Compliance and Getting Paid - Professional Issues Lecture
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
52 Terms
HIPPA Rules
Federal law, signed in 1996 that governs how health information can be used, shared, sent, and stored.
Privacy Rule (2002) governs use, disclosure, access of protected health information
Security Rule (2005) controls to keep health records secure and confidential
HITECH (2013) Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health
incentive to transition to electronic health records
requirement for breach investigation, tracking and violation penalty structure
HIPPA Terminology
buisness associate - person or entity that performs certain functions on behalf of a covered entity, using the covered entit’s PHI
covered entity - health plans, healthcare clearinghouse, providers
minimum necessary - always use or disclose only the PHI that is necessary to accomplish a task or activity
Protected Health Information - PHI
18 elements of individual’s indentifiable health information that is held or electronically transmitted by a covered entity, if that inofmration relates to:
a past, present or future physical or mental health condition
the provision of healthcare or
the past present or future payment for healthcare
EPHI - electronic PHI any protected health information in electronic form
Elements of PHI
name - initials
full address
all dates directly related to individual
phone numbers
fax number
email address
social security number
medical record number
health plan ID number
account numbers
vehicle identifier VIN
certificate/license numbers
device indentifiers
web addresses
computer IP address
biometric ids (fingerprint)
full face photo
any other unique identifier or characteristic
PHI and Social Media
Media release is between the company and the pt not the clinician.
Don’t acknowledge someone is a pt, unless they say so first. then say very little.
taking videos/photos in the clinic setting - risky!
Patient Rights OCR Hot Topic
access to health data/clinical record
find out who received health data
confidential communications
notification of privacy practices
restrit sharing health data - to whom/which elements
prompt notification of breached PHI
request correction of errors in health record
file complaint for privacy violation
Disclosure Authorization NOT Requried
treatment - provision of healthcare services
payment - seeking payment for healthcare services provided
healthcare operations - administrative, financial, legal, and quality improvement activities necessary to run a covered entity’s business, and to support treatment and payment activities
Disclosure Authorization Required
Family or friends of the patient
attorneys working on behalf of the pt
when posting any information or photos of the pt on social media
tacit permission required from the pt to text or email PHI unencrypted
HIPPA Breaches
an impermissible use or disclosure of Protected Health Information (PHI) that compromises its security and/or privacy
loss or theft or hard copy patient records
unauthorized use or disclousre of PHI by employees
improperly disposing of records containing PHI
releasing patient records without proper authorization
texting or e-mail unencrypted PHI - if hacked
Breach Notification Requirements
contact individual patients
if contact info out-of-date for 10 or more patients, psot on website, or provide notice to print/broadcast media
more than 500 patients in state or juristiction , also provide notice to prominent media outlets covering the area
report to Secretary HHS
> 500 pts, withing 60 days
< 500 patients, within 60 days of years end
fines range from $100-$50,000 per violation (or per record) up to maximum penalty of $1.5 million per year/each violation - can also be criminal charges filed
Reasonable Safeguards
avoid using patient’s names in public areas
speak quietly when discussing a patient’s condition in publicc area - move conversation to a private area
turn computer monitros away from pt view
always password protect computers and mobile devices
always encrypt emails containing PHI when sending to an external system
Never test PHI to referral sources
Who are the Payors?
