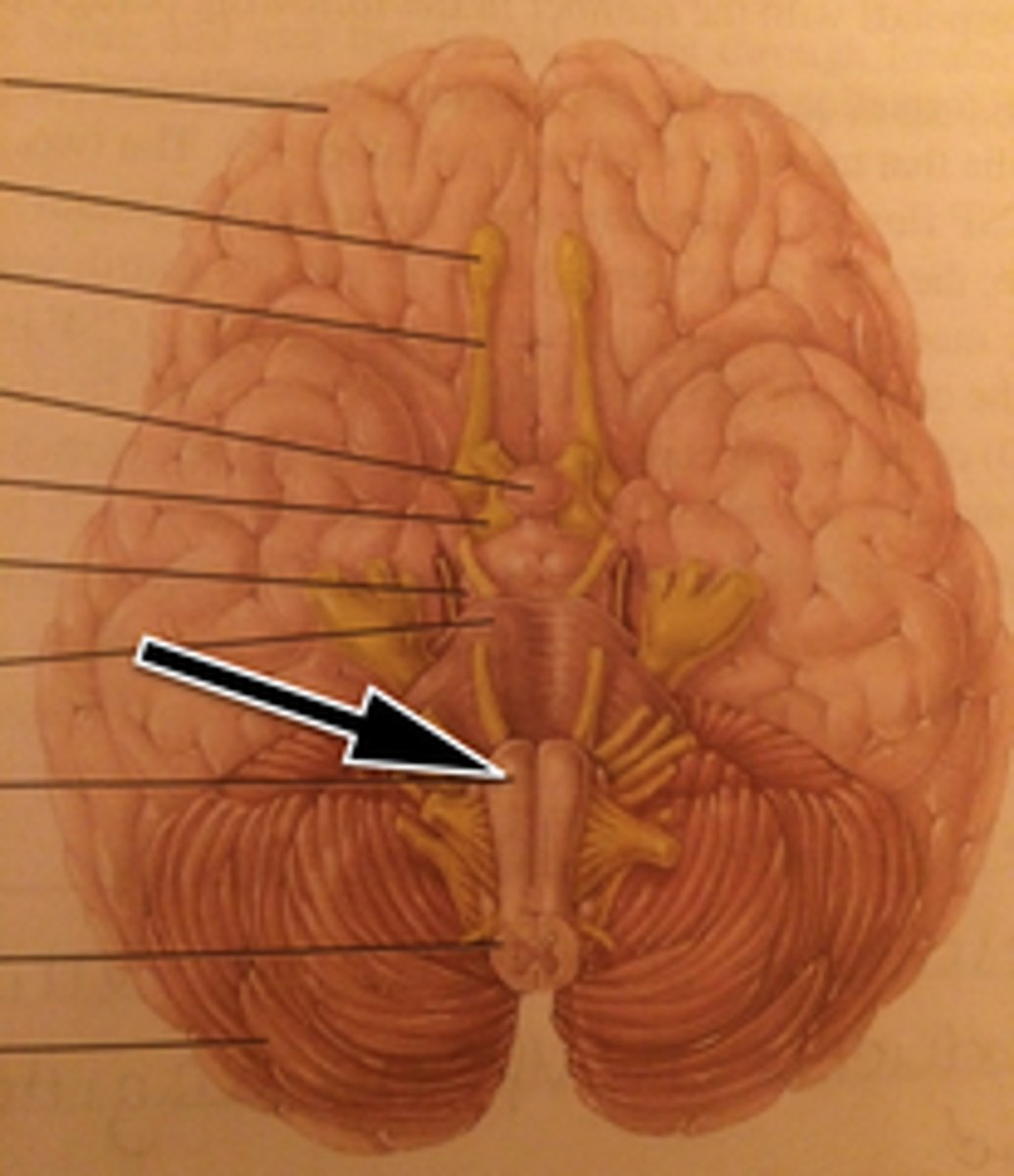
Midbrain
Midbrain
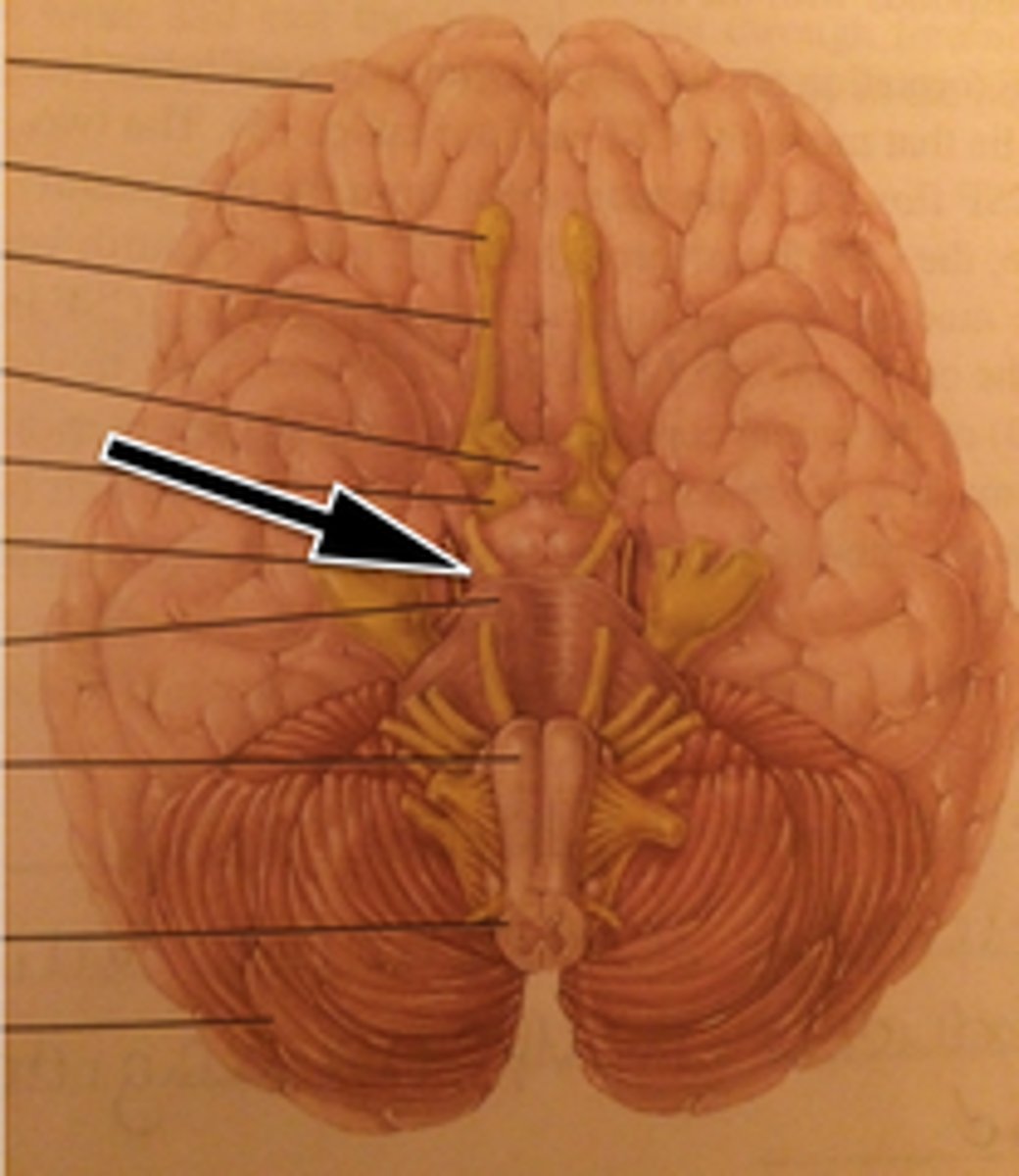
Olfactory Bulb
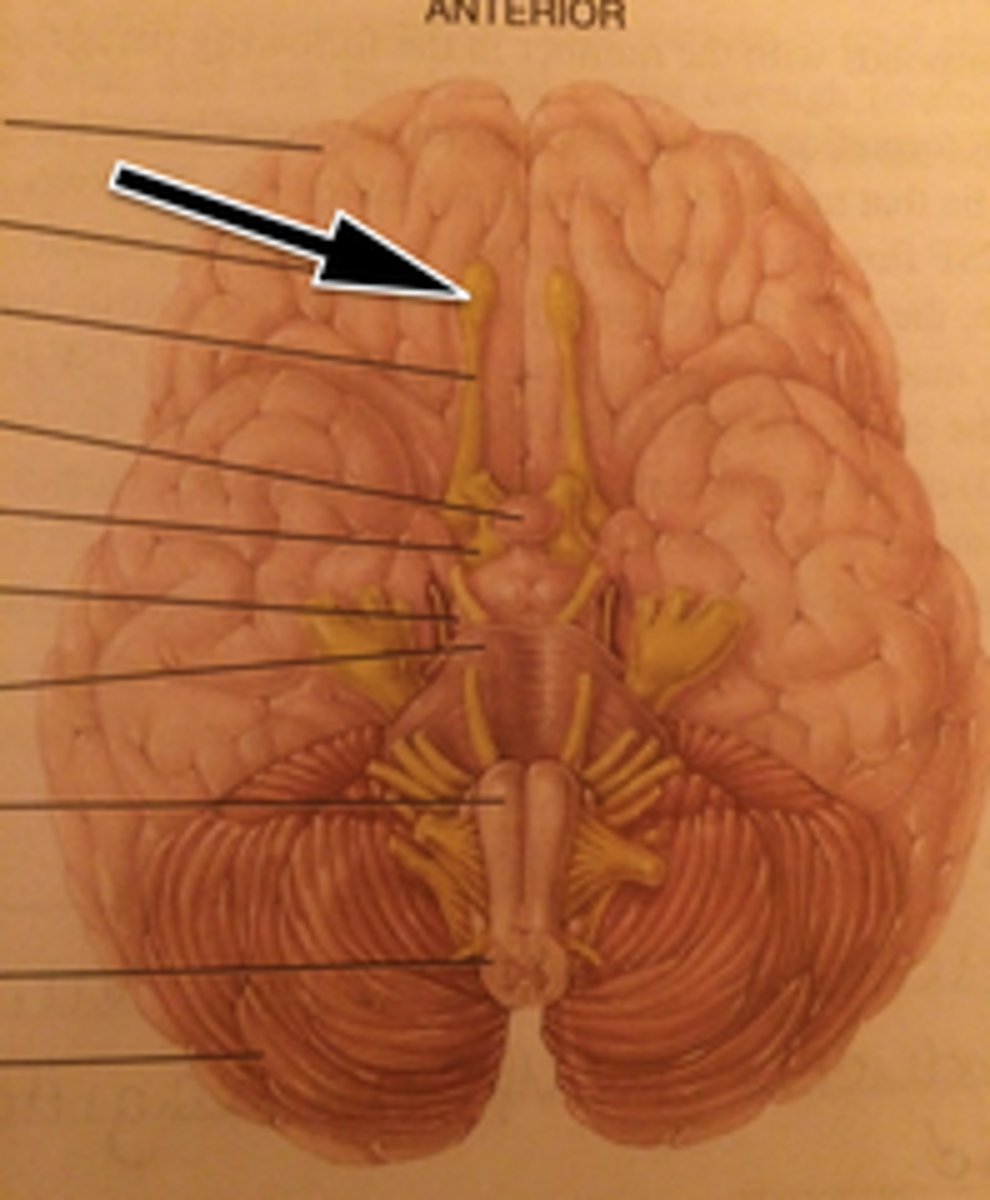
Olfactory Tract
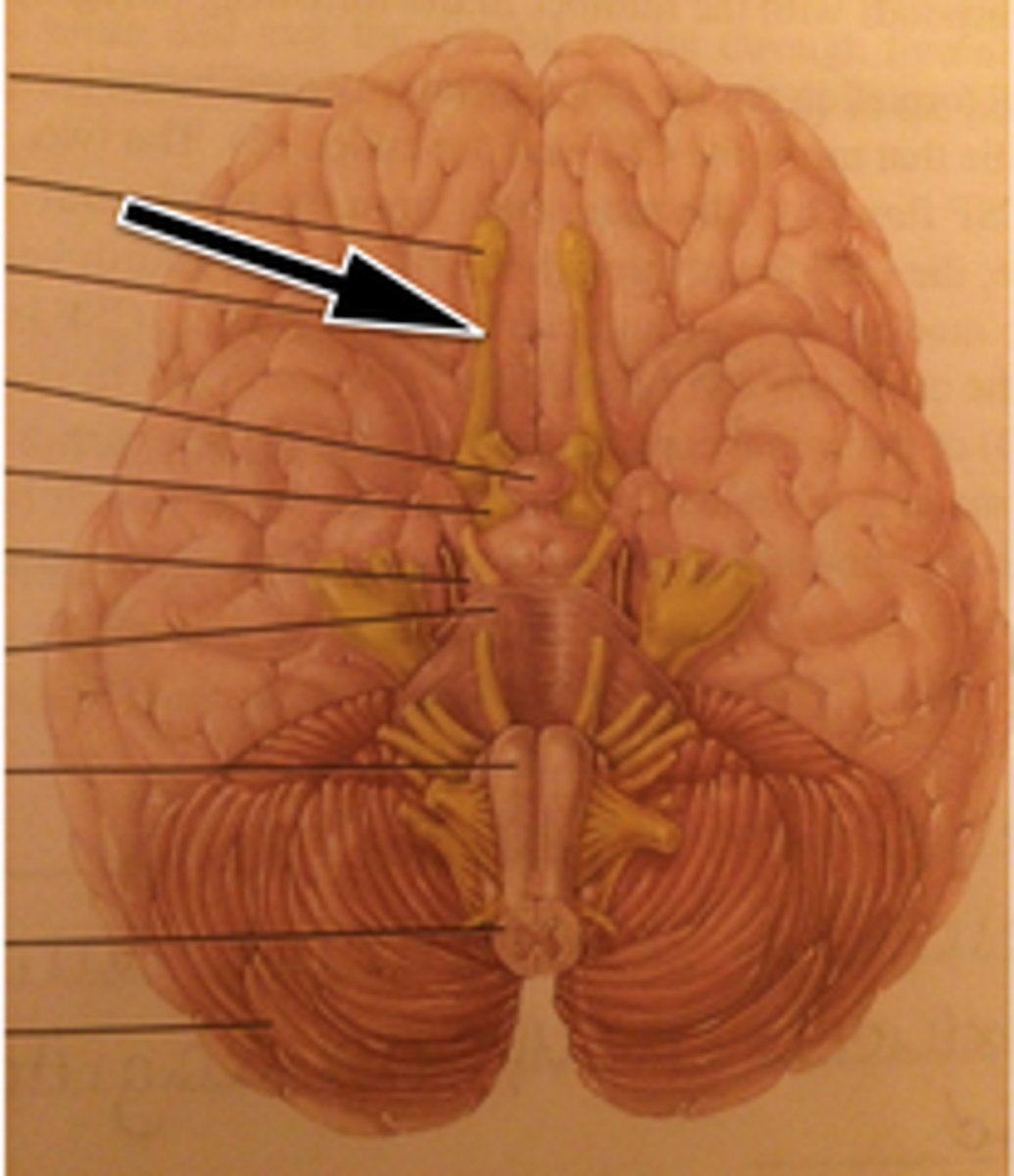
Optic Tract
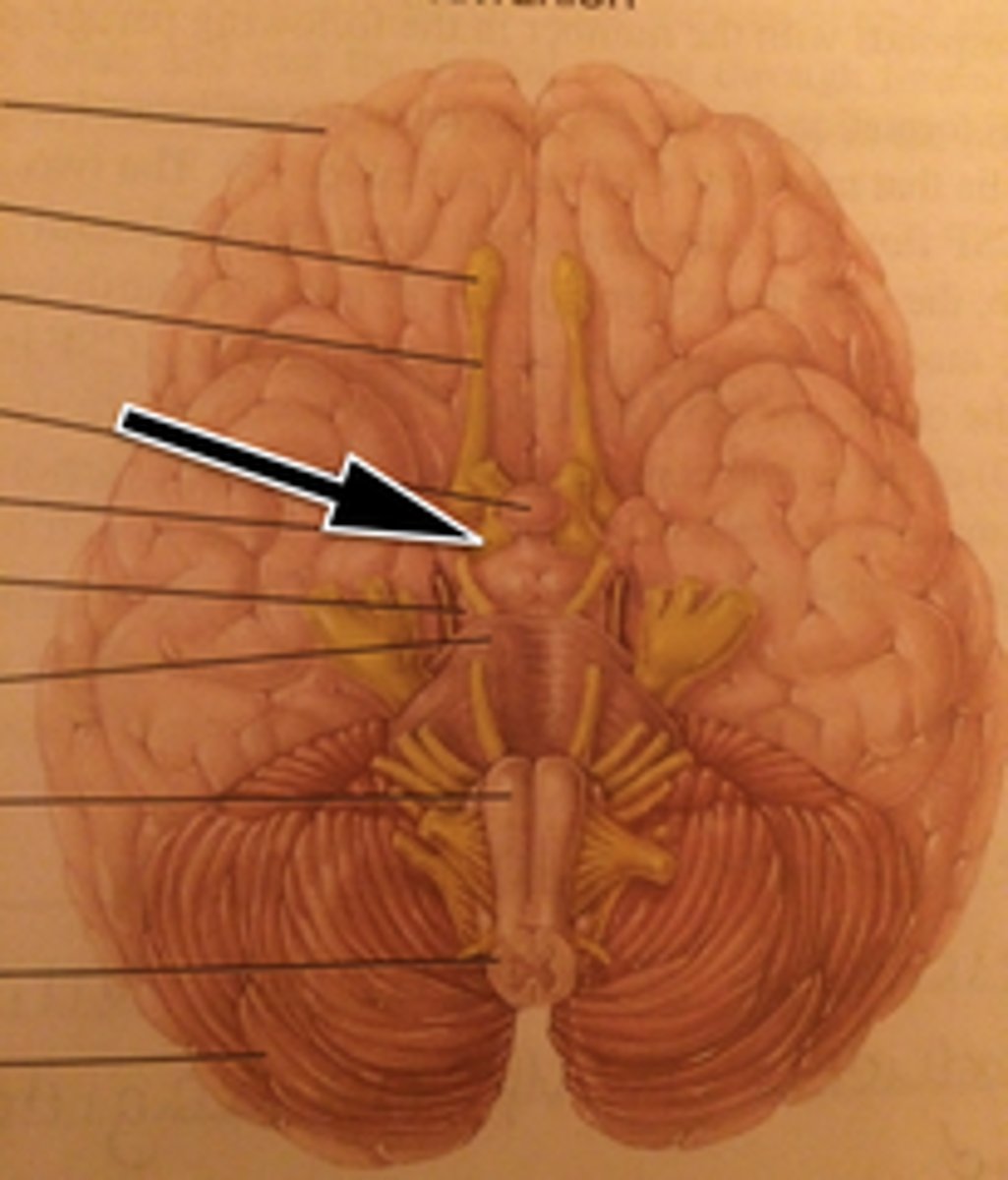
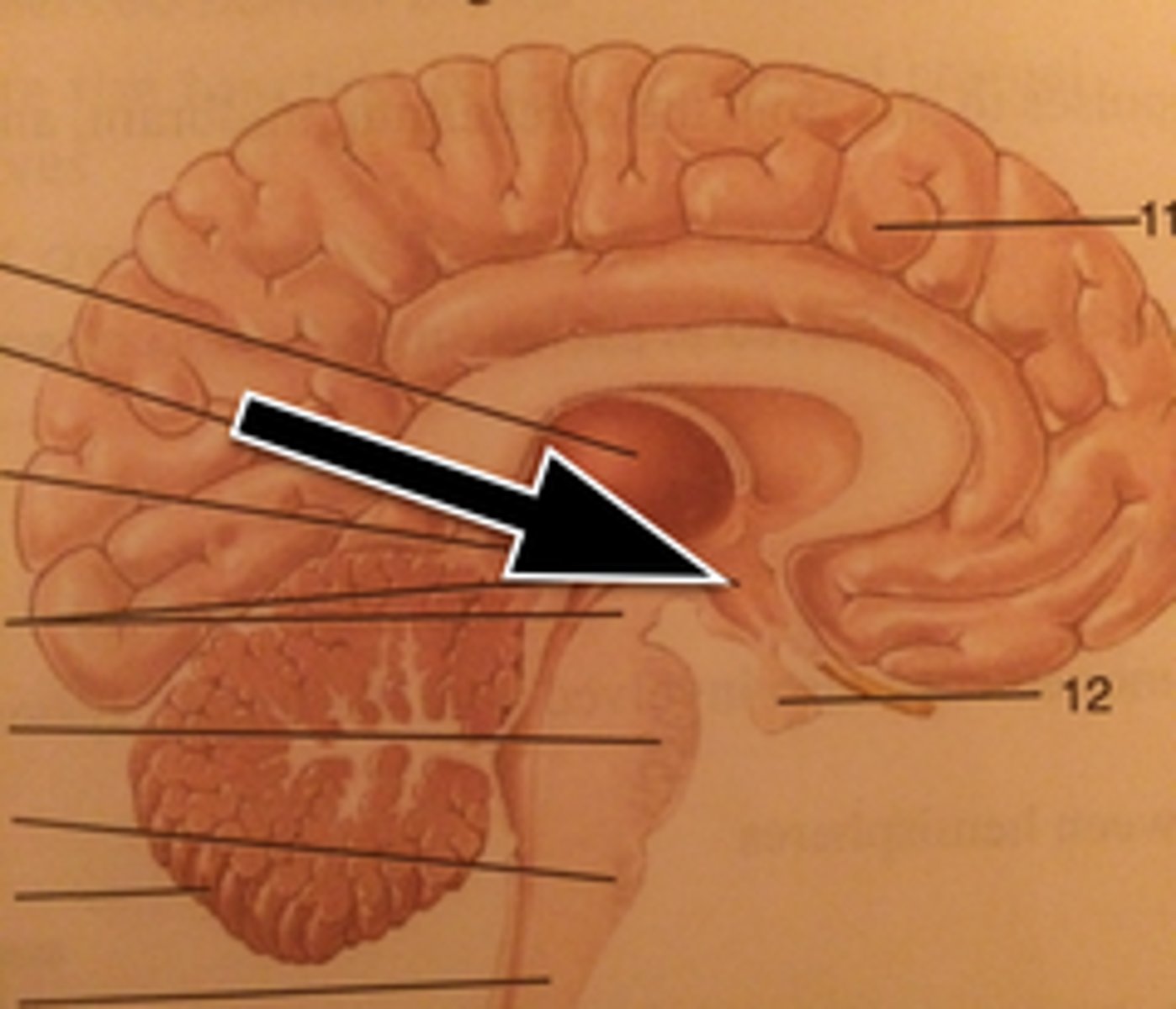
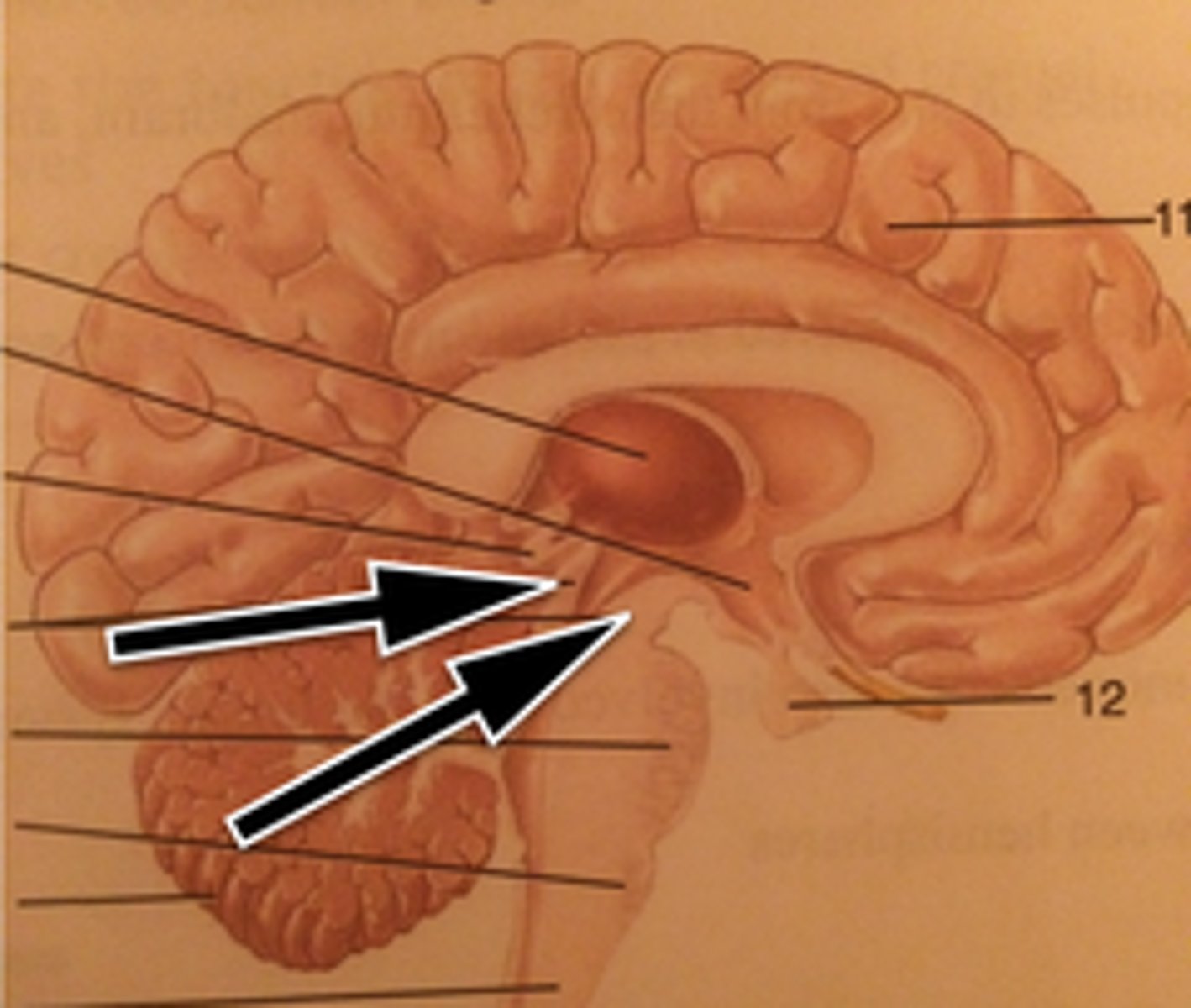
Pineal Gland
Pituitary Gland
Pituitary Gland
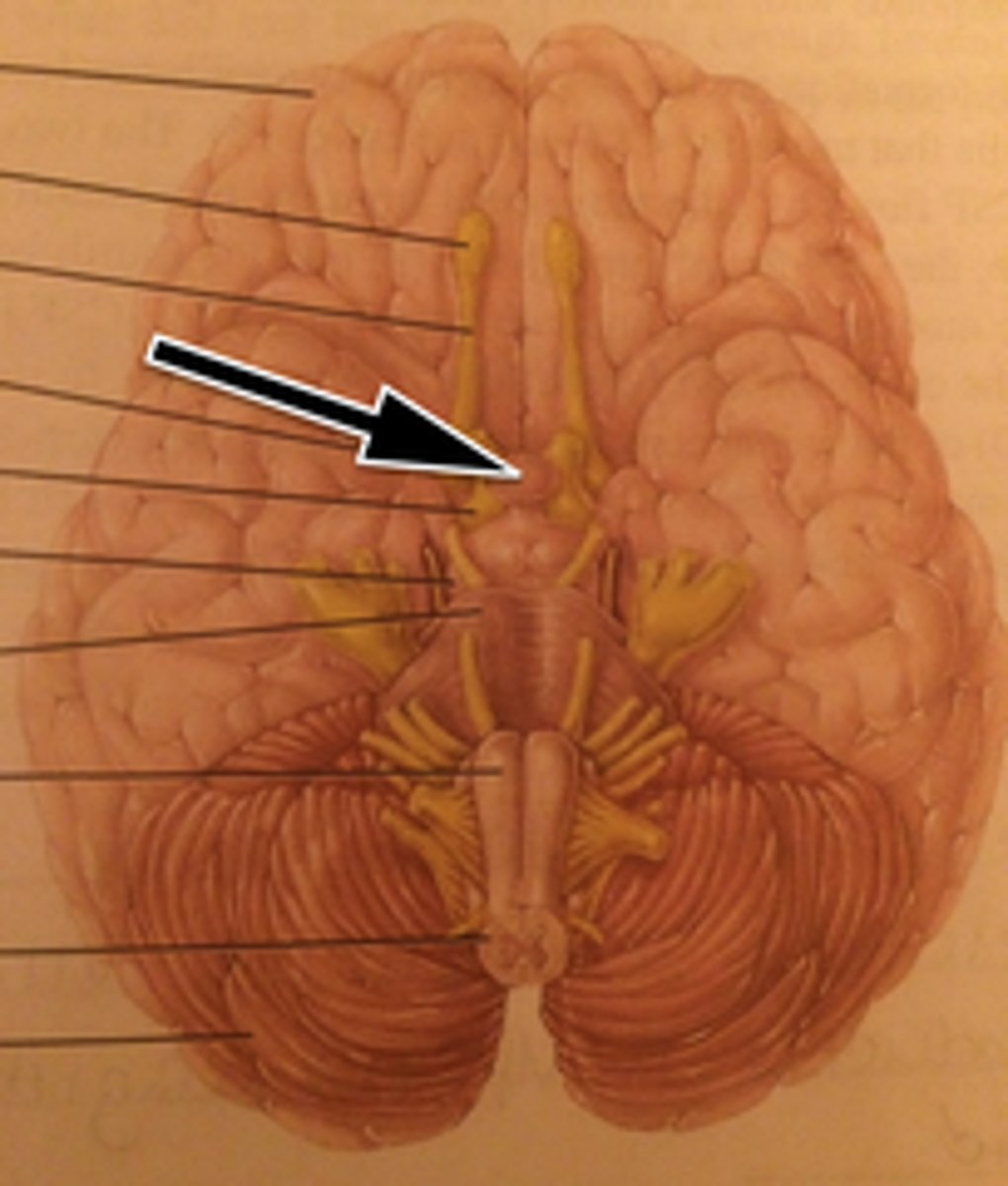
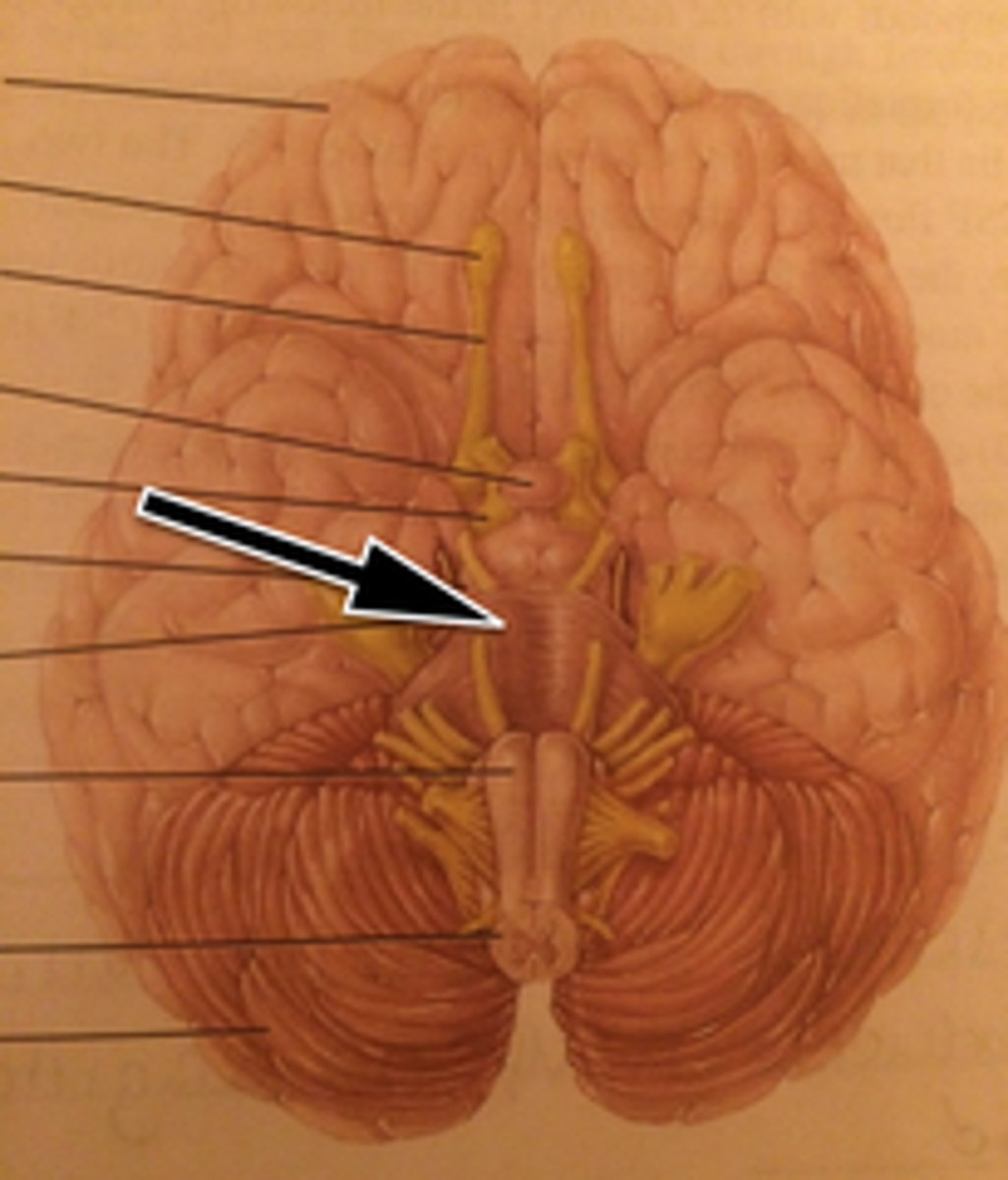
Pons
Pons
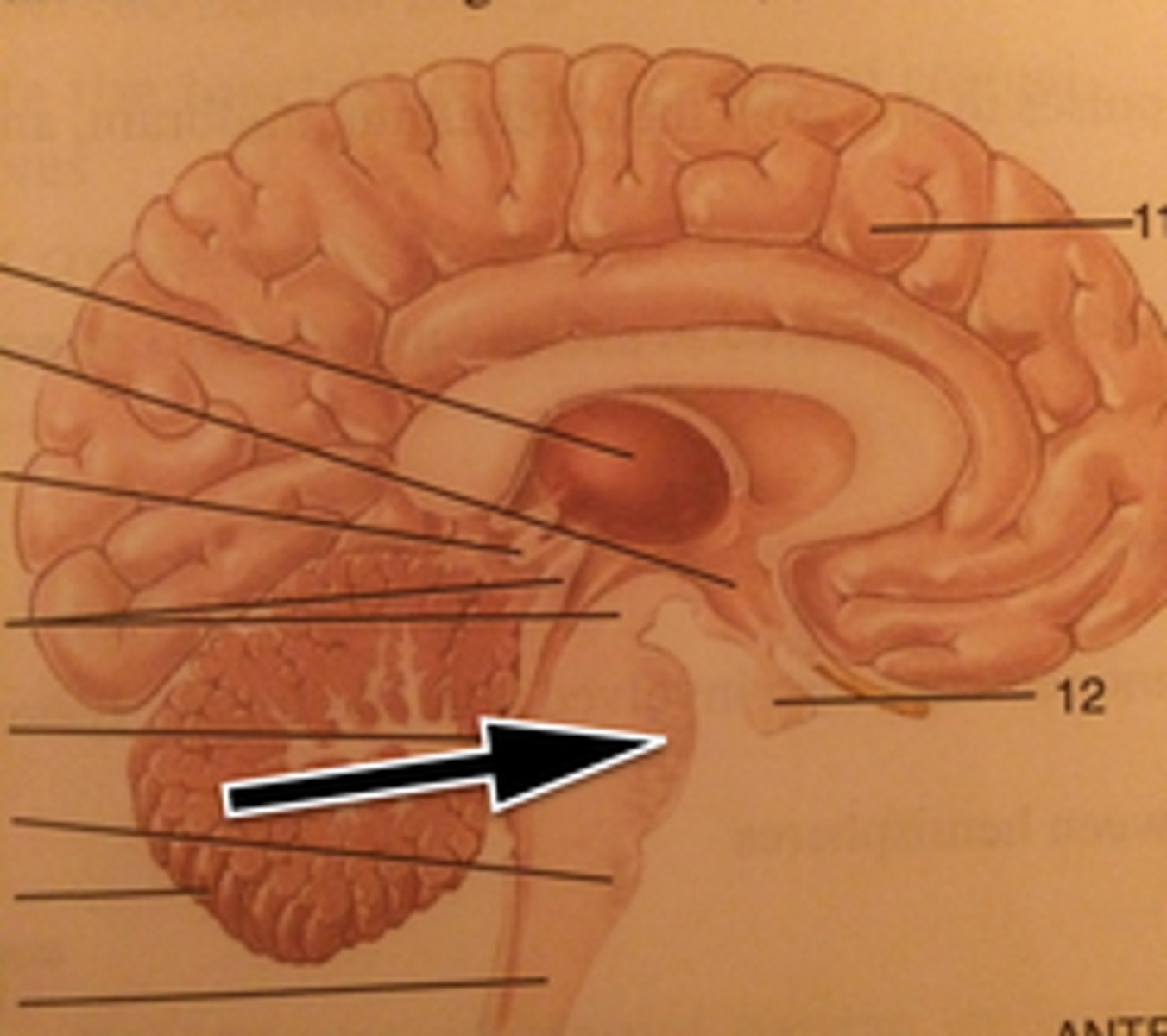
Spinal Cord
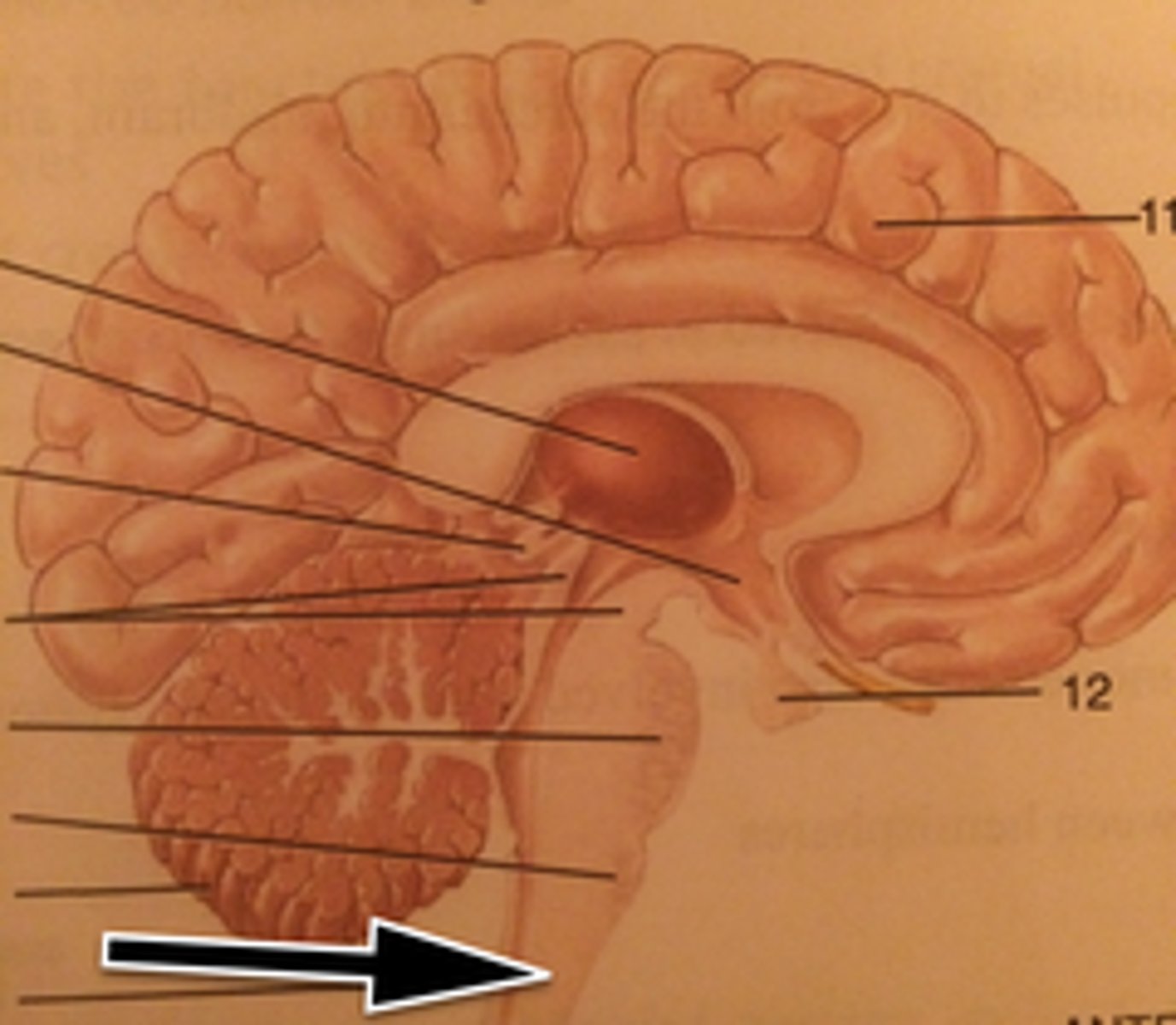
Spinal Cord
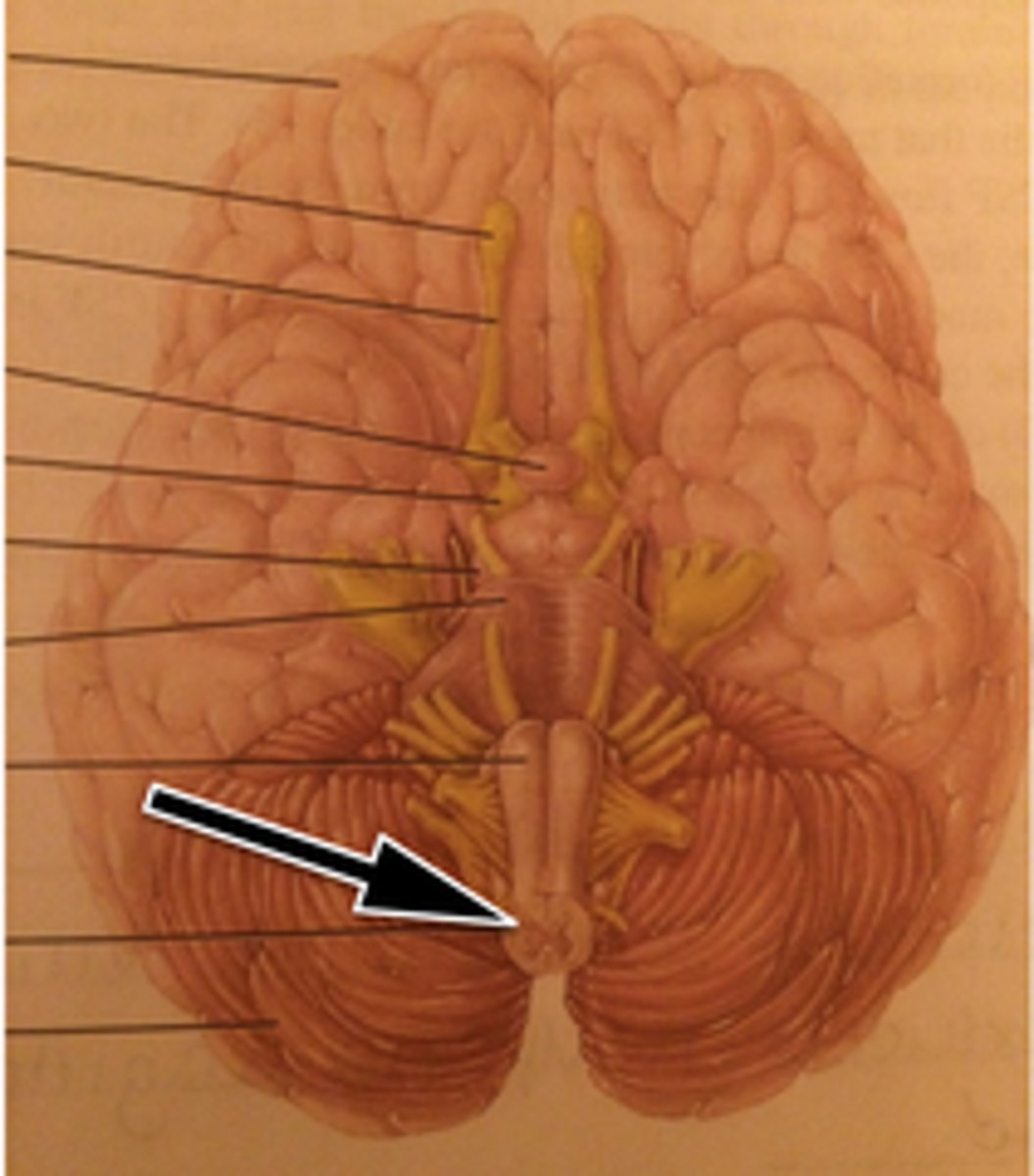
Thalamus
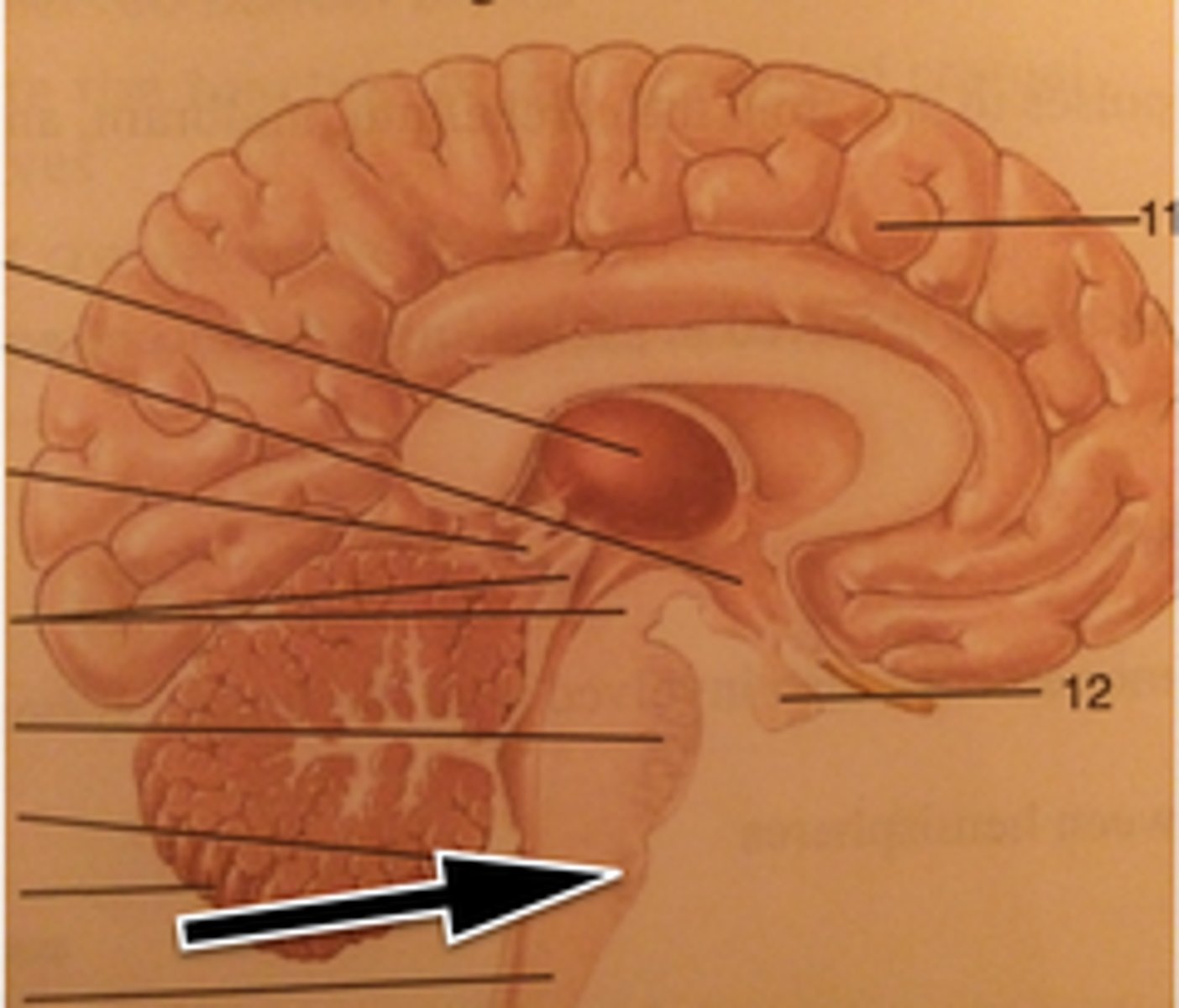
Medulla Oblongata
contains vital centers that regulate heartbeat, breathing, blood pressure, vomiting, coughing
Cerebellum
