cerebral cortex
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
the _______ ____ which surrounds the _____ ______ on a mid sagittal view of brain is bringing somatosensory info from legs to your primary motor cortex by connecting the primary somatosensory cortex to primary motor cortex
paracentral lobule central sulcus
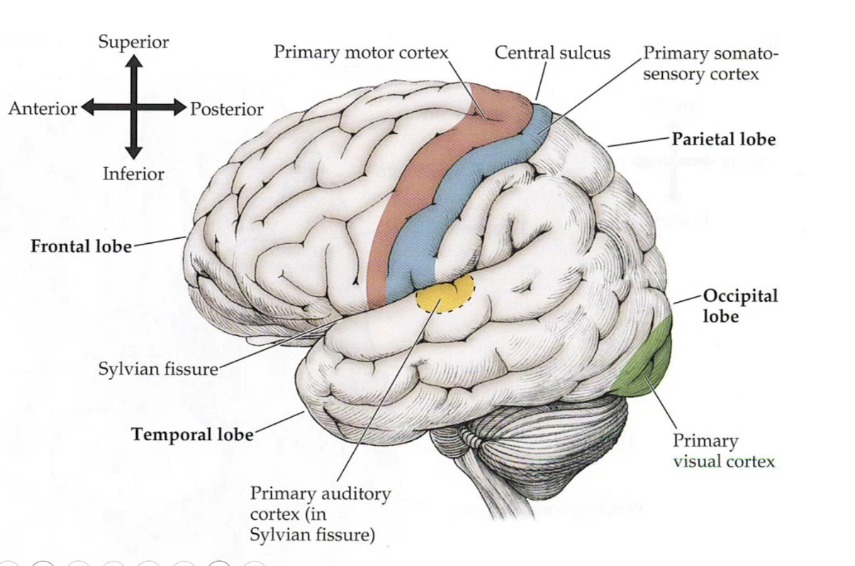
broadman area 17 is the _______ _______ ______ in occiptal lobe, primary motor cortex is also called _____ _____, primary somatosensory cortex is asloc alled _______ _______,
primary visual cortex precentral gyrus postcentral gyrus
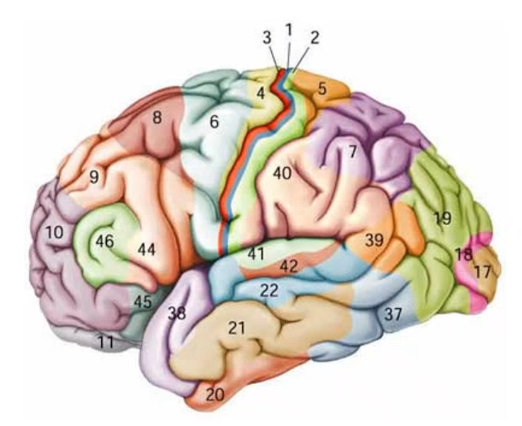
broadman areas: 3,1,2 (in that order) is _____ _______ cortex, 4 is ______ ___ cortex, 17 is ______ _____ cortex, and 41 is ____ ____ cortex
primary somatosensory primary motor primary visual primary auditory
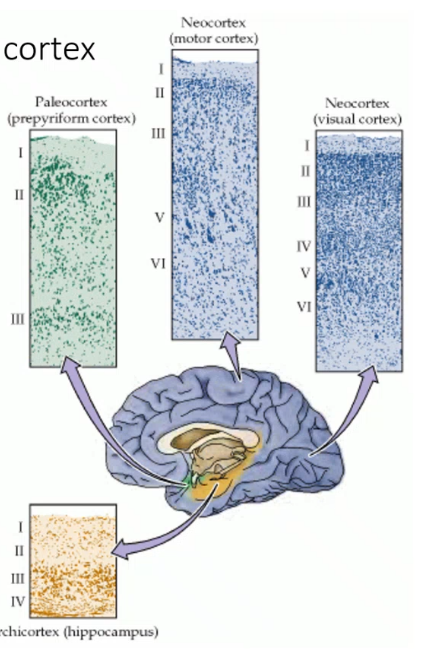
types of cerebral cortex, _____ has six layers and is 95% of surface, _____ has three layers and makes up parahippocampal gyrus and cingulate gyrus, the _____ has four layers and makes up the hippocampus, the rest of the limbic system has ___ layers
neocortex paleocortex archicortex three
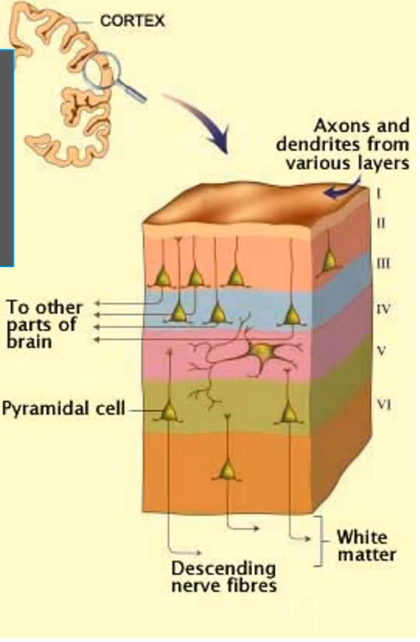
