Biology - Adaptations and Genetic Diversity
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
Population
a group of individuals of the same species living in the same location
Gene pool
the total number of individual alleles within a particular population
increased alleles in a gene pool cause
increased genetic diversity
meiosis, mutations and random mating cause
increased genetic variation
‘fittest trait’
new allele/trait that gives a survival advantage during environmental change
sexual reproduction
the fusion of two distinct haploid gametes to produce a single diploid zygote composed of two sets of chromosomes
reproductive strategies
adaptations to reproduction that improve the success of survival of a species
fertilisation
the process by which two gametes (such as sperm and egg cells) fuse and form a zygote
zygote
the diploid cell formed by the combination of two haploid gamete cells
asexual reproduction
producing offspring without the fusion of gametes
clone
a genetically identical organism or section of DNA
binary fission
a type of asexual reproduction where one organism divides into two identical organisms
budding
a type of asexual reproduction where a group of cells form a bud and break away from the original organism to form a clone
vegetative propagation
a type of asexual reproduction where a plant grows from fragments, such as stem or root cuttings, of its parents
parthenogenisis
a type of asexual reproduction where an embryo can develop from a single unfertilised gamete
reproductive cloning technologies
artificially induced human interventions to produce genetically identical clones
somatic cell nuclear transfer (SCNT)
the transference of a somatic cell nucleus into an enucleated egg cell
embryo splitting
the division of an early embryo into several individual embryos
plant tissue culturing (micropropagation)
the cloning of plant cells an a nutrient culture medium in a controlled environment
plant grafting
the attachment of two individual plant stems together
abiotic factor
a property of the environment relating to non-living things. e.g temp, nutrient and water availability
biotic factor
a property of the environment relating to living things. e.g predator-prey relationships, competition and symbiotic relationships
tolerance range
the range of environmental conditions in which an organism can survive
adaptation
a change that makes an organism better suited to its environment
structural adaptation
evolved modifications to an organism’s physical structure
physiological adaptation
evolved modifications to an organism’s internal function or metabolic processes
behavioural adaptations
evolved modifications to an organism’s actions
thermoregulation
the homeostatic process of maintaining a constant internal body temperature
biodiversity
the variety of life in the world or within a particular habitat
community
a group of interacting populations of different species in the same geographical region
ecosystem
multiple communities interacting with one another and their physical environment
population size
the number of individuals in a population
carrying capacity
the max population size than an environment can sustain indefinetely
population distribution
the range of geographical areas that members of a population can be found in
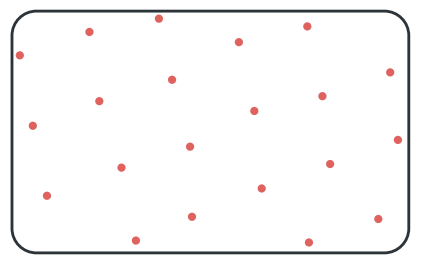
uniform distribution
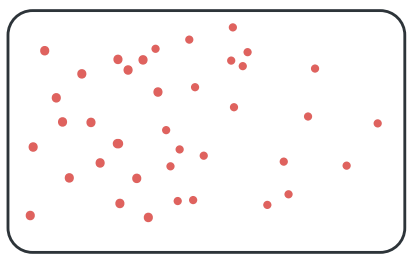
random distribution
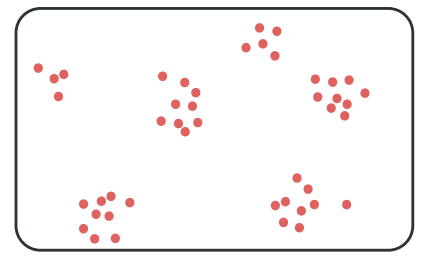
clumped ditsribution
symbiosis
an interaction between two organisms of different species living in close proximity to each other
mutualism
both parties experience some overall benefit
commensalism
one gains some benefit while the other experiences no significant benefit or harm
predation
one organism hunts and kills another organism for food
parasitism
one organism obtains nutrients at the expense of a host organism
amensalism
one organism experiences some negative effect while the other experiences neither a beneficial nor negative effect
competition
two or more organisms competing for the same pool of resources
interspecific competition
the competition for resources between members of different species
intraspecific competition
the competition for resources between members of the same species
food chain
the direction of movement of energy and nutrients
producer (autotroph)
makes own food through photosynthesis
consumer (heterotroph)
an organism that gets its energy by consuming other organisms as it cannot produce its own food
detrivore
an animal that feeds on dead organic material (worms)
decomposers
an organism that decomposes organic material (bacteria/fungi)
keystone species
a species whose effects on an ecosystem are greater than expected relative to its population size
apex predator
a predator that has no natural predators and is at the top of its food chain
ecosystem engineer
an organism that creates, significantly alters, or maintains the structure of an environment
food web
multiple food chains in an ecosystem all interacting together
pyramids of bio mass and energy
only 10% of the energy taken in becomes incorporated into the body of the consumer (next trophic level)
biomimicry
applying organism adaptations to their lifestyle
what do aboriginal peoples strive for
mutualism