smooths and coordinates skilled skeletal muscle movement; also posture and balance or equilibrium
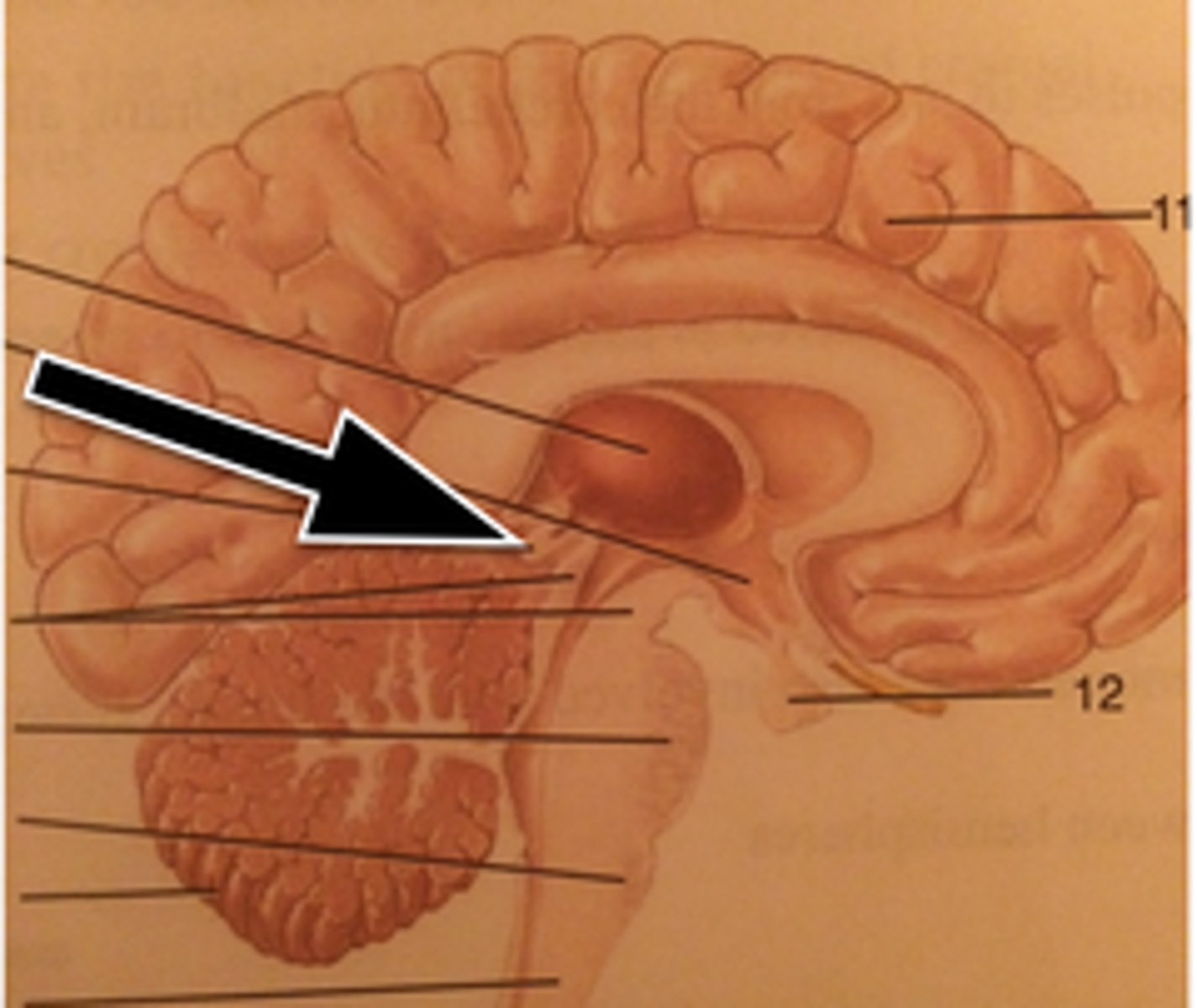
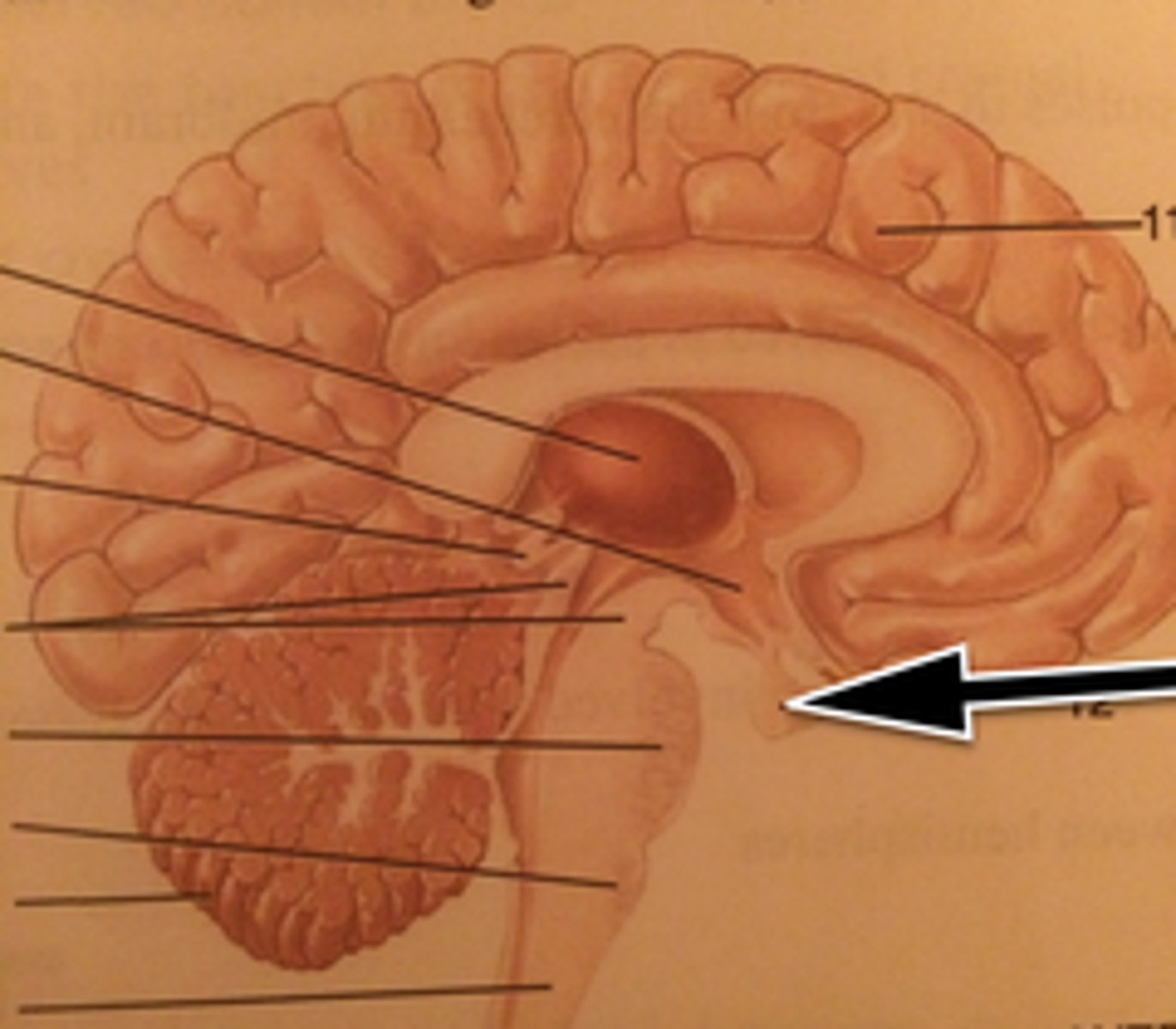
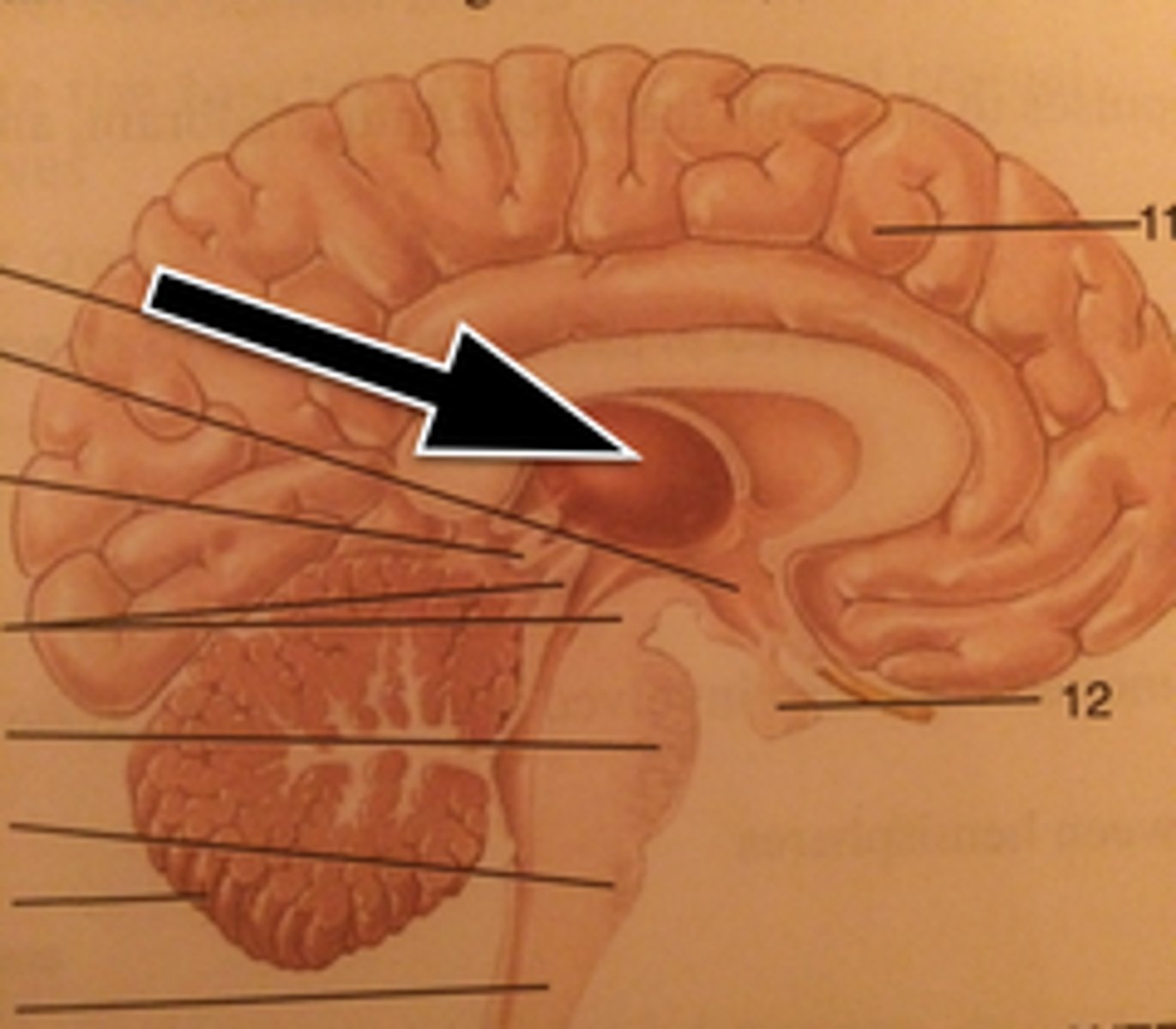
Pineal Gland
secretes melatonin that controls the sleep-wake cycle
Hypothalamus
controls and integrates the autonomic nervous system; regulates hormones, emotional behavior, temperature, eating, and drinking behavior
Cerebral Cortex
interprets sensory input, controls skilled skeletal muscle movements, and is involved in emotional and intellectual processes
Pons
helps control breathing; conducts impulses to and from the cerebellum, midbrain and medulla
Thalamus
relays all sensory input to the cerebral cortex; involved in skeletal muscle actions and memory processing
Corpora Quadrigemina
coordinates visual and auditory reflexes
Basal Nuclei
coordinates gross, automatic muscle movements; also involved with the limbic system
Corpus Callosum
white fiber tracts communicating between hemispheres
What areas make up the brain stem?
The medulla, pons, and midbrain
What areas make up the diencephalon?
Thalamus, hypothalamus, epithalamus
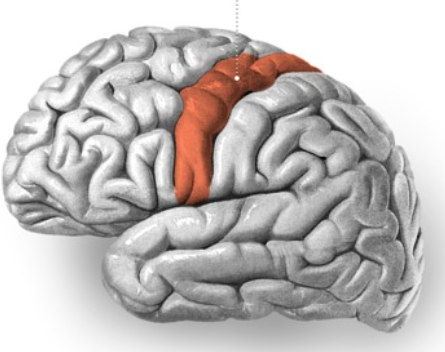
Precentral gyrus, in the cerebrum
Postcentral gyrus, in the cerebrum
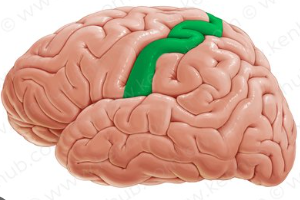
Postcentral gyrus
Primary somatosensory functions, processes touch
Precentral gyrus
Primary motor cortex, controls voluntary movements on the opposite side of the body
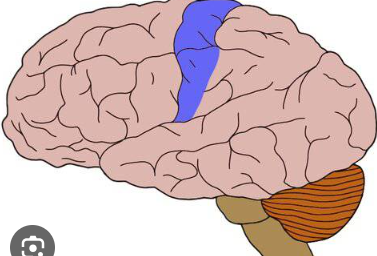
Central sulcus
A deep groove in the cerebral cortex that divides the frontal lobe from the parietal lobe and separates the primary motor cortex from the primary somatosensory cortex