Government
Traditional Fee For Service
Federal - Medicare
State - Medicaid
Workers Compensation
Veterans Administration (VA) healthcare services
Commercial
Employer plans (sample)
national - Aetna, United HealthCare, Humana
Regional - Blue Cross Blue Shield
government sponsored
managed Medicare and Medicaid
state exchanges
Health Insurance Terms and Definitions
Coinsurance - a percentage of the change of medical care that the patient must pay based on benefit plan
Copayment - a payment in accordance with plan design
Deductible - a dollar amount the patient must pay each policy year before benefits are payable by the insurance company
Premium - money that is paid to an insurance company in exchange for insurance benefits
Allowed Amount - payment in full by an insurance company - contracted rates
Exclusions - items or services that are not covered under the patient health plan and for which the plan will not make payment
Certificate of Coverage - patient’s benefit description
Timely Filing - submission of authorization, appeals, claims within payor designated timeframes
claim submission examples subject to change
CMS - within 1 calendar year
Anthem Blue Cross - 120 days
Aenta - 90 days
Common Health Insurance Plans 2023
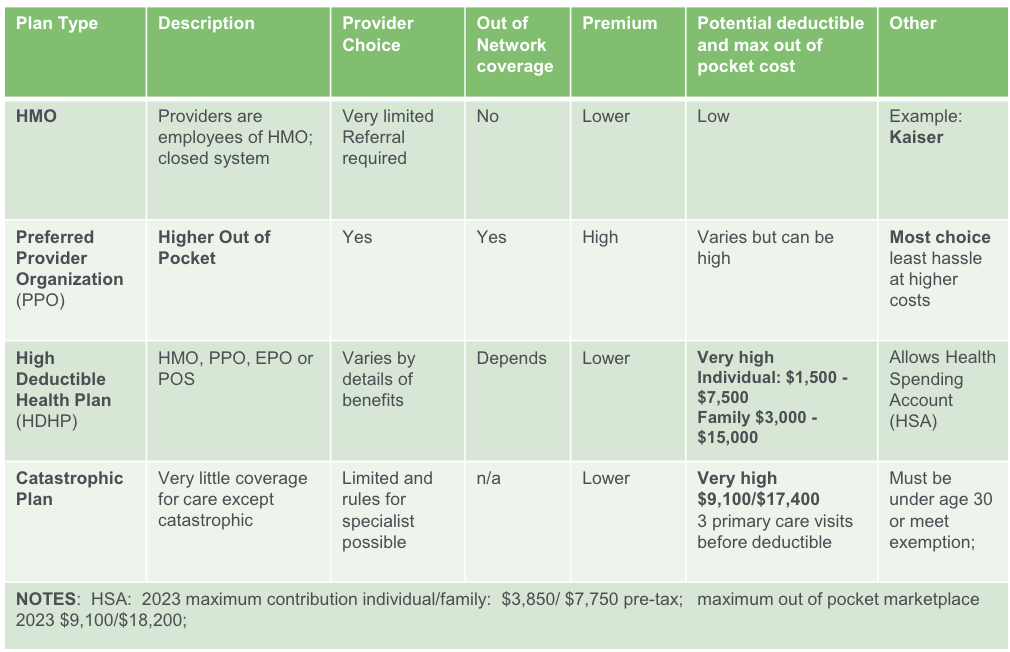
Other Plan Types
Administrative Services Only (ASO) increasing for some
self-funded
claim processing
Employer decides benefits and assumes risk for claim payment.
Affordable Care Act Highlights
ended pre-existing conditions exclusions
keeps yound adults covered under parents plan until 26
ended lifetime limits on coverage
covers preventive care 100%
full access to ER services at any hospital
Expanded Medicaid in most states (40) with federal government support
Established public insurance exchanges/marketplace helps individuals purchase insurance on their own
benefit plan levels - catastrophic/bronze/silver/platinum
eligible for a tax credit based on income to reduce cost
Regulatory Timeline

Rehabilitation Act 504: Update 2024
Discrimination on the Basis of Disability in HHS Programs or Activities
accessible medical equipment
medical treatment
integrated settings
child welfare programs and activites
web and mobile accessibility
aligned the Act with ADA
service anmals
mobility devices
communications
Medical Records (Medical Provider Records
- the document that explains all detail about the patient’s history, clinical findings, diagnostic test results, pre and postoperative care, patient’s progress and medication
Preauthorization (PreAuth)
- a decision by your health insurer or plan that a health care service, treatment plan, prescription drug or durable medical equipment is medically necessary. Sometimes called prior authorization, prior approval or precertification
Predetermination (PreD)
- formal review of a patient’s requested medical care compared to their insurance’s medical and reimbursement policies. The aim is to determine if the intended care meets medical necessity requirements
Detailed (Standard) Written Order (DWO/SWO)
detailed prescription
Letter of Medical Necessity (LMN)
a letter written by your healthcare professional detailing your care
Getting Payment Based on
meeting/demonstrating care meets payor’s clinical criteria
Patient’s Certificate of Coverage, verification of benefits
must follow payor pre-authorization process
validate policy exclusion diagnosis driven benefit
money limits in benefit category
Common Denial Reasons
Service provided was not -
a covered benefit
medically necessary
a contracted service, regardless of medical necessity
authorized or payor not given proper notification
Service deemed - experimental, investigational, unproven
Claim or appeal submitted outside of timely filing
Denial and Delay: Clincial Documentation
Inadequate Clinical Notes
incomplete evaluation forms
contradictory indormation
illegible
lack of payor friendly terms
Patient wants vs needs.