layers 1 is the _____ layer and contains _____ and ______ communicates with deeper pyramidal cells, layers 2 is called _____ _____ layers contains _____ _____ cells and communicates with _____ cortical areas, layers 3 is called _____ ____ layers and contains ____ _____ cells and communicates with other hemisphere cortical areas, layers 4 is called _____ _____ layers and contains dense stellate cells that is main input layers from ______ (especially sensory cortex), layers 5 is called _____ _____ layers and contains ____ _____ neurons (betz cells) and is main output to _____ structures like brainstem/spinal cord, layers 6 is called ______ layers and is main output to ________ (feedback loop)
molecular dendrites axons external granular small pyramidal local external pyramidal medium pyramidal internal granular thalamus internal pyramidal large pyramidal subcortical fusiform thalamus
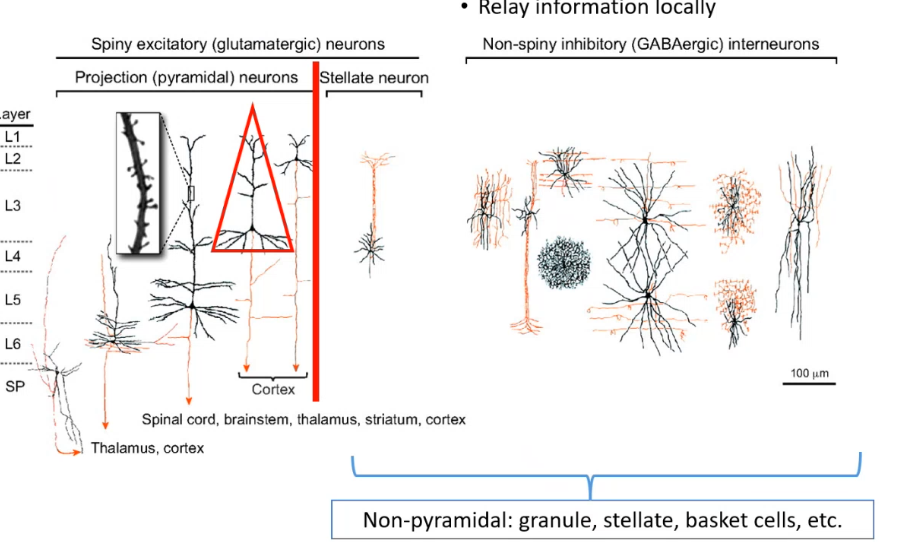
pyramidal neurons are spiny, _______ (glutamatergic), _____ cells are also spiny excitatory but are non-______, then there are interneurons which are ___-_______ and ______ (gabergic) which relay information locally
excitatory stellate pyramidal non spiny inhibitory
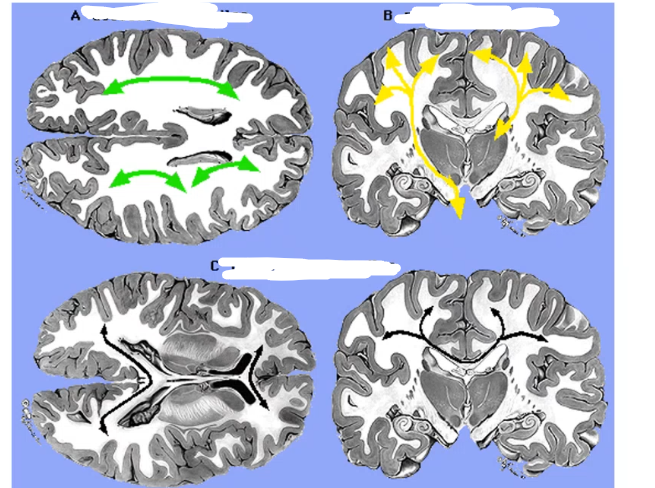
