Chapter 4 - Aural Skills Part 1: Fundamentals and Singing
- Aural skills - The process of identifying, producing, and notating the elements of music that we hear.
Aural Skills Components of the AP Music Theory Exam
Notating on One Staff
- Melodic dictation - Free response section that includes two melodies which will be performed either by instrument or by voice. You are expected to write down th pitch and the rhythm accurately.
- In the sight-singing portion, the melodic dictation will have one melody in treble clef and one melody in bass clef.
- One melody will be in simple meter and one will be in compound meter.
- One melody will be in a major key and one in a minor key.
Notating on the Grand Staff
- Harmonic dictation - Going one step deeper into hearing, identifying, and notating.
- There will be two of these.
- One will be in a major key and one in a minor key.
- The more challenging one usually includes chromatic harmony.
Identification, Error Detection, and Score Analysis
- Multiple choice portion. Part A uses recorded music. You’ll have to:
- Identify from four possible choices such as scales, modes, inverval quality, chord quality, and rhythm. These are usually played on piano.
- Error detection - Listen to a two-, three-, or four-part harmonization played by piano and recognize mistakes in the score in pitch and rhythm.
- Listen to short excerpts from various genres and answer questions based on the aural presentation.
Singing
Final part of the exam - Two sight-singing examples.
- One melody will be in treble clef and one will be in bass clef.
- One melody will be in simple meter and other one in compound meter.
- One melody will be in a major key and one in minor key.
Sight-singing - A method of training your brain to understand the relationship between notes within a specific scale or tonality.
Movable-Do - Commonly used method of solfeggio. It means that regardless of what key you’re in, the tonic (first note of the scale) is always Do.
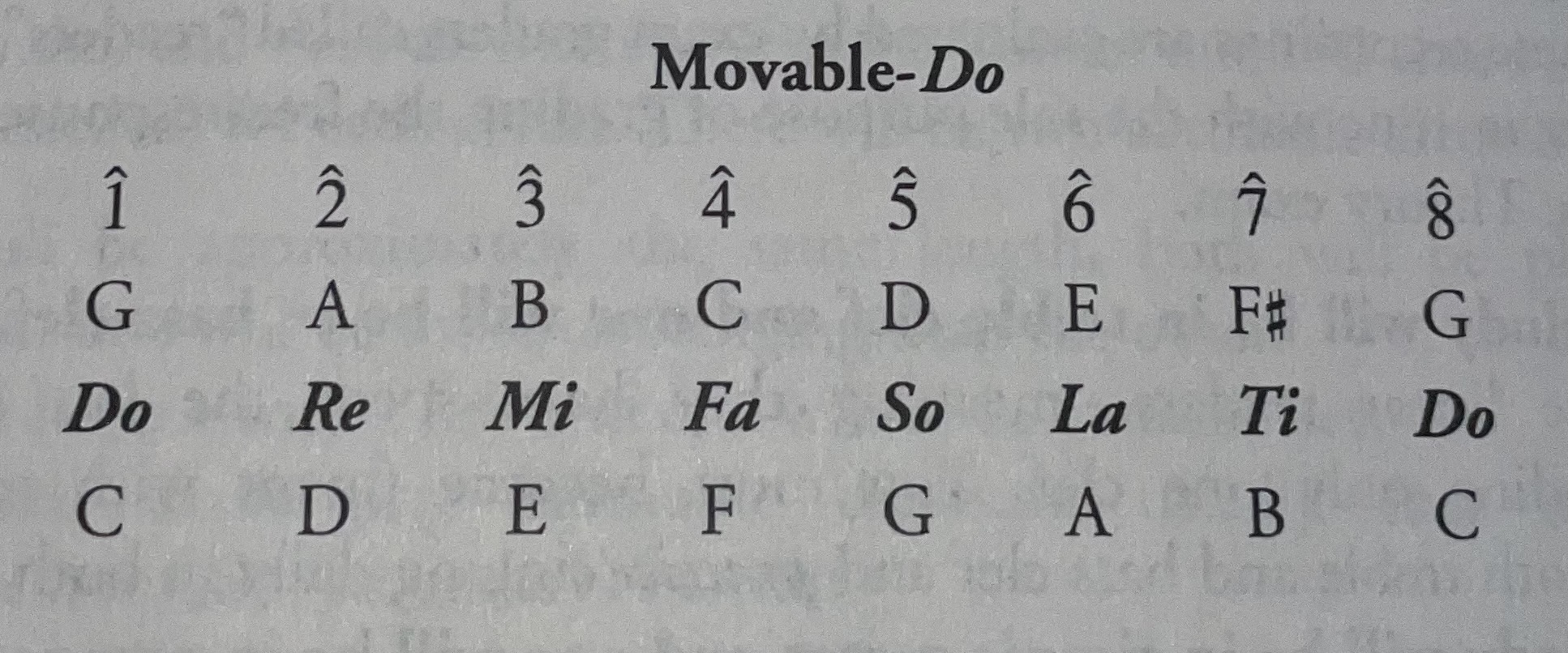
Fixed-Do - The opposite to movable-Do. This system attaches solfege syllables that remain with the pitch regardless of key.
