Unit 1 - Protein Synthesis, Structure and Function
1/323
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
324 Terms
Specificity and Flexibility of proteins causes
Risks
Functional Protein
Contributes to cell outcomes in usual conditions with tolerable fail rate
Shape and Structure specificies
Function of the protein
N Terminus
Amino End
C Terminus
Carboxyl end, new ones add to this end
Amino Acids
R groups + H + Amino Groups + COOH
Hydrophobic Amino Acids tend to be in
The core of soluable proteins
Aromatic Amino Acids
Phenylalanine
Tyrosine
Trytophen
Aliphatic Amino Acids
Hydrocarbon chains
Valine
Alanine
Leucine
Isoleucine
Methionine
Basic Amino Acids are
Positively charged
Lysine
Arginine
Acidic Amino Acids are
Negatively charged
Aspartic
Glutamic Acid
Hydrophilic Aminos
Asparagine
Theonine (neutral at 7pH)
Glutamine (polar amine)
Serine
Cysteine
Disulphide bridges with other cysteine
Glycine
Very small to sqeeze into small spaces and proteins to bend
Proline
R group covalently bonds with amino group creating kink for structure
Histidine
Has amino diethyl that changes positive or negative depending on pH
Peptide bonds forms by
Condensation reaction between amino and COOH
Translation
Ribosome subunits assemble to read mRNA
tRNA enters A site
tRNA shifts to P site, amino chain shifts
Used tRNA shifts to E site to be ejected
Primary Structure
DNA to mRNA
Introns removed from mRNA
Exits to cytosol
Random Coil Structure
Periodically ordered structure of protein
Statistical Coil
Protein spends most of its time in a certain structure
Native Structure
Functional protein structure
Hydrophobic Effect
Clumping of nonpolar, noncovalent molecules to aqueous solution to decrease interactions with water that add up for strong stability of folded structure
Setae Fibres in a Geckos Foot
Induces LD dipoles to let geckos walk sideways
Secondarry Structure
Periodic folding of polypeptide into distinct, conserved, geo arrangements
Motifs
Combinations of 2nd structure
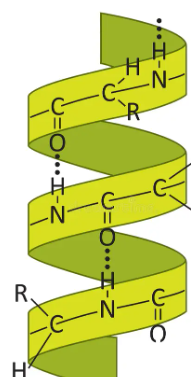
Alpha Helixes
Spiral, rod like structure by COO bonds with H 4 positions away, 3.6 aminos per churn
Beta Sheets
Planar structure with 2+ strands aligned by H bonds
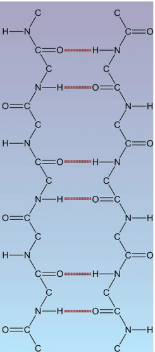
Beta Pleated Sheets
Laterally packed beta stranger from H bonds between COOH and amino from backbone in adjacent beta strand
Intramolecular H Bonds
Single polypeptide chain folds back on itself
Intermolecular H Bonds
Bonds between polypeptides in beta sheets
Turns/Loops
Connectors of beta and alpha
Beta Turn
3-4 aminos connecting beta strands of sheet
Coiled-Coil Motif
2 alpha helixes wrap aorund each other because both r groups are amphipathic and hydrophobic face inwards when aminos are at position 1 and 4 in repeat of 7 aminos
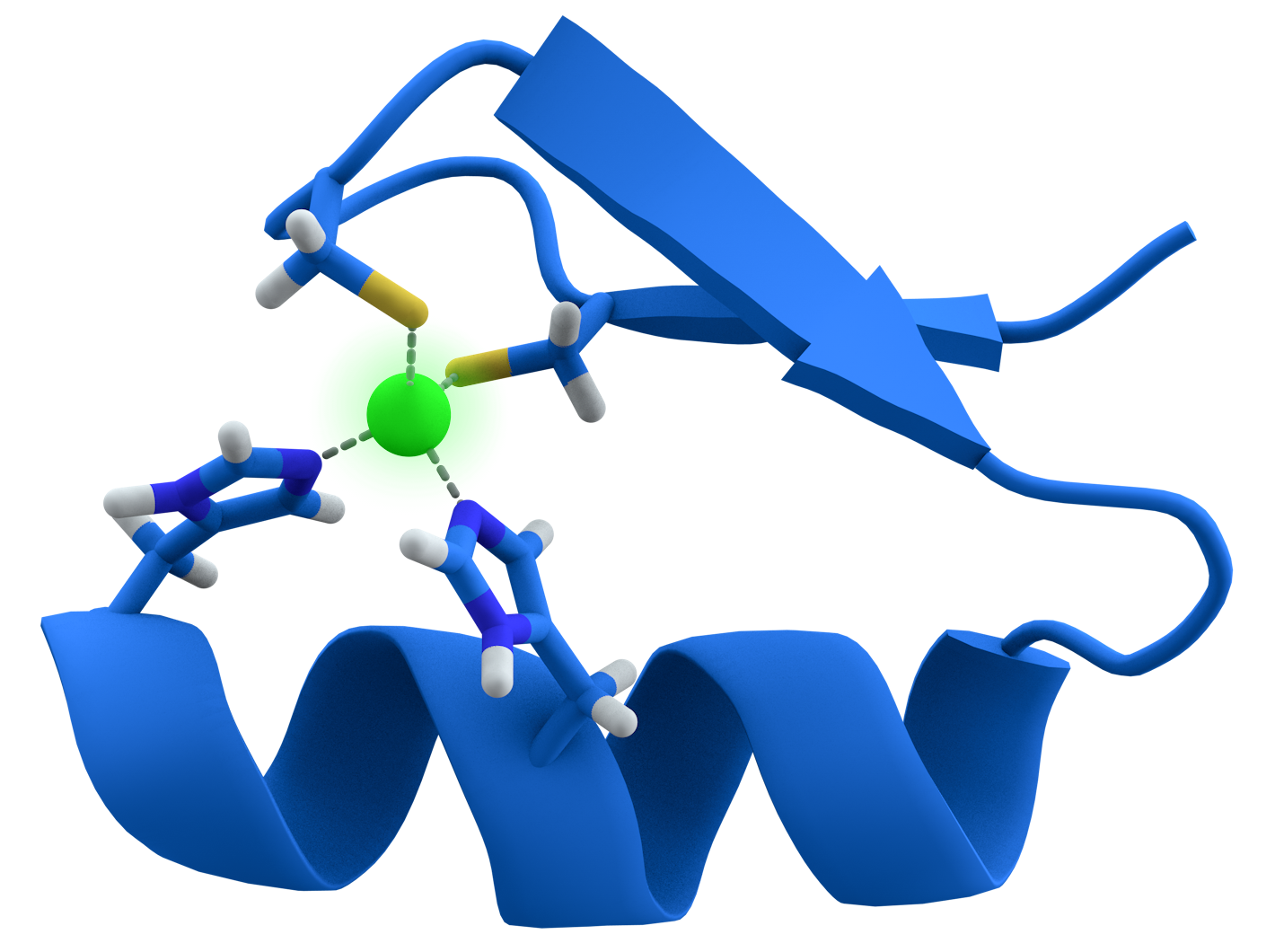
Zinc Finger Motif
Alpha helixes and 2 beta strands form 2 positioned residues with zinc atom
Beta Barrel Motif