pyramidal cells axons - white matter bundles, A _____ _____ are tracts that are anterior to posterior and include _____ ______, B ____ _____ are tracts that communicate with subcortical regions like brainstem and include _____ ______, C _____ ____ are tracts that communicate between hemispheres and include _____ _____ and _____ ______
association bundles arcuate fasciculus projection bundles internal capsule commissural budnels corpus callosum anterior commissure
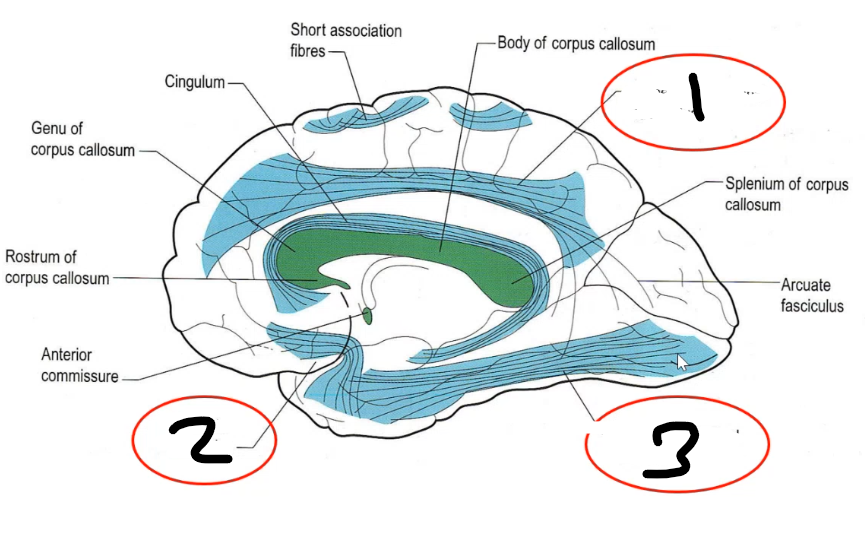
association bundles: 1 ____ ______ _____ carries the where pathway and to determine whether to respond to stimuli, 2 ______ ______ ______ carries the what pathway to temporal lobe, 3 ______ ______ carries the social emotional processing info from amygdala (frontal lobotomy is meant to break this up)
superior longitudinal fasiculus inferior longitudinal fasciculus uncinate fasciculus
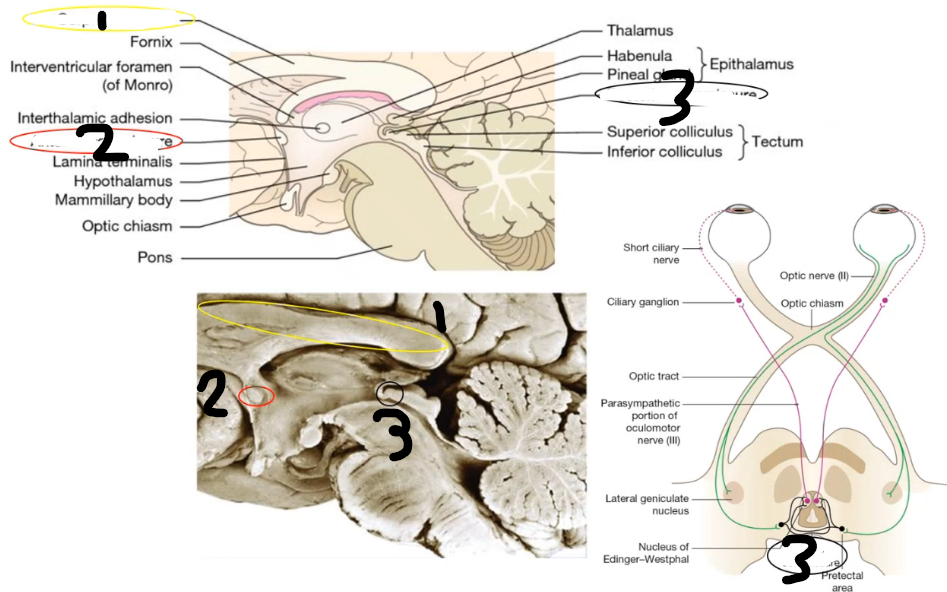
comissural bundles: 1 is ______ ______, 2 is ______ _____ and its function is nto really known, 3 is ____ _____ and coordinates pupillary light reflex via bilateral input to Edinger Westphal nucleus, pretectal nuclei are inside it
corpus callosum anterior commissure posterior commissure
