4. Potentials and Electrodes
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
1
New cards
A reference electrodes is an electrode acting as a ...
reference against which other potentials can be measured.
2
New cards
Desired characteristics for reference electrodes:
Known, constant and reproducible potential/voltage (E ref)
Reversible interfacial electrode reaction
Insensitive to chemical species in the electrolyte solution where they are used in.
Follow Nernst equation
Robust and easy to use
Reversible interfacial electrode reaction
Insensitive to chemical species in the electrolyte solution where they are used in.
Follow Nernst equation
Robust and easy to use
3
New cards
Different types of reference electrodes
The primary reference electrode:
- Normal hydrogen electrode (NHE)
- Provides the zero point for the electrochemical potential scale.
Secondary reference electrodes:
- Their potentials are not zero but exactly known in relation to the NHE.
-Ag/AgCl electrode
- Calomel electrode (seldom used, contains mercury)
- Normal hydrogen electrode (NHE)
- Provides the zero point for the electrochemical potential scale.
Secondary reference electrodes:
- Their potentials are not zero but exactly known in relation to the NHE.
-Ag/AgCl electrode
- Calomel electrode (seldom used, contains mercury)
4
New cards
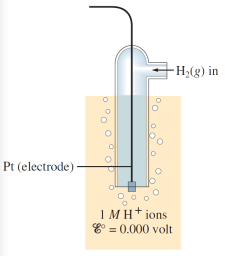
Normal hydrogen electrode (NHE)
Is a electrode with stable and reproducible potential with a potential of 0 V by definition.
5
New cards
Liquid junction potential (E'j)
where it develops?
Where is it estimated?
what does it depend on?
where it develops?
Where is it estimated?
what does it depend on?
Develops at the interface between two dissimilar solutions.
Can be estimated with the Henderson equation.
The liquid junction potential depends on the ion mobilities.
Can be estimated with the Henderson equation.
The liquid junction potential depends on the ion mobilities.
6
New cards
Liquid junction potential (wikipedia)
occurs when two solutions of electrolytes of different concentrations are in contact with each other. The more concentrated solution will have a tendency to diffuse into the comparatively less concentrated one.
7
New cards
Which is the cathode and anode?
Xa(s)│Xa2+(aq) || Fo+(aq)│Fo(s)
Xa(s)│Xa2+(aq) || Fo+(aq)│Fo(s)
THe left is the anode? and the right is the cathode
8
New cards
Case 1 for liquid junction potential
Two solutions of the same electrolyte with different concentrations.
9
New cards
Case 2 for liquid junction potential
Two solutions with the same concentration having a common ion.
10
New cards
Case 3 for liquid junction potential
Two different solutions with different concentrations.
11
New cards
The liquid junction potential (E 'j) depends on...
charge, mobility and concentration of ions