Mix Design and Concrete handling
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
why should aggregates be saturated?
to avoid absorption of needed hydration water
what two things sum up to the absolute volume of a material?
volume of solid + volume of its pores (permeable and impermeable)
difference between mix design and mix proportioning
mix design = selecting materials and desired properties.
mix proportioning = determining how much of each material is needed to produce 1 cubic yard of fresh concrete
What is not included in the absolute volume of a material
voids between particles
w/c ratio is determined by:
durability and strength
for the w/c ratio, which one of the two values for the w/c ratio is considered?
the lowest one
Purpose of air content in the cement paste
improve workability and increase resistance
typical air content
5-8% (commonly 6% +- 1%)
If the paste amount decreases as the aggregate maximum size (Dmax) increases, the air content increases or decreases?
increases
What is affected by the air content in mix calculations?
volume balance
Maximum aggregate size must be:
≤ 1/3 slab thickness
≤ 3/4 of spacing between bars
≤ 1/5 of minimum cover
True or False. Required compressive strength (f’cr) must be higher than specified f’c.
True
rounded vs angular shaped aggregates in a mix:
rounded = more workability, less water needed
angular = less workability, more water needed
The event where separation of the coarse aggregate from the fine part in the concrete mix occurs is known as:
Segregation
An example of a curing method that prevents the loss of moisture is:
Impermeable membranes
The common practice is to test the hardened concrete at the age of:
7 and 28 days
The method of measuring the air content in the concrete mix that is not affected by the elevation is:
Pressure and Gravimetric
In a PC concrete mix calculation, the formulas resulted in w/c ratios of 0.42 and 0.44 when there is statistical data. Also, the w/c must be not higher than 0.45 to satisfy exposure conditions. Which w/c ratios must be used in this mix?
0.42
If the concrete is maintained under an adequate moisture conditions for the hydration process to occur, it may continue developing its strength for how long?
1 year or more
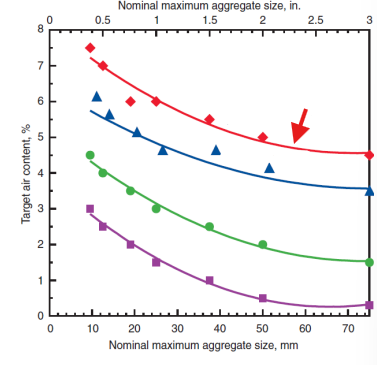
severe exposure
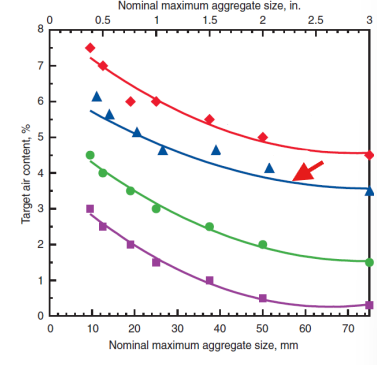
moderate exposure
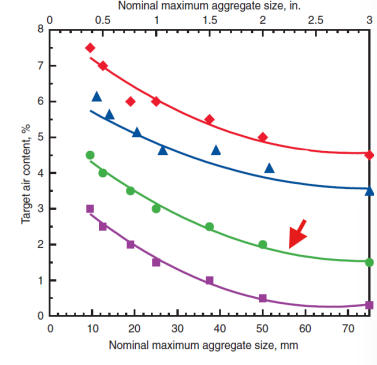
mild exposure
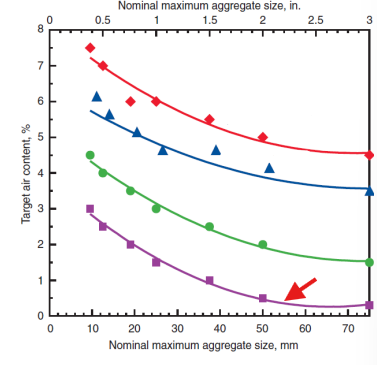
non-air entrained concrete
Mixing:
homogeneous mix with all ingredients evenly distributed
Consistency:
Measured by slump test (ease of flow).
Workability:
Ease of placing, consolidating, and finishing without segregation
Segregation
Coarse aggregates separate from the mix
Bleeding:
Type of segregation where water rises to the surface
general values for slump
between 1 in and 6in
slump for flowing concrete
>7 1/2 in
slump when segregation occurs
>10in
rpm for Central-mixed concrete (all mixing at plant)
2-6 rpm
rpm for Truck-mixed concrete (all mixing on the truck)
4-16 rpm
rpm for Shrink-mixed concrete (partial plant, partial truck)
4-6 rpm
How should concrete be placed on site
In horizontal layers and consolidated before adding another
Method used for consolidating concrete
vibration
what should vibration never be used for
moving concrete horizontally
Why is vibration used to consolidate concrete
removes air pockets and stone voids
what does over-vibration cause
segregation
when does slab finishing (floating) starts?
after bleeding stops
Purposes for Slab Finishing (Floating)
embed coarse aggregates, smooth surface, compact top mortar
Frequency of ASTM C172 and ACI 318-19
once a day, once every 150 yd3 of concrete, once for every 5,000 ft2 of surface for slabs or walls
From where is the concrete sample taken when sampling fresh concrete
from middle portion of truck batch
size of concrete when sampling fresh concrete
1ft3 (28L), taken within 15 min
When should slump, temperature, and air content be measured
within 5 min
measures of standard cone in slump test
4in top, 8in bottom, 12in high
3 volume layers mold should be filled in slump test:
70mm, 160mm and top
What is measured/tested in fresh concrete
slump, sampling, temperature, unit weight and yield, air content
Steps of sample molding:
Cylinders: 6×12 in. or 4×8 in. (based on agg. size)
Compact in 3 layers, 25 strokes each, plus tapping
Cure at 76.5 ± 3.5°F
Remove molds after 24 ± 8 hrs
Purpose of curing process
prevent moisture loss and maintain temperature
Curing Methods:
saturated water coverings
plastic sheets
steam/electric heat for fast curing
Primary cause of cracking
drying shrinkage
True or False. f’c increases over time
True
Normal concrete compressive strength
3000-6000 psi
High concrete compressive strength
>6000 (up to 20,000)
tensile strength of concrete
8-12% of f’c
conventional methods for evaluating hardened concrete
compression, tension, flexural tests
non-conventional methods for evaluating hardened concrete
rebound hammer, penetration probe, ultrasonic pulse, maturity test
What causes an Alkali-silica reaction
reactive silica + high pH + moisture
Control methods for Alkali-silica reactions
use supplementary cementitious materials, low-alkali cement, lithium compounds
density of lightweight concrete
85-115 pcf
density of heavyweight concrete
400 pcf
strength of High-strength concrete (HPC)
10,000psi
What type of concrete flows and consolidates under its own weight
self-consolidating concrete SCC
what type of concrete has a dry mix, no slump is needed and is compacted like pavement
roller compacted concrete RCC
Which type of concrete is applied by being sprayed on
Shotcrete
What type of concrete is added for impact/crack resistance
Fiber-reinforced concrete