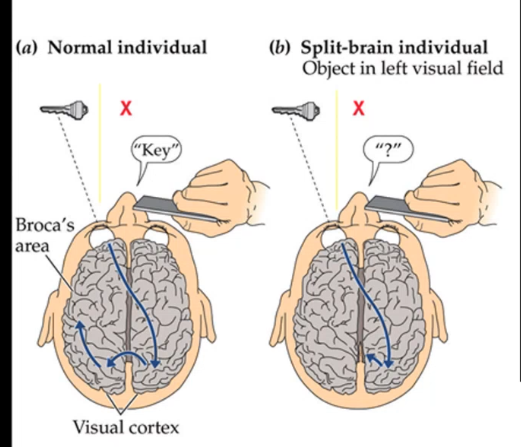
corpus callosum connects closely related cortical areas in each hemisphere, exception is primary ____ cortex, if someone is missing a corpus callosum and their primary visual cortex is left hemisphere if you show them an object on the _____ side they will not be able to tell u the word for it as the corpus callosum is severed and the info is unable to travel to primary visual area, this is also true for explaining objects the ___ hand will be able to tell you what the object does but the other wont
visual left right
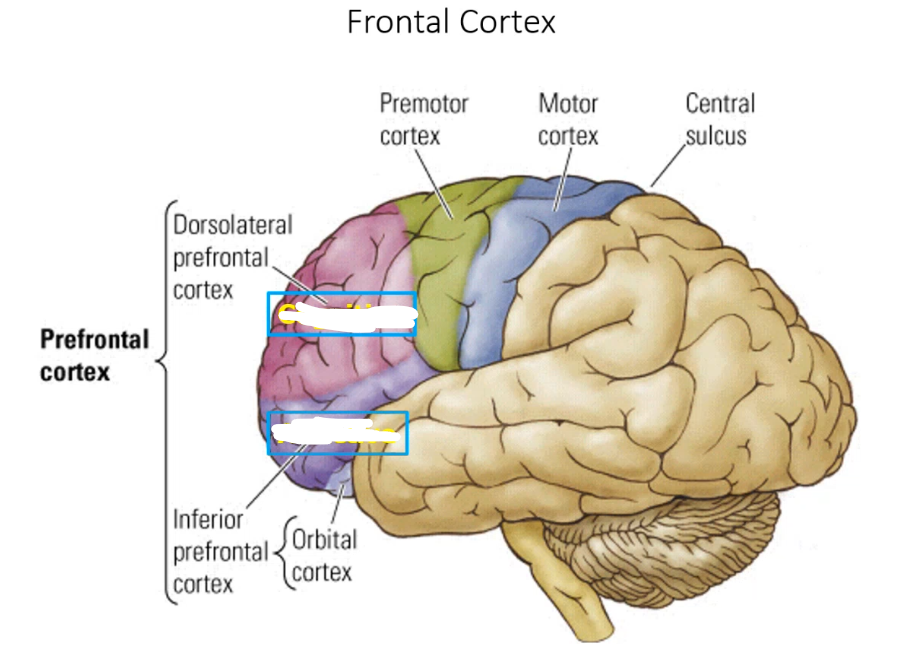
Frontal cortex: _____ _____ cortex handles more executive functioning and cognitive function while _____ ____ cortex is more personality and affective functioning
dorsolateral prefrontal inferior prefrontal
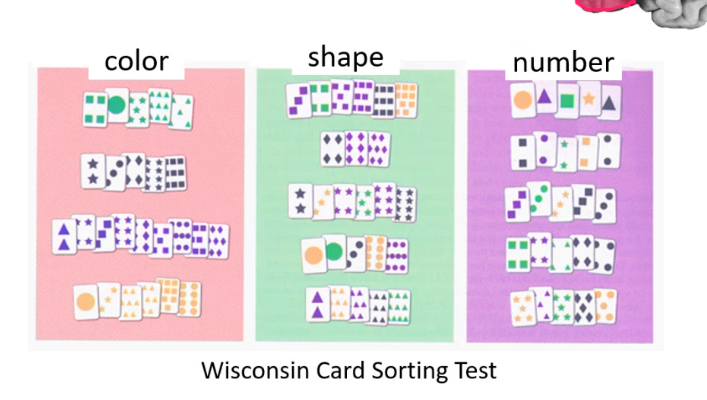
a person with lesion in _____ _____ cortex will be unable to complete Wisconsin cord sorting test and will exhibit perseverance where they are unable to switch focus or tasks , ____ which is repetition of sounds or words and ____ which is repetition of actions or movements
dorsolateral prefrontal echolalia echopraxia
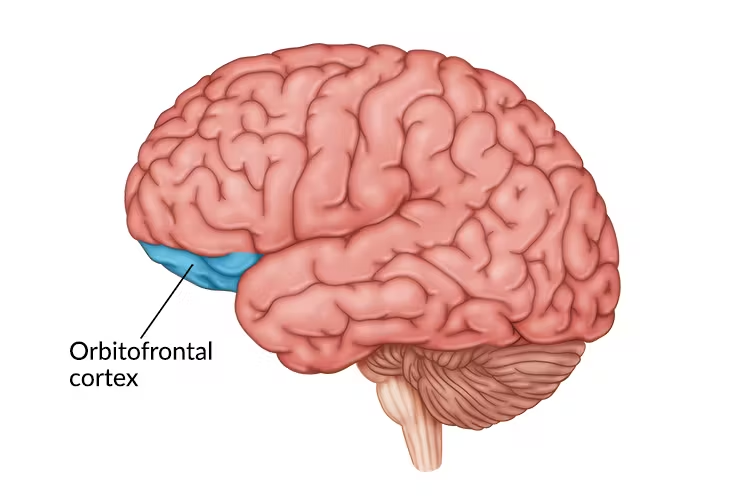
