Module 4 PowerPoints
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
human papilloma virus (HPV)
>99% of cervical cancer worldwide is caused by _______________
transformation zone
area where glandular cells of endocervix and squamous cells of exocervix meet
aka squamocolumnar junction
transformation zone
the _______________ is also known as the squamocolumnar junction
transformation zone
the region where most cancers occur
squamous cell
most common cervical cancer
arises from the exocervix
post-coital bleeding
one symptom of cervical cancer is:
adenosarcoma
____________ has a composition similar to phyllodes tumor of the breast
uterine adenosarcoma
can occur outside uterus
related to endometriosis
endometrial carcinoma
most common gynecologic cancer in USA
50-65
the typical age endometrial carcinoma is diagnosed is:
estrogen
endometrial sarcoma is linked to:
Lynch syndrome
women with ____________ have a 70% chance of developing endometrial cancer as well as an increased risk of colon and ovarian cancer
endometrioid
most common endometrial cancer
3
grade _______ endometrial cancer has <50% glandular tissue present
1
type ____________ endometrial carcinoma is associated with unopposed estrogen
2
type ___________ endometrial carcinoma is not associated with unopposed estrogen
ovarian cancer
leading cause of death from cancer of the reproductive system
epithelial
more than 90% of primary ovarian malignancies are _______________ in origin
germ cell tumors
least common ovarian primary malignancies are ______________
serous cystadenocarcinoma
most common ovarian malignancy
CA-125
___________ is elevated in more than 90% of cases of serous cystadenocarcinoma
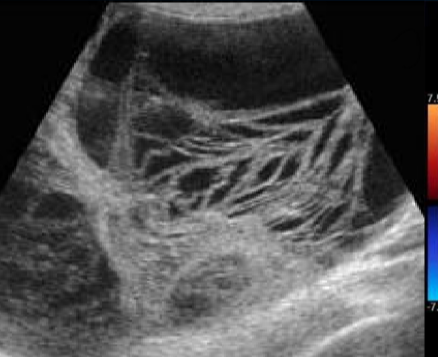
serous cystadenocarcinoma
this image is demonstrates:
mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
a _________________ is more likely to rupture than mucinous cystadenoma
mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
______________ is much less common than serous cystadenocarinomas
pseudomyxoma peritoneum
ascites that is thick and loculated (compartmentalized by septations) and has mass effect (causes enlargement of the abdomen and compresses abdominal structures)
better prognosis
mucinous cystadenocarcinoma has a ________________ than serous cystadenocarcinoma because it is more often diagnosed in stage 1
endometrioid tumor
second most common epithelial ovarian cancer
malignant
endometroid tumor is almost always _____________
endometriosis
endometrioid tumors are associated with ______________
clear cell tumor
always high grade carcinoma
poor prognosis
does not respond well to chemotherapy
granulosa cell tumor
most common malignant stromal tumor
estrogen
granulosa cell tumors produce _____________
benign
granulosa cell tumors start out ________________ but occasionally become malignant
Meig Syndrome
granulosa cell tumors are associated with _____________
Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor
an androblastoma/arrhenoblastoma is also known as a ________________
dysgerminoma
most common malignant germ cell tumor
30
dysgerminoma is seen in women under _______________ years old
gonadoblastoma
dysgerminoma may develop from a ________________
solid and hypervascular
sonographic appearance of dysgerminoma
stage I ovarian cancer
limited to the ovaries
stage II ovarian cancer
beyond ovaries but limited to pelvis
stage III ovarian cancer
extends beyond pelvis into retroperitoneal or inguinal lymph nodes, and/or intraperitoneal implants into the omentum, and/or superficial liver metasteses
stage IV ovarian cancer
distant metastases to bone, lungs, brain, or liver parenchyma
tamoxifen
____________ is a risk factor for uterine adenosarcoma, endometrial carcinoma, and carcinosarcoma
malignant
a simple ovarian cyst less than 5 cm in a postmenopausal woman is unlikely to be _______________
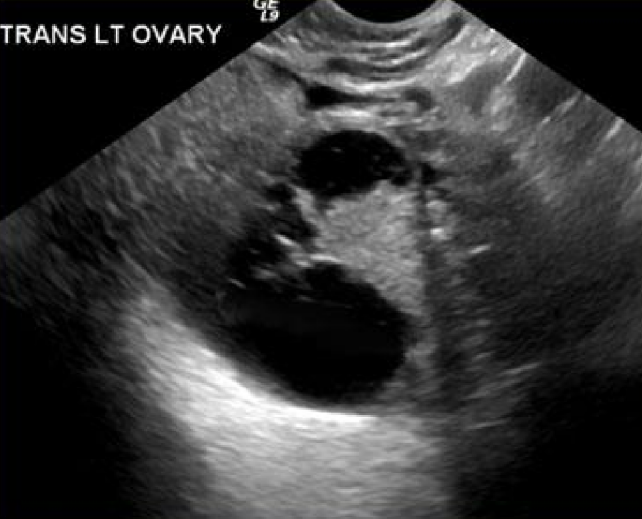
mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
this image is of a: