Applications of nuclear fission, induced fission and nuclear power plants
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
How is nuclear fission used?
In nuclear power plants in order to create electricity without the emission of greenhouse gases.
What are the risks of using nuclear power plants?
daughter nuclei produced are radioactive
meltdowns can cause devastating harm to the environment
How do nuclear power plants deal with the radioactive daughter nuclei released?
They have to be stored safely in areas far from people for thousands of years for them to decay fully
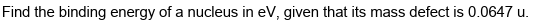
how would you do this?
(1st method preferred)

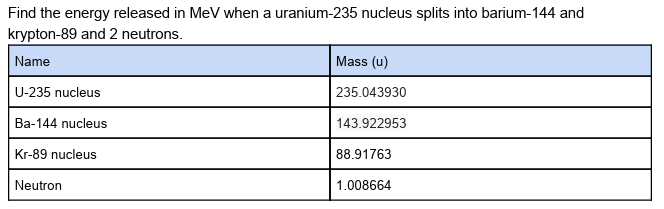
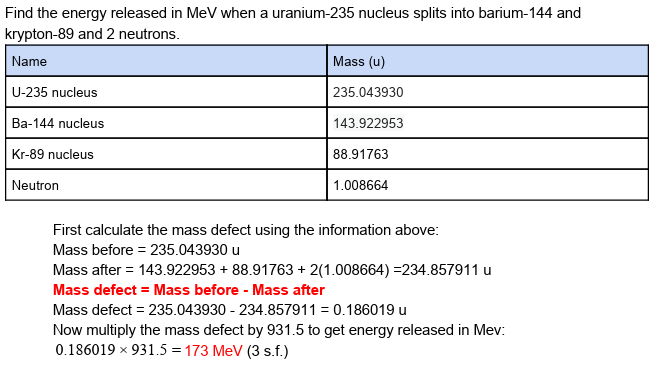
how would you do this?
(can also use method 1 from earlier at the end)
how can fission be induced in certain elements (such as U-235)
firing a thermal neutron into the uranium nucleus, causing it to become extremely unstable.
What are the products of nuclear fission?
2 daughter nuclei, and at least one neutron.
What happens to these neutrons after the collision?
The neutrons released cause more fission reactions, forming a chain reaction, where each fission goes on to cause at least one more fission.
What is the critical mass?
The critical mass is the minimum mass of fuel required to maintain a steady chain reaction.
What are the 3 key features of nuclear reactors?
moderator
control rods
coolant
What is the purpose of the moderator?
Slows down the neutrons released in fission to thermal speeds.
How does it do this?
Through elastic collisions between the nuclei of the moderator and of the fission. (these cause the momentum to transfer and decrease for the fission nuclei)
What 2 compounds are often used as moderators?
Water - as it is cheap, has hydrogen and not very reactive
Graphite (rarely)
What is the purpose of control rods?
To absorb the neutrons in the reactor in order to control chain reactions, controlling the energy produced in fission.
What materials are used to make control rods?
materials which absorb neutrons without undergoing fission, such as: boron and cadmium
What is the purpose of the coolant?
to absorb heat released during fission reactions in the core of the reactor, making it into steam which powers electricity-generating turbines.
What is often used as a coolant
sometimes, water can be used as both a coolant and moderator as it has a high specific heat capacity, meaning it can transfer lots of energy.
Molten salt or gas (e.g. helium) can also be used.