Central sulcus
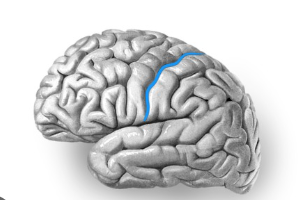
Lateral sulcus
Lateral sulcus
A major groove on the lateral surface of each cerebral hemisphere that separates the temporal lobe from the frontal and parietal lobes
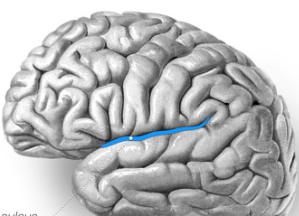
parieto-occipital sulcus
Separates the parietal lobe from the occipital lobe (separates the sensory and visual areas).
parieto-occipital sulcus
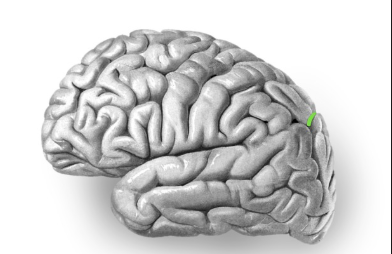
Longitudinal fissure
the deep groove that separates the left and right cerebral hemispheres of the brain
Longitudinal fissure
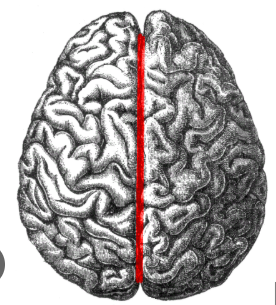
Transverse fissure
A deep groove in the brain that separates the cerebrum from the cerebellum
Transverse fissure
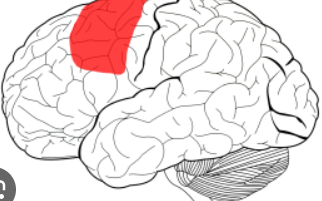
Primary motor cortex (precentral gyrus)