out of warranty verbiage without specific rationale
lack of patient specific functional level documentation
lack of justification for definitive prosthesis vs. replacement socket
Other Documentation Considerations
Always document
communications with therapist, O&P clinician, physician
functional changes noted from patient use of device (pt report and/or clinical observation)
recommended use of device
wearing schedule
skin integrity
pain
risks and concerns
recommendations for device mods
Medical Records (Physician Records): Requirements supporting O&P Services
clearly document device justification
physician should be specific to the device i.e. MPK, MPF, myoelectric device, Myomo, CBrace if providing high end componentry
face to face encounter with MD
amended records; updated records
socket replacements do not need to justify the functional level
clinicians should be involved - this is an opportunity to get in front of the referral source and develop a relationship
Prior-authorization Process
Follow payor’s requirements for prior-authorization make sure to include
review clinical record for completeness nad accuracy
search for payor’s medical policy on internet
review clinical record in alignment with payor Medical Policy to ensure that medical necessity requirements are met
Tenets of Prosthetic Documentation
Allows physician ability to stablish and to justify medical necesity.
desire to ambulate (LE)
current funcitonal level with supporting activites (prosthetics)
expected functional level with supporting activities (difference between the 2 if applicable) (prosthetics)
agreement in proposed plan (specifically address any high end componentry)
are there any co-morbidities that will affect the patient from utilizing the device?
Right Now - Right Later- Better Care!
Pre-authorization (pre-auth) Cycle - defined by state statues, mandates timeframe for payor decision on pre-auth.
varies by state and based on urgency of service
shortest - 15 calendar days
Appeal Cycle
defined by state statutes, mandates timefrane for payor decision on appeals
varies by state from 30 days to 60 days
Relevance to Pre-auth Discovery
avoid 30-60 appeal cycle
pre-auth decision results
- 90% first pass approval rate (CMS = 40-50%)
days from submission to auth - 5 days
Myths
A LMN can be considered a Medical Record.
false - per CMS, LMNs, as well as DWO/SWOs, are NOT considered a medical record. You may use a LMN to support an encounter note/visit with the physician
MD Records are not needed if preauth is not required.
false - even though some insurance plans may not require MD Records for preauth is not needed insurance companies can still come back at claims adjudication and request MD Records. You cannot amned records after the device has been provided
Cautions
medical necessity does not equal benefit
suthorizations do NOT guaranteed payment
authorizations may NOT be aligned to patient’s benefit
claims payment is based upon
eligibility
benefits
medical necessity
clean coding
Review of Payor Medical Policy
defines:
payor’s position on medical necessity of services
defines criteria required to meet medical necessity
terms regarding medical policy
supported by payor’s research of outcomes based studies
established by payor’s Medical Management staff and reviewed annually
does not take into consideration a member’s benefit plan or certificate of coverage
Updated LCD allows. . .
MPKs for K2 users
Health Saving Accounts
Tax free saving opportunities.
Health Savings Account (HSA)
allows individuals to pay for current health expenses and save for future qualified medical expenses on a pretax basis. Funds deposited into an HSA are not taxed, the balance in the HSA growws tax-free, and that amount is available on a tax-free basis to pay medical costs
Flexible Spending Account (FSA)
allows an employee to set aside a portion of earnings to pay for medical expenses. Money paid into an FSA is not subject to payroll taxes.
Fully Insured Plan
insurance carrier collects the premiums and pays the health care claims based on the coerge benefits outlined in the policy purchased.