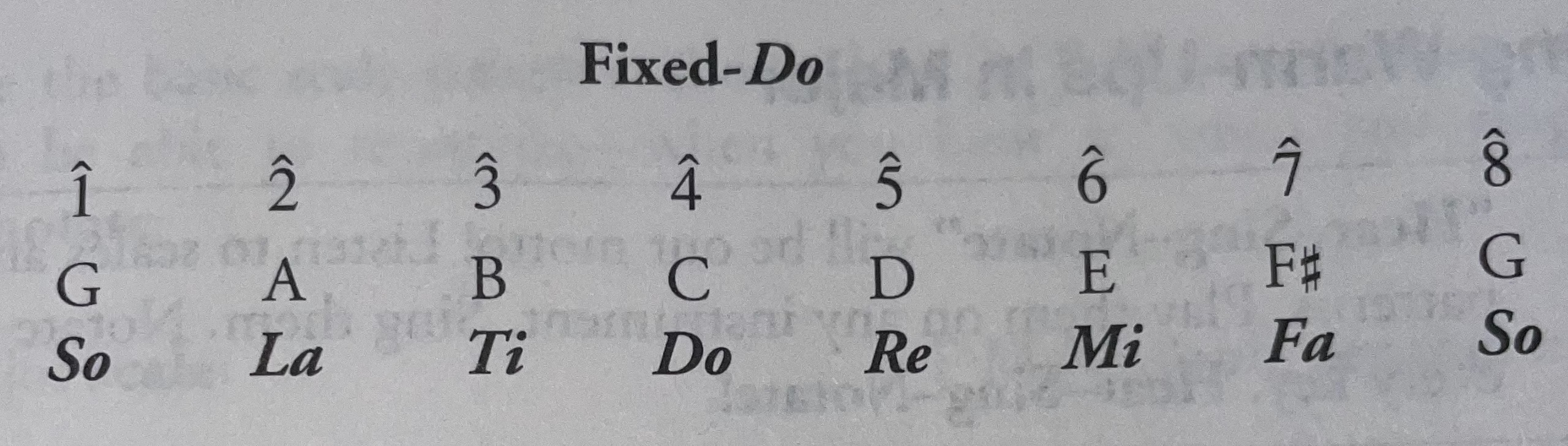
Two prevalent systems for singing in a minor mode:
- Do-based minor
- La-based minor
Do-based minor - Movable-do system in minor. Here the Do-based minor is the parallel of Do-based major.
La-based minor - It reflects the relative minor of any major scale and uses the same pitches starting on the sixth scale degree or La. This system is prevalent in choral music to facilitate moving from a major key to the relative minor.
Scale degree finder - An exercise used to quickly go through the scale and find the pitch you need. It contains the tonic triad and common diatonic intervals.
Top Ten Melodic Patterns in G Major

Minor Scale Review
- Natural - There’s no alterations from the key signature.
- Harmonic - The 7th degree is raised both ascending and descending.
- Melodic - Minor scale with both the 6th and the 7th scale degree raised.
- Minor pentachord - All three begin with the same first five notes.
- Scales 6 and 7 are different, based on the form of the minor.
- Parallel - Major and minor keys with different key signatures but with the same tonic.
Top Ten Patterns in G Minor