a part of the frontal lobe that initiates voluntary muscle movements by sending signals to the body's muscles
Premotor cortex
a brain area located in the frontal lobe that helps plan and select voluntary movements based on context and sensory cues
Premotor cortex
Broca’s area
A region of the brain concerned with the production of speech, the muscle movements needed for speech, and helping to form words and sentences
Broca’s area
Primary somatosensory cortex
processes somatic sensations like touch, pressure, temperature, pain, and proprioception (body position)
Primary somatosensory cortex
Primary visual cortex
the first cortical region in the brain to process visual information received from the eyes
Primary visual cortex
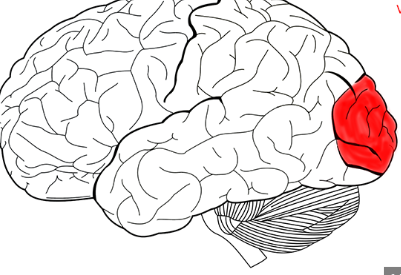
Primary auditory cortex
processes basic auditory information, such as pitch, volume, and sound localization
Primary auditory cortex
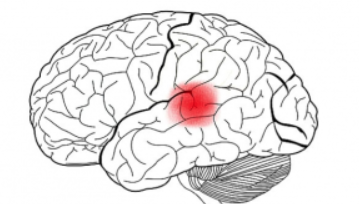
Primary gustatory cortex
the brain region responsible for the conscious perception of taste
Primary gustatory cortex
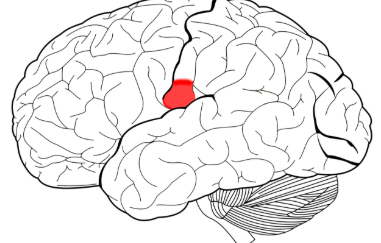
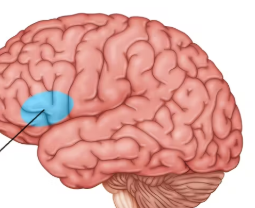
Primary olfactory cortex
a region of the brain responsible for processing smells, receiving direct input from the olfactory bulb
Primary olfactory cortex
Pink
Somatosensory association area (behind the postcentral gyrus, as the somatosensory area and postcentral gyrus are similar. The somatosensory area is the functional name, while the postcentral gyrus is the anatomical name)
Light blue near back
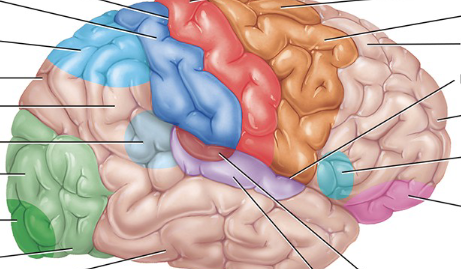
Somatosensory association area
the part of the brain that processes tactile information to recognize and interpret objects by touch
