Psych/Soc Experimental Design
1/30
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Independent Variable
Controlled by researcher.
Dependent Variable
Measured by researcher.
Quasi-experimental
Lack random assignment that is needed for a true “experiment”
Mixed-methods
Contains the use of both quantitative and qualitative data collection methods.
Case-control Studies
Observational studies that aim to compare two groups: a “case group” that exhibits the condition the researchers aim to understand and a “control group” that does not exhibit the condition.
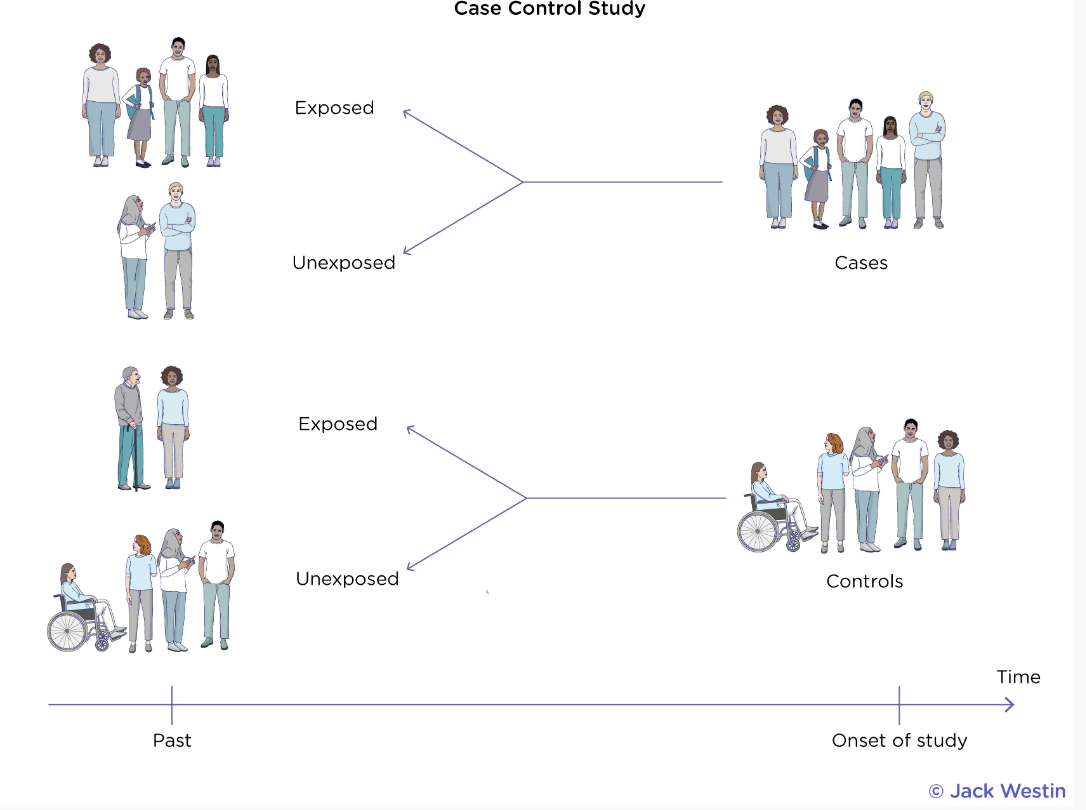
Confounding Variables
Other variables that can impact the results of a study.
Cross-sectional study
Observational research that analyzes data collected at a single point in time.
Surveys often used to provide data.
Longitudinal Study
Data collected repeatedly over time.
Cohort Study
Longitudinal observational study that aims to find a potential cause to a condition of interest.
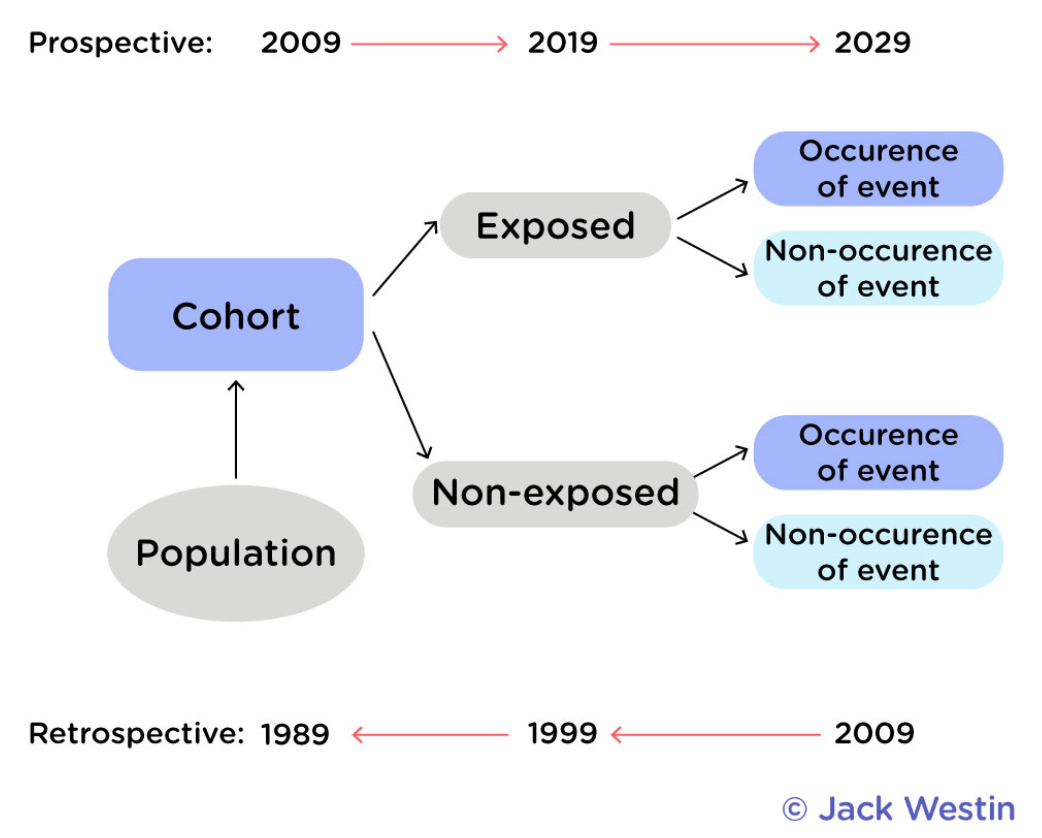
Experimental Study
Aims to understand the cause-and-effect relationship between certain independent variables and dependent variables.
Ethnographic Study
Aims to understand people in their environments (emphasizing understanding of that group’s culture and practices).