insurance company assumes risk and manages its own administrative tasks
employer contracts with health plan and pays a monthly premium
Self-Funded Plan
employer assumes risk (becomes the insurance company) but hires a company for all administrative tasks
employer chooses network, plan design, managed care provider
employer maintains reserves and all unspent portions are retained by employer
Worker’s Compensation
insurance covers job-related injuries only
no monthly premiums
adjusters price shop
full reimbursement for approved medical expenditures
Health Insurance
preventative care and episodic
monthly premiums
set reimbursement rates
cost sharing deductible/coinsurance/copay
Texting with Patients Dos
determine if PHI is required
alert patient on risks of non-secure email/text
obtain specific permission to communicate without encryption and document in EHR before proceeding
delete patient photos/videos from personal cloud accounts
follow minimum necessary rule at all times, limit PHI use
Texting with Patients Don’ts
send PHI unencrypted without consent
refuse sending unsecure PHI if you have consent
think hackers aren’t watching and waiting for mistakes
store PHI, patient photos/videos, emails on personal accounts
provide more than the minimum PHI in any communication
Texting with Referral Sources/Payers Do’s
delete text message with PHI
delte PHI before replying to a text
reply to texts/emails if it doesn’t include PHI
encrypt emails containing PHI to referral sources
Texting with Referral Sources/Payers Don’ts
include PHI on texts
foward patient text messages to the referral source
reply to texts with PHI. If email has PHI, do not reply with an unencrypted email
include PHI in the subject line of your email
False Claims Act (FCA) 1863
purpose - to combat fraud against the federal government
Key Provisions
imposes liability on individuals and companies who defraud governmental programs
allows whistleblowers (qui tam actions) to report fraud and share in any recovered damages.
penalties include treble damages and civil penalties ranging from $5,500 to $11,000 per false claim
Anti-Kickback Statute (AKS) 1972
purpose - to prevent fraud and abuse in federal healthcare programs
key provisions
prohibits the exchange of renumeration to induce or reward referrals for services covered by federal healthcare programs
applies ot both sides of the transaction (giver and receiver).
violations can result in fines, imprisonment, and exclusion from federal healthcare programs
Stark Law (Physician Self-Referral Law) 1989
purpose - to prevent conflicts of interest in physician referrals
key provisions
prohibits physicians from referring Medicare patients for designated health services to entities with which they have a financial relationship, unles an exception applies
penalties include fines up to $15,000 per infraction and exclusion from Medicare and Medicaid programs
Civil Monetary Penalties Law (CMPL) 1981
purpose - to impoe penalties for various forms of fraud and abuse in federal healthcare programs
key provisions
authorizes the imposition of civial monetary penalties for a wide range of violations, including false claims, violations of the Anti-Kickback Statute, and Stark Law violations
penalties can include fines up to $50,000 per violation and assessments of up to three times the amount claimed.
What Constitutes Fraud?
knowingly misrepresenting a material fact in oder to gain a financial benefit

So how does a CPO defraud the US Government?
What is a False Claim?
when a provider or supplier knowingly omits critical elements from their claim and submits it for payment it is intentionally dishonest and is legitimately considered fraud
in a hurry
taking shortcuts
just don’t want to do the work
trying ot get paid for what they didn’t provide
punishable under the law
What is a Reverse False Claim?
when a provider or supplier realizes they have recieved an overpayment but does not take steps to refund it within 60 days, their administrative error becomes a Reverse False Claim
gosh, i wont do that again
i earned this money and learned my lession
no one knows this but me
i need this money
punishable under the law
Penalties for submitting False Claims
Civil Penalties
fines - up to $11,000 per flase claim
damages - up to three times the amount of damages the government sustains due to the false claims
Criminal Penalties
fine - up to $250,000 for individuals
imprisonment - up to 5 years
Risk Areas and Scenarios
OIG- 1 Billing for items or services not provided
OIG - 6 Upcoding
OIG - 7 Unbundling
OIG - 2 Billing for services the DMEPOS supplier believes may be denied
OIG - 5 Billing for items or services not ordered
Practicing without a license
15 states require a license to practice O&P
some of those states require Residents or students to register before practicing
2 states require certification but not a license
not all licensure states require ceritfication in order to get a license to practice
not all licensure states that DO require certification to get a license require you to maintain certification as part of the license. People will drop their certification and keep the license
Affordable Care Act Marketplace Plans
DC and 17 states have their own state run marketplaces. 33 states rely on federal government marketplace
Platinum - covers 90% on average of your medical costs - you pay 10%
Gold - covers 80% on average of your medical costs; you pay 20%
Silver - covers 70% on average of your medical costs; you pay 30%
Bronze - covers 60% on average of your medical costs; you pay 40%
Catastrophic - catastrophic policies pay after you have reached a very high deductible. Catastrophic plans must also cover the first three primary care visits and preventive care for free, even if you have no yet met your deductible.