Visual association area
a region of the brain in the occipital lobe that processes and interprets visual information received from the primary visual cortex
Visual association area
Light green
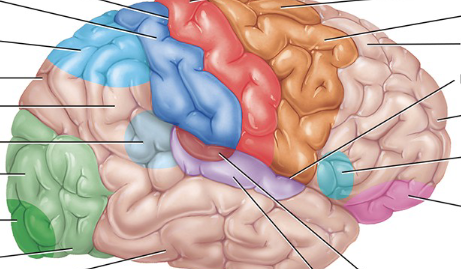
Auditory association area
a region in the brain's temporal lobe that interprets and processes raw sound data from the primary auditory cortex; gives meaning to sounds and identifies sounds
Auditory association area
Maroon
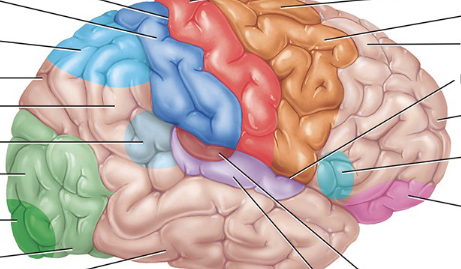
Orbitofrontal association area
A region in the frontal lobe of the brain crucial for decision-making, emotion, and reward processing. It receives and integrates information from multiple sensory modalities, including taste, smell, touch, sight, and sound, as well as emotional signals from the amygdala.