unilateral lesion to orbitofrontal lobe causes _____ syndrome which is low motivation reduced insight reduced impulse control but they exhibit no difficulty with card sorting tasks, however bilateral lesion causes complete lost motivation and no initiation
orbitofrontal
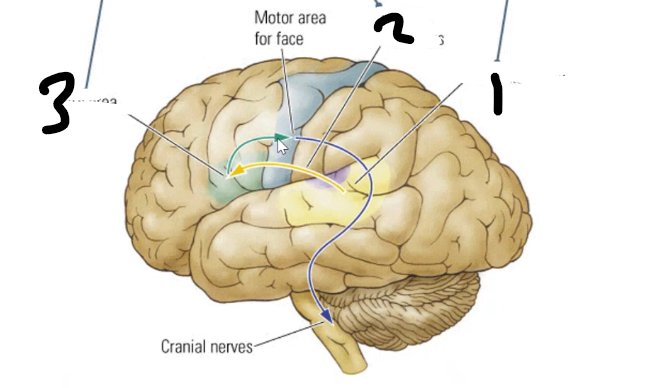
1 ______ area is where sound images of words are stored like a dictionary it is connected to 2 _____ area where motor programs to talk are stored by the 3 _____ _____ connects these areas
wernickes brocas arcuate fasciculus
______ aphasia is where patient is unable to comprehend commands and able to speak without meaning while being unaware of their problems while _____ aphasia is whee the patient can understand words but can not speak properly they are aware of their problems
wernickes brocas
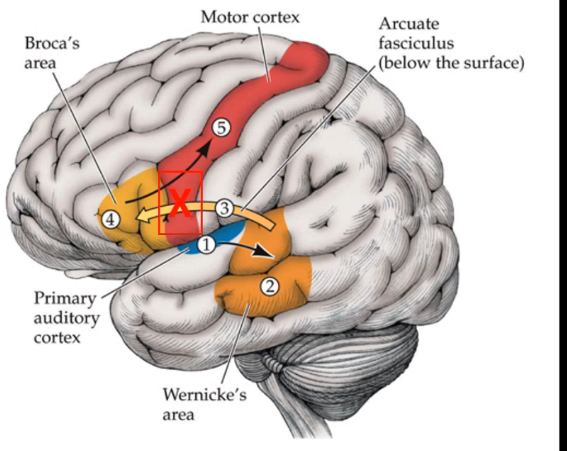
_____ ____ is impaired repetition of words only and is normally caused by damage to ____ ______
conduction aphasia arcuate fasciculus
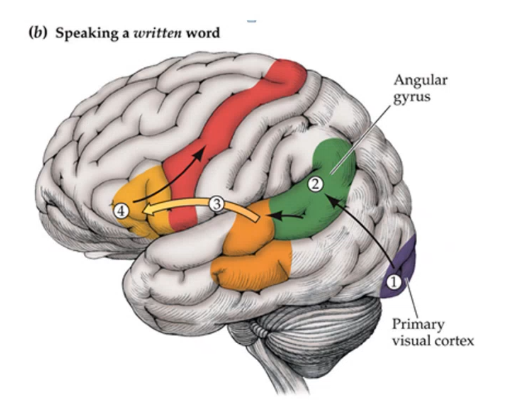
_____ _____ is when comprehension is not affected but naming of things is impaired, caused by damage to ____ ___
anomic aphasia angular gyrus
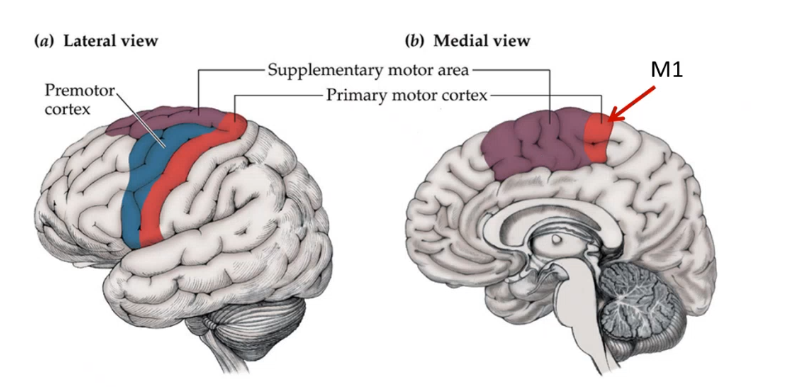
