Ligand Substitution
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
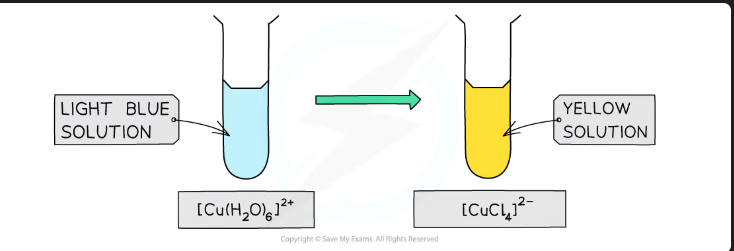
Write the equation for the reaction of Hexaaquacopper(II) with concentrated Hydrochloric Acid (Cl-). State the colour change.
Equation:[Cu(H_2O)_6]^{2+}+4Cl^{-}\rightarrow[CuCl_4]^{2-}+6H_2O
Colour: Pale Blue solution → Yellow/Green solution.
![<p></p><ul><li><p>Equation:$$[Cu(H_2O)_6]^{2+}+4Cl^{-}\rightarrow[CuCl_4]^{2-}+6H_2O$$ </p></li><li><p><strong>Colour:</strong> <strong>Pale Blue</strong> solution → <strong>Yellow/Green</strong> solution.</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/217f745e-be9a-4628-be39-fca1d1b02569.png)
Why does the coordination number change from 6 to 4 when water ligands are replaced by chloride ligands?
Chloride ions (Cl⁻) are larger than water molecules. There is not enough space for 6 chloride ions to fit around the central metal ion (steric hindrance/repulsion).
State the shape of the complex ion [CoCl4]2- and its colour.
Shape: Tetrahedral.
Colour: Blue.
(Remember: Cobalt goes from Pink water → Blue chloride).
Define the Chelate Effect.
The substitution of monodentate ligands by bidentate or multidentate ligands leads to a more stable complex. This is driven by a large increase in entropy.
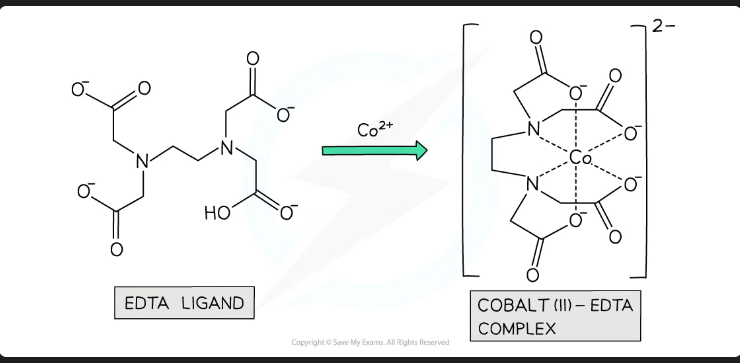
Explain, in terms of entropy (∆S), why the reaction below is feasible:
[Cu(H_2O)_6]^{2+} + EDTA^{4-} \rightarrow [Cu(EDTA)]^{2-} + 6H_2O
There are 2 moles of particles on the left and 7 moles of particles on the right.
This represents a large increase in disorder (positive ∆S).
Therefore, ∆G becomes negative (feasible).
Haemoglobin transports oxygen. Why is Carbon Monoxide (CO) toxic in terms of ligand substitution?
CO is a better ligand than O2.
It binds irreversibly (strong coordinate bond) to the Fe2+ ion in haemoglobin, replacing the oxygen.
This prevents the haemoglobin from carrying oxygen to the body's tissues.
State the observation when excess Ammonia is added to a solution of Hexaaquacopper(II).
[Cu(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}{}_{(aq)}+4NH_{3}{}_{(aq)}\rightarrow [Cu(NH_{3})_{4}(H_{2}O)_{2}]^{2+}{}_{(aq)}+4H_{2}O{}_{(l)}
Pale blue solution forms a pale blue precipitate, which redissolves to form a deep blue solution.
![<ul><li><p>$$[Cu(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}{}_{(aq)}+4NH_{3}{}_{(aq)}\rightarrow [Cu(NH_{3})_{4}(H_{2}O)_{2}]^{2+}{}_{(aq)}+4H_{2}O{}_{(l)}$$ </p></li><li><p><span>Pale blue solution forms a </span><strong><span>pale blue precipitate</span></strong><span>, which redissolves to form a </span><strong><span>deep blue solution</span></strong><span>.</span></p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/f31be67a-5bbb-41a5-bc73-4ce443fd1360.png)
State the observation when Concentrated HCl is added to a solution of Hexaaquacobalt(II).
[Co(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}\text{\ (pink)}+4Cl^{-}\rightleftharpoons [CoCl_{4}]^{2-}\text{\ (blue)}+6H_{2}O
![<p>$$[Co(H_{2}O)_{6}]^{2+}\text{\ (pink)}+4Cl^{-}\rightleftharpoons [CoCl_{4}]^{2-}\text{\ (blue)}+6H_{2}O$$ </p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e8da9917-aad1-48c7-bc38-f91e5e6befbe.png)