PLTW- Principles of of Biomedical Sciences 2024 Midterm
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms

Plain Arch

Tented Arch
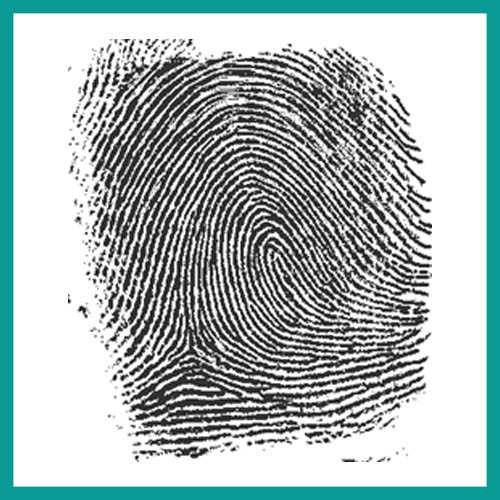

What kind of fingerprint is this?
Loop
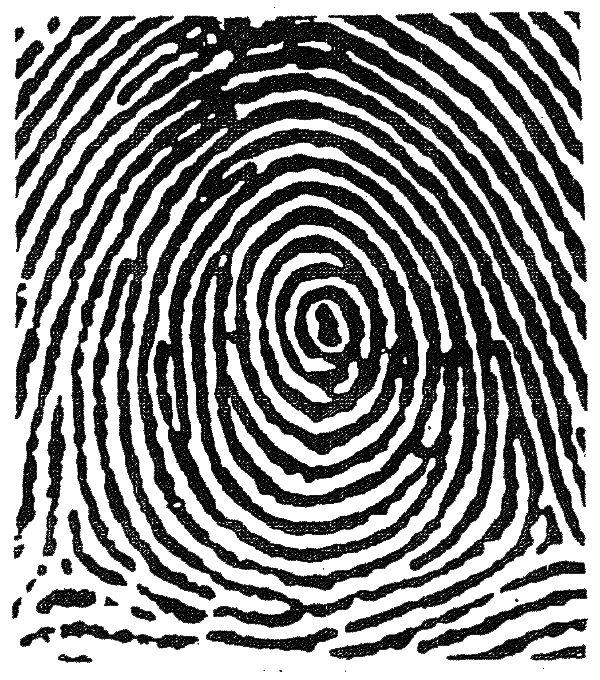

Whorl
Minutae
Tiny fingerprint details. Most common one is ridge ending
How many minutae are needed to confirm that two fingerprints are identical?
12-15
Plasma
Liquid portion of blood that consists of water and dissolved substances
Red Blood Cells (Erythrocytes)
Blood cells that transport oxygen throughout the body
White Blood Cells (Leukocytes)
Blood cells that are active in immune response
Platelets
Assist in blood clotting by adhering to other platelets/ damaged epithelium
Micropipettes are used to measure liquids in _____.
microliters
How do you convert from µl to mL?
1000 µl = 1 mL
Rigor mortis
Stiffening of joints and muscles after death
Livor mortis
Pooling of blood in the body following death (lividity)
Algor mortis
The change in body temperature after death
What happens to the body within the first 24 hours of death?
Within the first 2-4 hours, rigor mortis sets in. Within 3-4 hours, the corneas cloud. From 0-24 hours livor mortis sets in, and algor mortis sets in, making the body cool down to match the temperature of its surroundings. At 36-48 hours, the body begins decomposition, rigor mortis fades, it turns greenish and swells.
Frontal lobe
Controls emotions and behaviors and organizes information
Parietal lobe
Integrates sensory and visual information
Temporal lobe
Processes language and stores information
Occipital lobe
Receives and processes sensory information from the eyes
Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)
a brain dysfunction caused by an outside force to the head
Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)
the death of brain cells caused by repeated head injuries
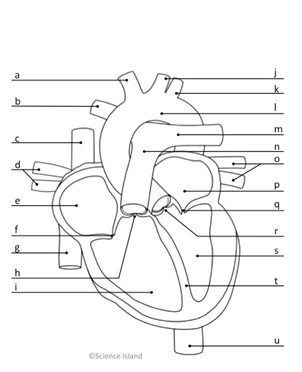
What is l, and is it oxygenated or deoxygenated?
Aorta; oxygenated
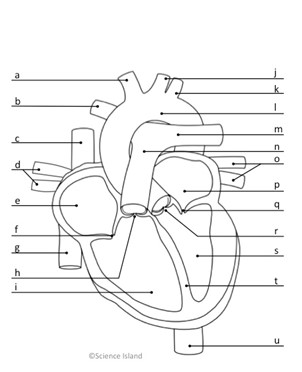
What is n, and is it oxygenated or deoxygenated?
pulmonary artery; deoxygenated
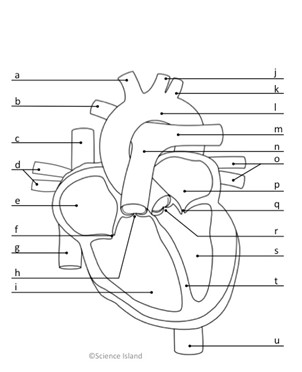
What do c & g represent, and is it oxygenated or deoxygenated?