Internal Validity
A study’s ability to establish a cause-and-effect relationship between two factors.
For a high internal validity, we should not be able to attribute the value of the dependent variable to anything other than the independent variable.

External Validity
The extent to which researchers can generalize the findings of a study to other situations or the general population.

Construct Validity
How well a test is able to measure the concept it was designed to evaluate.
Predictive Validity
The ability of a test to predict a future outcome. Can be better understood through correlations.
The stronger the correlation between the test and the outcome of interest, the higher the degree of predictive validity.
Placebo
An inactive substance or intervention that is indistinguishable from the active drug or treatment being tested. Designed to have no therapeutic value to give insight into if the drug of interest is truly the cause of the observed effect.
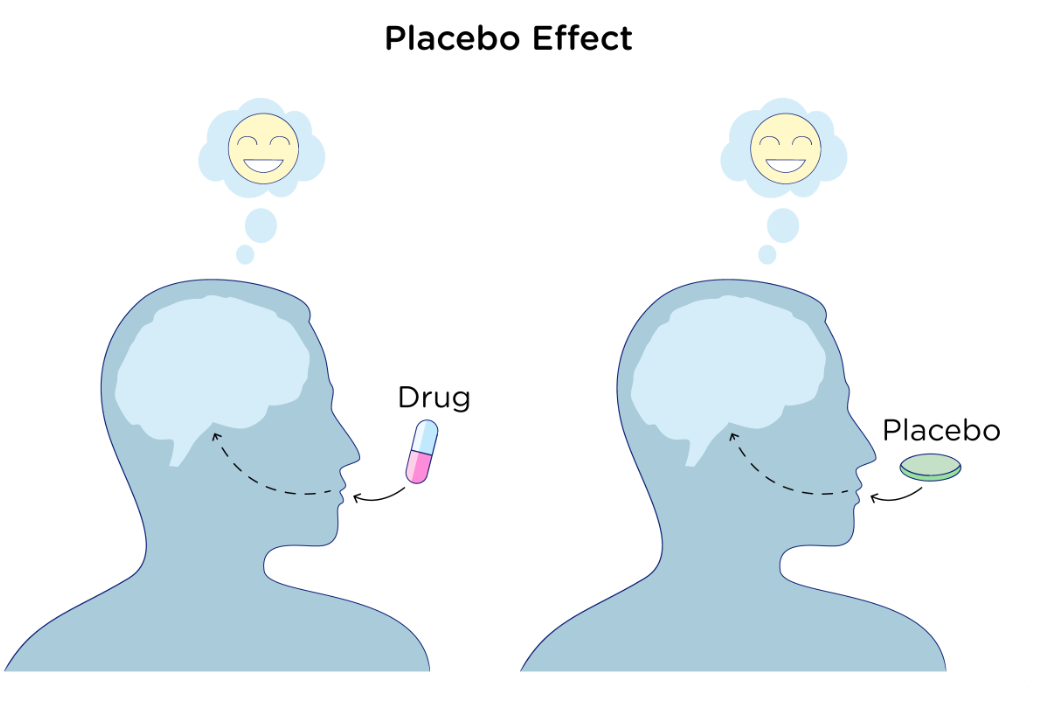
Control
Element that is unaffected by other variables in the study.
Negative Control
Not expected to cause changes in the dependent variable.
Positive Control
Some other treatment that is expected to produce an effect that is similar to that of the independent variable.
Bias
Occurs when error introduced to the study results in a higher prevalence of one outcome over another.
Selection Bias
There is allocation of participants to different treatment groups in a way such that proper randomization is not achieved.
Experimenter Bias
Errors in the methods or data interpretation that can be attributed to the researcher’s behavior or beliefs.
Implicit Bias
Occurs unintentionally and affects an individual’s judgement and behavior.
Social Desirability Bias
Prevalent when participants provide answers that align with societal expectations rather than their personal beliefs. (Colin Bridgerton lmao)
Observational Studies
Involve observing participants in their most natural settings. Data is collected solely through observation. Researchers do not interfere with participants or their environments.

Experimental Studies
Researchers assign participants to treatment and control groups. Interfere with the participants.
Longitudinal Observational Studies
Follows a group of participants over an extended period to observe and analyze changes in the variables of interest. Allows researchers to study the same individuals or groups repeatedly, collecting data multiple times to assess trends, patterns, and associations over time.
Retrospective Observational Study
Involves analyzing data or records from the past to study the relationship between variables over a period of time. Allows researchers to explore how factors may have influenced outcomes in the past.
Correlation
Measurement that describes the extent to which two variables are related.
Positive - Variables move in the same direction
Negative - Variables move in opposite directions
No correlation - no effect between variables
Repeatability
The ability to collect similar results upon data recollection.
Practical Significance
The findings of research being practical to implement into everyday life.
Considered such when the consequences of the independent variable are significant enough to be meaningful in real life.