Barrel form when last beta strands forms H-bonds with first strand
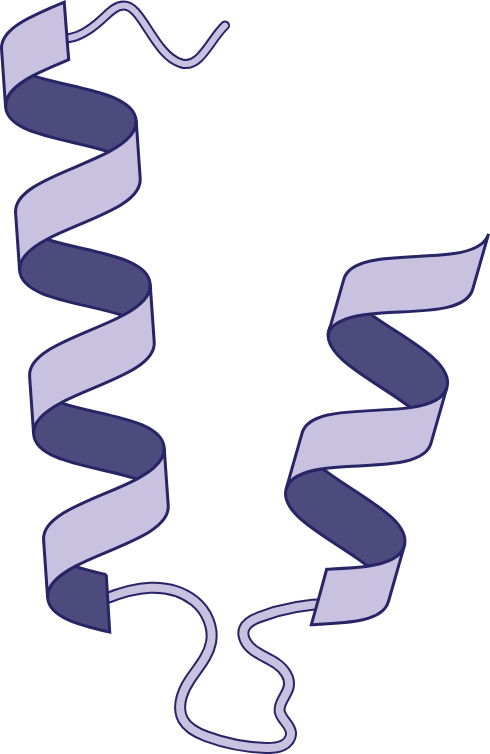
Helix Loop Helix Motif
2 alpha helixes joined by a loop region by non covalent interactions between aminos and calcium ion
Tertiary Structure
3D arrangement of all aminos
Domain
Functional unit of protein associated with a unique function and fold independently
Functional Domain
Region with specific activity of protein
Structural Domain
Region with a recognizable shape
Sre protein regulates
Cell cycle
Sre Protein Structure
Small and large functional kinase domains
SH2, SH3 structural domains
Quaternary Structure
Number and organization of subunits in a multiple protein complex
Multimeric Protein
Functional protein with multiple polypeptides
Dimer
2 polypeptides or subunits
Trimer
3 polypeptides
Homodimer
2 same polypeptides
Heterodimer
2 different polypeptides
Instrinsically Unstructured Proteins
Proteins that lack teritary structure when alone
Lysine + Acetyl
Acetyl Lysine, to protect proteins from proteases
Methylation
Histidine residues methlated into 3-methyl histidine altering gene expression
Phosphorylation
PO4 from ATP to OH group of serine, tyrosine, threonine by kinases
Collagen
3 hydroxylated proline
Carboxylation adds
Negative charge
Glycosylation
Add carbohydrates, protect proteins and helps folding
Sugar add to
OH groups of serine and threonine
Lipidation
Anchors proteins to hydrophobic biomembranes
Protein folding is
Spontaneous, reversible, and unique
Reversible Denaturation Experiment
Denatured protein with urea to break H bonds, and beta mercaptoethanol to break disulfide bridges
Dialysis to remove denaturants which brought it back to original shape
Villin
36 residue, alpha helical protein with hydrophobis core of 3 phenylalanines
Sickle Cell Anemia
Misfolded haemoglobin tetramer from glutamate to valine at position 6 causes it hydrophobic instead charged and forms polymers which gets stuck in capillaries
Challenges with Protein Folding
Folding driven by chemistry
Protein collisions
Folding must match rate of translation
Exposure of hydrophobic areas can cause other hydrophobic areas to stick
Cystic Fibrosis
Genetic disease from deletion of phenylalanine 58 of CFTR gene making it unable to bring Cl into cell causing thick mucus
Specificity
Ability to preferentially bind to few molecule only through shape, charge, flexibility
Affinity
Strength of binding, better fit = stronger, longer signal through surface matching and H bonds
Molecular Complementarity
Molecular shape fit well that favorable non covalent interactions form, both specificity and affinity dependent
Chaperons
Stop inappropriate interactions between amino acids and increase efficiency of protein folding
Molecular Chaperons
Monomeric proteins, binds to hydrophobic residues to stop wrong hydrophobic interactions
Heat Shock Proteins
Proteins for high temperature to help refold denatured ones
HSP 70