Vena Cava; deoxygenated
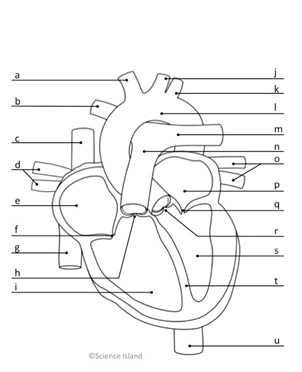
what does e represent, and is it oxygenated or deoxygenated?
right atrium; deoxygenated
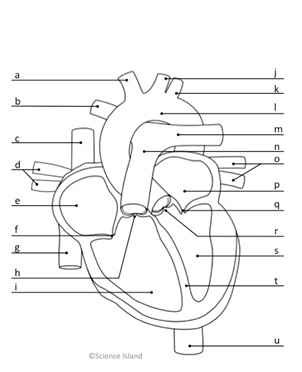
What is i and is it oxygenated or deoxygenated?
right ventricle; deoxygenated
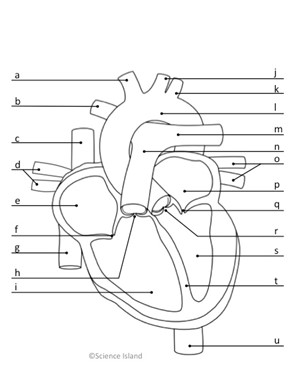
What is p, and is it oxygenated or deoxygenated?
left atrium; oxygenated
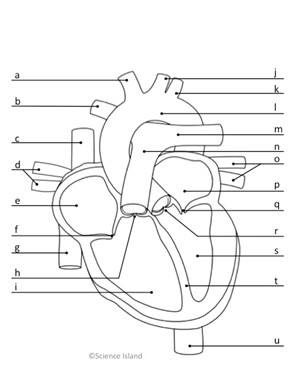
What is s, and is it oxygenated or deoxygenated?
left ventricle; oxygenated
Ventricular Septal Defect
A hole in the wall separating the ventricles, causes oxygenated and deoxygenated blood to mix together, so the heart must work harder to provide oxygen.
Symptoms of Ventricular Septal Defect
Heart palpitations, shortness of breath, fatigue
Homeostasis
The maintenance of stable internal physiological conditions; the tendency to resist change
Negative feedback loop
causes the system to stop doing original action
Positive feedback loop
reinforces the original action the body was doing
Diabetes
disorder caused by broken feedback loops involving insulin
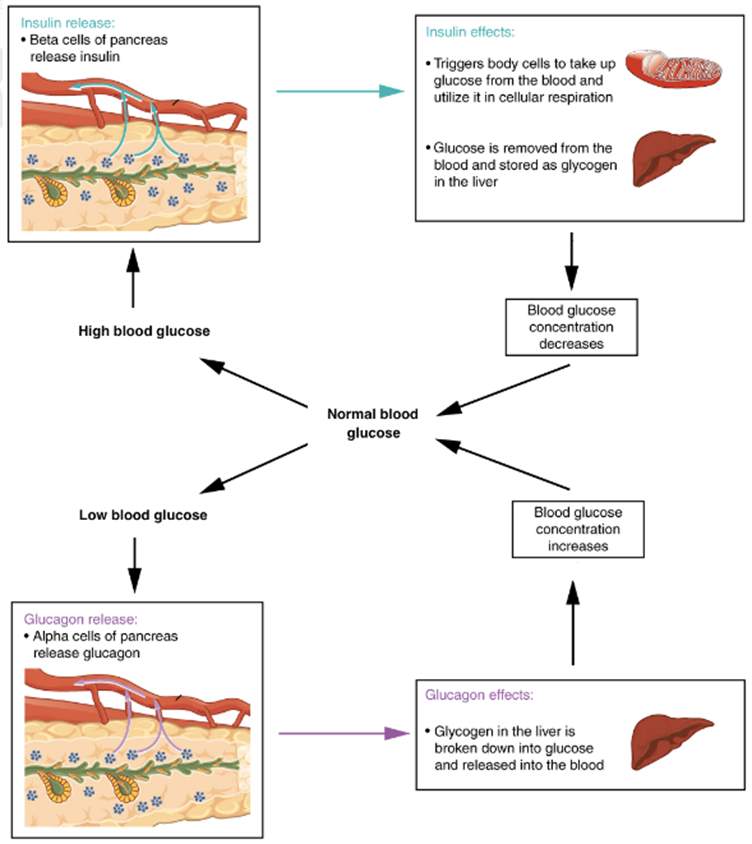
What kind of feedback loop is this?