red is ___ ____ cortex, purple is only visible in mid sagittal view and is _____ motor area which receives info from thalamus from cerebellum and encodes sequences of movements and info goes from there to ______ cortex which is blue, this is where neurons fire before performing an activity
primary motor supplementary premotor
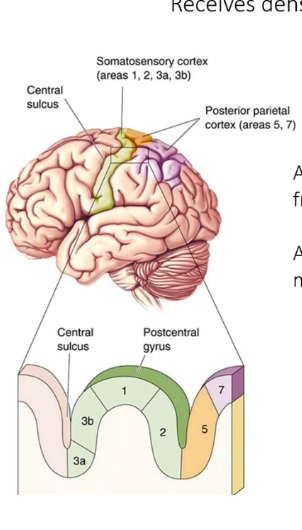
area ___ receives projections from superficial skin, area ___ receives input from muscle spindles, Area ___ and ___ have large receptive fields and are direction sensitive and are able to determine direction, area __ handles identifying the texture and size/shape (stereogenesis), area _ combines info from differnet modalities like auditory adn visual
3a 3b 1 2 5 7
_____ is the inability to recognize an object by touch but can draw and recognize drawing of it, ____ is the inability to recognize letters or numbers drawn on the patients hand , these are both caused by lesions to _____ lobe
astereognosis agraphesthesia parietal
empathy can cause somatosensory broadman area ___ and ___ to be activated when watching videos of people in pain
5 7
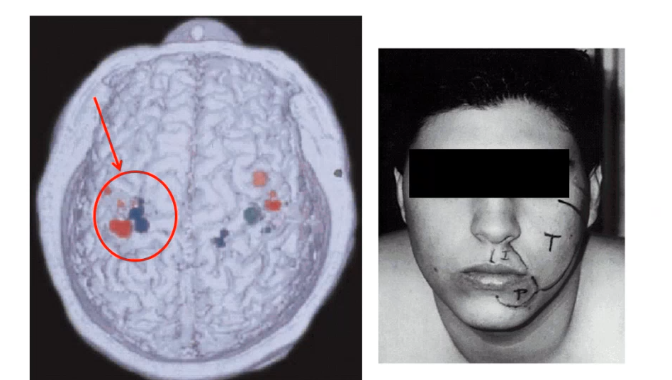
when patients lose a limb they can start experiencing phantom limb pain, due to _______- as arm and face regions start to fused together ipsilatearl to lost limb
neuroplasticity
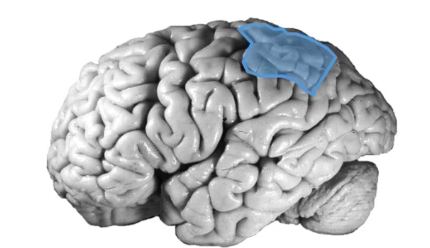
the ______ _____ cortex handles higher sensory function (polysensory) and language function depending on hemisphere, and stereognosis , damage can cause _____ neglect more common in neglecting left side
parietal association contralateral
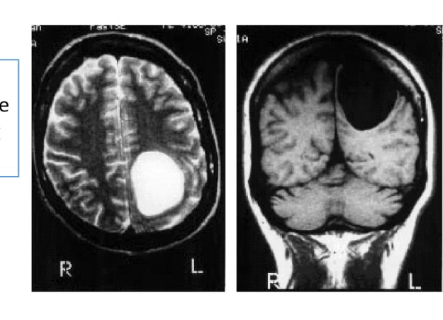
patient has large left hemisphere cyst, causes her to experiencing vanishing arm on ___ side, unabel to identify items by touch on that side, if limb is touched however she is able to be aware of its position and can regain limb by using vision
right
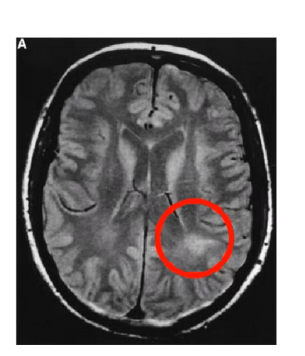
____ syndrome presents as agraphia, right left confusion ( used to write with right hand but now thinks htey are left handed) , inability to understand and use numbers, typically caused by damage to ______ ______ lobule
Gerstmann inferior parietal
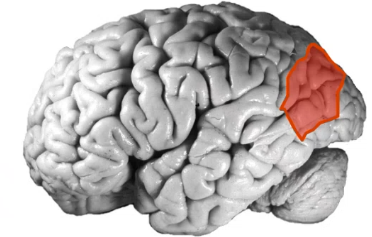
damage to ______ _____ cortex can cause the inability to recognize objects (visual agnosia) and stimulation can cause complex visual hallucinations like objects changing size or distorting shape (alice in wonderland syndrome) which can happen if they get mono in young children
occipital association
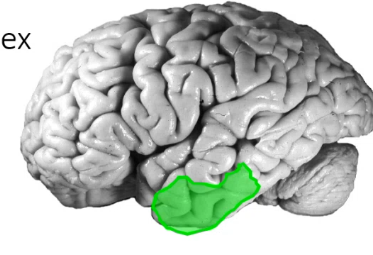
damage to ____ _____ cortex can lead to visual memory problems if on left side and visual discrimination problems on right side, but can cause prosopagnosia (inability to recognize faces) on both sides
temporal association
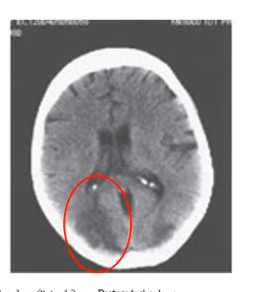
damage to _____ ____ cortex can cause ____ where patients are unable to see more than a limited area of the visual lied at a time, they can see individual objects but cannot perceive a visual scene as a whole
inferior temporal simultagnosia
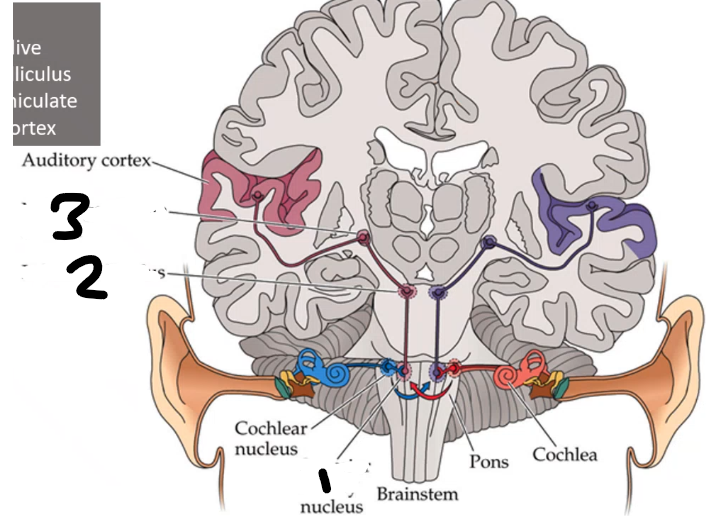
name all
superior olivary inferior colliculus medial geniculate nucleus
primary auditory cortex has ____ organization where higher frquencies are more ____ (anterior/posterior)
Tonotopic posterior
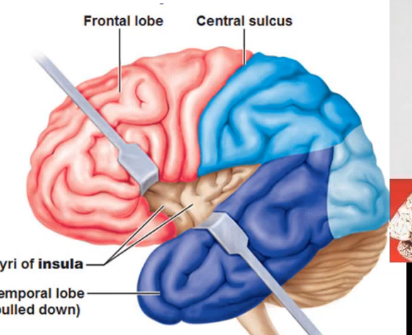
the _____ is a deep cortical structure covered by the ____ (“lips”) of frontal parietal and temporal cortex
insula opercula
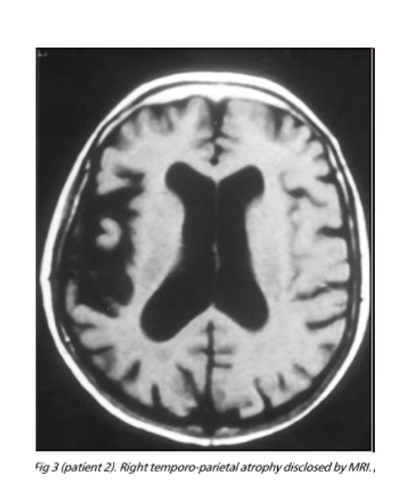
lesion to ________ _____ lobe can cause alien hand syndrome where there hand acts on its own and patients are unable to control their hand, can also be caused by damage to _____ ______
temporal parietal corpus callosum