Nucleotide site for ATP, substrate site for folding using hydrophobic residues to help hydrophobic patches bind with ATP
DNA J/HSP 40
Stimulates ATP hydrolysis in HSP 70
BiP
ER residin protein that recognizes and binds to unfolded proteins to help transfer protein to ER through translocon by binding once
Where is Dnak
Bacteria
Chaperonins
Large macromolecular complex with many different proteins to form chamber or barrels to fold in isolation
TCiP
Eukaryotic cytosol
HSP 60
7 subunits per chamber, 1 subunit of GroEL = apical + intermediate + equatorial domain
HSP 60 Bacterial Chaperonin
2 GroEL + GroES cap and a hollow chamber inside
Chaperonin Catalyzation
Bottom releases GroES cap and ADP, the top chamber binds to ATP and peptide
GroES cap binds to the top of GroEL
Change enlarges chamber to allow it to fold inside
ATP hydrolysis allows GroES to come off and protein diffuses out, if misfolded the protein enters the bottom chamber
Tight Confirmation
GroEL without cap
Relaxed Confirmation
GroEL with GroES, larger
Protein Degradation
Protein tagged with ubiquitin
Proteasome recognizes ubiquitin and protein cut in 7-8 residue peptides
Ubiquitin
Small protein, 76 residues
E1
Ubiquitin activating enzyme that picks up free ubiquitin
E2
Ubiquitin conjugating enzymes that facilitates ubiquitin to protein attach
E3
A ubiquitin ligase made up of a bunch of proteins that recognize specific targets to degrade and attach it
Ubiquitinylation
Addition of ubiquitin using E1,E2,E3
Ubiquitinylation Steps
E1 attaches to ubiquitin using ATP
Ubiquitin transfers to E2
E3 recognizes, captures protein and E2 and E3 interacts and ubiquitin transfers from E2 to protein
Repeat many times for the same protein
Proteasome
Central hollow cylinder with caps on ends, forming narrow openings which unfolded polypeptides are threaded through
Proteasome Steps
Protein recognized by cap enters the proteasome unfolded and ubiquitin removed as it goes in
Cleaves non specific proteolytic activity
Small peptides further degraded by cytosolic proteases or in lysosome
Spinocerebellar Ataxia
Mutation in ataxin 1 gene causes misfolded ataxin protein but can’t be unfolded by proteasomes causing build up and lethal aggregation
Ligand Binding Pocket
Area where ligand binds, protein with cAMP pocket has 6 chains h bonding to areas of cGMP
Binding Affinity
Free energy of interaction between a protein and ligand, measured by binding
Higher Keq
More ligands bound to protein
Kd
Dissociating constant, strength of affinity
Vmax
Maximal rate of reaction because all enzymes are saturated
Takes higher concentration for a
Low affinity enzyme to get to Vmax as more dissociation
Km
Concentration when Vm is hald of max, indicates affinity between substrate and enzyme
Decreased Km
High affinity
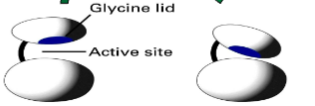
PKA
Kinase enzyme that adds PO4 to protein using binding pocket with glycine lid and kinase core by the glutamic acids recognizing arg-arg-X-ser-hydrophobic amino