HB TOPIC 1 NERVOUS/ENDOCRINE
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the ROLE of the endocrine system
Influences the activity of cells by the release of hormones to maintain homeostasis
What are the 2 types of gland?
List them
Explain each
Examples
Exocrine glands- secretes hormones through ducts to body surface or cavities- eg. Sweat glands, salivary glands, mucous glands
Endocrine glands- secretes hormones into extracellular fluid surrounding gland, and then travels through blood to target cells
Define Hormones
how are they transported
Chemicals secreted by specialized cells, which contain proteins, amines, or steroids- TRANSPORTED BY BLOOD.
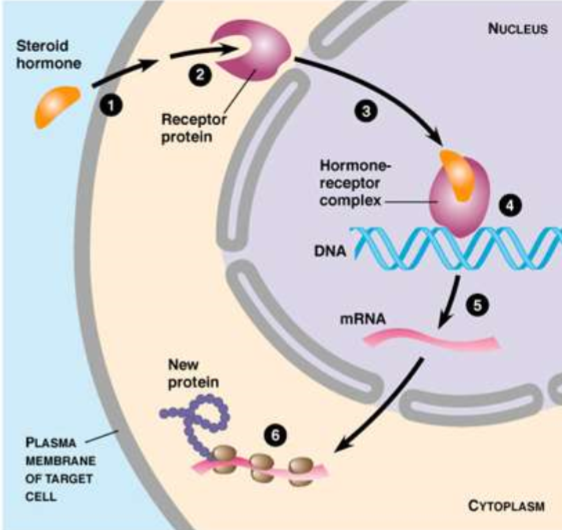
Steps of STEROID hormones
Enter target cell
Combine with receptor protein in cell
Hormone receptor complex (HRC) enters nucleus
HRC activates genes that control protein synthesis
Transcription
Translation and protein produced
How do hormones change function of cell?
change SHAPE / STRUCTURE ofenzymes by turning genes on n off
produce SPECIFIC PROTEIN SHAPE / STRUCTURE by turnin genes on n off
change rate of protein production
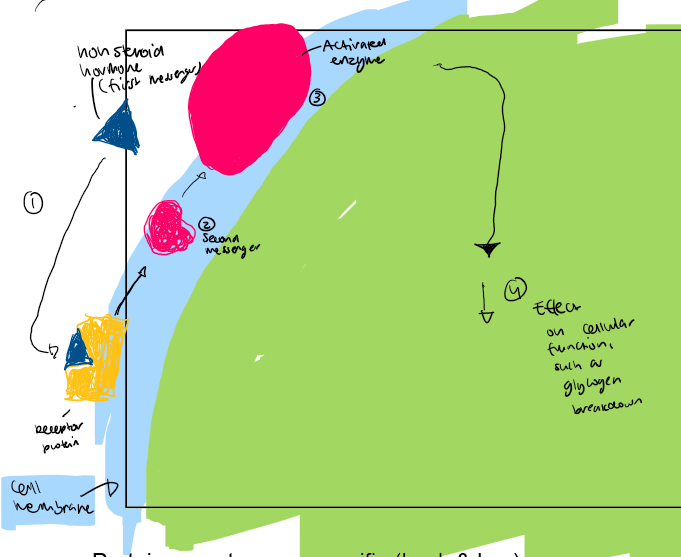
Steps of Protein and amine hormones
Attach to protein receptor on cell membrane of target cell
Secondary messenger diffuse through cell
Specific enzymes activated
Cellular function is affected
How do protein receptors prevent continual increase in cell activity?
Specific lock and key
Cells have different numbers and types of protein receptors varying response to different hormones
Limited number of PR in each membrane
Define ezyme amplification
one hormone can activate billions of enzymes which can trigger more and more
Define hormone clearence and where it occurs
Break down of hormones after they have indicated a response
Most broken down via liver and kidney or target cell and excreted in bile or urine.