Normal blood glucose feedback loop
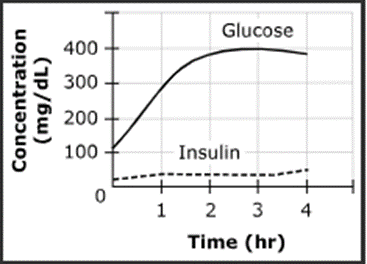
Type 1 Diabetes
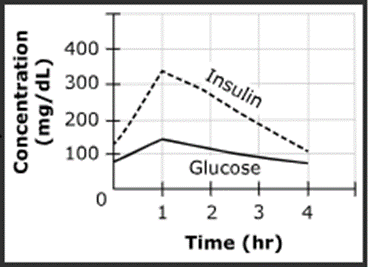
Which type of diabetes is this?
Type 2 Diabetes
What is the difference between type 1 and type 2 diabetes?
In type 1 diabetes there is no insulin production, in type 2 diabetes there is insulin resistance
How is diabetes monitored?
Glucometer
Blood Pressure
the force of blood moving through blood vessels; sphygmomanometer
Pulse
Number of heartbeats per minute; stethoscope
Respiratory Rate
Number of breaths per minute; stethoscope
What is a Complete Blood Count (CBC) test and what does it look for?
Blood test that looks for potential conditions impacting blood cells
Lipid panel test
blood test that tests cholesterol levels; looks for/prevents heart disease
LDL
lipoprotein that transports cholesterol to cells; considered high if at 160 mg/dl or above
HDL
lipoprotein that removes excess cholesterol from bloodstream & transports to liver; considered high if less than 40 mg/dL
What level is considered a high level of total cholesterol?
240 mg/dL or above
What is HIPAA?
Set of standards and practices designed to give patients specific rights regarding their protected health information
What is the main purpose of HIPAA?
Protect the privacy of patients
Prevent the use of confidential information without permission
Provide continuous health insurance for patients switching jobs
Who can you discuss a patient’s information and test results with?
Other professionals working with the patient
Nucleotide
Building block of nucleic acids
Chromosome
DNA tightly coiled around proteins called histones
Gene
sequence of nucleic acids that code for a hereditary trait
What is protein synthesis (translation)
the creation of a protein from a DNA template
DNA is ______ into mRNA
transcribed
mRNA is ______ into proteins
translated
Transcribe the following DNA sequence into mRNA, then translate the mRNA into amino acids.
T A C G T G A C C T G A C C T A T C
AUG CAC UGG ACU GGA UAG
MET HIS TRP THR GLY STOP
mutation
a rare change in genetic material
substitution
a type of mutation where one DNA base is substituted for another
Insertion
A type of mutation where one DNA base is added to the sequence
Deletion
A type of mutation where one DNA base is removed from the sequence
Phenotype
physical appearance/characteristics. ex: blue eyes
Genotype
genetic constitution represented in letters. Ex: Bb
Allele
different variations of the same gene
Dominant Allele
genes that keep other genes from showing their traits
Recessive Allele
Genes that do not show their traits when dominant genes are present
Heterozygous
2 different alleles (Ex: Tt)
Homozygous
2 identical alleles (Ex: TT or tt)
Pedigree
chart showing a record of the family of an individual
Autosomal dominant
One mutated allele is sufficient to cause symptoms in the individual
Autosomal recessive
two mutated alleles are required for the individual to experience disease symptoms
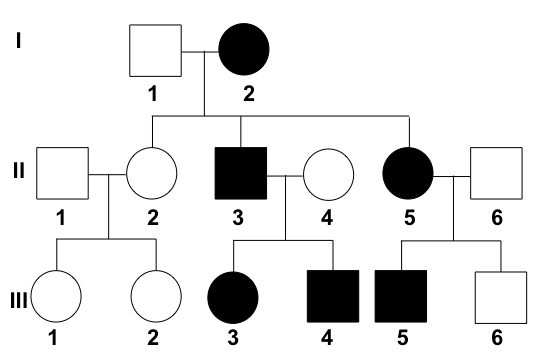
What kind of inheritance pattern is this?
Autosomal dominant
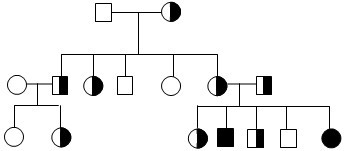
What kind of inheritance pattern is this?
Autosomal recessive
Sickle Cell Anemia
An inherited disorder that changes the shape of beta-chain hemoglobin inside the red blood cells
Why do some individuals with Sickle Cell Anemia get blood transfusions?
To increase the number of normal red blood cells and increase oxygen concentration in blood