Orbitofrontal association area (orbitofrontal cortex)
Light pink
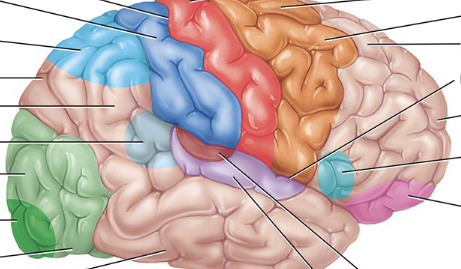
Wernicke’s area
a region in the left cerebral hemisphere, typically in the posterior part of the superior temporal gyrus, that is primarily responsible for language comprehension
Wernicke’s area
Light translucent blue
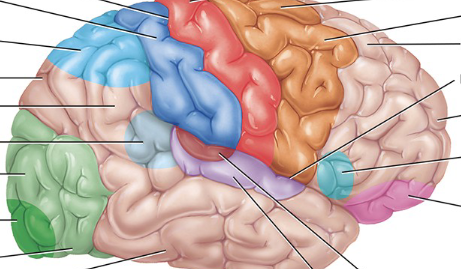
Common integrative area
It integrates sensory information from various areas to form a complete understanding of language, emotions, and complex sensory experiences. This area is crucial for interpreting both written and spoken language.
Common integrative area
Between all the blue
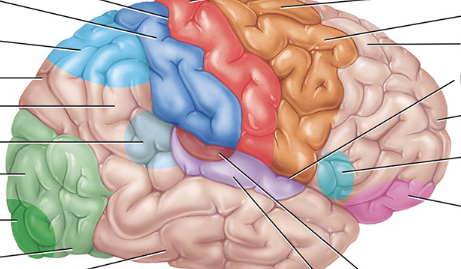
Prefrontal cortex
a center for higher-order cognitive functions like planning, decision-making, working memory, and appropriate social behavior
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater
Superficial to deep, what are the layers of the meninges?
Around the brain and spinal cord in the subarachnoid space
Where does CSF circulate?
A choroid plexus, found in each ventricle
What makes CSF?
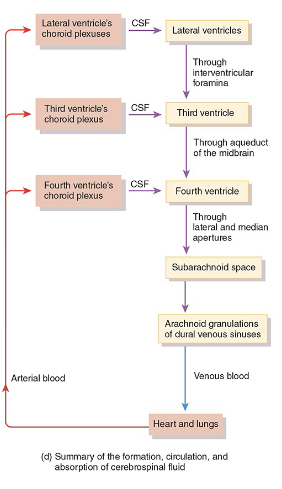
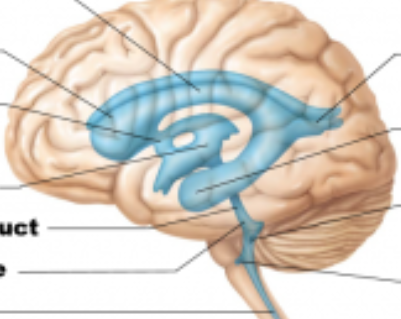
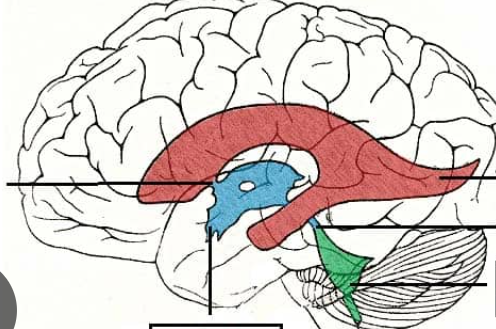
Flow of CSF
Lateral ventricles; one in each hemisphere
Red
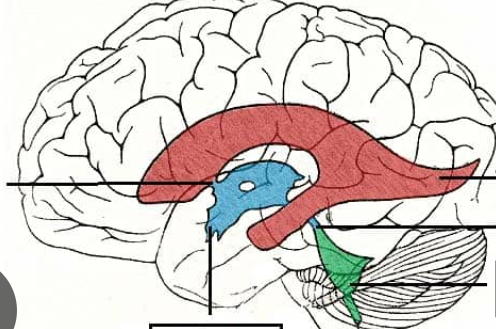
Septum pellucidum
The wall that separates the lateral ventricles
Interventricular foramen of the lateral ventricles
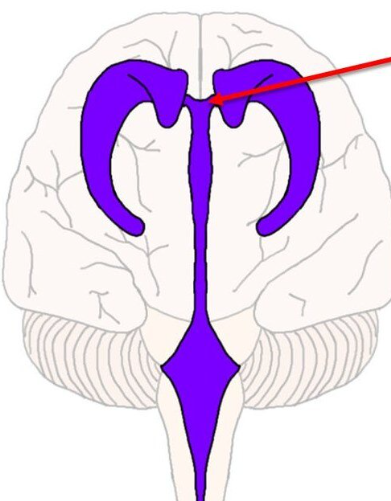
Third ventricle
Blue
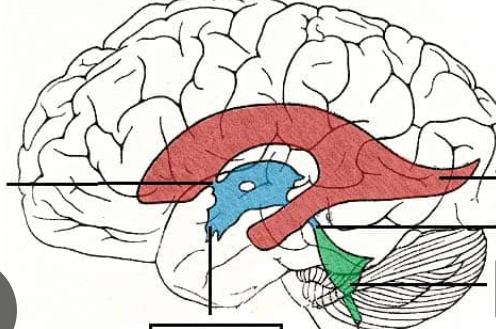
fourth ventricle
green
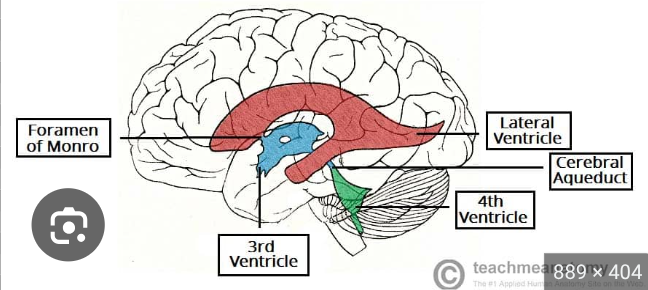
3rd ventricle
Where is the cerebral aqueduct?
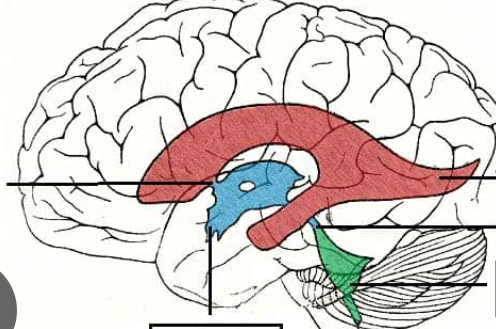
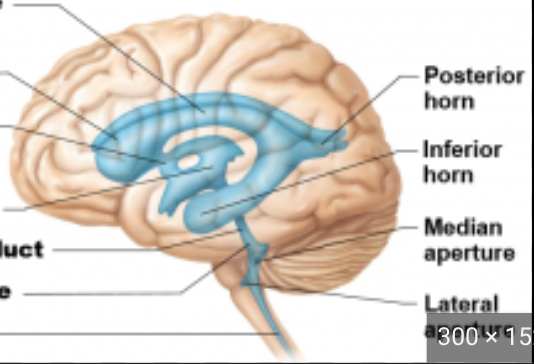
4th ventricle
Where are the lateral and medial apertures?