Pituitary gland- where is it located and how is connected?
below hypothalamus and connected via a thin stalk called Infundibulum
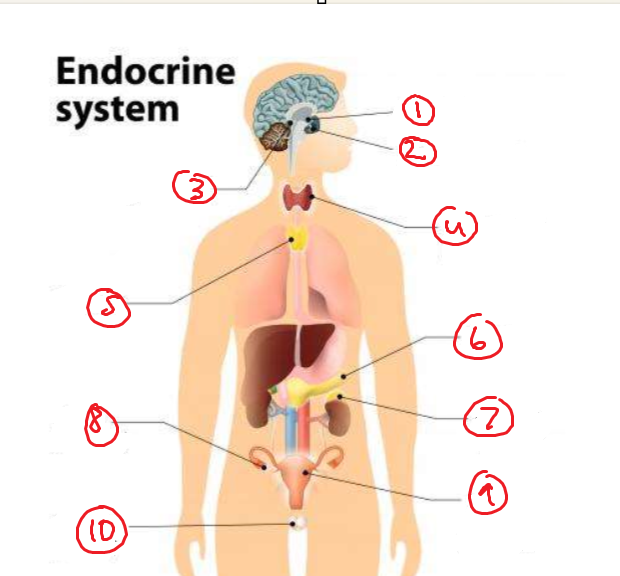
Label the parts
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Pineal
Thyroid and parathyroid
thymus
Pancreas
Adrenal cortex and medulla
ovary
placenta
testicles
Structure of Pituitary gland and how is connected to hypothalamus
2 lobes
Anterior Lobe- connected via blood vessels
Posterior Lobe- connected via nerve fibres
Anterior Lobe
how is it controlled and examples of hormones released
Controlled by releasing and inhibiting factors from hypothalamus into blood into anterior
TPFLAG
TSH
target organ
role
thyroid and parathyroid
stimulates release of hormones
FSH
target organ
role
ovaries and testes
stimulates growth and maturation of follicles/sperm and release of hormones
Luteinising hormone
target organ
role
ovary
stim of ripe follicle and prod of corpus leuterm
stim prod of eostrogen and progesterone
Growth hormone
target organ
role
most tissues
growth in size and mass
increases fat utilization and decreases glucose utalization
Prolactin
target organ
role
mammary glands
promotes growth of mammary and milk secretion
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
target organ
role
adrenal cortex
stim prod and secretion of corticosteroids
Posterior Lobe
how is it controlled
examples of hormones released
hormones produced in hypothalamus and stored in posterior lobe
oxytocin, ADH
Thyroid Gland
what does it secrete and how is it stimulated
Thyroxine (T4), T3 and Calcitonin
Stimulated by TSH
Thyroxine and T3 HORMONE
target organ
effect
Small intestine
Controls metabolism and synthesis, increased absorption of of glucose
Calcitonin
target organ
function
BONES- decreases blood calcium via excretion of urine and suppresion of osteoclast activity
INTESTINES- INC absorbtion in intestine
Parathyroid gland
secretes what hormone
effect
stimulated by…
secretes parathyroid hormone
controls blood calcium and phosphate levels
TSH
Pancreas
2 types
secretes what hormones?
Exocrine- digestive enzymes into small intestine
Endocrine- Islet of Langerhans secrete insulin and glucagon
Difference between insulin and glucagon in terms of
produced by…
role
impact on blood sugar levels
Insulin produced by beta cells- converts glucose into glycogen and fat= DECREASE BSL
Glucagon produced by alpha cells- glycogen and fat into glucose= INCREASE BSL
Testes
hormone secreted
role of hormone
secrete testosterone
develop and maintain features
Ovaries
hormone secreted
effect of hormones
oestrogen and progesterone
develop and maintain female features, regulate menstrual cycle and changes during pregnancy
Pineal Gland
secretes what hormone
role of hormone
how is it stimulated
melatonin
regulated sleep patterns
stim by darkness
Adrenal Medulla
secretes what hormones
effect of hormone
adrenaline and noradrenaline
stimulates fight or flight response and responses (HR)
Adrenal Cortex
secretes what hormones
role of each
cortico steroids of
1. Cortisol-ALL CELLS promotes metabolism, stress and repair damaged tissue inbody cells
2. Aldosterone- KIDNEYS to increase sodium reabsorbtion and pottassium excretion in urine
Thymus
secretes what hormone
role of hormone
what happens after purbety
thymosins
maturation of T lymphocytes
shrinks after puberty